Coronavirus infection is a viral disease in which a person has upper respiratory tract injury and the gastrointestinal tract. The causative agents of the disease tolerate low temperatures and freezing well (they remain viable for up to 10 years when frozen at temperatures down to -70 ° C), and the peak incidence occurs in winter and spring.
Symptoms of pathology can range from a mild "commonplace" cold to severe pneumonia. The susceptibility to infection is high among both children and adults. Microorganisms also infect domestic animals. The coronaviruses got their name from the structures around the shell, which resemble a jagged frame or solar corona during an eclipse.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Folk methods
- 8.3 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Coronavirus video
Views
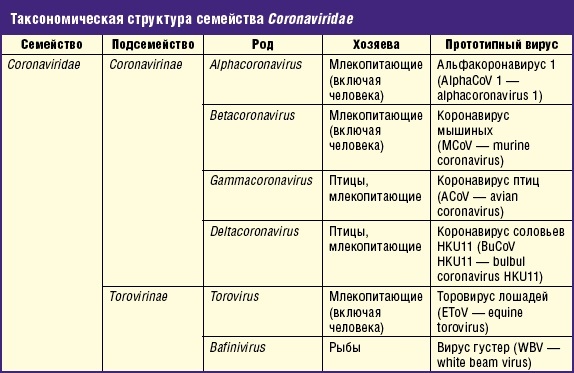
Human coronavirus infection is classified according to several criteria:
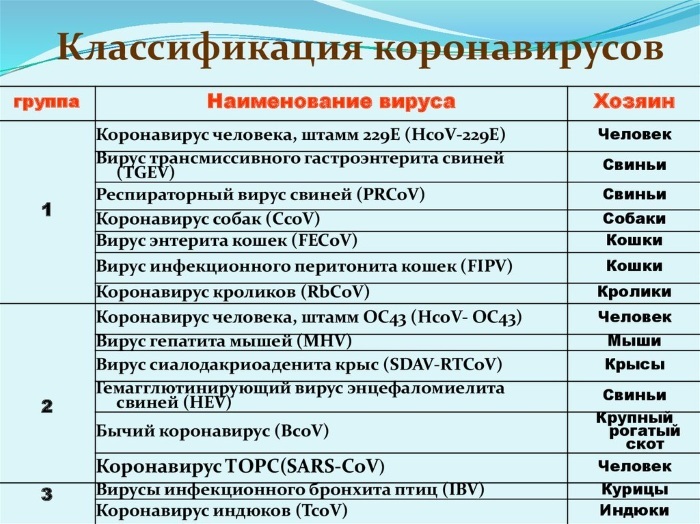
- Depending on the genome configuration and animal species (3 groups):
- Human coronovirus HCoV-229E, as well as strains infecting cats, dogs, pigs and rabbits.
- Human virus strain HCoV-OC43, as well as varieties that infect rodents, turkeys, pigs, cattle. Like viruses of the first group, these pathogens cause cold symptoms (prevalence is 10-15% of cases).
- Intestinal coronoviruses (viruses of the genus Alphavirus) that infect humans and birds. They cause gastroenteritis, an inflammation of the stomach and small intestine.
- According to the clinical course of the disease:
- With signs of ARVI. Until 2002 in medicine, it was believed that all coronaviruses can only cause symptoms of a mild "cold", however epidemics in Southeast Asia and the Middle East with high mortality forced to reconsider this position.
- In the form of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS or SARS). In nature, carriers of SARS-CoV are ferret badgers, raccoon dogs, bats, civets and other mammals. The syndrome causes SARS. By 2003 more than 8 thousand were registered cases of the disease, the mortality rate from which ranged from 4-10%. It is most prevalent in Southeast Asia, the United States and Canada, some cases have been reported in European countries. The movement of the pathogen to other regions occurs mainly through transport airlines. Basically, the disease develops in people aged 15-70 years, it has not been registered in children.
- In the form of Middle East Respiratory Coronavirus Syndrome (MERS, MERS). This pathology is accompanied by a high mortality rate - 40% of patients died in Saudi Arabia. In European countries, the number of cases was small, but the mortality rate was even higher - 50-60%. Like the causative agents of the previous group, these viruses belong to the genus Betavirus. In nature, various species of bats are long-term host carriers of MERS-CoV. MERS was first identified in 2012. in Saudi Arabia. This strain has not previously been found in the human population and is genetically distinct from SARS. The peak incidence occurs in March-April.
In addition, carried out in the 80-90s. studies show that coronaviruses can be involved in the development of bronchitis, ear inflammation, and some diseases of the central nervous system.
Stages and degrees
Coronavirus infection in humans develops according to the following mechanism:
- The virus enters the human body through airborne droplets, oral (through contaminated feces and unwashed hands) or by contact.
- The incubation period in the normal course of the disease is 2-3 days, with SARS - 5-7 days, with MERS - 7-14 days.
- There is a lesion of the upper respiratory tract, mainly in a mild or moderate form, in children of the 1st year of life, intestinal syndrome is noted in 75% of cases.
- In severe cases of SARS infection, diffuse damage to the pulmonary alveoli develops, their walls are damaged.
- The permeability of the capillary system is impaired, pulmonary edema develops.
- The surfactant is destroyed - a mixture of surfactants lining the pulmonary alveoli and bronchioles (terminal branches of the bronchial tree, gradually turning into the alveolar passages) from the inside.
- Gas exchange in the human body is disrupted.
- Oxygen deficiency develops, the amount of oxygen in the blood decreases.
- Respiratory acidosis occurs, in which the acid-base balance is disturbed, the blood becomes acidic.
- The inflammatory infiltrations coalesce, resulting in fibrous scarring in the lungs.
SARS develops in 3 successive stages:
- Feverish phase (fever, symptoms of intoxication).
- Respiratory stage, developing 3-7 days from the onset of the disease. Respiratory failure occurs. If after this the patient's condition improves, then the course of the disease is moderate.

- Stage of progressive respiratory failure. The patient needs artificial ventilation for a long time. This stage corresponds to a severe form of the disease and often ends in the death of the patient.
Symptoms
Coronaviruses of the strains HCoV-229E, HCoV-OC43, HCoV-NL63 and HCoV-HKU1 most often cause respiratory diseases of the upper respiratory tract of mild to moderate severity.
In this case, symptoms such as:
- general malaise, weakness;
- an increase in body temperature up to 37 ° C;
- headache (moderate gravity);
- rhinorrhea (inflammation of the nasal mucosa, runny nose) with a large amount of mucous discharge from the nose;
- sore or sore throat, dry cough;
- in some patients (9-24%) - fever, severe intoxication, wheezing in the lungs.
Children may show additional signs:
- cough;
- chest pain with deep breathing;
- wheezing in the lungs;
- enlargement and soreness of the cervical lymph nodes;
- respiratory failure due to impaired patency of the bronchial tree;
- high fever, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain in intestinal syndrome that lasts about 2-5 days.
As a rule, the duration of these symptoms does not exceed 5-7 days. By their nature, they practically do not differ from the defeat of rhinoviruses and other pathogens of respiratory diseases.
Symptoms of SARS include:
- At the first stage:
- general weakness;
- mild cough and sore throat (20-30% of patients);
- rise in body temperature to 38 ° C or more (in all patients);
- rhinitis (23% of patients)
- feeling cold, muscle tremors;
- headache and muscle pain, dizziness (80% of patients);
- loss of appetite;
- diarrhea.
- At the second stage, additional signs appear:
- dry cough that does not produce phlegm;
- tachycardia;
- shortness of breath, shortness of breath, feeling short of breath;
- hyperthermia, which can lead to metabolic disorders and death in cardiovascular diseases;
- some patients have nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
- In the third stage:
- the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome and severe respiratory failure, requiring resuscitation;
- tachycardia;
- dry cough;
- rapid shallow breathing;
- lowering blood pressure.
A feature of SARS is also the cyclical course of the disease.
MERS has not yet been adequately studied by medicine.
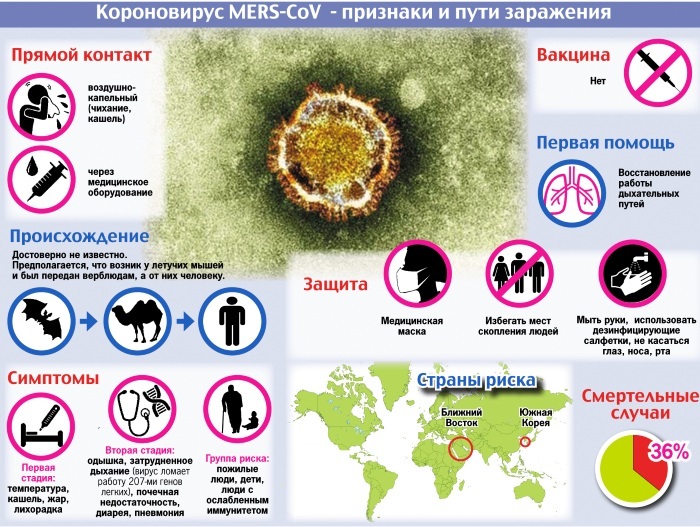
This syndrome is characterized by the following manifestations:
- high body temperature;
- cough;
- labored breathing;
- diarrhea;
- signs of renal failure (a decrease in the amount of urine excreted or its complete absence, disruption of the cardiovascular system, and others);
- pain in the region of the heart, palpitations.
Reasons for the appearance
The cause of infection and its source is a sick person. Healthy people can also carry the virus for an indefinitely long time. The mechanism of development of the disease is based on the cytopathic effect of viruses, in which degenerative changes occur in cell cultures.
Since different strains of the virus have antigenic heterogeneity, the likelihood of reinfection is high. Immunity is developed to a specific pathogen, and not to the entire group of coronaviruses, and is short-lived.
The category of persons at increased risk of developing infection and its complications include:
- children and adolescents, students;
- medical staff;
- hospital patients (nosocomial infections) or people who have undergone recent hospitalization;
- aged people;
- persons with reduced immunity;
- patients suffering from cardiovascular diseases, pathologies of the respiratory system and cancer patients.
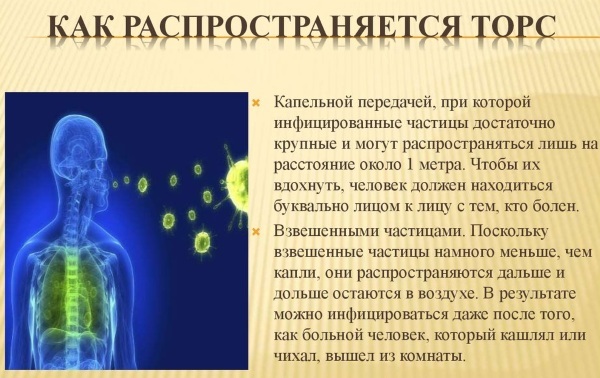
SARS coronavirus infection can occur in humans as a result of the transmission of viruses from infected animals, through insufficiently processed meat and waste products of bats living in attics in residential houses.
People with diabetes mellitus, chronic renal failure and respiratory diseases, with reduced immunity, as well as health care workers are at greatest risk. As statistics show, without taking control measures, 1 patient on average infects 3 more people.
Transmission of MERS in 75% of cases occurs from person to person through close contact. Camels, which become carriers of the virus almost immediately after birth, and bats are also sources of infection.
A high incidence was noted among the pilgrims of the Hajj. Persons in contact with livestock are also at risk. Since bats carry out seasonal migrations, there is a possibility of the spread of infection in Russia.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out as follows:
- Collecting anamnesis, information about travel and contacts with people and animals in the last 2 weeks, about the types of transport used by the patient, food consumption food, hookah use, gastrointestinal symptoms, visits to medical facilities and other factors that indicate infection.
- Clinical and biochemical blood test, which allows you to determine the markers of the inflammatory process and changes in the internal organs.
- Specific laboratory tests to determine the pathogen:
- Virological methods: electron microscopy; immunofluorescence reaction - detection of the pathogen antigen in the epithelial cells of the nasal mucosa;
- serological reactions (ELISA, RSK - complement binding reaction, RNGA - indirect hemagglutination reaction), which can determine diagnostic antibody titers on the 5th day after infection;
- molecular biological methods (PCR).
- ECG to detect violations of the cardiovascular system.
- Plain radiography, tomography to determine the degree of lung damage.
- Other research methods in the presence of complications.
For immune and microscopic studies, the following types of biomaterials are collected:
- blood serum;
- urine, feces;
- swab from the nose, nasopharynx, or throat;
- sputum with natural expectoration;
- flushing from the bronchi;
- the contents of the tracheobronchial tree, collected using a vacuum aspirator;
- a sample of lung tissue obtained by a biopsy method.
Studies for the presence of SARS and MERS can be carried out not in all laboratories, but only in those that belong to the second level of biological hazard (for example, the Federal State Budgetary Institution "Research Institute of Influenza"). Cultivation of the virus is allowed in specialized institutions of the 3rd security level.
When to see a doctor
A mild coronavirus infection, in the form of ARVI, is treated under the supervision of a local therapist at home.
Seeing a doctor and hospitalization is necessary in the following cases:
- if SARS or MERS is suspected;
- with high fever;
- if the patient was previously in a medical facility where cases of SARS or MERS were detected;
- when detecting pathogens of SARS and MERS by microscopic and immunological methods;
- if symptoms of pneumonia occur (described above).
For SARS and MERS, the patient should be placed in a separate box or single ward, for pulmonary insufficiency, in the intensive care unit. To prevent the spread of infection, strict adherence to a sanitary and epidemiological regime is required.
Prophylaxis
No specific vaccines have been developed for immunoprophylaxis of coronavirus infection. Of the drugs used to prevent the development of the disease, Ribavirin, human leukocyte interferon and its inducers, stimulating the production of this substance (Arbidol, Amiksin, Neovir, Cycloferon and other drugs used in flu).
Studies show that prevention of infection with viruses transmitted by airborne droplets is more effective than treatment of such diseases.
As a non-drug prophylaxis, the following recommendations must be observed:
- avoid close contact with sick people, as well as with wild and domestic animals;
- wash your hands more often;
- do not eat meat that has not undergone sufficient heat treatment, as well as unpeeled raw vegetables and fruits;
- drink only boiled water;
- use protective medical masks;
- for those already infected, keep a distance when coughing and sneezing, use disposable handkerchiefs, limit contact with relatives and friends;
- when visiting countries with a high prevalence of the disease, avoid mass events, contact with animals, camels, and eating raw foods.
Treatment methods
A mild coronavirus infection in humans is treated as follows:
- bed or semi-bed rest;
- drinking a lot of fluids;
- a dairy-vegetable diet rich in vitamins;
- symptomatic agents - antitussives (Codelak, Libeksin and others), to reduce the manifestations of rhinitis (Nazivin, Naftizin, Otrivin, Lazolvan, Nazol and others);
- rehydration therapy for diarrhea.
Medications
For severe and moderately severe disease, the medications listed in the table below are used.
| Name | Dosage per day | Peculiarities | Average price, rub. |
Antiviral agents | |||
| Ribavirin | 8-12 mg / ml every 8 hours or 400-600 mg every 6 hours for 7-10 days | Effective in high dosage, has shown good results in the treatment of SARS | 330 (30 capsules) |
| Arbidol | 200 mg 4 times | The drug is "second echelon", effective at the initial stage | 350 (20 capsules of 100 mg) |
| Antibacterial agents for the prevention and treatment of secondary bacterial infection | |||
| Levofloxacin | 250-500 mg 1-2 times | Prescribed to all patients with pneumonia | 400 (7 tablets of 500 mg) |
| Ceftriaxone | 1-2 g | 30 (1 bottle 1 g) | |
Interferons and their inducers | |||
| Interferon-α2b (IFN-α2b, Altevir) |
100 mcg 2 times (sc) | Effective in the early stages | 1000 |
| Proteolysis inhibitors | |||
| Aprotinin (Aerus) | 85 KIE in each nasal passage after 2-4 hours | In the form of inhalation | 460 |
Detoxification therapy | |||
| Glucose solution (5% and 40%) with ascorbic acid and panangin | Up to 1.5 l | Elimination of intoxication against the background of respiratory failure | 30 (200 ml 5% solution) |
| Albumin (10-20%) | 5-10 mg / kg (intravenous) | 3500 (100 ml 20% solution) | |
| Cytoflavin | 5.0-10.0 ml (intravenous) | 600 (5 ampoules of 10 ml) | |
| Antipyretic, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs | |||
| Paracetamol | 500 mg (for adults) up to 4 times a day | Recommended for children in the form of suppositories | 10 (20 tablets of 500 mg) |
| Ibuprofen | max - 2.4 g (in several steps) | There is a suspension form. Contraindicated in ulcerative lesions | 40 (50 tablets 200 mg) |
| Analgin | 10% solution, 0.2 ml per 10 kg of body weight (intramuscularly) | Used in severe cases | 100 (10 ampoules of 2 ml) |
The following can be used as additional medicines:
- vitamins and flavonoids (Ascorutin, Dihydroquercetin, vitamins E and C);
- expectorant drugs;
- cardiovascular drugs;
- corticosteroids for septic shock.
