 There is no such cracks in the world - neither in the ground, nor under water, nor in the air( a gap in the air is a gap in the clouds) - wherever a curious nose a person thrusts.
There is no such cracks in the world - neither in the ground, nor under water, nor in the air( a gap in the air is a gap in the clouds) - wherever a curious nose a person thrusts.
And what happens when this nose is crushed by a slammed door? After annoyance, pain comes, followed by fainting. But pain is not the only cause of this phenomenon.
Contents
- Understand in the terminology of
- A little lyricism, or victory at any cost!
- Get out of life during life!
- Neurologic nature
- Neurogenic nature
- Somatogenic nature
- Other provocateurs
- Decay of the spirit with the "decay" of the body
- "Insensibility" of life complete and incomplete
- Diagnostic criteria
- What to do in the first minutes after a syncope
- Treatment of a syncope? No - its reasons!
- "Afterword" syncope
- Prevention: find and neutralize!
Understand in the terminology of
And before starting to disassemble the "bones" of the phenomenon itself, it is necessary to determine what the word that means it: syncope?
"About-" means: something wrapped up, covered, immersed in something, something captured or seized( cooked, frostbitten, etc.).Well, what about the second half of the word?
The Old Russian word "morok" has two meanings. The first: darkness, absence of light, the second: the distorted perception, a state of stupor - the darkening of the mind.
Hence the "faint" - a journey in the darkness, because our ancestors believed that when a person lost consciousness, a person's spirit enters the other world, where he is able to remain forever, lost in his horrors and darkness.
Of course, the body left by the departed spirit, falls, pausing in anticipation of the return of the master.
There comes a semblance of death - the mind and body do not participate in real physical events and actions. Temporarily.
"Non-return" of the spirit "home" can be delayed for an indefinite time - or it may not take place at all, and this means the death of the body is already final, biological.

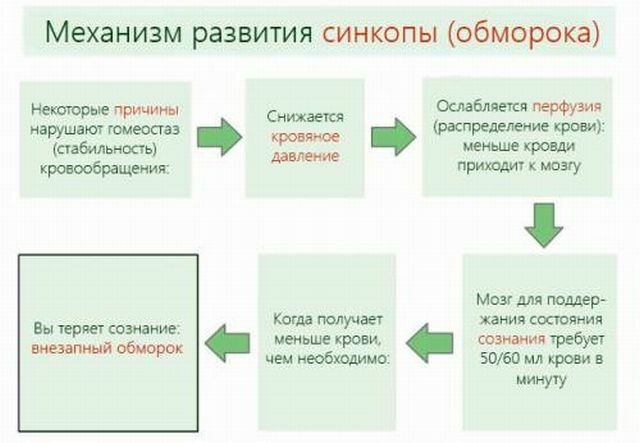
In fact, the same concept of mini-death as in paganism, only it is not a question of spirit, but of "staying in the dark" of the brain that experiences oxygen starvation - ischemia.
So, fainting is "plunging into darkness".How does it happen, and, most importantly, why?
Little lyrics, or victory at any cost!
This is how a person lives: everything that is good, as it were, goes without saying. 
But everything that does not fit into the plan - is equated with the "end of the world".It does not matter if it's a broken deal, a "hanging" computer, landing on the wrong bus or an unplanned operation on said: stop!- a heart.
But now all the difficulties are overcome, the "enemies" around are defeated. And the person becomes bored. At once.
And now all the minor troubles begin to literally "look at the magnifying glass"( especially in old age, when the great forces are already lacking in strength, and ambitions have not atrophied yet).
Yes, mankind simply can not live without acute "ochumleny", it is used to live in hysterics. He must necessarily periodically from something "die" and "go crazy."
So what happens to a person who is horrified by what he himself created? He starts frantically searching for a way out of the situation, straining so that his head "buzzes", and the brain "boils."He needs an "office" and he is looking!
Finally, the situation is resolved, causing a sigh of relief, and the person is again "on horseback."
And this happens more than once, and not two, but constantly. But one day the brain tells the master: there is no way out.
Accustomed to be a winner( and win at all costs) to endure this is simply not in a position. It embraces malice, fear of punishment, the body stretches to the point in the desire to escape to where it is safe.
But you can not escape. Service, family( equating to service), social status, "jump out" of which is scary. ..
The incredible tension of mental and physical forces leads to the fact that the "main computer" "hanging" in an indecision is "cut down".
He can not solve the problem.
And then he just "extinguishes light over it" - comes "plunging into darkness".Fainting.
Get out of life during life!
So, fainting is "a way to escape responsibility"?
That's right. Because the requirement to "be responsible" has long passed from the category of emergency incidents to the norm of life - responsibility has become excessive and constant.
The same became the fear of inadequacy of one's place in life and in society( which replaced life).
And grief and vexation become just as excessive when the door to the world of oneself is shut. Prischimiv nose, remaining on the other side of the door, where "their", and causing a faint.
But sometimes the syncope saves. Saves everything.
And life, and the situation, and prestige - because the performer strained and lost consciousness, saving the "office"!He achieved the goal, not sparing health and life itself! Order him!
And together with the presentation of the next order - a short message about "granted honor and increased responsibility".The circle is closed.
Syncope is not without reason
 Whatever the reason, which caused a syncope - it is always "the transition of Suvorov through the Alps."This is a situation where, despite the excessive tension of the body( a strain that has been accumulating over the years, and which is accustomed to overlook), the brain declares: the solution is impossible!- and extinguishes the light inside.
Whatever the reason, which caused a syncope - it is always "the transition of Suvorov through the Alps."This is a situation where, despite the excessive tension of the body( a strain that has been accumulating over the years, and which is accustomed to overlook), the brain declares: the solution is impossible!- and extinguishes the light inside.
In addition to the vicissitudes of service and family - the causes of the neurogenic property - the "foundation" of syncope can be:
- somatogenic;
- extreme;
- multifactorial.
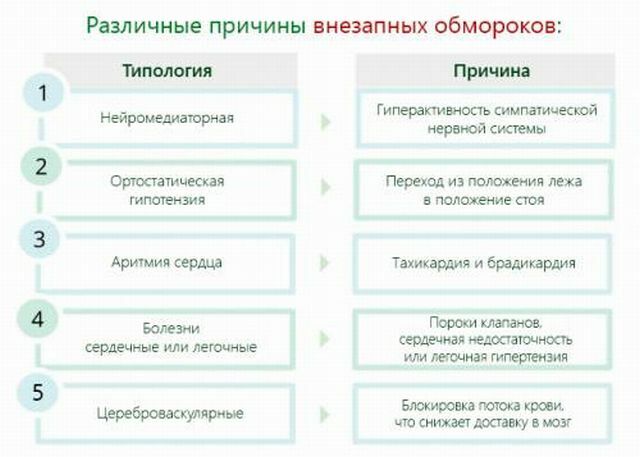
This means that the fainting causes can be of 4 species, divided into several forms with different state genesis.
Neurogenic nature of
Neurogenic syncope refers to conditions that have arisen on the soil of changes in the nervous system. They can be:
- reflex;
- dyscirculatory;
- is maladaptive;
- associative;
- orthostatic.
Reflex disorders of the nervous system lead to the fact that the result of stimulation of a group of receptors when the reflex arc is closed at the same time as the activation of the parasympathetic nervous system is the depression of its sympathetic component.
This leads to:
- peripheral vasodilation;
- slowing heart rate;
- drop in total resistance at the periphery of the vascular system;
- blood pressure drop;
- reduced systolic cardiac output.
As a result of the vascular perturbations that occur, blood is deposited in the muscles, and the blood does not flow to the brain in the required amount.
The cause of this mechanism may be irritation of the receptors:
- of the sino-carotid zone of ( too tightly tied with a tie, located in this area by a tumor and other reasons) - sinocarotid syncope;
- pain zones - pain syncope( intense pain in response to appendix, renal colic);
- of the respiratory tract ( with development of bettlepsy - cough syncope), stomach and intestines( syncope caused by food intake or defecation due to excess of intrathoracic pressure, cardiac output deficit and deficit of venous return from the lower limbs);
- of mucous membranes examined by optical organ devices( PHAGS, fibrocolonoscopy) - irritative syncope;
- of the reflexogenic zones of the vagus nerve , caused by swallowing, diseases of the larynx, esophagus, mediastinum.
Syncope of another neurogenic nature:
- Emotional syncope states are of the same form, because they are of the same nature. Occur in individuals with dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system( with neuroses or neurosis-like conditions, with a tendency to hysteria).
- To subgroup of discirculatory reflex syncope, one should include those caused by neurologic pathology: migraine, DAP, cerebral vasculitis - conditions that have arisen due to the disruption of vascular tone.
- Depressive disorders of the nervous system( inadequate response to high physical activity,
 overheating and the like) cause fainting, called as maladaptive .
overheating and the like) cause fainting, called as maladaptive . - Associative reflex syncope - a condition that develops in situations resembling earlier episodes that ended in a similar way( typical for people with violent imagination).
- For the onset of orthostatic syncope due to orthostatic dysfunction( lack of sympathetic regulation of the arteries of the lower extremities), it is necessary that the transition from a lying position to a standing position does not cause proper restriction of the arteries of the lower limbs. Increase in blood pressure in this case does not occur and the flow of blood into the head( as in the upper half of the body) is inadequate. This is possible in the version with the intake of diuretics, hypotensive drugs, in cases of dehydration or blood loss.
Somatogenic nature of
Syncopathies of somatogenic nature caused by pathology in any body system other than the nervous one include fainting, called
- , cardiogenic ( due to lack of left ventricular ejection in arrhythmia, stenosis of the aortic aorta and similar conditions);
- hypoglycemic ( due to severe hypoglycemia, which can be caused not only by diabetes mellitus, but also hypothalamus deficiency, starvation, pancreatic tumors or fructose intolerance of ancestral sense);
- with anemic ( due to low hemoglobin content or lack of red blood cells in the blood);
- respiratory ( due to a decrease in the lung capacity due to pulmonary diseases or on the basis of hyperventilation, resulting in a low concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood - hypocapnia due to pertussis, bronchial asthma, pulmonary emphysema).

Other provocators
The names of forms of syncope states reflect the reasons why a person faints, which can be:
- by hypovolaemic ( due to lack of fluid in the body due to severe sweating or blood loss);
- by hypoxic ( due to low oxygen content in rarefied ambient air - at high altitude and in similar situations);
- hyperbaric ( associated with hardware breathing - in scuba divers or performers of similar types of work);
- intoxicated ( as a result of any acute poisoning: carbon monoxide( furnace) gas, alcohol or other toxin);
- with iatrogenic ( medication) caused by taking a medication that caused a decrease in blood pressure, either with a purposeful or mistaken( for ignorance) application, or because of an overdose( the most common cause is the use of neuroleptics, tranquilizers, diuretics).
Fainting of a multifactor nature is the result of a combination of several causes at once.
In nictic fainting, occurring during the nighttime urination( or soon after it) in older men, several factors work simultaneously.
This is a dramatic change in the horizontal position occupied for sleep( when the influence of the parasympathetic nervous system is dominant) on the vertical, and the deposition of blood in the bladder vessels enlarged after its emptying with the termination of the stretching of its wall.
Because of the acute lack of oxygen, ceased to act with arterial blood due to the triggering of this mechanism, and a syncope occurs.
Decay of the spirit with the "decay" of the body
In the development of syncope, three phases are traced:
- is lipotymic, or pre-occlusive;
- itself is faint;
- post-syncopal, or after a fainting.

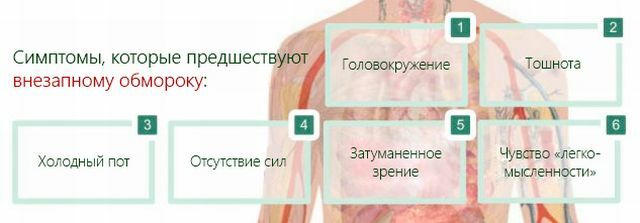
The state of lipotymia occurs shortly before unconsciousness( within a minute) and has a duration of 5-20 seconds to one or one and a half minutes.
For this stage of fainting is characteristic of wave rolling weakness accompanied by a feeling of faintness( nausea), ringing or noise in the ears, dizziness is joined by visual disorders in the form of "cloudiness of sight" "fog", "shroud", "flashing of flies before the eyes."Become "wadded" feet cease to obey the will of the owner, on the pale face and skin acts cold sweat.
At the same time, there may be a feeling of fear, anxious heartbeat, as well as a "coma" in the throat, feelings of suffocation or a sense of "lack of air";comes yawning, "fingertips" fingertips, lips, tongue.
The final of the stage is the feeling that "the ground is floating out from under your feet," outwardly looking like a slow "slipping" of the body to the floor.
In case when the victim has time to lie down, the banal syncope from overheating can end with this - there is no loss of consciousness. With syncope of another, deeper and rare genesis( due to swallowing disorders, arrhythmic disorders), fainting can occur, bypassing the stage of lipotymia.
For the stage of the actual fainting, lasting from 5 seconds to 1 minute, a loss of consciousness characterized by a simultaneous sharp loss of the muscle tone of the whole body due to which there is a smooth slippage, a "slipping" of the body to the floor, without a picture similar to the fall of a tin soldier( inIn the case of sudden and rapidly developing fainting, the appearance of bruises from falling may occur).
The skin of a person's body with a lack of consciousness has a shade of pale gray( ashy) to almost greenish, cold to the touch.
There are signs of a fall in cardiac activity - a fall in blood pressure( with a systolic index of 60 or less mm Hg), a weak( up to a threadlike) pulse.
Breathing becomes superficial( giving the impression of missing).
Depression of all deep reflexes occurs, pupils with a poor response to light come on( they hardly narrow down during a light test).
With not recovered within 15-20 seconds, blood flow in the brain occurs involuntary emptying of the bladder and intestines, the occurrence of single muscle cramps.
The picture of the post-syncopal phase( after a faint) lasting for several seconds, resembles a "scrolling movie back" - the senses of  are awakened in a sequence that comes back in the process of fainting until the consciousness returns completely.
are awakened in a sequence that comes back in the process of fainting until the consciousness returns completely.
As if someone "includes" the vision, then "approach" and gain the full power of the voice of those present, initially sounding "from afar", the feeling of full presence in one's body returns.
Completely restored consciousness allows the victim to immediately navigate both in time and place, and in his own personality.
The first reaction to "awakening" is anxiety and fear of awareness of what happened with increased respiration and heart rate. Then, "breakdown" and a feeling of fatigue "piled on", there may be a painful sensation in the heart and in the abdomen.
There is no memory of the faint itself, the last fragments of memories are feelings due to a sudden change in state of health.
"Insensibility" of life complete and incomplete
Syncope is a special case of such a more general concept as loss of consciousness:
- short-term ;
- long-term ( resulting in severe disorders of vital processes);
- aggravated ( when the increasing severity of the disorders leads to coma and death of the body).
A person who has passed out a syncope does not need a long recovery of his personality - they return with consciousness.
By and large, fainting is the ability of the brain to "rest" from the oppressive picture of its surrounding "nightmarish" reality, after which it becomes possible to look at life and yourself in it with other eyes.
But such radical changes in life with a complete "revaluation of values" are rare.
The most convincing in this regard are syncope in vestota-vascular dystonia( in particular, having a vagotonic and hypotonic type with very low tonus of cerebral vessels) belonging to a subgroup of emotionally( neurogenic) faints, when a neurotic, hysteria-prone personality type provokes their frequentoffensive.
Scientifically proven fact: in people-dystonics who "found themselves" in interesting and fascinating classes in physical education, games in the air and in other physical activities, the tone of the sympathetic part of the nervous system is activated. This leads not only to an adequate expansion of coronary and pulmonary vessels, but also to an increase in the tone and expansion of the cerebral vessels, and, hence, to an increase in the supply of blood to the brain and prevention of syncope.
Diagnostic criteria
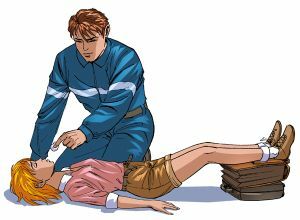 The issue of diagnosis of syncope states has several aspects. This is either an "investigation of the history" of an unfeeling body, or a conversation with a living person.
The issue of diagnosis of syncope states has several aspects. This is either an "investigation of the history" of an unfeeling body, or a conversation with a living person.
"Stumbling" alone, without witnesses on the body, very similar to dead, how to determine if it is alive?
A simple "test" - bringing to the nose of a "vague" bottle with ammonia, as a rule, helps to resolve the contentious issue of its belonging to the world of the deceased - with ordinary shallow fainting it is enough, the victim is able to wake up.
In case of no first fainting in a close environment of the victim, the question of diagnosis does not arise at all - he gets up at a condition that happened for the first time.
Here, in addition to the general quick familiarity with the situation and the examination of the body( the character of the build, the pose, the smell of acetone, coming from the body, the nearby medicinal packaging), helps a quick "collection of the initial anamnesis" - information about chronic diseases, preferential complaints, medications, habits, personality stock are able to significantly help diagnosis.
It is a different matter when it is necessary to clarify the nature of the often occurring loss of consciousness in a self-sustaining carrier of an unhealthy body.
In this case, a careful study of the functions of the brain, respiratory and cardiovascular systems is necessary:
- EEG, CT( MRI) of the brain helps to recognize the tumor of the subtleties of the cerebral vascular pattern;
- craniogram of - elimination of bone and other pathology of the skull and brain;
- ECG or Holter monitoring for fixing diurnal changes in heart rate;
- blood and urine tests for glucose to exclude diabetes mellitus.
In the formulation of the diagnosis, such research methods as regular monitoring of blood pressure, orthostatic EEG provocation, a test with a sinocarotid zone massage, and a test for hyperventilation that can reveal the dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system can help in the diagnosis.
The question of the need for other methods of investigation is decided by a neuropathologist or medical consultation.
What should I do in the first minutes after a syncope
What should I do if a syncope is suspected? - In this case, the actions of the first aid person should be clear and fast:
- immediate call of "emergency aid" ;
- ensuring the flow of blood to the brain ( giving the body a horizontal position or with a raised leg end);
- maximum release of the body from the tightening clothing elements ( belt, belt, tie) to facilitate breathing, for the same purpose it is necessary to open the door or window;
- body warming ( rubbing with vodka, alcohol, dry hands, warmers to the feet, plaid, blanket);
- stimulation of breathing ( by submitting to the nose of the affected tampon with ammonia, vinegar, with another substance having a sharp odor), with the same purpose it is necessary to spray the face with cold water, light flip flops on the cheeks.

After the victim comes to him, he should be given a sweet tea( coffee), give a light heart( valocordin 10-15 drops in 1/4 cup water, 20-30 drops of valerian).
Doctor Komarovsky knows what to do in case of a syncope: first emergency:
Treatment of fainting? No - its reasons!
It is not necessary to talk about the treatment of syncope as such, considering that a single, once in a lifetime, extreme faint happened - a short-term, passing without consequences state.
Another thing when it comes to a fairly frequent loss of consciousness on the basis of this or that pathology. Here the goal of treatment is to prevent the occurrence of these conditions.
And here it is appropriate to "tie" the methods of treatment to the classification of fainting.
Fainting of somatogenous genesis need treatment of the main pathology: the appointment of antiarrhythmic drugs in rhythm disorders, containing iron compounds - with the same anemia, as well as in the application of other, depending on the cause, measures. 
In the treatment of recurring fainting of the neurogenic nature, it is possible to use both non-medicamentous and medicinal methods.
But the results of the latter( such as β-adrenoblockers( Propranolol, Metoprolol, Atenolol), mineral corticoid( Fludrocortisone) or α-adrenomimetiki( Midodrin), as well as their combinations) are inconsistent.
More reliable methods are physical plan, which are more likely to prevent( prevent) fainting - to avoid provoking situations and to prevent loss of consciousness when approaching syncope.
The provocative moments that should be avoided by a syncope of neurogenic nature include:
- wearing tightly tied, body-tight clothes and its elements : ties, collars, belts, belts;
- rapid, abrupt change in the body position ( getting up from the bed, straightening after putting on shoes, squatting);
- stay indoors stuffy, not ventilated , with stagnant air or with air, saturated water vapor or other vapors;
- surveillance of alarming medical procedures .
Effective means of preventing - or delaying - neurogenic syncope are the techniques of crossing the legs or compressing the hands into fists with a clearly perceptible approach.
When performing these actions, the blood pressure rises to a level sufficient to prevent fainting or delay it( until it is possible to lie down or sit down).
People with frequent fainting of orthostatic genesis are able to benefit from daily orthostasis training, in order to reduce the delay of blood( deposition) in the lower extremities, the use of bandage or the use of compression knitwear( especially for the elderly) should be recommended.
For the treatment of persons with vegetative dystonia, there are various methods for correcting psycho-vegetative disorders( the nature and volume of which are selected individually), the application of which leads to the disappearance of the cause of fainting.
"Afterword" of syncope
 Does syncope always have consequences? And if so, which ones?
Does syncope always have consequences? And if so, which ones?
Single fainting does without consequences, but this "procedure" should not be repeated often, especially - to become regular.
After all, every syncope is an experience of an episode of oxygen starvation of the brain. And, depending on the degree and duration of ischemia, the nature of the metabolism of individual brain structures is able to change not in the best for the host organism side.
Possible consequences of frequent loss of consciousness may be attention deficit disorders, memory loss.
No less serious consequences can be the sudden fall from height, into water, on hot surfaces or just on the floor - these are injuries in the form of bruises, cuts, burns, fractures, craniocerebral trauma.
Syncope for lonely living people is especially dangerous, and especially for those suffering from various nervous or somatic pathologies. After a prolonged ischemia of the brain can lead even to death in the elderly or old man.
Prevention: find and neutralize!
Given that many conditions can lead to fainting, with frequent offensive, all of them should be analyzed. Unfavorable physical conditions of existence can either be changed, or try to avoid them.
As for the warehouse of the person and the peculiarities of the psyche, then a qualified consultation of a neuropathologist or psychiatrist is necessary.
Only he alone is able to find and neutralize a "bomb" buried deep in the subconscious, "collected" from fears and a complex of inferiority. 
And only then, based on the received psychological support and taking into account his recommendations, you can begin to expand the range of your physical abilities.
The general problem for the neurotic person is the maximum clear awareness of the surrounding reality and its role in it, with the transition from self-pity to self and fear of life to full and bright participation in it.
No less important is "physical labor" for the benefit of the body.
And if not everyone suffering from fainting can "send" himself to the stadium or to the section of "lightweight" physical education, then everyone can afford a leisurely walk at night. After all, at stake - not only career and family, but also physical and mental health!



