Diseases and their symptoms associated with the pathology of cerebral vessels, are at the first place of calls to the neurologist. Many are terrified by the "scary and incomprehensible" research titles that the doctor recommends to go through, because people who are far from medicine often associate them with suspicion of a sufficiently serious diagnosis. But this is far from being the case, so it's worth settling down and sorting out everything in order.
One of these "incomprehensible" studies is the rheoencephalography( REG) of cerebral vessels, after hearing the name of which some patients embrace horror because of ignorance. So what is this procedure?
Contents of
- 1 What is the rheoencephalography of
- 2 Advantages and disadvantages of the diagnosis of
- 3 vessels. Indications and contraindications for the rheoencephalography
- 4 Preparation for the
- 5 survey How is the
- 6 diagnosed Possible consequences after the REG REGISTRATION
- 7 Decoding of the results
- 7.1 Important indicators of the rheoencephalogram in the table
- 7.2 Example of rheoencephalographic parameters in the norm
- 8 Patient feedback
- 9 What survey methodsThe
reoencephalography is a reoencephalography. Reoencephalography helps to determine the state of the cerebral vessels.
. Reoencephalography( REG) is a modern functional method of studying the states of the cerebral vessels, which allows one to evaluate their damage, blood filling, tone, elasticity,the rate of blood flow in them, the viscosity of the blood being delivered, the ability of the vessels to narrow and relax, the symmetry of the blood supply to the hemispheresof the brain and outflow of venous blood.The method of rheoencephalography consists in passing an alternating electric current through the brain tissue and fixing the parameters of electrical resistance, which depends on the volume and viscosity of blood in the vessels of the brain. Specifically, the current resistance parameters allow us to estimate the above parameters. When the vessels are full-blooded and expanded, the resistance of the current rises, and if they are narrowed, then the opposite picture is observed.
Advantages and disadvantages of the diagnosis of
vessels Currently, rheoencephalography is not used as often as before, because there are more accurate methods for diagnosing the states of the brain and its vessels, for example, electroencephalography( EEG), computed tomography( CT) or magnetic resonance imaging(MRI is the most accurate method of diagnosis).Due to the fact that not every hospital or polyclinic( for example, in rayon centers) can boast of the availability of modern equipment, REG is becoming an excellent assistant in the diagnosis.
If there is a tomograph in the treatment and prophylactic institution, and the doctor still directs to go through rheoencephalography, then the question arises: "Why REG, not magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography, because the second and third methods are much more informative?".
Many doctors, despite the existence of more modern diagnostic methods, all the same choose rheoencephalography
Firstly, this is the safest way to diagnose the pathology of cerebral vessels. Secondly, not everyone can withstand the noise and the closed space of the tomograph( especially this is important in the examination of children, since not all children are able to remain in a calm state, especially in the absence of a mother).Thirdly, MRI and CT in comparison with REG are an expensive method of examination. Also, the advantage of rheoencephalography is that it helps to examine vessels, not touching "unnecessary and unnecessary" areas. On magnetic resonance and computed tomography, both skull bones and soft tissues are visible( most often these methods become relevant when a serious diagnosis is suspected, for example, the tumor process and others).
The essential disadvantage of REG is that any excitement, experience( and, as a rule, there is no such person who would not experience such emotions before passing any diagnostic procedure), failure to follow the recommendations on preparation for the procedure can affect the results of the survey.
Indications and contraindications to the rheoencephalography

Frequent headaches may be an indication for the
examination. A doctor may give the direction to undergo rheoencephalography if the patient has the following pathological conditions:
- headaches of varying intensity, localization and duration;
- dizziness;
- ischemia of the brain;
- strokes;
- noise in the ears and the appearance of "flies" before the eyes;
- concussions and bruises of the brain;
- bruises and fractures of the cervical spine and bones of the skull;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- disorders of blood circulation of the brain;
- arterial hypertension;
- vegetovascular dystonia;
- arterial hypotension;
- pathology of the hypothalamic-pituitary region( in particular, tumor formations);
- encephalopathy;
- Parkinson's disease;
- frequent fainting;
- atherosclerosis;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- memory and sleep disorders;
- visual and auditory disorders;
- meteorological dependence.
Rheoencephalography is considered a completely safe method of functional diagnosis, it can be applied to all categories of the population( from infants to the elderly).The study is not carried out in cases where the patient has defects( wounds and abrasions) and infectious diseases of the scalp.
Preparation for examination

For accurate results, it is necessary to observe the emotional calmness of
the day before and immediately before the study. There is no special preparation for the survey. It is only necessary to try to adhere to the following recommendations:
- before the study, do not take any medications that can affect the condition of blood vessels;
- to try to avoid stressful situations the day before and immediately before the research;
- on the day of the study in the morning not to drink coffee and strong tea;
- on the eve and before the study do not smoke;
- immediately before the test rest for 15-20 minutes;
- in advance to prepare napkins and a towel in order to remove excess gel after the procedure.
Such measures are necessary for the tranquility of the nervous system and minimal vascular changes( as is known, any disturbance or the influence of certain chemicals can change the vascular picture).Observance of such simple rules will help a specialist to accurately assess the state of the vessels of the brain and make the correct diagnosis.
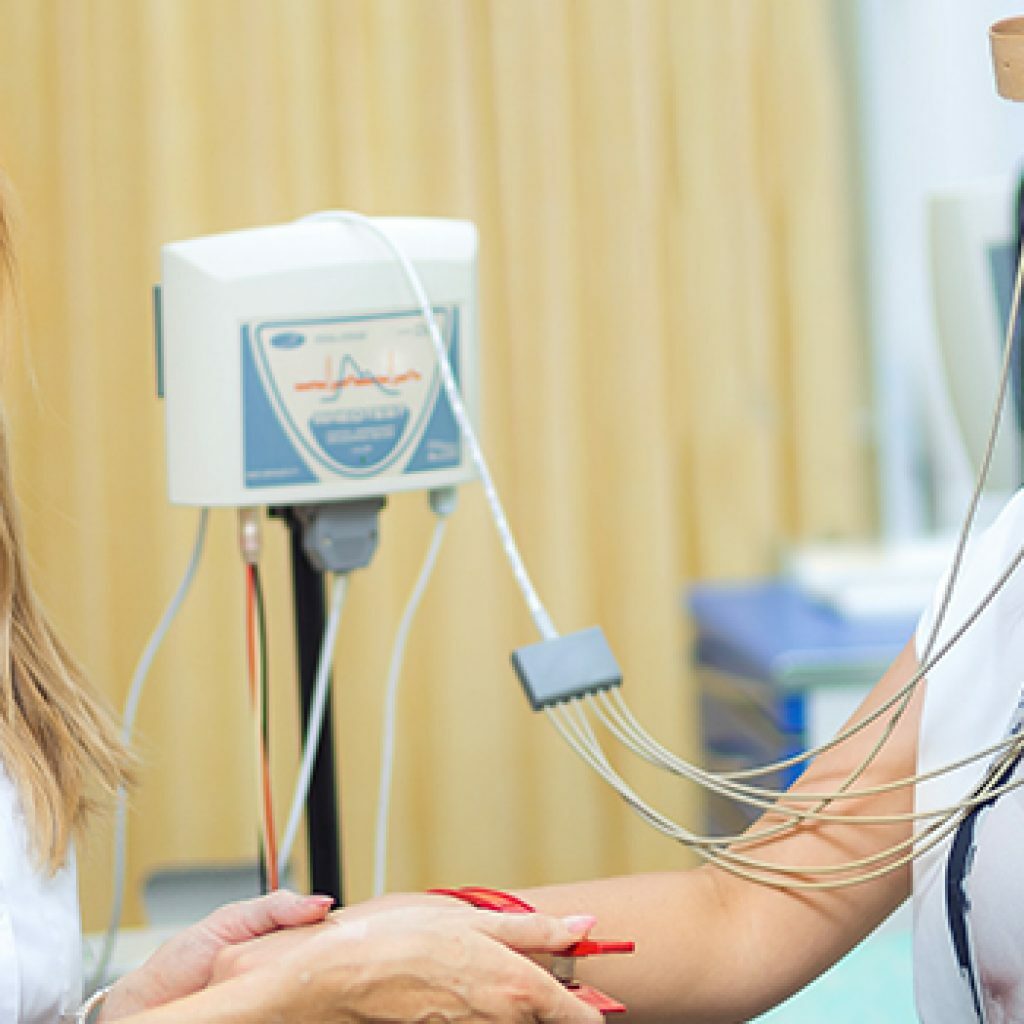
In the office of functional diagnostics, the specialist prepares the patient for examination by degreasing the skin of the areas to be examined and applying the reoenzelograph electrodes to them.
How is the
diagnosed?Diagnostics is carried out with the help of a special rheograph device( rheoenzelograph), connected to the device, recording and issuing indications( electrocardiograph, computer, electroencephalograph and others).During the study, the patient should be in a comfortable and relaxed posture. Most often he is put in a special chair. A nurse or doctor puts electrodes on the patient's head and fixes them with a special elastic band, pre-lubricated with paste or gel. For convenience, the ribbon is positioned so that it passes along the circumference of the head: above the area of the superciliary arches, above the ears and along the occiput.
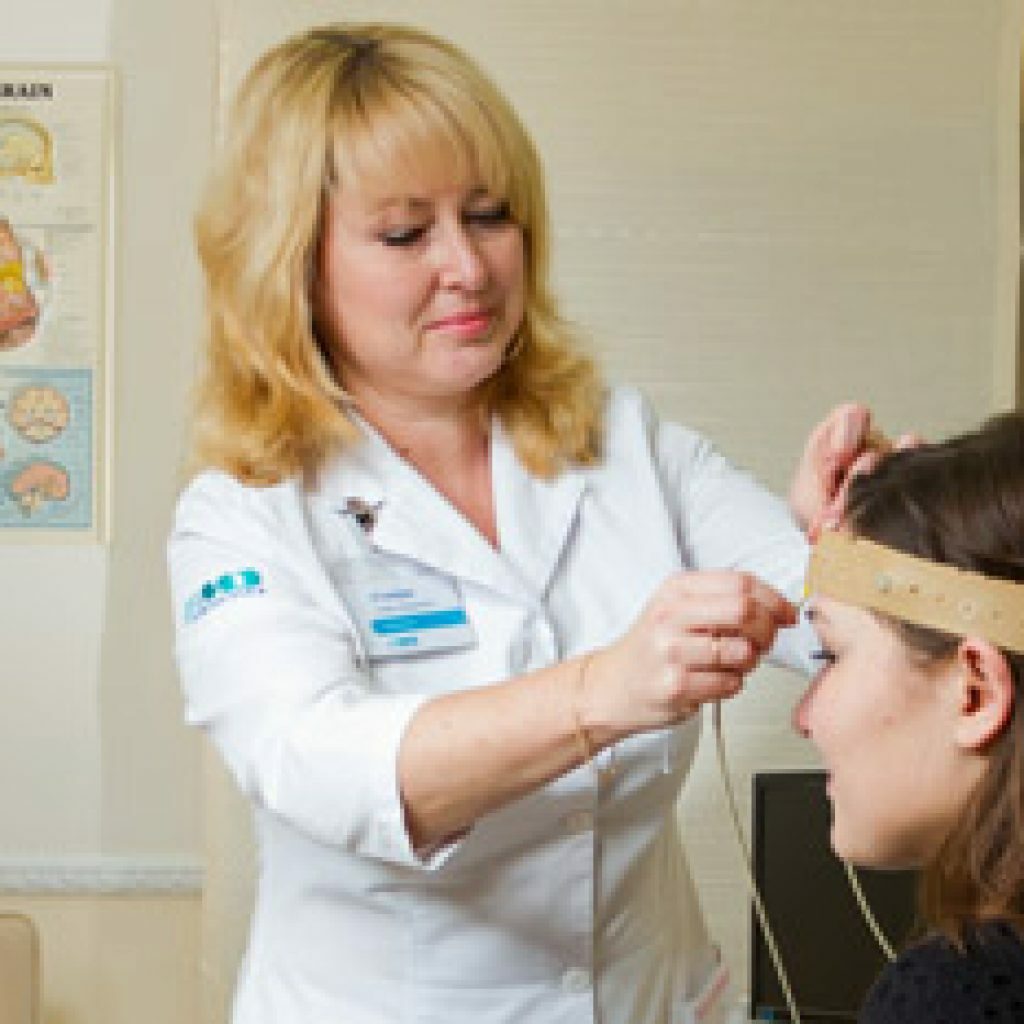
Rheographic tape is placed along the head circumference line
The electrode overlapping areas will always be different and depend on which vessels should be examined:
- if it is necessary to examine the vertebral arteries, electrodes must be applied to the region of the occipital mounds and mastoid processes;
- if the object of the study is the external carotid artery, the electrodes should be located in the temporal region;
- when examining the internal carotid arteries, electrodes are superimposed on the region of the mastoid processes and the bridge of the nose.
Basically, all the vessels are examined immediately. The survey takes an average of no more than twenty minutes.
One of the main conditions for carrying out rheoencephalography is patient calm and relaxation.
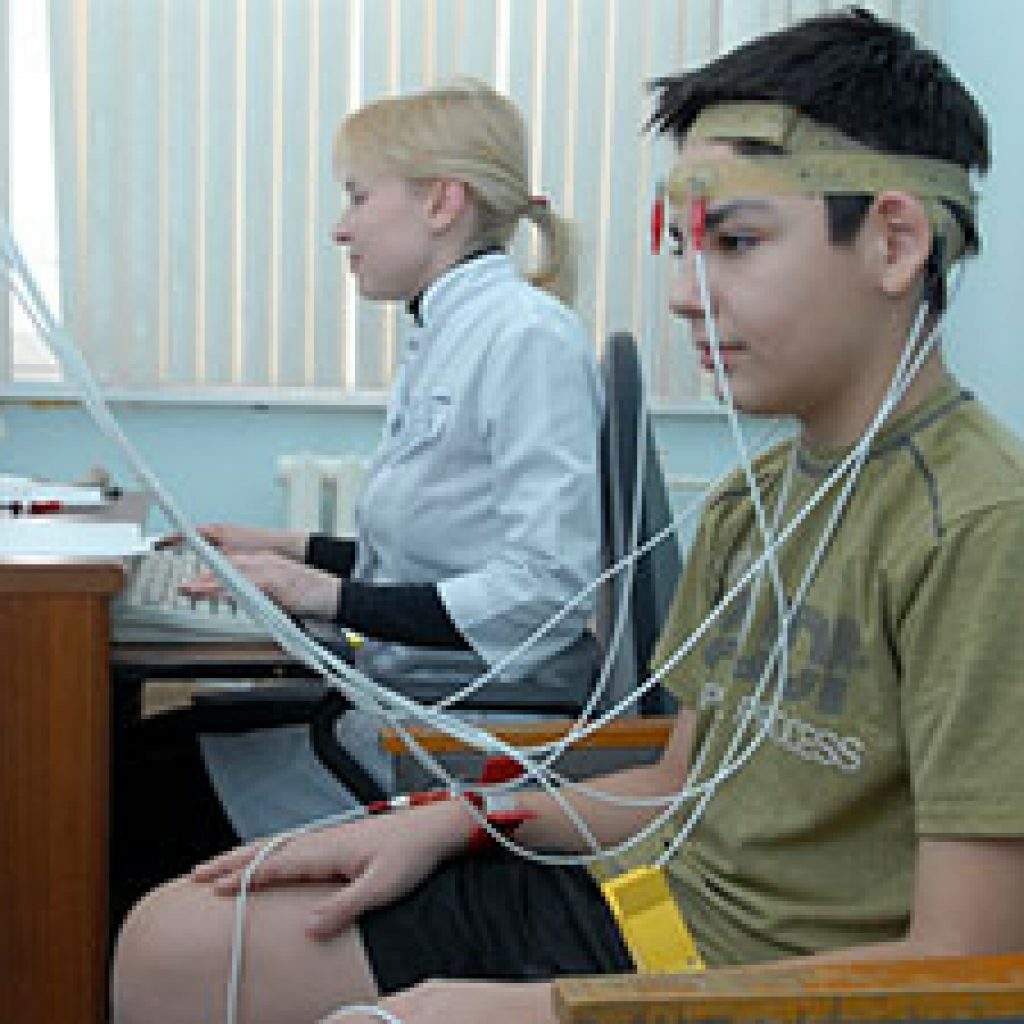

The location of the electrodes of the rheoence- cograph is dependent on the location of the vessels under study.
In addition to the standard procedure for conducting REG, there is a study using so-called functional tests. The most common are samples with turns and inclinations of the head in different directions, taking nitroglycerin( under the tongue), holding the breath, deep breaths and full exhalations, changing the position of the body, exercise. All indications are also recorded, and then compared with those that were made at rest.
Possible consequences after REG REGISTRATION
As already mentioned, rheoencephalography is a safe diagnostic method used for examining patients of any age group. As a rule, there are no consequences after a given diagnostic procedure at rest.
When performing functional tests, a headache may occur( nitroglycerin has such a side effect) and dizziness( after head turns or physical exertion).
Interpretation of the results
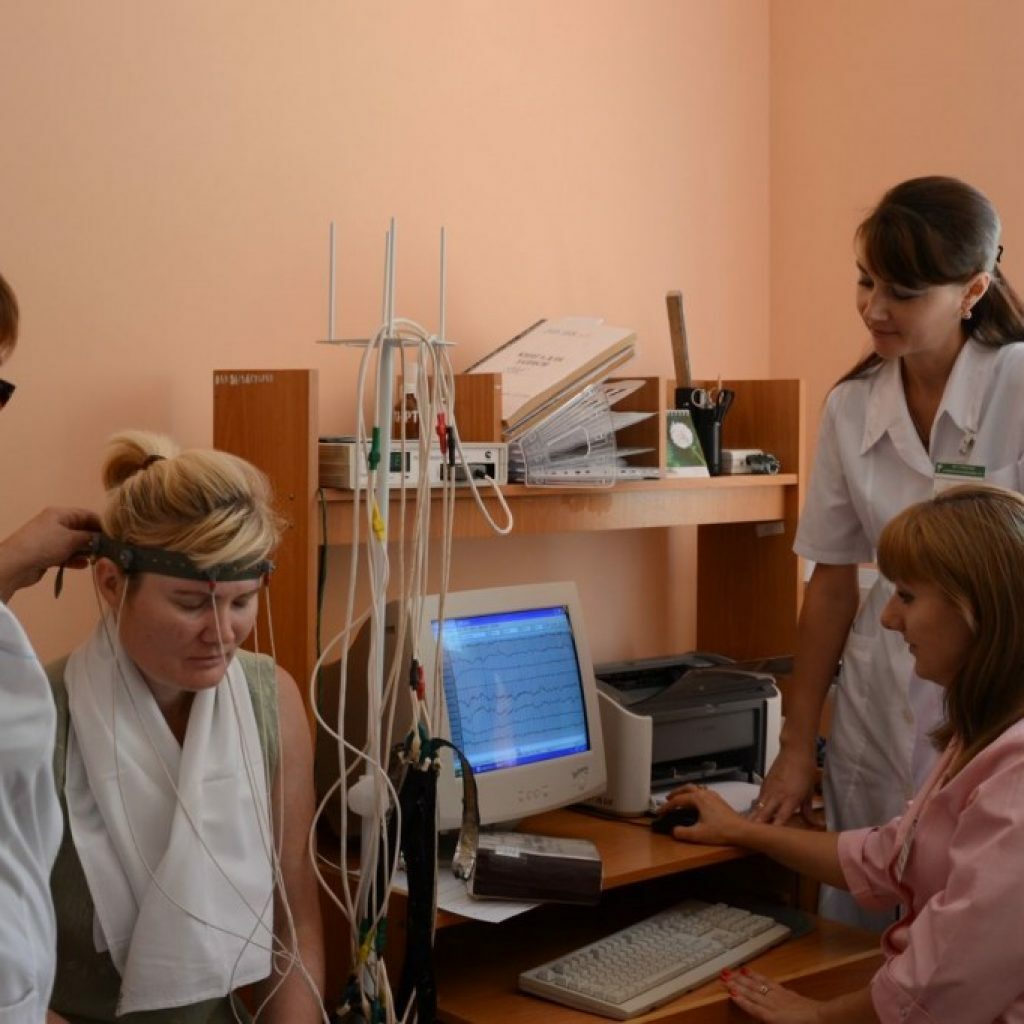
The evaluation of the parameters obtained is performed by specialists in the interpretation of the rheoencephalogram
. The doctor evaluates the obtained parameters of the study. Modern technologies have simplified the complex procedure of deciphering by applying specialized computer programs. Due to this, the patient can receive the results of his examination within ten minutes after the end of the procedure( and not after several days, as it was before in many medical institutions).The age of the patient is of great importance, since the parameters of the rheogram vary for each age group.
All the data obtained as a result of the survey are converted into a graphic picture( graph), which is very similar to an electrocardiogram in appearance. The device gives them either on paper or on the screen of a computer monitor.
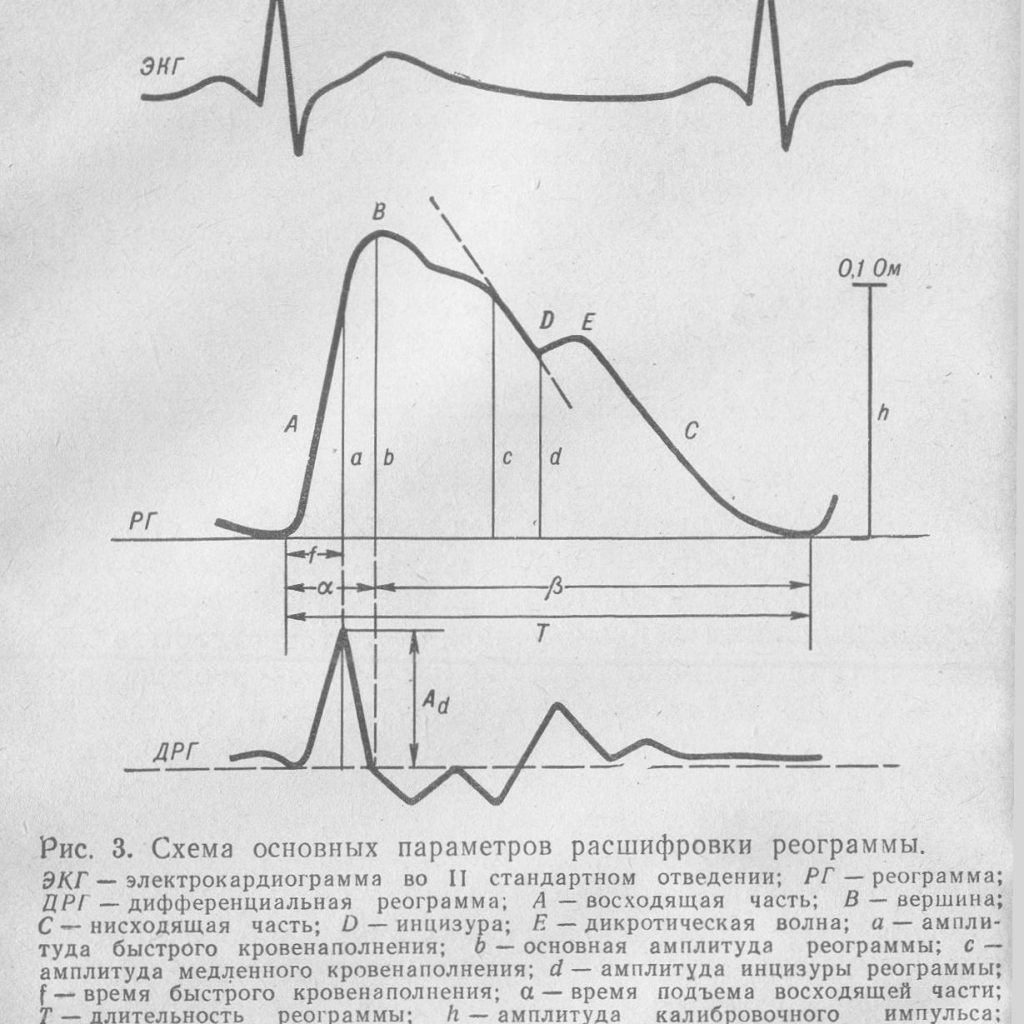
Parameters evaluated by the rheoencephalograph
The undulating image( each tooth of the rheogram) is divided into special segments bearing their names:
- anacrotic( ascending part of the graph);
- the top of the graph;
- of the catacros( the descending part of the chart);
- incision( teeth on the descending part of the graph);
- of a dikrotic or dicrotic wave( the descending part of the graph, located after the incision).
The parameters of these segments are estimated values such as:
- roundness or sharpness of the tops of the graph;
- wave regularity;
- depth of the dicret;
- where the incision is located;
- appearance of anacrots and catacros;
- presence or absence of additional waves in the cell.
It should be noted that such parameters of teeth as amplitude and slope are not less important. They determine the correspondence of the obtained values with the age of the patient. For example, young teeth are more pronounced and inclined more strongly than in older people.
Important indicators of the rheoencephalogram in the table
The values of these indicators build a general picture of the state of the blood vessels of the brain.
Indicator Value Informativeness A rheovole( its amplitude) Degree of vascular opening. Pulse oscillations. Vascular blood vessels. A / E rheographic index In diastolic wave( its amplitude) Peripheral resistance of blood flow from large vessels to small ones. The higher the value, the higher the resistance. AS / 17 diastolic index With of dicron Peripheral resistance of arterioles. The higher the value, the higher the resistance. C / A dicrotic index A1 late diastolic wave Peripheral blood flow resistance from small vessels to large vessels. The higher the value, the higher the resistance. A1 / A ratio of late diastolic wave to amplitude of rheovole A anacroda The ability of large vessels to stretch. The index depends on the elasticity of the vessels. The lower their tone, the higher the index. a / T anacrotic to basic wave ratio AB diastolic wave( its location) Value of vascular tone. The higher the indicator, the lower the tone. ab / T ratio of diastolic wave to the main wave of the chart Rheoencephalographic parameters in the norm
Normally, the rheoencephalographic curve is characterized by:
- pointed tops( with age they flatten and smooth out), clear incisors and dikrots;
- rise time of the tooth up to 0.1 s, with age increases to 1.9 s;
- indicator ab / T should not exceed 15%;
- indicator A1 / A should not exceed the value of 70%;
- , the C / A ratio should not exceed 75%;
- asymmetry in the circulation of the cerebral hemispheres should not exceed 10%.
Reviews of patients
What methods of examination of the brain can prescribe a doctor - video
So, it is now clear that rheoencephalography is a simple procedure that allows to reveal the pathology of blood vessels and blood supply of the brain. Despite the fact that modern medicine offers more advanced diagnostic methods, REG is successfully applied to this day, allowing doctors to make an accurate diagnosis to their patients.