Folk methods
In folk medicine, there are many recipes for eliminating the symptoms of ARVI.
Among them are the following:
- For sore throat - 1 tbsp. Dissolve ½ tsp of water. l. salt and baking soda. Gargle the throat with the solution several times during the day.

- Antiviral and antibacterial properties are possessed by a remedy based on honey and onions. Peel ½ kg of onion, chop, put in a saucepan, add 50 g of honey and 400 g of sugar. Cook over the lowest heat. Cool, pour into a glass jar. Keep refrigerated. Take 1 tbsp. l. 6 times a day.
- Scroll the onion through a meat grinder, squeeze the juice through cheesecloth and drink it for 1 tsp. l. 3-4 times a day.
- Cut the black radish into thin slices, sprinkle with sugar. In half an hour, the radish will give juice. Drink it every hour for 1 tsp. l. Juice can also be prepared using the previous method by grating.
Other methods
The following are used as non-drug treatments:
- inhalation of oxygen with respiratory failure;
- non-invasive or mechanical ventilation;
- physiotherapy:
- an ultra-high frequency electric field, to reduce puffiness, enhance the antibacterial effect, restore microcirculation;
- inductothermy (exposure to a high-frequency magnetic field) - increased blood circulation and metabolism, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect;
- inhalation with antibiotics;
- irradiation with infrared or ultraviolet rays - anti-inflammatory effect.
Possible complications
Coronavirus infection in humans with a severe course of pathology can cause the following complications:
- multiple lesions of peripheral nerves;
- pneumonia;
- bacterial or fungal superinfection (simultaneous infection with several pathogens);
- swelling of the brain;
- acute renal, respiratory or multiple organ failure, which can be fatal;
- inflammation of the heart muscle;
- septic shock;
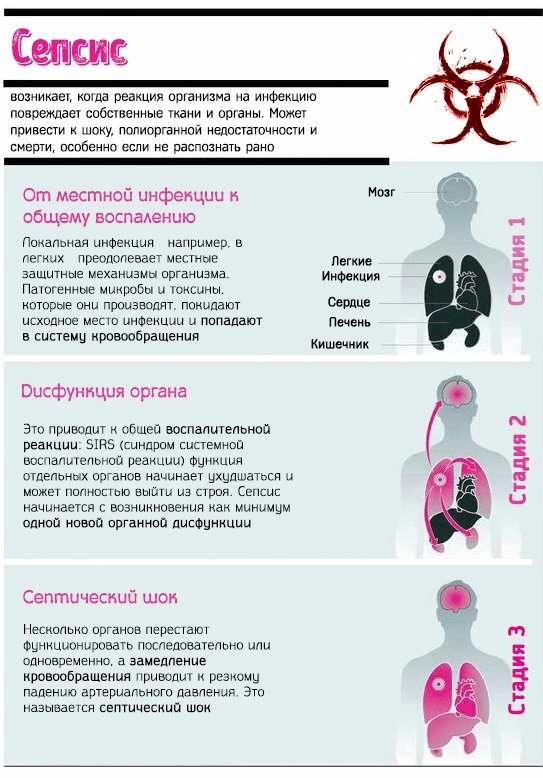
- intravascular blood coagulation (disseminated intravascular coagulation).
Microorganisms that cause coronavirus infection in humans are capable of mutating, adapting to new conditions. Along with rhinoviruses, coronoviruses are the main causative agents of colds.
Epidemics 2002 and 2012 also led to the discovery of new strains capable of causing severe pneumonia with high mortality. Antiviral drugs and interferons are most effective in treating this disease.
Coronavirus video
Komarovsky on coronavirus 2020 in China: