Reduced the number of red blood cells in the blood may indicate a serious health problem. It is important to know why abnormalities occur, what treatment options are available, and how to avoid blood disorders.
Record content:
- 1 The role of red blood cells in the body
- 2 How are red blood cells and hemoglobin related?
- 3 Types of erythropenia
-
4 Reasons for a decrease in blood concentration in adults, children
- 4.1 Acute or chronic blood loss
- 4.2 Insufficient production of red blood cells
- 4.3 Hereditary blood disorders
- 4.4 Enhanced destruction
- 4.5 Infections
- 4.6 Oncology
- 4.7 Autoimmune diseases
- 4.8 Taking certain medications
- 4.9 Pregnancy
- 5 Symptoms of a lack of red blood cells
- 6 Why is erythropenia dangerous?
- 7 Normal red blood cell count
- 8 Diagnosis of pathology
- 9 How is the blood test done?
-
10 How to increase red blood cells?
- 10.1 Drug treatment
- 10.2 Diet therapy
- 10.3 Lifestyle
- 10.4 Folk remedies
- 11 Features of the treatment of erythropenia in pregnant women
- 12 Features of the treatment of children
- 13 Possible complications
- 14 Video about red blood cells
The role of red blood cells in the body
Red blood cells are blood cells that perform one of the most important functions in human life - breathing. They deliver oxygen from the lungs to all tissues of the body, and remove carbon dioxide.
Red blood cells perform several other important functions:
- Move proteins, carbohydrates, amino acids and other substances between the cells of the body;

- bind and neutralize toxic substances in the blood, cleansing the body;
- participate in the process of blood clotting;
- regulate the pH level of the blood;
- act as carriers of vitamins B and C, as well as a variety of enzymes.
How are red blood cells and hemoglobin related?
Hemoglobin is a complex iron-containing protein. It is contained in red blood cells and ensures the delivery of oxygen to the tissues of the body by attaching to itself its molecules obtained from the inhaled air.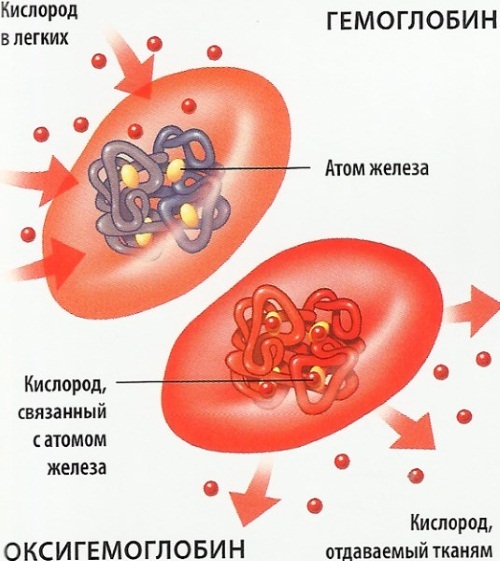
Erythrocytes act as a kind of conductor of hemoglobin, and the direct supply of oxygen to the tissues of the body is provided by this particular protein. In a similar way, hemoglobin attaches to itself the carbon produced by the body and transports it to the lungs.
Types of erythropenia
A decrease in the number of red blood cells in the blood below the established norms is called erythropenia.
It is of 2 types:
- Relative. The number of red blood cells decreases in the blood under study due to the intake of a large amount of fluid into the body. This leads to blood thinning. But in the total volume of all blood, the level of red blood cells remains unchanged.
- Absolute - characterized by a low level of red blood cells in the blood. This indicates a violation of the process of blood formation.
Reasons for a decrease in blood concentration in adults, children
Red blood cells in the blood can be lowered for various reasons.
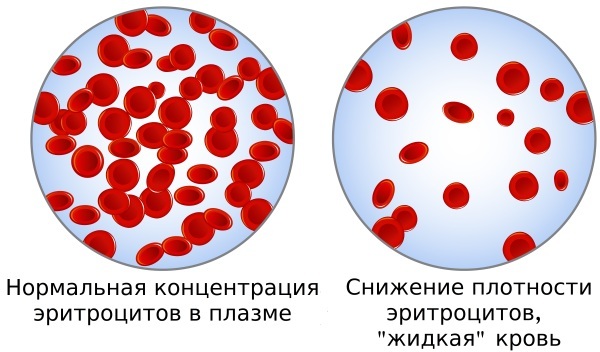
The most common of these are the destruction of blood cells when moving through the capillaries and heavy bleeding accompanying large blood loss.
Acute or chronic blood loss
Acute blood loss is characterized by a sharp decrease in blood volume - more than 10%. Most often, bleeding occurs after serious injury, during surgery, stomach ulcer.
Women can lose a lot of blood during childbirth and with uterine bleeding (spontaneous miscarriage, fetal freezing, inflammation). Acute blood loss in children, most often, occurs with injuries of the brachial, femoral, iliac arteries.
Chronic blood loss occurs with continuous or repeated bleeding.
It occurs more often than acute blood loss. Bleeding can occur when:
- inflammatory processes of the gastrointestinal tract;
- the presence of tumors (in the intestines, bladder, kidneys);
- profuse menstrual flow.
Insufficient production of red blood cells
Red blood cells perform their function for 3-4 months, after which they are replaced by new blood cells produced by the bone marrow. It produces more than 2 million red blood cells per second to replace blood loss in various situations.
Insufficient production of blood cells occurs for 2 main reasons:
- limited intake of trace elements with food (folic acid, iron, copper, vitamin B12) necessary for the production of red blood cells;
- a pathological process in the body that interferes with the normal absorption of substances involved in the formation of blood cells.
Hereditary blood disorders
Low red blood cell counts can cause some hereditary blood disorders:
-
Hemophilia - the disease is accompanied by increased bleeding with minor cuts, injuries due to the fact that the blood is poorly or does not clot at all - it is very difficult to stop it. As a result, a person loses a lot of blood, and the bone marrow does not have time to produce the required number of red blood cells.
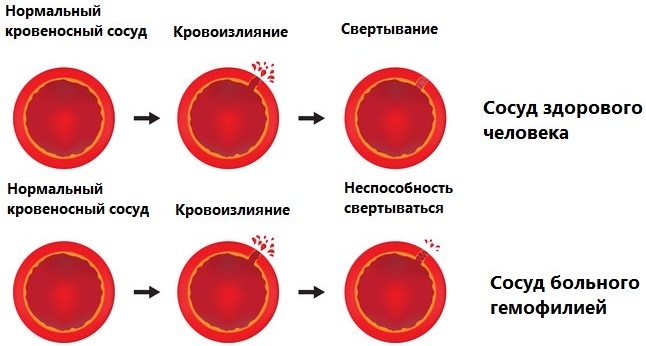
- Ovalocytosis - a rare disease in which from 40 to 90% of red blood cells are oval. Such blood cells die quickly, not fully performing their functions.
- Microspherocytosis is a disease in which red blood cells have a genetic defect in their membranes, as a result of which their life expectancy is reduced.
Enhanced destruction
The destruction of erythrocytes mainly occurs during their circulation through the vessels as a result of mechanical injury. Young blood cells that have just left the bone marrow succumb to such death.
Also lead to permission:
- decrease in osmotic pressure (osmotic hemolysis);
- enlargement of the spleen.
Infections
Once in the body, the causative agent of an infectious disease disrupts the work of the bone marrow. The organ stops producing the required number of red blood cells, which leads to their decrease.
In children, as in adults, after ODS and other infectious diseases, the analysis can show a reduced level of red blood cells in the blood. This phenomenon is mostly asymptomatic and after the destruction of the pathogen, the level of red blood cells is normalized.
Reduction of blood cells is also caused by parasites that enter the blood of a person through mosquito bites. These parasitic organisms feed on red blood cells.
Oncology
A decrease in the level of red blood cells in oncology is associated with various reasons:
- Suppression of work or complete blockage of bone marrow functions. Malignant tumors that develop in an organ or get there through metastases stop the production of red blood cells.
- Insufficient intake of iron and other substances involved in the formation of red blood cells due to lack of appetite in patients or caused by the presence of nausea / vomiting.
- Radiation and chemotherapy suppress the process of hematopoiesis.
Autoimmune diseases
If the immune system malfunctions, the body begins to produce antibodies that destroy red blood cells, because they mistakenly perceive them as foreign cells.
The manifestation of an autoimmune reaction occurs in the presence of diseases such as lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, cirrhosis of the liver, chronic hepatitis, pyelonephritis (more often in children). The causes of the autoimmune reaction have not yet been established.
Taking certain medications
A decrease in red blood cells can also occur while taking the following drugs:
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal drugs (aspirin, ibuprofen) reduce blood viscosity, increasing the risk of bleeding;
- antacids - agents designed to neutralize hydrochloric acid in the stomach, which ensures effective absorption of iron;
- medicines that bind iron in the body (ferritin, transferrin);
- anti-tumor drugs containing platinum - they partially inhibit the production of erythropoietin in the kidneys (a hormone that controls the formation of red blood cells).
Pregnancy
A decrease in red blood cells during pregnancy is associated with an increase in body fluids. As a result, the blood thinns, the hemoglobin level drops. A level of indicator below 110 g / l is considered dangerous for a woman with a norm of 120-140 g / l.
Lack of oxygen supply can lead to a number of complications:
- lowering blood pressure;
- risk of miscarriage;
- delayed fetal development;
- premature birth;
- anemia in a child in the first year of life.
Also, a decrease in red blood cells causes an increased consumption of iron for the blood formation of a pregnant woman and the need for the development of the fetus.
Symptoms of a lack of red blood cells
Symptoms of a lack of red blood cells are manifested by the following signs:
- general weakness of the body;
- lethargy and drowsiness;
- feeling of constant tiredness;
- pallor of the skin, lips and mucous membranes (symptoms are pronounced in children);
- shortness of breath;
- rapid pulse;
- low pressure;
- wet, cold skin
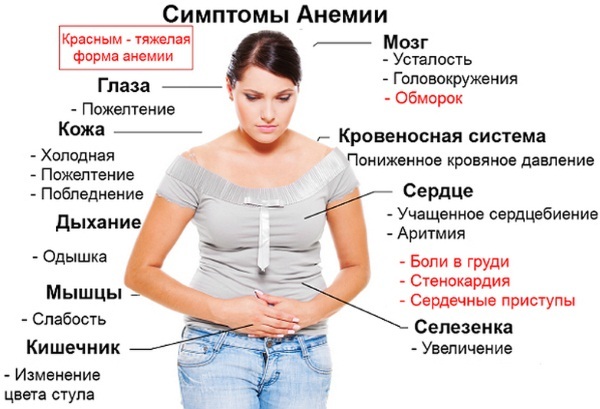
Iron deficiency anemia is when the red blood cells in the blood are low
In a chronic condition, a person has a slowdown in reactions, lethargy, fainting. At a critical level of decrease in erythrocytes in children, muscle atrophy may develop, blood appears in feces and urine, coordination of movements is impaired, swelling appears, and the color of urine becomes dark.
Why is erythropenia dangerous?
Red blood cells in the blood are low - this condition in children can lead to developmental delays, since insufficient the supply of oxygen to the cells of the body and poor excretion of carbon dioxide cause malfunctions in the internal organs. Also, the child's immunity decreases, he starts to get sick often, there are problems with blood clotting, memory and concentration are impaired.
Oxygen starvation is dangerous for adults as well, as it causes a number of complications:
- The risk of heart attack, stroke, or heart failure increases as the heart muscle has to contract more often and the heart wears out faster.
- Structural changes in cells, disruption in the work of all organs and systems of the body (the liver and kidneys are the first to suffer).
- Brain activity worsens - a person may experience confusion of consciousness, memory impairment.
- Decreased immunity. After the infection enters the body, the disease begins to develop rapidly and may worsen.
- In women during menstruation, weakness, dizziness, and low blood pressure may appear.
Normal red blood cell count
The normal indicator of the level of red blood cells in the blood of people of different ages and different sexes is presented in the table below:
| Age | Level (mln / 1 mm3 blood) |
| Newborn babies (up to 28 days) | 4-6,6 |
| Children from 28 days to 1 year old | 3-5,4 |
| One year old children | 3,6-4,9 |
| Children aged 1-14 years | 4,2-4,8 |
| Women | 3,7-5,1 |
| Men | 3,8-5,3 |
| During pregnancy | 3,5-5,6 |
Diagnosis of pathology
Diagnosis of a decrease in the level of red blood cells is based on a laboratory (general) blood test and on the symptoms of a sick person.
The following changes in the analyzes indicate the presence of erythropenia:
- Decreased blood color index;
- the number of red blood cells is below normal;
- the presence of red blood cells of different shapes and sizes;
- a decrease in iron;
- high erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
If the pediatrician, after receiving blood tests, could not find the cause of the decrease in red blood cells, then a full examination is prescribed. It includes biochemical, immunological tests, ultrasound and CT of organs, research for tumor markers, genetic tests, and so on.
How is the blood test done?
A blood test is a comprehensive study, the result of which helps doctors determine the general state of health. Blood is taken from a finger or vein in a special room for fasting manipulations. The day before the test, a person should not drink alcohol. Also, half an hour before the procedure, smoking, physical activity and stress are prohibited.
The day before the test, a person should not drink alcohol. Also, half an hour before the procedure, smoking, physical activity and stress are prohibited.
How to increase red blood cells?
An integrated approach to treatment will help to increase the level of red blood cells in the blood. Taking the necessary medications along with maintaining a correct lifestyle and adjusting the diet can quickly eliminate this violation and consolidate the result.
Drug treatment
Red blood cells in the blood can be lowered for various reasons, therefore, drug treatment is prescribed only after receiving all the data on the pathology. The table below lists medications that can help increase the level of blood cells in the body.
| Name | Active substance | Indications for use | How to use? | Contraindications |
| Ferroplex | Ferrous sulfate, vitamin C | Iron deficiency, decreased rate of iron absorption, prolonged bleeding. | For treatment, take 100-200 mg per day, for prophylactic purposes, take 100 mg. | Children under 12 years of age, aplastic anemia, individual intolerance to the components. |
| Cyanocobalamin | Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) | Various types of anemia, liver cirrhosis, hepatitis. | With iron deficiency anemia, take 30-100 mcg 2-3 r. in Week. Children with aplastic anemia are prescribed 100 mcg per week until performance improves. | Not accepted for thromboembolism, angina pectoris. |
| Maltofer Foul | Iron (III) hydroxide, folic acid | Treatment of iron deficiency anemia, prevention of iron deficiency. | For the treatment of anemia, take 1 table. 2-3 p. in a day. | Diseases of the digestive system, allergies to the components of the drug, excessive amounts of iron in the body. |
Diet therapy
You can increase red blood cells by taking iron-containing products:
- apples (additionally enrich the body with vitamin C);
- beets and freshly squeezed beet juice diluted with water in a 1: 1 ratio.
- buckwheat;
- oatmeal jelly (infused with boiling water);
- meat offal (beef and pork liver, kidneys, lungs);
- tomatoes;
- dried fruits - prunes, grapes and dried apricots;
- legumes;
- chicken and quail egg yolks;
- seafood.

The diet should be balanced and correct. For greater efficiency from the use of healthy products, you can turn to a nutritionist for help - a specialist will tell you how to correctly introduce iron-rich products into your daily diet.
Lifestyle
Maintaining the level of red blood cells within the normal range will help to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Regular sports, walking in the fresh air, good sleep and rest after exertion are recommended. It is worth giving up the use of alcoholic beverages and smoking, since nicotine and alcohol reduce the concentration of red blood cells in the blood and slow down the process of their formation.
Folk remedies
In the fight against a low level of red blood cells, folk remedies help.
The following recipes are popular:
- Rosehip and mountain ash tea. These fruits contain large amounts of vitamin C, iron and other beneficial components. To prepare a drink, it is necessary to take equal amounts of mountain ash, rose hips and brew tea from them. It is taken for 1 tbsp. daily.
- Radish, beet and carrot juice. Take vegetables, grate, squeeze juice from them and in equal quantities, add it to a dark glass dish. It must be covered with a lid (only loosely so that the liquid evaporates), placed in the oven and left to simmer for 3 hours. at a slow temperature. The resulting product is taken in 1 tbsp. l. 3 p. a day before meals for 3 months.
-
Oat drink. 1 tbsp. pour oats or cereals with 5 tbsp. water and cook (the consistency should resemble liquid jelly). Strain the broth, add milk to it (the amount should be the same) and boil again. Add 4 tsp to the resulting mixture. l. honey and send to the fire to boil. Take the resulting drink 2-3 p. in a day.

- Garlic alcohol tincture. Pour 300 g of chopped garlic with 0.5 l of alcohol and insist in a dark place for 21 days. Use the tincture 3 r. 20 drops per day, after dissolving it in 100 ml of milk.
- Chicory juice with milk. 1 tbsp. l. Stir the juice in a glass of milk. Drink the resulting mixture in 3 doses during the day.
Features of the treatment of erythropenia in pregnant women
With a mild form of erythropenia, pregnant women are advised to change their diet and add foods containing iron and other trace elements to it. In more severe cases, the gynecologist prescribes a course of treatment based on the intake of vitamin complexes that contain B vitamins and iron. The table below shows the drugs approved for use during pregnancy.
| A drug | Main components | dosage |
| Totem | Iron, manganese, copper | 2-4 ampoules per day |
| Ferro-Folgamma | Vitamin B12, ferrous salt, folic acid, vitamin C | 1-2 capsules 3 r. in a day |
| Fenuls | Ferrous iron, B vitamins, ascorbic acid | 1-2 capsules per day |
| Gyno-tardiferon | Iron, folic acid | 1-3 tab. per day (depending on the severity of the disease) |
The course of taking drugs intended to normalize the process of hematopoiesis is 1-3 months. If the decrease in erythrocytes is associated with impaired renal function, the attending gynecologist may prescribe diuretics. They prevent fluid retention and normalize blood cell levels.
When the pathology develops against the background of oncology or heart failure, pregnant women are placed on inpatient treatment under the constant supervision of medical professionals. The treatment regimen is selected individually, depending on the disease and its severity.
Features of the treatment of children
The primary task of the pediatrician in the treatment of children is to establish the cause of the decrease in red blood cells. If the development of pathology is associated with a violation of the production of blood cells in the bone marrow, drugs are prescribed that stimulate the process of hematopoiesis. Bleeding that causes acute blood loss requires surgery and blood transfusion.
If the decrease in red blood cells is caused by a lack of iron in the body, the pediatrician prescribes special iron-containing drugs.
Among the large number of remedies, the most popular and effective drugs are:
-
Maltofer. Drops have no age restrictions. The daily dosage is 1-2 drops per 1 kg of the child's weight. Before use, the drug is mixed with water, juice or compote.
- Ferrum-Lek. The syrup is intended for children over one year old. 1 scoop contains 50 mg of active iron. When treating children aged 1-12 years, the daily dose is 5-10 ml. When taking the drug for prophylaxis, the dosage is 2.5-5 ml.
- Aktiferin. The drops are taken before meals or during meals. They should be diluted with a little water or juice. The daily dose for children under one year old is 10-15 drops 3 r. in a day. Children aged 1-2 years are given 15-25 drops of the drug three times a day. The daily dosage for children aged 2 to 6 years is 25-35 drops. For children over 6 years old, it is advisable to take the drug in the form of capsules.
Possible complications
Red blood cells in the blood are lowered most often due to iron deficiency anemia. According to statistics, every 4th resident of the country has this disease. Its early stage (when fatigue and slight malaise is felt) quickly turns into a more severe form - a person has memory gaps, disorientation occurs, cramps and persistent muscle pain.
Complications, if the pathology is not treated, can be partial or complete paralysis, memory loss, complete muscle atrophy and even death.
A decrease in the level of red blood cells in the blood can be caused by various reasons. Timely diagnosis and implementation of the recommendations of the attending physician will help eliminate this pathology with minimal damage to health.
Video about red blood cells
About the function of erythrocytes:



