AIDS today is one of the most dangerous diseases transmitted from an infected person to another person in various ways. In this case, the pathology is incurable and rather quickly worsens the patient's condition, gradually leads to death from some other disease.
Today, experts classify the condition as a pandemic, since it may well destroy humanity as a biological species, is transmitted in several ways and progresses rapidly.
Record content:
- 1 What is HIV, AIDS
- 2 The incubation period of the immunodeficiency virus
-
3 Human-to-human transmission of a dangerous virus
- 3.1 Sexual route
- 3.2 Vertical path
- 3.3 Parenteral route
- 3.4 Other routes of infection
- 4 At-risk groups
-
5 Signs and symptoms of HIV infection
- 5.1 Asymptomatic phase
- 5.2 Acute phase
- 5.3 Generalized lymphadenopathy
- 6 In what cases AIDS does not occur
- 7 What is the likelihood of infection and how to avoid it
- 8 How to determine if a person could have been infected
- 9 Development of HIV infection
- 10 Diagnostics
- 11 Treatment methods
- 12 Forecast
- 13 AIDS video
What is HIV, AIDS
HIV, or Human Immunodeficiency Virus, is an infectious disease caused by a virus in the body that suppresses the patient's immune system. At the same time, a significant, but gradual weakening of the body occurs, it cannot fight any, even mild, diseases.
AIDS, or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, is the terminal stage of HIV infection, when a sharp decrease in the cells responsible for immune defense occurs in the patient's body. At the same time, the level of these cells is not restored, which leads to death as a result of any disease. Most often, death occurs with infection with tuberculosis, as well as the development of pneumonia, anemia.
Such conditions are considered very serious, and the patient poses a danger to other people.
The incubation period of the immunodeficiency virus
AIDS is transmitted from person to person in several ways, but the disease does not manifest itself in the initial stages, that is, it is in a latent form. Doctors call this an incubation period. The patient is already a carrier of the virus, but there are no symptoms.
This time may differ for different patients. Some feel the first changes within 2 weeks, others notice symptoms after 3 months. In some cases, the incubation period from the moment of infection lasts up to 12 months. At this time, antibodies to the pathogen cannot be detected in the patient's blood, there are no symptoms.
The end of the incubation period is accompanied by the appearance of symptoms on the part of the internal organs of the systems.
Human-to-human transmission of a dangerous virus
There are several ways in which the causative agent of a dangerous disease is transmitted to humans. In each case, development can occur slowly or rapidly, depending on the individual characteristics and age of the patient.
Sexual route
More than 60% of all patients suffering from acquired immunodeficiency syndrome were infected from a sick person through sexual contact. It is believed that the highest concentration of the virus is found in blood and semen, as well as in vaginal secretions.
Unprotected contacts will certainly lead to the penetration of the virus through the mucous membranes of the genital organs. This is due to the fact that during the act, microdamages are formed on the mucous membranes, which contributes to the rapid spread of the virus through the human blood.
If he often changes partners and does not use barrier contraceptives. The risk of infection increases several times.
However, doctors also draw the attention of patients to the fact that during unconventional sexual intercourse, for example, oral or anal sex, the risk of infection is also much higher. This is due to the greater likelihood of damage to the mucous membranes. Rough intercourse is also considered one of the predisposing factors.
Vertical path
AIDS is not only transmitted from an adult to another person through sexual intercourse. The vertical pathway involves the transmission of the virus from a sick mother to her baby during childbirth. This is due to the fact that the woman's body fully provides the fetus with nutrients and oxygen through the umbilical cord.
It should be noted that the virus is able to penetrate the placental barrier. Despite this, infection does not always occur. Even today, doctors cannot determine exactly why in one case the child becomes infected, and in the other he is born absolutely healthy. The vertical path is also considered to be quite common.
In addition, a healthy baby can, after birth, become infected from a sick mother through breastfeeding, since the virus is present in milk.
Parenteral route
The parenteral route involves the transmission of the virus through the blood. Most often, this method is typical for patients who inject drugs. Often, patients use one syringe for several people, which leads to instant infection.
At the same time, drug addiction only aggravates the patient's condition, the virus develops much faster, the incubation period is shortened, and death occurs after a few years. Also, the parenteral route of transmission is typical for people who come into contact with the blood of the infected, for example, in a medical institution, laboratory.
