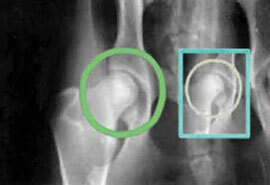
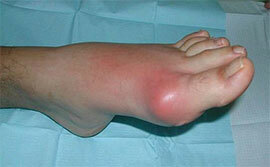
Prevalence of
About 20% of all osteoarthritis occurs in the interphalangeal. This is the most common disease in the group of arthrosis. In women, it is more common, especially in the menopausal period and with weaker heredity.
Diagnosis of arthrosis of interphalangeal joints
To diagnose this disease, you need to question the patient to know:
- The sex of the patient - in women the arthrosis of interphalangeal joints is 10 times more common than in men.
- Age of patient - older people are more likely to suffer from this pathology.
- Genetic burden. If such a disease was in the immediate family, then the probability of its appearance in the subject increases.
- Postponed diseases. If the subject had joint disease or joint surgery, the risk of developing osteoarthritis increases.
- Professional anamnesis. If a person's work is associated with an excessive load on interphalangeal joints, the risk increases.
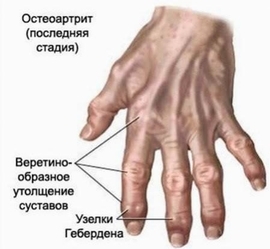 After the survey, you need to evaluate the clinical picture of the disease, identify the symptoms:
After the survey, you need to evaluate the clinical picture of the disease, identify the symptoms:
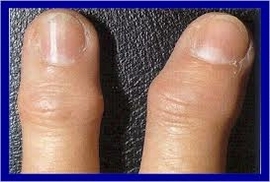
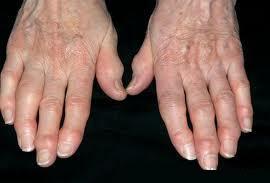
- Deformed( spindle-shaped) joint form
- Geberden and Bouchard knots - bony outgrowths around the affected joint.
- Redness, tenderness, swelling of the joints - in the acute period of the disease.
- Deviation( curvature) of joints:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Palmarous - distal phalange bends from the longitudinal axis of the finger towards the palm.
- Ulnarnaja - the distal phalanx deviates aside the ulnar bone( the ulnar bone on a Latin - osulne).
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- In the acute stage of the disease in the joints of , pain can occur when moving , as one of the signs of inflammation.
A key role in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis is inflammation. Infected tissue around the joint disturbs its nutrition. At the same time, various harmful substances are released into the joint, which further oppresses its existence. Therefore, therapy aimed at fighting inflammation is considered to be the most reasonable treatment for such a disease.
The final diagnosis is based on the data of the radiograph of the joints of the hand.
X-ray diagnosis provides the basis for the identification of three stages of arthrosis of interphalangeal joints:
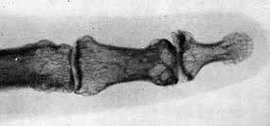 Stage I:
Stage I:
- no bony proliferation
- joint surface rough
- articular joint narrowed 1/2
II stage:
- Appearance of bony outgrowths
- The joint gap is narrowed more than 1 /2
- Subarachnoid sclerosis
III stage:
- Strong joint deformity
- Joint gap almost completely absent
- Possible appearance of "joint mice"
Treatment of arthrosis of interphalangeal joints
1. Reduction of the load on the affected joints.
2. Articular exercises.
Articular surfaces( cartilage) are not blood supply. Their nutrition occurs through synovial fluid, which is synthesized inside the joint capsule. If the joint does not move for a long time, the articular fluid flows roughly downward, under the influence of the force of gravity. Therefore, the "upper" parts of the joint do not receive food and are forced to starve and atrophy. A cartilaginous surface refers to tissues that do not regenerate on damage. Therefore, it can only decrease and be replaced by a bone tissue.
When performing articulation, we accelerate the synovial fluid over the entire surface of the cartilaginous tissue, which as a result is adequately nourished and capable of withstanding heavy loads and lasting longer .
3. Treatment of joints with drugs.
3.1.Treatment of pain syndrome.
A) Paracetamol is the first line treatment for pain. Paracetamol not only reduces heat, it still acts as an anesthetic. In anesthesiology, recently, it has been used as one of the components of the complex therapy of postoperative pain. But there is a restriction on taking this drug - no more than 4 grams per day.
B) Local treatment - ointments with NSAIDs. The active substance in ointments can be different: diclofenac, nimesulide, ketoprofen and other NSAIDs.
From the diclofenac series, it is best to use Voltaren Emulgel( 200-300 rubles per tube), since the domestic analogue( 20 rubles per tube) leaves much to be desired.
Ibuprofen - well fights inflammation, but causes a lot of side effects. It is very dangerous for peptic ulcer.
Ketorol is a good product at a reasonable price. It is active in terms of reducing pain, but can cause severe complications of treatment with prolonged use. Therefore, it should always be used cautiously.
Nimesulide is one of the new generation drugs. It has a reduced number of side effects, and it really works against any musculoskeletal inflammation.
Meloxicam - works only in the inflammation zone, which practically reduces the complications from the use of this drug.
Ketoprofen is one of the best drugs for anesthetic and anti-inflammatory effect, but its cost makes you think hard about its purchase. Medical representatives advertising this drug, assure that the strength of the analgesic effect, it is almost equal to morphine( !) - narcotic analgesic.
B) Systemic treatment - tablets, capsules and granules with the same NSAIDs described above. If local action of drugs( ointments) we act locally on a certain joint and in small doses, then the systemic action covers the entire body, where it is necessary and not necessary. Moreover, treatment takes place at higher doses, and as a consequence, with more likely complications and side effects.
It should be remembered that any organism will sooner or later become accustomed to any analgesic. Therefore, treatment should begin with the weakest means( paracetamol) and move on to stronger ones, as a last resort.
3.2.Treatment of cartilaginous tissue
There are medicines that improve the trophism( nutrition) of cartilaginous tissue - chondroprotectors. These include chondroetin sulfate( structum), glucosamine and others. These drugs should be taken in long courses of 3-6 months per year. Take them only during an exacerbation is meaningless. Some orthopedists say that in order to prevent osteoarthritis, people over 30-40 years old have a reason to start taking chondroprotectors.
 4. Physiotherapy.
4. Physiotherapy.
- Joint heating
- Laser therapy
- Diadynamic currents
- Sanatorium treatment
5. Surgical treatment.
Endoprosthetics of deformed joints .The joints are changed to prostheses, made mainly of silicone. As a result of the operation, mobility returns to the joint, but not in full.
Prevention
For the prevention of arthrosis of interphalangeal joints it is necessary:
- Do not overload your joints, protect them from traumatization
- Do joint exercises
- Start taking in advance the chondroprotectors
Video: Exercises for the joints of the brush
 Interphalangeal arthrosis is a disease that is manifested by deformation of the distal interphalangeal joints of the hands.
Interphalangeal arthrosis is a disease that is manifested by deformation of the distal interphalangeal joints of the hands.