In modern medicine, there is a tendency to develop and improve minimally invasive interventions in the human body. Increasingly, anesthesia and large incisions are replaced by local anesthesia and several punctures. Such interventions are appreciated by patients with a variety of different diseases, whose treatment involves operations. Such methods include the surgical method of arrhythmia treatment - radiofrequency catheter ablation of the heart.
Contents
- 1 Essence of the method of radiofrequency ablation
- 2 Advantages and disadvantages of the
- 3 method Indications for
- 3.1 Cardiac arrhythmias and their causes are video
- 3.2 Contraindications
- 4 Preparing for operation
- 4.1 Procedure for
- 4.1.1 RFA - Schemes of Operations
- 4.1 Procedure for
- 5 Rehabilitationand postoperative period
- 5.1 Complications
- 6 Radiofrequency ablation of the heart: patient feedback
- 6.1 Heart RF: opinion of the cardiologist
The essence of the method of radiofrequency ablation
Radiofrequency ablation is a minimally invasive intervention for the treatment of arrhythmias accompanied by a pathological frequent pulse( tachyarrhythmias).
Synonyms of radiofrequency ablation are: RFA, catheter destruction.
Normally, the pulse of a healthy person is 60 to 90 beats per minute. At the heart of rhythmic contraction is the passage of an electrical signal through a special tissue of the cardiac muscle( myocardium) - the conducting system. Normally the signal is formed in the main rhythm driver - the sinus node. In the second node - atrioventricular - it undergoes a delay for synchronous reduction of the chambers of the heart, after which it reaches directly to the heart muscle, causing the release of blood into the vessels.
The considered path of the electrical signal forms a normal picture of the electrocardiogram. The reason for the formation of arrhythmias with a high heart rate is a pathological pulse passage through the cardiac muscle. The aim of the operation is to: make certain anatomical areas of the conductive tissue of the heart inactive by means of the surgical treatment.
The method is based on the effect on the heart tissue of the energy produced by the radio-frequency generator. It has certain parameters for temperature, power and duration of exposure.
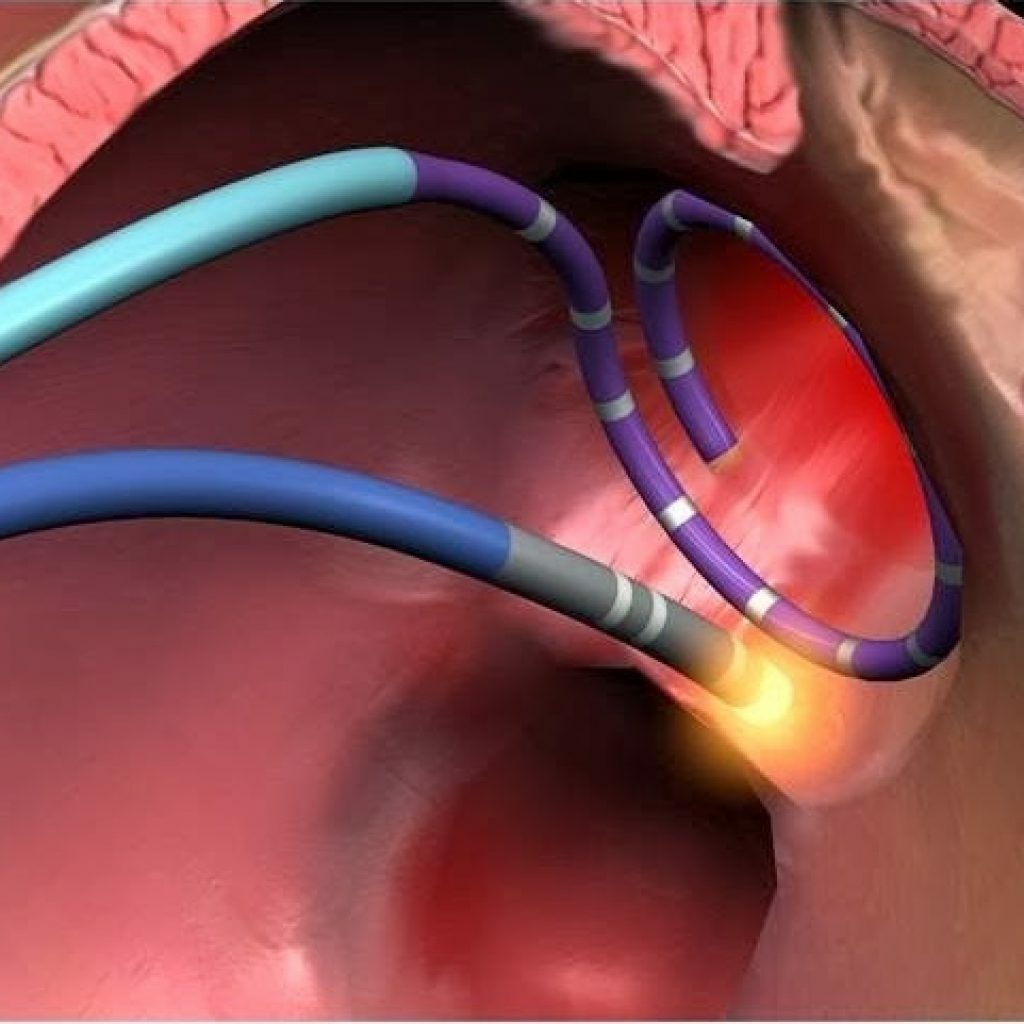
Electrode arrangement for RFA
Advantages and disadvantages of the
method The advantages of the method include:
- absence of anesthesia and incisions;
- point targeted impact;
- minimal complications from the normal pathways of the heart;
- checking the effectiveness of treatment during surgery;
- rapid recovery after surgery;
The disadvantages of the intervention are:
- stopping the arrival of radio-frequency energy to the foci of arrhythmia with prolonged exposure, as a result of which it is necessary to repeat the procedure;
- intervention for a single arrhythmia does not prevent the appearance of other species in the heart;
- not all types of arrhythmias are amenable to surgical treatment by RFA;
- with a large heart size complicates the diagnosis of the location of the arrhythmic focus and, as a consequence, the percentage of successful treatment decreases;
There is a method of treating arrhythmias by exposure to extremely low temperature heart tissue - cryoablation. Her conduct is preferable in children, in places close to normal and pathological conductive pathways, large vessels. With cryoablation, the effect is less persistent and, as a consequence, the need for repeat procedures increases compared to radiofrequency ablation.
Indications for
Atrial fibrillation( synonym for atrial fibrillation) is a popular indication for radiofrequency catheter destruction. This pathology is now extremely common among the population. The reason - a lot of foci located in the left atrium in places where large vessels fall into it - the four pulmonary veins. As a result, the rhythm consists of indiscriminate contractions of the heart.
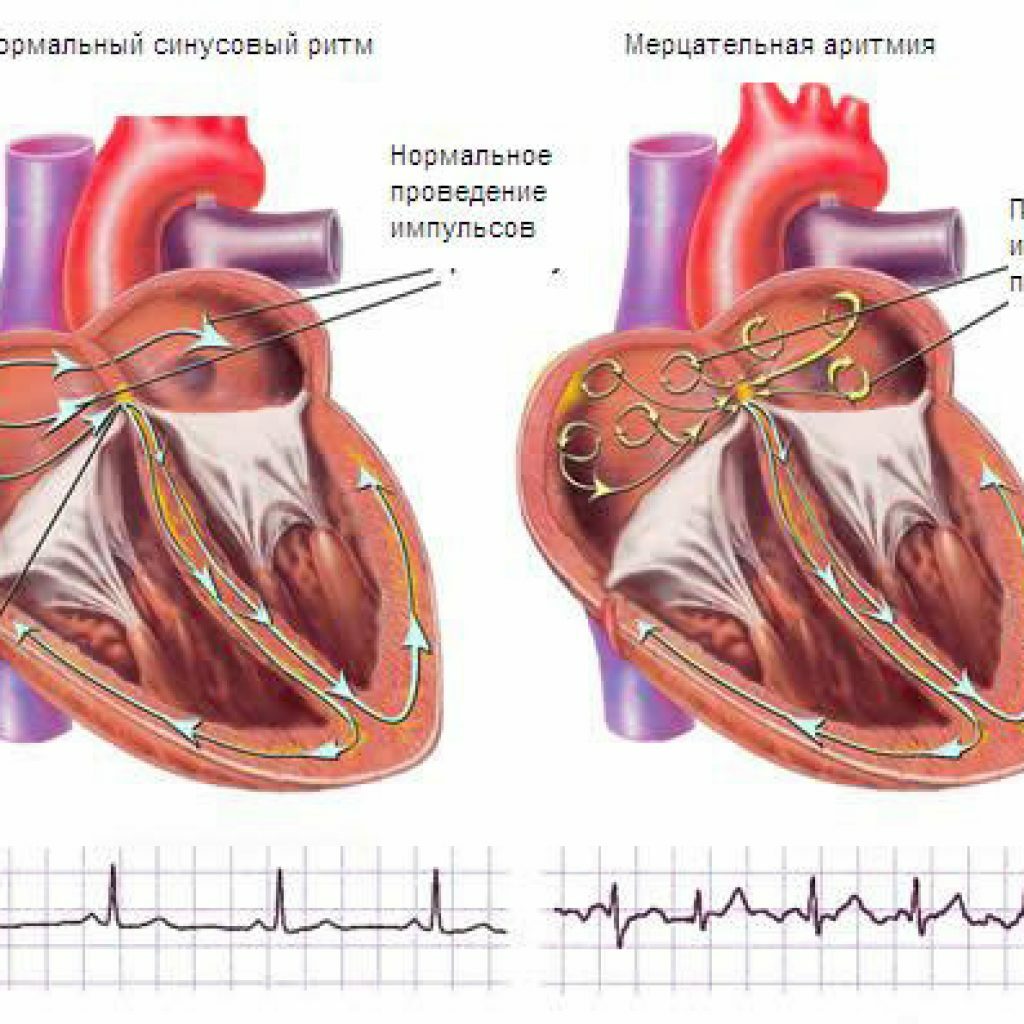
Scheme of the mechanism of the development of atrial fibrillation
Also an indication for catheter ablation is the congenital anomaly of the conducting pathways - the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. At the core is the activity of the pathological way of conducting - the atrioventricular bundle. As a consequence, an altered form of the ECG appears. When an electrical signal passes through the normal and abnormal path, an arrhythmia with a high frequency of cardiac contractions is observed, which can lead to a fatal outcome due to its transition to more dangerous types of rhythm disturbances.
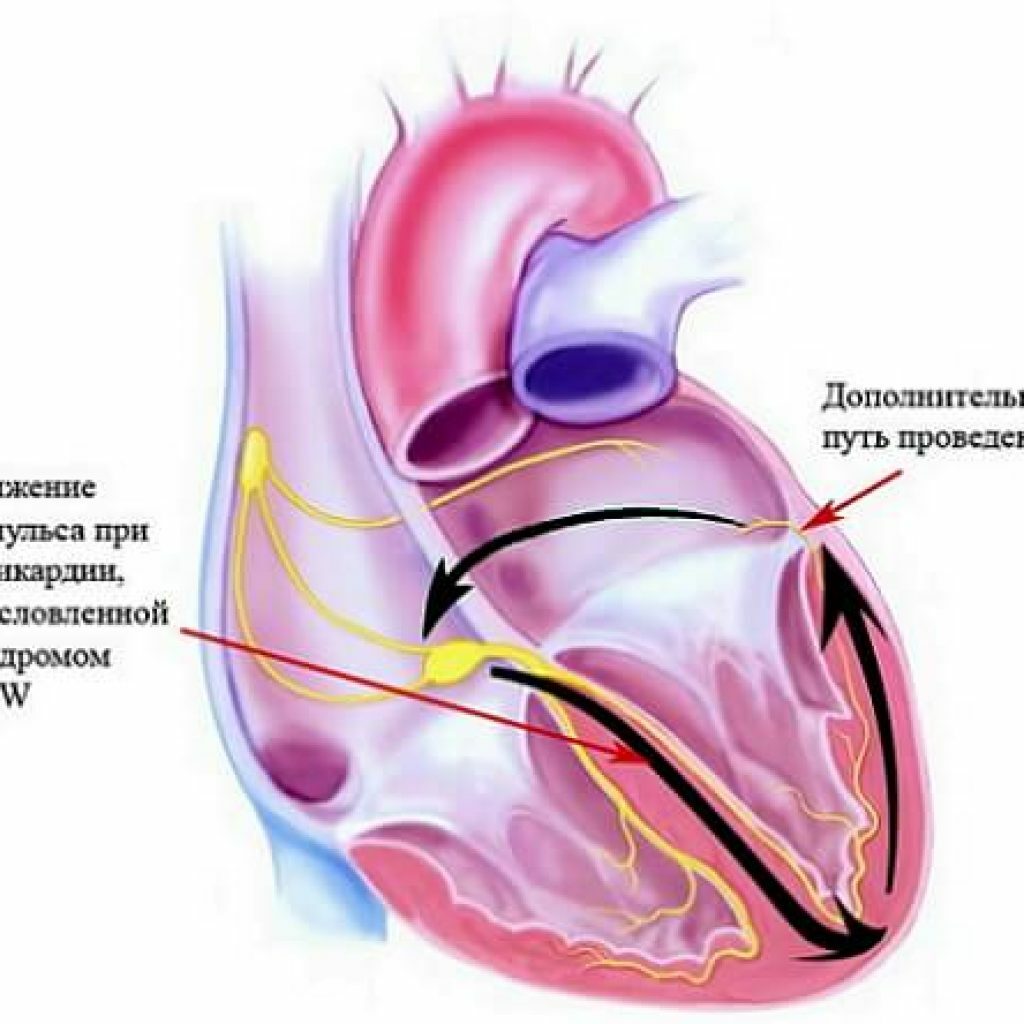
Scheme of the mechanism of development of tachycardia in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
Very similar to the previous other kind of arrhythmia - atrioventricular nodular tachycardia. It is characterized by the circulation of an electrical signal along two paths - normal and anomalous. However, both pass as part of one anatomical entity - the atrioventricular node.
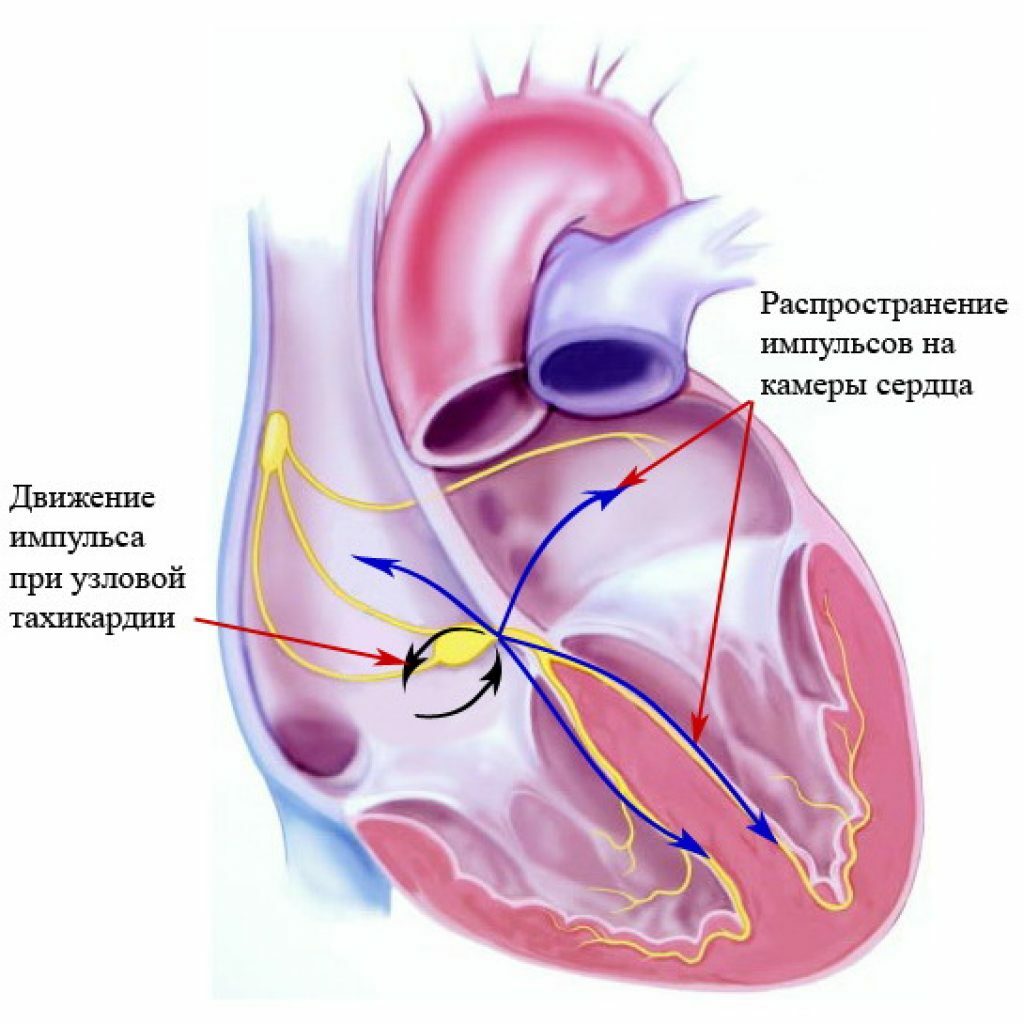
Scheme of the mechanism of development of atrioventricular nodular tachycardia
Atrial flutter is another important aspect of indications for RFA.This kind of arrhythmia is a closed electrical circuit. Passing along it, the electric signal forms on the ECG a picture of large waves( hence the name of arrhythmia).The goal of RFA is to make the weak point of this chain inactive.
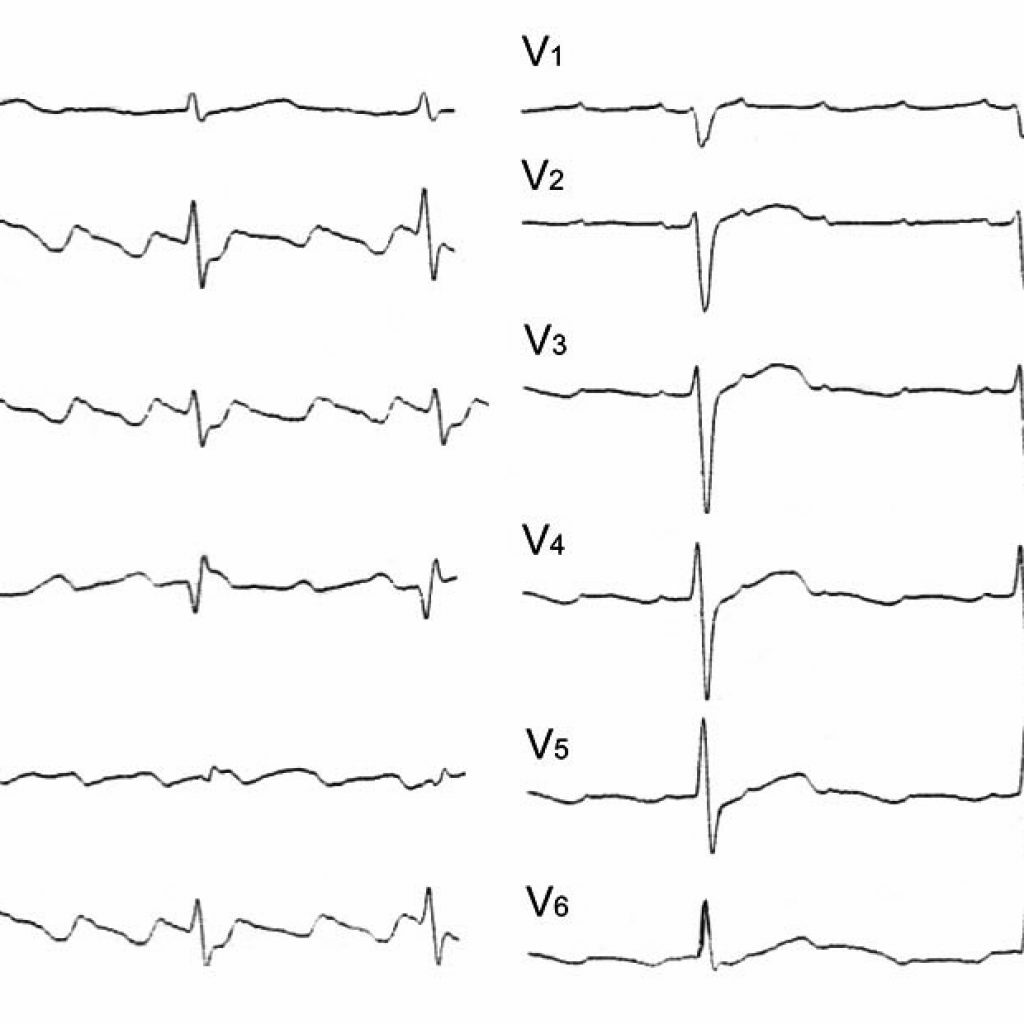
ECG pattern of atrial flutter
An important indication is ventricular extrasystole. This term refers to an electrical signal that caused a shortening of the heart out of turn. The cause is the active electrical portion of the heart tissue located in the ventricles of the heart( the main pumping elements).For the decision to conduct RFA, an important parameter is the number of such reductions per day. Operation is applied at presence on a background of a normal rhythm more than twenty thousand extrasystoles.
Cardiac arrhythmias and their causes - video
Contraindications
Contraindications include:
- acute respiratory infections;
- acute period of stroke and myocardial infarction;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- abnormalities in the laboratory;
Preparation for operation
Before the operation, the following:
- examination of the doctor with detailed clarification of the details of the disease( beginning, stages of development, tried methods of treatment);
- recording of electrocardiography - the visual picture of the passage of an electrical signal along conductive paths, including on archival films, is analyzed;
- daily recording of the electrocardiogram( holter monitoring) is necessary for recording rhythm disturbances that appear at a certain time of the day. In addition, it is necessary for calculating the number of ventricular extrasystoles;
- when suspected of the ischemic nature of arrhythmia, a study of the blood vessels is performed - coronary angiography;
- is mandatory to study the general analysis of blood, blood type and Rh factor;
- before the operation for atrial fibrillation, a blood test for thyroid hormones is mandatory;
Methodology of the
Radiation partial ablation is performed under local anesthesia( Lidocaine, Ultracaine).For the placement of catheters( ablative and diagnostic), two punctures are most often used: under the left collarbone and in the right inguinal region. Then, under the radiological and electrocardiographic control, the arrhythmia zone is searched. After this, a point effect of radio-frequency energy on the tissue of the myocardium is made. In this case, the patient may feel pain and burning sensation in the heart area that passes after the end of the exposure. The number of exposures per procedure for different types of arrhythmias ranges from a single to several dozens, depending on the area of the anatomical zone. After checking the immediate effect of the intervention, the tools are removed, aseptic dressings are applied.
RFA - Schemes of Operations
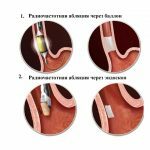 Conducting Radio Partial Ablation with Cylinder and Endoscope
Conducting Radio Partial Ablation with Cylinder and Endoscope 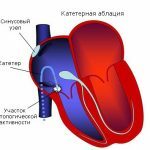 Scheme of Arrangement of Heart Routes and Foci of Arrhythmia
Scheme of Arrangement of Heart Routes and Foci of Arrhythmia 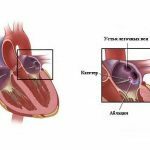 Atrial Fibrillation: Scheme of Operation
Atrial Fibrillation: Scheme of Operation 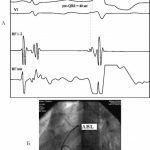 Radiographic and ECG Pattern for Ablation of the Additional Atrioventricular Beam( Wolf-Parkinson-White Syndrome)
Radiographic and ECG Pattern for Ablation of the Additional Atrioventricular Beam( Wolf-Parkinson-White Syndrome)Rehabilitation and postoperative period
In the normal course of the operation the patient returns to the ward after the end. When accessing through the veins( vessels with low pressure) in a short period of time allowed to lead a normal lifestyle. If an artery was used, then strict bed rest is observed until the morning before the morning of bruising, and a bandage is applied for this time. Further, electrocardiography, Holter ECG monitoring can be used to diagnose the long-term effect of surgery. After this, in a conversation with a doctor, the need to take certain medications, the timing of repeated consultations and research is discussed.
Complications of
Complications of this type of intervention include:
- blood loss;
- bruising at the puncture site;
- allergic reaction to drugs for local anesthesia;
- damage to the lung during puncture and the accumulation of air inside the chest;
- development of cardiac blockade( cardiac pacemaker may be required);
- relapse arrhythmia;
This intervention, due to the absence of anesthesia and incisions, presents the patient with minimal danger. Lethality is less than 1%.
Radiofrequency ablation of the heart: patients' reviews
Heart RFA: opinion of the cardiologist
Radiofrequency ablation is an effective radical method of correcting many arrhythmias. The absence of anesthesia and operational trauma makes the operation procedure comfortable for the patient, and also provides a quick return to the normal way of life.