A small amount of contaminated blood entering an open wound will inevitably lead to the penetration of the virus into the body.
Other routes of infection
There are several other routes of infection. They are not as common as the sexual and parenteral routes, but they can also cause the virus to enter the bloodstream.
| Transmission path | Peculiarities |
| Contact of the wound surface with contaminated blood | Such cases are very rare. As a rule, this happens in some kind of emergency, for example, in an accident, when an infected, injured person assists the wounded. In this case, it is possible for contaminated blood to enter the wounds. |
| Bite | As a rule, people are not inclined to bite each other, but patients with mental disorders may well do this, which will lead to infection. In addition, monkey bites, which can also be affected by the virus, lead to infection |
| During dental procedures | Improper performance of the procedure, as well as insufficient sterilization of instruments, leads to the penetration of the virus into the blood. This usually happens when teeth are pulled out. |
| With blood transfusion or organ transplant |
 This route of transmission is quite rare, only in countries where the health care system is almost undeveloped. As a rule, infection occurs when the rules are violated during the check of donor organs and blood This route of transmission is quite rare, only in countries where the health care system is almost undeveloped. As a rule, infection occurs when the rules are violated during the check of donor organs and blood |
| Hygiene items | Using an infected razor or toothbrush can lead to infection. As a rule, a healthy person has lesions in the oral cavity or on the skin that become a lesion focus |
Such transmission routes are rare, but the possibility of infection should not be ruled out.
At-risk groups
AIDS is transmitted from person to person under adverse circumstances, but doctors draw the attention of patients to the fact that there are risk groups that are more susceptible to infection:
- Drug addicted patients who inject drugs.
- Patients suffering from chronic venereal pathologies with regular exacerbations.
- People who provide sexual services for a certain amount of money.
- Men and women who have promiscuous sex life with frequent partner changes and complete rejection of condoms.
- People who regularly come into contact with the blood of patients infected with the virus.
- Low-income and homeless people.

In addition, at risk are people in whose family a person infected with the pathology lives.
Signs and symptoms of HIV infection
The first signs of the disease can be confused with other pathologies of internal organs. Doctors distinguish 3 main stages, which are accompanied by certain clinical manifestations.
Asymptomatic phase
There is no symptomatology of the disease at this stage. Usually, this stage occurs simultaneously with the incubation period, lasts from 2 weeks to 1 year, depending on the patient's body, his lifestyle and other factors.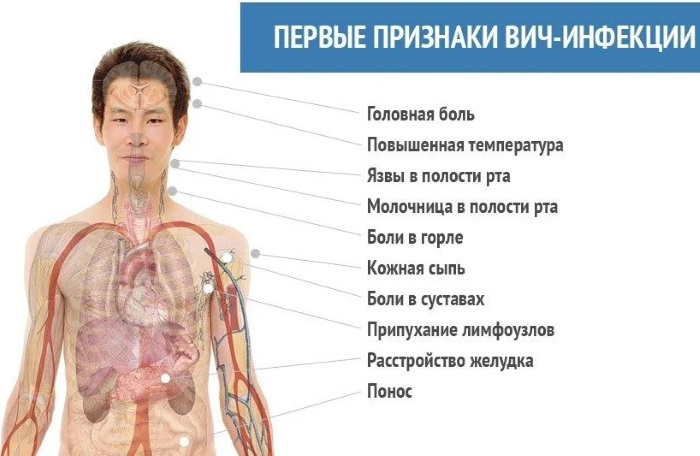
The only manifestation after infection is a slight decrease in the body's immune defense. At the same time, the patient notes an increase in the frequency of colds and difficulties when trying to lower body temperature. There are no other symptoms, so the patient does not visit the doctor, continues to lead a normal life and independently takes anti-cold remedies.
Acute phase
It is at this stage that the development of the clinical picture of the disease occurs. After the end of the incubation period, the patient notes pronounced manifestations. Usually, an exacerbation of the disease resembles a severe flu.
The patient has the following symptoms:
- Significant increase in body temperature.
- Joint and muscle pain that makes it difficult to move.
- Headache, dizziness.
- Weakness, drowsiness.
- Lack of appetite, nausea, bouts of vomiting.
- Indigestion, characterized by frequent loose stools, abdominal pain, flatulence.
- Women may develop thrush, which is difficult to treat.
- Stomatitis is considered a frequent symptom of the disease, which is associated with damage to the mucous membranes by pathogenic bacteria as a result of weakening the body's defenses.
- Intense thirst.
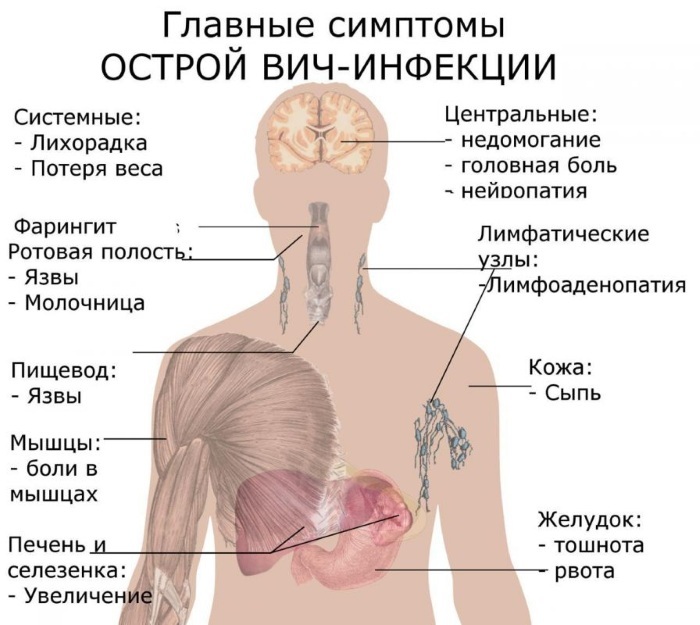
The acute phase lasts from 7 to 30 days, depending on the patient's body. In this case, the severity of symptoms also differs.
Generalized lymphadenopathy
This stage is considered terminal. The largest lymph nodes in the neck, armpits and genitals are affected. On palpation, the doctor discovers their significant increase, as well as hardening.
At this stage, HIV usually turns into AIDS, that is, there is a rapid multiplication of the virus in the blood and damage to all internal organs. At the same time, there are almost no symptoms. Lymph nodes are painless, do not cause discomfort to the patient.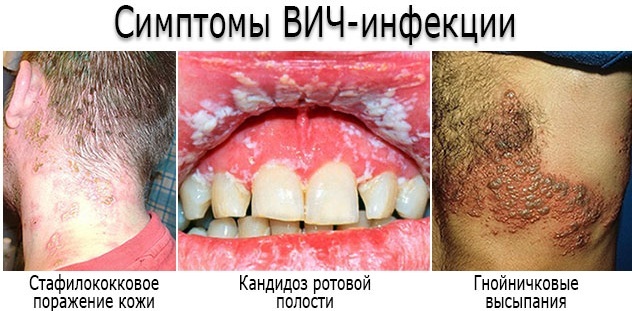
Among the manifestations are weakness and frequent colds. With a favorable course, this stage can last for 5-10 years. With the timely initiation of special therapy, the period can be significantly extended.
The generalized stage almost always ends in death as a result of a severe course of any disease of the internal organs.
In what cases AIDS does not occur
AIDS is transmitted from person to person in several ways, but even through contact with an infected person, infection does not always occur. It is impossible to get infected with a kiss and a handshake, so you should not limit your communication with sick people.
In addition, there is no risk of infection in public pools, saunas and latrines. The virus is not transmitted by airborne droplets.
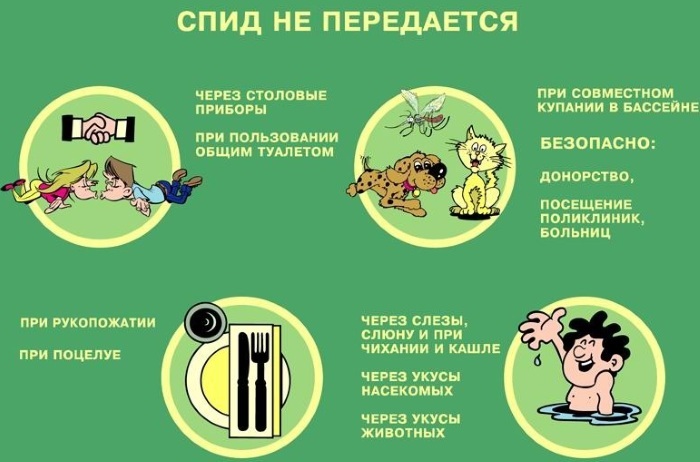
There is a theory that insects that feed on human blood can carry the virus from sick to healthy. This opinion is erroneous, doctors refute it, so you should not be afraid of insects and their bites.
What is the likelihood of infection and how to avoid it
People who lead a healthy lifestyle, have a regular examined sexual partner and regularly visit a doctor, the likelihood of contracting the virus is not so great. It rises with frequent hospitalization and receiving donated blood. Despite this, the affluent segments of the population are less susceptible to infection.
Poor people, sexually promiscuous patients and injecting drug users are more likely to become infected. To prevent infection, it is worth following some rules to reduce the risk of the virus entering the blood to a minimum.
The first and most important rule is the use of condoms when in contact with a new sexual partner. The best option is considered a preliminary examination by both partners, but this is practiced only in developed European countries.
In addition, it is recommended to have a permanent partner, as well as to minimize unconventional contact (anal). To exclude the vertical transmission route, it is worth abandoning breastfeeding in the event of a healthy baby being born. Additionally, antiretroviral therapy is provided to mother and child.
The easiest way to prevent infection through blood is to give up injecting drugs and generally from using drugs. In addition, you should not have unprotected sex with a person who uses or previously used drugs without first examining his blood. Compliance with simple rules will minimize the risk of infection.
How to determine if a person could have been infected
After unprotected intercourse or trauma to the skin, many patients wonder if the virus could have entered the bloodstream.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to determine its presence in the body immediately after infection by means of examination or questioning.
For this, human blood is examined with an interval of 6 months. The first result may be negative, therefore, after 6 months, a repeated sampling of the biomaterial and diagnostics in the laboratory are required. Other methods are ineffective, since some of the symptoms resemble the course of many diseases and cannot serve as a reason for diagnosing AIDS.
Development of HIV infection
AIDS is transmitted from person to person in one of the most common ways, after which it spreads and develops in the body. The end of the incubation period is accompanied by the defeat of CD lymphocytes and macrophages by the virus. It penetrates into their structure and begins to multiply actively.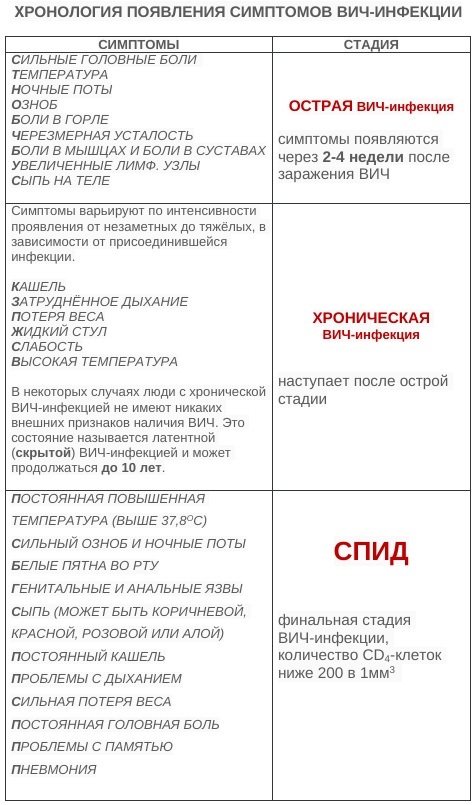
Gradually, the virus captures more and more cells, which leads to their death. The patient's immunity is weakened, since it cannot resist staphylococci, streptococci and other microorganisms that provoke various diseases. Gradually, the virus destroys monocytes, T-helpers and Langergas cells. At the same time, an increasing weakening of the body occurs.
To date, experts have not been able to study the entire process of the spread of the virus in the body. However, they pay special attention to the destruction of dendritic cells, which provide a significant part of the patient's immunity.
The bulk of the virus is located in the lymphatic tissue, which explains the defeat of large lymph nodes. About 12% of pathogens are localized in the blood.
It is worth noting that viruses found in lymphoid tissue infect the mucous membranes of the intestines and stomach, making them more permeable to various bacteria. As a result, these microorganisms enter the bloodstream and lead to an aggravation of the condition.
Excessive accumulation of viruses in the lymph nodes will certainly lead to their fibrosis and impaired lymph drainage. The combination of several factors leads to the progression of the disease.
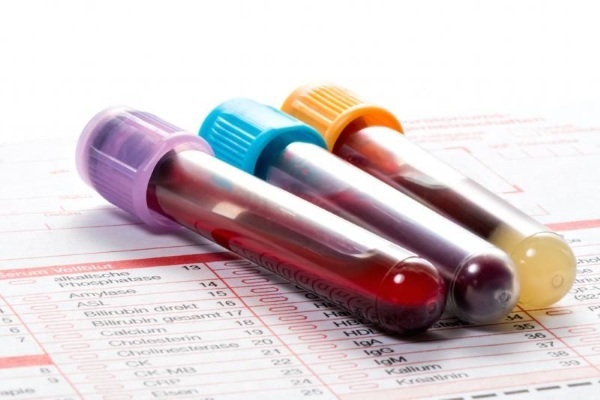
Diagnostics
Several methods are used to diagnose the disease, despite the fact that it is possible to clarify the presence of the virus using one blood test.
The most important methods:
- Examination and questioning of the patient. At the same time, the doctor specifies the time of the onset of the disease, the severity of the symptoms, and also examines the skin, mucous membranes of the patient. Such an examination allows you to visually assess the patient's condition, to determine the degree of neglect of the condition.
-
General blood analysis is also considered a required method. In this case, the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation and the number of leukocytes are of particular importance.
- Chest x-ray usually required to exclude or confirm the presence of foci in the lungs, for example, with tuberculosis or pneumonia.
- Abdominal ultrasound is considered an additional diagnostic method, allows you to assess the condition of the liver, pancreas.
The most important and informative method is considered to be a blood test using a special screening test or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. In this case, the patient's blood is taken for analysis. Additionally, an analysis is carried out for the polymerase chain reaction. That is, the presence in the blood of antibodies produced in response to the introduction of the virus is detected.
If a positive screening test result is obtained, a more accurate study is carried out using immune blotting. This method involves taking blood to confirm the presence of antibodies in it.
In patients who have been infected, after a few months, the blood is examined in order to determine the number of CD cells. Their number helps to determine the degree of neglect of the disease.
Based on all the results, a diagnosis is made and appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Treatment methods
To date, there is no method that would help completely cure patients with HIV and AIDS. Highly active antiretroviral therapy is considered the only way to prolong the patient's life and slow the progression of the disease.
In this case, various drugs are used, the action of which is aimed at improving the patient's condition, increasing the number of lymphocytes, as well as preventing complications.
Most popular remedies:
- Nikavir.

- Virolam.
- Regast.
- Zerith.
It is worth remembering that it is impossible to independently choose the dosage of medicines, it is prescribed individually. Most of the drugs are taken for life and can prolong the patient's life for decades. However, without observing the regimen, the effectiveness decreases, therefore it is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, to exclude the use of alcohol and drugs. Better to give up cigarettes.
During the course of treatment, the doctor may make adjustments, change the dosage, or alternate funds to achieve maximum effectiveness. At the same time, blood is regularly taken from the patient for examination and determination of the level of CD cells.
Forecast
Subject to the recommendations of a specialist, the patient can lead a normal life, work, play sports. Correctly selected medicines can support his body. In this case, the prognosis for the patient is favorable.
However, with refusal of treatment, alcohol and drug use, the prognosis is poor. Typically, young patients die 3-5 years after infection. The cause of death is pneumonia, anemia, or tuberculosis.
In some cases, if the patient does not use drugs, the life expectancy after infection is 10 years. In each case, this period can be extended or shortened depending on many factors.
AIDS is by far the most dangerous and incurable disease that is transmitted from an infected person to another person in several ways. To prevent infection, it is recommended to follow some rules and regularly visit a doctor for a preventive examination.
AIDS video
AIDS / HIV = conspiracy ?: