Diphtheria is a serious and dangerous infectious disease. The first symptoms in children appear after 2 days or after a while. It all depends on the condition of the baby, the individual characteristics of his body.
It is important to differentiate the disease, since many of the symptoms are similar to the manifestations of other pathologies. The examination and treatment is carried out by a pediatrician; if necessary, consultation with an infectious disease specialist is required.
Record content:
- 1 general information
- 2 Classification
- 3 The causative agent and its incubation period
- 4 Main clinical symptoms
-
5 Diagnostics
- 5.1 Anamnesis
- 5.2 Physical examination
- 5.3 Laboratory research
- 6 Differential diagnosis
- 7 Treatment
- 8 Prophylaxis
- 9 What to do if there was contact with the patient
- 10 Diphtheria Videos
general information
Diphtheria belongs to the category of infectious diseases. The causative agents of pathology are bacteria - Leffrell. Microorganisms secrete a toxic toxin during reproduction and life. Protein synthesis is blocked, and the cell of the human body cannot perform its functions.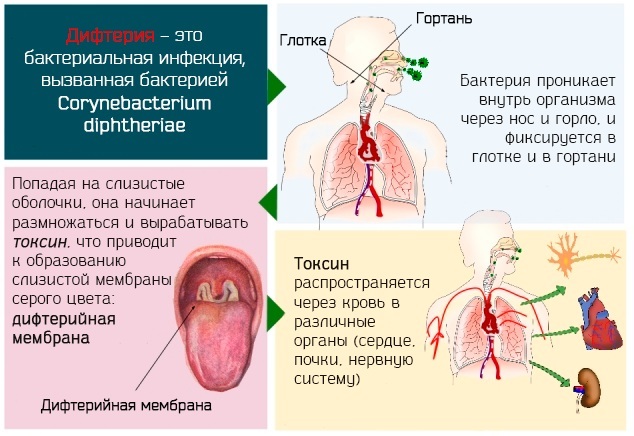
In most cases, the infection of the child's body occurs by airborne droplets. In rare cases, a child can become infected through water or food. Infection is also possible from a healthy person who is a carrier of pathogens.
Classification
In medicine, the following types of diphtheria are distinguished, taking into account the area affected by infectious pathogens:
- larynx (diphtheria croup);
- oropharynx;
- nose;
- skin;
- eye;
- external organs of the reproductive system;
- combined diphtheria.
In each case, characteristic symptoms appear, with which it is important to immediately consult a pediatrician:
| Name | Symptoms |
| Larynx | A rare type of pediatric infectious pathology. The danger of the disease lies in the gradual narrowing of the larynx. A dense film is formed, which spreads to the vocal cords and throughout the larynx, the respiratory process is disrupted. |
| Oropharynx | A common type of disease that affects the tonsils and provides subspecies (localized, widespread, toxic and hypertoxic diphtheria). |
| Nasal sinuses | More common in young children. It is accompanied by purulent discharge, the mucous membrane swells, as a result of which the respiratory process is disturbed. Crusts and cracks form around the sinuses due to skin irritation. There is a slight increase in body temperature. |
| Leather | Infection occurs when pathogens enter an open wound (scratches, erosion, diaper rash). Nearby tissues swell, a gray plaque forms. Skin diphtheria is more often diagnosed in newborn babies. |
| Eyes | As a result of infection, the conjunctiva turn red and swell up the eyelids. A pain syndrome appears, a yellow plaque is formed. Mucous discharge from the eyes is replaced by purulent exudate. |
| External genital organs | The disease is characterized by pain during urination. Boys are affected by the foreskin, girls are characterized by infection on the labia, inside the vagina. |
Laryngeal diphtheria develops in stages, accompanied by characteristic symptoms in children:
| Name | Description |
| Dysphonic (catarrhal) | The disease provokes a hoarseness of the voice and the occurrence of a barking paroxysmal cough. There is no plaque on the mucous membrane. |
| Stenotic | At this stage of diphtheria, breathing is disturbed, the skin acquires a bluish tint, and aphonia occurs. Pupils dilate, blood pressure decreases, pulse quickens. Over the next few days, stenosis develops. |
| Asphyxia | The stage of diphtheria, at which asphyxia appears. Pathological processes affect the vasomotor centers and organs of the respiratory system. In most cases, asphyxia diphtheria does not respond to treatment, the patient dies. |
A pediatrician will help to establish an accurate diagnosis. It is important to consult a specialist when the first signs of diphtheria appear in a child, undergo a full diagnosis and start treatment.
The causative agent and its incubation period
In children with weak immunity, the first symptoms after infection appear on the 2nd day. Pathogenic microorganisms enter the child's body more often through the nasal sinuses or oropharynx.
The pathogen, developing in the human body, provokes the following changes:
- Vascular permeability in the inflammatory focus increases.
- An effusion is formed in which fibrinogen is present.
- Diphtheria bacillus negatively affects cells, destroying them.
- Fibrin is released.
- In the area of the inflammatory focus, a strong film forms on the surface of the mucous membrane.
If you try to remove the pathogenic layer, bleeding appears. It is necessary to immediately contact a pediatrician, undergo a full examination and start treatment in order to prevent serious complications.
Main clinical symptoms
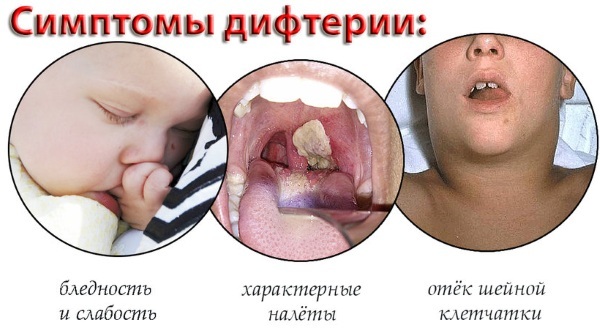
Diphtheria in children (symptoms will help the pediatrician to determine the degree of development of pathological processes in a small organism and localization of the inflammatory focus) is characterized by clinical signs depending on the area of the lesion by pathogenic bacteria.
But there are general symptoms that occur with any form of the disease:
- during swallowing, the child complains of acute pain syndrome;
- the tonsils turn red;
- fever appears as a result of high body temperature;
- the lymph nodes are enlarged.
The mucous membrane of the oral cavity is covered with a gray diphtheria film. It grows tightly with the upper layer of the epidermis, so it is difficult to remove it. At the place where it breaks off the skin, an open wound is formed, which is overgrown with the same film.
There are also certain forms of diphtheria in children, each with specific clinical symptoms: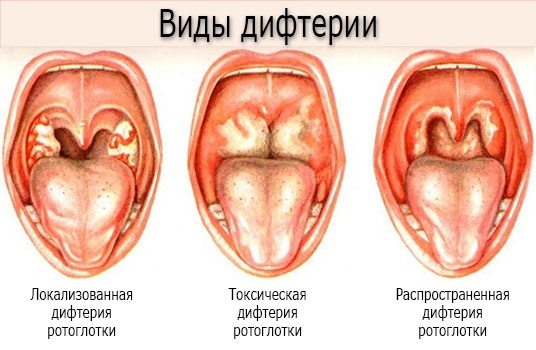
| Name | Description |
| Localized form | Pathogens accumulate exclusively in one place. The disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
|
| Common form | Pathological processes extend beyond the tonsils and provoke the appearance of the following clinical signs:
|
| Hemorrhagic form | The hematopoietic system of the human body is affected. Hemorrhagic rashes appear on the body. The mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract is also covered with hemorrhages. |
| Toxic form | A dangerous type of diphtheria, which is accompanied by tissue edema. The rapid course of the disease provokes various complications, including paralysis of the lower extremities, epileptic seizures, neurotic syndrome and damage to the heart vessels. Typical symptoms of the toxic form of the disease:
|
| Hypertoxic form | A dangerous type of diphtheria, which is accompanied by the following symptoms:
|

The hypertoxic form of diphtheria requires urgent medical attention, as symptoms develop quickly. In the absence of timely therapy, coma occurs in 2-3 days. Failure of the cardiovascular system will lead to death.
Diagnostics
Diphtheria in children (symptoms require careful medical examination and timely therapy) is determined by a pediatrician pediatrician. Given the area of the lesion, it may be necessary to consult other specialized specialists (infectious disease specialist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, neurologist, cardiologist).
Anamnesis
The doctor visually examines the skin of the child, the mucous membrane of the throat, listens to the lungs. It also conducts a survey what the child is concerned about, what complaints there are. The information received will allow the specialist to choose the most informative diagnostic method in order to correctly establish the diagnosis and select effective means to combat diphtheria.
Physical examination
The doctor conducts a thorough examination of the patient.  At this stage of the diagnosis, the specialist identifies a dense fibrous film that is difficult to remove.
At this stage of the diagnosis, the specialist identifies a dense fibrous film that is difficult to remove.
Laboratory research
Special tests will help to identify the causative agent of diphtheria, which the pediatrician prescribes to the child after examination, taking into account the condition of the small patient and existing complaints:
| Name | Description |
| Blood analysis | Tests detect antibodies against pathogens. |
| Bacteriological culture | The test material is taken from the affected area. A diagnostic method that allows you to isolate a diphtheria bacillus. |
| Bacterioscopy | Determine the pathogens under a microscope. |
| General blood analysis | Based on the results, the doctor can assess the general condition of the child, and also see inflammation in the body. |
| General urine analysis | |
| Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) | Research helps to identify the gene toxigenicity in the DNA of diphtheria pathogens in children. |
Additionally, patients are prescribed echocardiography to determine abnormalities in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Differential diagnosis
Many parents, without the help of a pediatrician, confuse diphtheria and angina. They begin to treat the child on their own, without the appointment of a specialist. The disease progresses rapidly and provokes dangerous complications.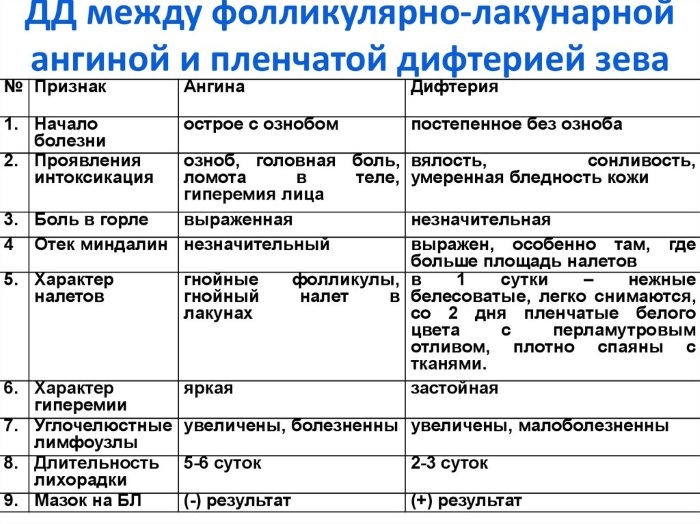
There are characteristic symptoms that help distinguish diphtheria from sore throat:
| Name | Angina | Diphtheria |
| Tonsils | They turn red, inflamed and covered with a yellow coating. In some situations, pus appears. | Covered with a white film. |
| Sky | Only the tonsils are affected. | The inflammatory process, as it progresses, affects the entire palate. |
| Pain syndrome | The painful sensations are strong. | Mild pain is accompanied by discomfort in the throat. |
A pediatrician will help differentiate diphtheria in children. It is impossible to diagnose and give the child medication on your own, there is a high probability of serious complications, up to and including death.
Treatment
Diphtheria in children (symptoms depend on the area affected by pathogenic microorganisms) is treated in an inpatient department of a medical institution.
After an accurate diagnosis is made, a small patient is immediately injected with antitoxic serum in order to neutralize the negative effect of diphtheria pathogens on the child's body. The baby should be provided with maximum care and bed rest.
Auxiliary methods of complex therapy that will help make breathing easier for the child:
- creating a healthy indoor climate - ventilate the room and perform wet cleaning;
- water the child abundantly;
- control so that nasal breathing is free.
The pediatrician selects medications, taking into account the age of the child, the stage of development of the disease, the degree and area of damage to the body.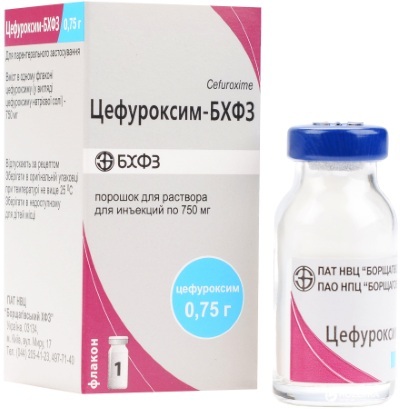
| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Antibacterial drugs | Cefuroxime | Medicines neutralize pathogenic flora and prevent the emergence of new pathogens. The drug is administered intravenously or intramuscularly. The pediatric dosage is 60 mg / kg per day. The treatment regimen and the course of therapy are selected by the pediatrician, taking into account the condition of the child. |
| Antipyretic drugs | Nimesil, Panadol | The medicine in the form of a suspension is prescribed for children at 15 mg / 3-4 times a day. The time interval between doses is 4-6 hours. |
| Antihistamines | Tavegil, Suprastin | The tablets should be taken orally before meals. Children's dosage is 0.5-1 tablet 2 times a day (morning and evening). |
| Corticosteroids | Dexamethasone, Prednisolone | The daily dosage for children depends on the patient's condition - 2.5-10 mg / m2. The medicine is taken 3-4 times a day. |
Additionally, vitamin therapy is carried out to maintain immunity. The severe course of diphtheria in children requires intravenous medication to relieve symptoms. In severe cases, the patient is transferred to artificial ventilation of the lungs or special drugs are prescribed to expand the bronchi.
Diphtheria in children (symptoms will help determine the stage of development of the disease and the area of the lesion pathological processes) provides for comprehensive treatment and compliance with a gentle and easily digestible diet. Meals should be semi-liquid or liquid (baked apples, alkaline broth, soy milk, fruits and vegetables).
In the absence of serious medical contraindications, you can use the recipes of healers and healers, but strictly after consulting a pediatrician. Diphtheria is treated with complex methods, it is impossible to eliminate the underlying disease with folk remedies alone.
Effective recipes for healers and healers:
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Echinacea decoction | Grind the roots of the plant and pour 30 g of cold water (750 ml). The resulting mass must be placed in a water bath and heated for 30 minutes. Infuse the mixture in a closed container until it cools completely. The finished medicine should be filtered and taken orally. | Echinacea decoction strengthens the immune system. It is recommended to take 30 ml orally 3 times a day warm before meals. |
| Chernogolovka | Brew dry plant flowers and grass (15-20 g) with boiling water (1 l). Put on a steam bath and heat for 20 minutes. cool the finished medicine, strain and use for irrigation of the oral cavity. | A medicine based on chernogolovka reduces the symptoms of diphtheria, increases the body's defenses and promotes the regeneration of damaged cells. |
| Herbal collection | Mix in equal parts the leaves of coltsfoot and raspberries (20 g). Add 10 g of oregano to them. Mix and grind all components well. Pour 2 tbsp. herbal collection with hot water (2 tbsp.). Cover the container and leave for 10 minutes in a warm place. | The filtered herbal decoction is recommended to be drunk warm 3 times a day. The medicine strengthens the child's body and eliminates the unpleasant symptoms of diphtheria. |
If there is no positive dynamics after drug therapy, the patient is shown surgery.
Prophylaxis
Infection of the child's body occurs in a matter of minutes. Even if the parents isolate the child after contact with a sick person, the possibility of infection remains. The main prophylaxis against diphtheria in children is vaccination (DPT, AKC). The first vaccination is given at 3 months, the next 2 with an interval of 45 days.
One year after vaccination, you must adhere to the schedule and repeat the vaccination:
- at 2 years old - DTP;
- at 7 years old - toxoid;
- at the age of 14 - toxoid;
- at 24 - ADS-M.
If the child becomes ill with diphtheria, to avoid spreading the infection, he should be isolated from other family members for at least 7 days. To prevent the disease, you should also treat all baby toys with disinfectants.
What to do if there was contact with the patient
After contact with a sick person, you must immediately consult a pediatrician, undergo a full medical examination and, if necessary, preventive treatment. The child is injected with toxoid to prevent the development of an infectious disease.
Against the background of diphtheria, serious complications can occur:
| Name | Description |
| Myocarditis | A disease characterized by an inflammatory process in the area of the heart muscle. An infectious lesion disrupts the functioning of the cardiovascular system, provokes a breakdown and muscle weakness.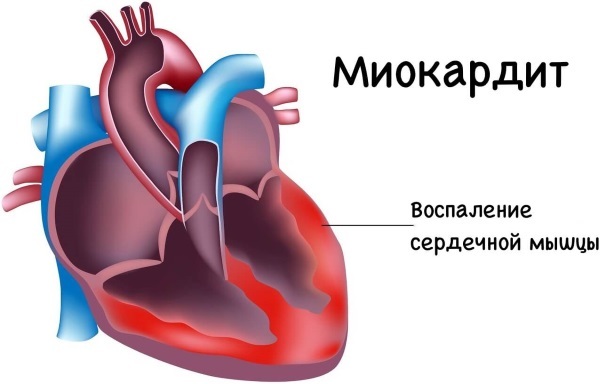
|
| Infectious toxic shock | A pathological condition that occurs as a result of the aggressive effects of the infectious pathogenic flora and the toxins secreted by it. |
| Respiratory failure | The disease is characterized by impaired gas exchange in the lungs. |
| Polyneuropathy | Complication of diphtheria croup, which is characterized by damage to the peripheral nerves. Nasalness appears. Liquid food flows out through the nose. |
A complication of the pathology is also toxic nephrosis, otitis media, pneumonia, cardiovascular failure. Examination of a child after contact with a sick person is necessary to interrupt the process of reproduction of pathogens of an infectious disease.
Diphtheria in children is acute with a strong inflammatory process. The upper respiratory tract is affected, and characteristic symptoms appear. The disease is dangerous to the life of the child, therefore it is important to diagnose it in a timely manner and begin correctly selected therapy based on the results of the examination.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Diphtheria Videos
Komarovsky on diphtheria and tetanus: