The disease occurs when an inflammatory reaction develops inside the salivary gland tissue and is called sialadenitis( or sialadenitis).Most often, sialadenitis affects the parotid glands, less often submandibular and sublingual.
The disease develops in both adults and children, although for each age group, a certain type of sialadenite can be characteristic, taking into account the causative factor. Depending on the nature of the course of the disease, sialadenites are divided into acute and chronic.
Contents of
Main causes of sialoadenitis
- 4 Treatment of inflammation of the salivary gland( sialoadenitis)
- 4.1 Prevention of inflammation
- 5 Which doctor should I consult?
The main causes of sialoadenitis

symptoms of inflammation of the salivary gland, photos
The cause of acute inflammation of the salivary glands is always the presence of any infectious agent inside the gland. Depending on the pathogen sialadenitis can be:
1. Viral. It develops when infected with an epidemic parotitis virus( in the people this condition is called "mumps"), to which the salivary glands are very sensitive. The virus is transmitted by airborne droplets.
After entering the body through the mucosa of the respiratory tract, it penetrates into the tissue of the parotid salivary gland, multiplies in its cells, causing inflammation. When generalizing the infection, it falls into the testicles of boys, leading to their damage, which in the future can lead to infertility.
Possible inflammation in cytomegalovirus infection.
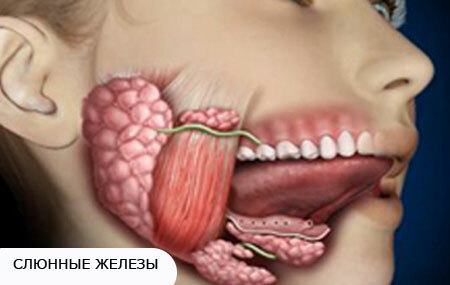
2. Bacterial , or nonspecific. Occurs when the infection from the oral cavity - through the ducts of the glands, as well as from the inside - through the blood and lymph.
The microflora of the oral cavity can lead to the development of acute sialadenitis as a result of the following factors( circumstances):
- With poor oral hygiene.
- Because of reactive obstruction. Its occurrence is facilitated by operations on the abdominal organs, as well as diseases leading to general malnutrition, such as malignant neoplasms, chronic gastrointestinal diseases, stress, eating disorders, diabetes mellitus. With these conditions, a reflex narrowing of the lumen of the ducts arises and a decrease in salivary secretion. Saliva begins to accumulate in the salivary gland, which is a good medium for the reproduction of microorganisms present in the oral cavity;
- Because of mechanical obstruction, when the duct is blocked by a stone or a foreign body. In this case, bacteria from the oral cavity also actively begin to multiply inside the gland, resulting in inflammation.
Infection through the blood can be observed in severe infectious diseases, such as typhoid, scarlet fever. Through lymph, sialdenite develops in inflammatory diseases of the face, pharynx, and oral mucosa: furunculosis, purulent facial wounds, tonsillitis, periodontitis.
Chronic sialadenitis in most cases is not a consequence of acute sialadenitis( they are independent in their development).This disease is initially chronic, since there is a predisposition of the salivary gland to changes in its tissue. The causes of chronic sialadenitis may be due to genetics, may be a consequence of autoimmune processes in the body, may occur as a response to a common disease.
Some factors contribute to the development of chronic sialadenitis - stress, illness, hypothermia, trauma, general weakening of the body.
Often the development of chronic inflammation is observed in the elderly, which is associated with a worsening of the blood supply of the salivary glands as a result of atherosclerosis, as well as the effects of free radicals and the general aging of the body.
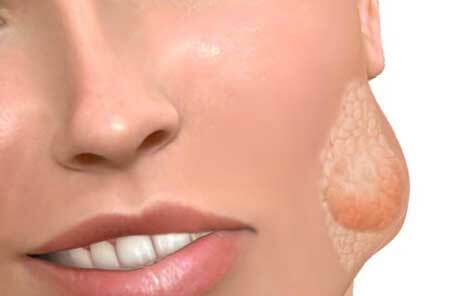
Symptoms of inflammation of the salivary gland, photo
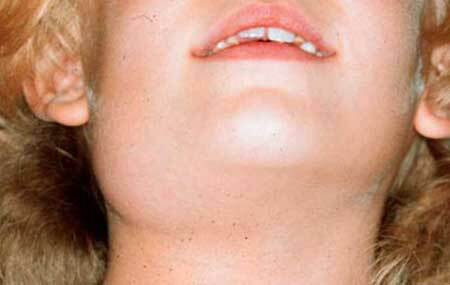
photo 3
Epidemic parotitis is characterized by an acute onset, body temperature of 39-40 ° C. There is swelling of the parotid salivary glands from both sides, pain near the ears, which is enhanced by chewing. Edema of the parotid gland is well noticeable and spread out to the sides, so this disease was called "mumps".
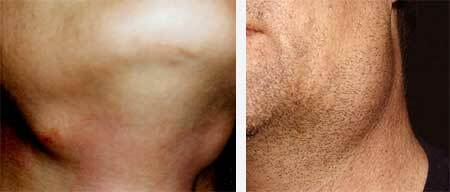
symptoms of sialadenitis, photo 4
In adults, sublingual and submandibular glands can be involved in the process. Thus, the clinical manifestations of sialdenite are divided into local and systemic.
In acute nonspecific inflammation of the salivary gland, symptoms depend on the type of inflammation. The manifestations of acute sialadenitis in the parotid salivary gland with untimely rendering of assistance pass through a series of successive stages - serous, purulent and gangrenous.
Serous sialadenite is characterized by dry mouth, the appearance of tenderness and swelling in the ear region, while the lobe of the ear is elevated.
Pain is aggravated by eating, as well as after reflex salivation at the sight of food. The skin around the gland is not changed. The body temperature may increase slightly. When pressing on the iron, saliva is not released at all or very little is released.
Purulent sialadenitis is manifested by a sharp increase in pain, which leads to sleep disorders, an increase in body temperature above 38 ° C, there is a restriction on opening the mouth, swelling spreads on the temples, cheeks, lower jaw.
When pressing on the gland in the oral cavity, pus is released. The gland is dense at the palpation, painful, above it reddening of the skin.
Gangrenous sialadenite can flow violently, with a rise in temperature, although, with a general weakening of the body, its manifestations can be moderate. Above the gland is revealed the site of destruction of skin tissue, through which there is a constant separation of the rejecting parts of the necrotic salivary gland.
The disease can be fatal if the infection spreads through the body and the development of sepsis, as well as to fatal bleeding when the walls of large vessels of the neck are melted.
Inflammation of the submandibular salivary gland is characterized by the appearance of edema in the submaxillary region. The gland becomes enlarged, bumpy and very painful when probed. With increasing inflammation, edema increases, pain occurs when swallowing. In the mouth, redness and swelling are noted under the tongue, it is also possible to observe the secretion of pus from the duct of the gland through its duct.
Inflammation of the submandibular salivary gland can often be calculous. In this case, the cause of inflammation is the overlapping of the duct with a stone, which is formed when a foreign body enters, frequent inflammations in the ducts, and also with an increased amount of calcium in the blood plasma.
Signs of calculous inflammation will be:
- Sharp stitching pain, aggravated during eating;
- Impaired discharge of saliva;
- Dry mouth;
- Swelling and tuberosity of the submandibular gland.
When the gland is massaged, pus appears under the tongue. The patient can note the enlargement of the gland during meals, which makes eating uncomfortable, and in the worst case impossible.
Inflammation of the sublingual salivary gland develops extremely rarely and is a complication of abscess or phlegmon of dental origin. Appears in swelling and soreness, localized in the hyoid area. The development of suppuration aggravates the situation.
The manifestations of chronic inflammation of the of the salivary gland also differ depending on the form:
1 .Chronic interstitial sialadenitis in 85% affects parotid salivary glands. Most often they suffer from elderly women. For a long time can occur without symptoms. The appearance of clinical signs is associated with a slow progression of the pathological process and a gradual narrowing of the gland ducts.
The aggravation may begin dramatically, with the appearance of dry mouth. The gland is enlarged in size, painful, its surface is smooth. After an exacerbation of iron the sizes of a gland do not correspond or meet to norm or rate( it is a little bit more than the necessary sizes).
2 .Chronic parenchymal sialadenitis in 99% of cases develops in the parotid gland. Women are more often ill. Due to congenital changes in the structure of the ducts, the age range is very wide - ranging from 1 year to 70 years. Sometimes the disease lasts for decades without any manifestations.
The aggravation develops according to the type of acute sialadenitis. The initial stage of the disease can have only one sign - the allocation of a large amount of brackish mucous fluid when pressing on the gland.
In the future, you may experience a feeling of heaviness in the gland, its densification, salivation with an admixture of pus and lumps of mucus. Opening the mouth is free( unlimited).The late stage is characterized by an enlarged and bumpy, but painless gland, secretion of purulent saliva, rarely dry mouth appears as a sign of the disease.
3 .Sialodochitis( defeat only the ducts) occurs in the elderly, due to the expansion of the ducts of the parotid salivary glands. A characteristic feature is increased salivation during conversation and eating. This leads to maceration of the skin around the mouth( formed seizures).
When exacerbation occurs swelling of the gland, secretion of purulent saliva.
Diagnosis
Acute sialadenitis is detected by examining and interviewing the patient. Sialografiya did not find wide application in practical medicine, tk.is accompanied by aggravation of the pathological process with the introduction of a contrast agent. Against this background, pain is intensifying.
In chronic sialadenitis, on the contrary, an effective method of diagnosis will be a contrast sialography - X-ray examination of the salivary glands with the introduction of iodolipol.
In the interstitial variant, narrowing of the ducts will be detected, and the amount of contrast medium will be small - 0.5-0.8 ml, compared to the usual normal "capacity" of 2-3 ml.
In parenchymal form, multiple cavities are observed, 5-10 mm in diameter, the gland ducts and tissue are not visually determined.6-8 ml of contrast medium is required to fill the cavities.
Treatment of inflammation of the salivary gland( sialoadenitis)
When symptoms similar to an acute inflammation of the salivary gland appear, treatment should be performed in a hospital. Most often, therapy is performed with conservative methods, only with the development of purulent process is shown a surgical opening of the abscess.
Epidemic parotitis
Symptomatic treatment is performed and interferon preparations, for example leukinfer, are prescribed. Symptomatic means in this case are those that reduce temperature and reduce pain in the area of the inflamed gland.
Acute nonspecific sialadenitis
The goals of the treatment are the elimination of the inflammatory process and the restoration of saliva secretion. Therefore, the following activities are shown:
- Salivary diet. It consists of the use of rusks, sour cabbage, cranberries, lemon, supplemented by the ingestion of 5-6 drops of a 1% solution of hydrochloric acid pilocarpine( it contributes to the reflex reduction of the muscles of the excretory ducts of the salivary gland and secretion);
- Antibiotics are introduced into the duct - penicillin, gentamicin, and also antiseptics - dioxidin, potassium fugaginate;
- Apply compress to the gland area with 30% dimexide solution, once a day for 30 minutes. It has an anti-inflammatory, analgesic effect, stops the development of infection;
- Physiotherapy: UHF, heating pad;
- With increased edema and inflammation - novocaine-penicillin blockade;
- Inside antibiotics;
- Intravenously injected solution of trasylol, kontrikala.
Surgical treatment - With the development of purulent inflammation, an abscess is performed from the outside. With gangrenous form, urgent surgery is performed under general anesthesia. When there is a stone, it is removed, asotherwise, the process will repeatedly become aggravated.
Chronic sialadenitis
During the exacerbation the treatment is carried out as in acute sialadenitis. Outside the exacerbation, the following activities are shown:
- massage ducts with the introduction of antibiotics to eliminate purulent masses;
- for the purpose of increasing the secretory activity of the gland, the novocaine blockade is performed in the subcutaneous fat, electrophoresis with galantamine or its subcutaneous injection for 30 days;
- daily galvanization for 1 month;
- Introduction to the gland 4-5 ml iodolipol once every 3-4 months, which prevents the development of exacerbations;
- intake of 2% solution of potassium iodide inside by 1 tbsp.3 times a day 30-35 days, the course is repeated after 4 months;
- X-ray therapy on the salivary gland area. It has a good anti-inflammatory and anti-infective effect;
- removal of the problematic salivary gland.
Prevention of inflammation
There is no specific prophylaxis( introduction of vaccines) against sialadenitis, except for mumps. In the latter case, a three-component vaccine effective against measles, mumps and rubella is introduced. She is a living inactivated. The vaccine is given to children at 1.5 years of age.
Persistent immunity persists in 96% of children.
Nonspecific prevention includes the following activities:
- standard oral hygiene;
- sanation of foci of infection in the mouth;
- prevention of stagnation of saliva and multiplication of infection in common infectious diseases, by taking pilocarpine inside, mouthwash solutions of furacilin, manganese, rivanol and other antiseptics.
To which doctor should I apply?
If you suspect a salivary gland inflammation, you should consult your dentist or maxillofacial surgeon. If you suspect a "mumps" you need to turn to the pediatrician, and adults - to the therapist.
These specialists will promptly send the patient to the infectious disease specialist who is engaged in the treatment of mumps.