A disease called toxic hepatitis happens acute and chronic. And also this is a pathology that develops when chemical or other harmful substances (drugs, alcohol, etc.) enter the body.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Traditional methods
- 8.3 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Toxic hepatitis video
Views
Toxic hepatitis is a disease that has a classification. Depending on the cause of occurrence, pathology is divided into types.
Namely:
-
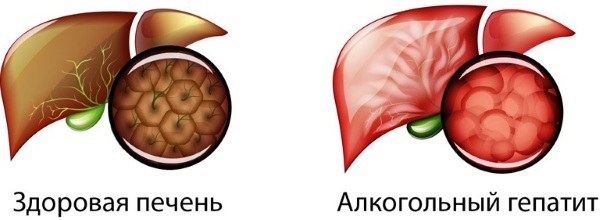
Alcoholic toxic hepatitis. The disease develops with the abuse of alcoholic beverages.
- Medication. If a person takes medications without the recommendation of a specialist, and also does not control the dosage, hepatitis may appear.
- Food grade. The item provides for the penetration of substances into the body with food. Most often, toxic hepatitis occurs with the use of poisonous mushrooms.
- Chemical. Hepatitis develops if harmful substances enter the body. Often, chemical components get into when safety precautions are not followed at work or at home.
According to the type of contact, the following types of hepatitis are distinguished:
- random;
- deliberate;
- accidentally intentional (associated with work).
The substances that provoke the disease can enter the body in various ways.
Namely:
- through the digestive tract - first the pathogen enters the stomach, then into the blood and liver;
- by breathing - the substance enters the lungs through the nasal cavity, is absorbed into the blood, and then into the liver;
- through the skin - the pathogen enters the bloodstream, and then into the liver.
Stages and degrees
In addition to species, toxic hepatitis has grades.
Namely:
- Sharp. The disease develops if a large (weak irritating properties) or small (strong components) amount of a substance enters the body. As a result, the symptoms of pathology are pronounced. The disease develops within 2 - 5 days from the moment the pathogen enters the body.
- Chronic. The pathogen has a long-term effect on the body, but in small quantities. Pathology can form gradually. The term comes up to several years. At first, the symptoms appear slightly, during an exacerbation they intensify.
Toxic hepatitis is divided into stages.
There are 3 of them:
- Latent period. The pathogen enters the human body. The stage continues until symptoms of the disease appear.
- Clinical manifestation. The person develops symptoms of the disease.
- Exit stage. Lasts from the maximum manifestation of symptoms to recovery or death.
Symptoms
With toxic hepatitis, various symptoms appear. They depend on the type of disease. Details are shown in the table.
| The degree of toxic hepatitis | Symptoms |
| Sharp | In acute toxic hepatitis, the following symptoms appear:
|
| Chronic | This degree of toxic hepatitis is characterized by the following general symptoms:
The listed symptoms may subside for a while, and then appear again. The first case is called remission, and the second is called exacerbation. The activity of chronic hepatitis is determined by the severity of the symptoms. Additional symptoms: 1. The minimum degree of activity. The person feels good, there are no acute complaints. Sometimes weakness may appear, appetite decreases. Additionally, the mood changes, the person does not sleep well. There is pain in the head, nausea. A person cannot tolerate products that were on the list of favorites - most often this concerns fried products, alcoholic beverages. The liver is palpated 2 - 4 cm below the costal arch. On palpation, there are no bright painful sensations. 2. Low degree of activity. In humans, the skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow. Additionally, the discharge of blood from the nose, dilated capillaries on the face are noted. But such signs are rare. The most common symptom is an enlarged liver. The disease can develop for a long time. 3. Moderate activity. A person constantly experiences weakness, and sweat is excreted in an increased amount. In addition, sleep worsens, there is excessive excitability. Spider veins can be seen on the limbs and chest. And bruises are also present. The liver increases in size, sometimes tenderness appears on palpation. If there is no therapy, this degree develops rapidly. 4. A high degree of activity. A person develops a bitter taste in the mouth, and vomit is released after eating. Additionally, there is bloating, diarrhea, or constipation. Sleep is disturbed, pain in the heart or head appears. Efficiency decreases, mood worsens. The skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow, and blood is secreted from the nose and gums. Soreness is noted on palpation of the liver. |
Reasons for the appearance
There are risk factors that increase the likelihood of toxic hepatitis.
Namely:
- people working in hazardous work;
- alcohol abuse;
- women - in the weaker sex, metabolism is slower, therefore, a high concentration of harmful components is maintained in the liver for a long time;
- children in the age group under 3 years old;
- people over 45 years old;
- pregnant women;
- being overweight;
- smoking abuse;
- the presence of malignant or benign tumors;
- the presence of diabetes mellitus;
- liver diseases - cirrhosis, hepatosis;
- existing hepatitis - if a person has this disease, it can turn into a toxic form;
- heredity - if genetic mutations affect the production of liver enzymes, the likelihood of toxic hepatitis may increase;
- drug abuse.
Toxic hepatitis is a disease that can appear for a variety of reasons. The most frequent ones are shown in the table.
| Reasons why toxic hepatitis may appear | Description |
| Drug use | The doctor prescribes medications in the dosage required to achieve a therapeutic effect. And also drugs are prescribed only after the diagnosis has been clarified. If you take medications without a doctor's recommendation, and also do not follow the dosage for a long time (it is indicated in the instructions), toxic hepatitis may develop. Or, the disease appears with a single use of too much of the drug. The group includes many medicines. For instance:
Chemotherapy can be singled out separately. The appearance of toxic hepatitis after the course is allowed. Cytotoxic drugs that are administered to a person inhibit the growth of cancer cells, but negatively affect the entire body, and especially the liver. |
| Impact of alcoholic beverages | Alcohol poisoning accounts for 60% of all deaths due to intoxication. In addition to the fact that alcoholic beverages damage the liver, they have a negative effect on the entire body. The situation worsens in the case of low-quality alcohol. |
| Exposure to industrial poisons | Substances can penetrate through the respiratory organs and skin. Poisons are absorbed into the bloodstream, then enter the liver. The following substances have a harmful effect on the organ:
|
| Influence of poisons of plant origin | Substances have a negative effect on the liver, disrupt the functionality of the organ. This group includes the poisons of mushrooms (fly agaric, toadstool), weeds (wild rose, gorchak). |
Toxic hepatitis is not contagious. Pathology cannot be transmitted to a healthy person from a sick person.
Diagnostics
Toxic hepatitis needs diagnosis. This is due to the fact that a person alone will not be able to accurately determine the disease.
Diagnostics includes the following procedures:
- Delivery of a general analysis of blood and urine. According to the results, it is possible to identify indicators that are important for the body (hemoglobin, erythrocytes, etc.).
-
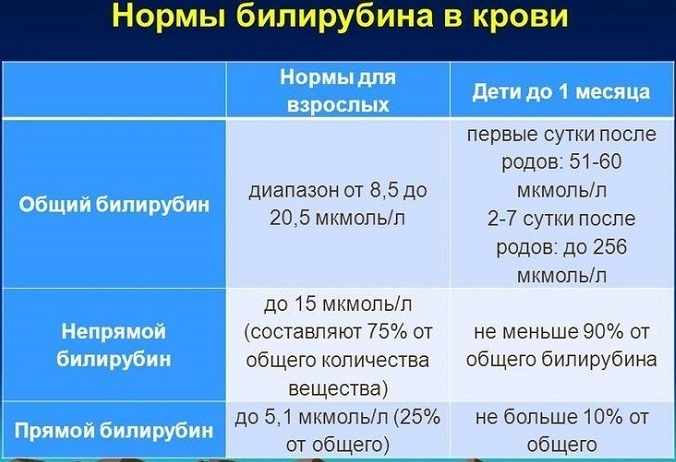
Blood donation for bilirubin. Determine the overall indicator, as well as direct and indirect. The analysis is prescribed for suspected liver disease.
- Determination of alkaline phosphatase. The substance is in an active state if it gets into conditions of high alkali content. There is a minimum amount of the component in the blood of a healthy person. Moreover, the activity is not shown. According to the level of alkaline phosphatase, diseases of the liver and biliary system can be detected.
- Determination of ALT and AST. These enzymes are involved in metabolic processes. Another name for AST is aspartate aminotransferase. This enzyme is found in large quantities in the heart, liver, kidneys. The value of the indicator may increase with diseases of the listed organs. Another name for ALT is alanine aminotransferase. The component is found in large quantities in the liver. Exceeding the indicator occurs when the cells of the organ are damaged. It is necessary to evaluate the result jointly, since ALT and AST are liver tests, by which the functionality of the organ is judged.
- Donating blood for viral hepatitis (A, B and other). Symptoms of toxic hepatitis are similar to viral hepatitis.
- Determination of total protein. This analysis must be prescribed if liver disease is suspected.
- Coagulogram. The procedure is a comprehensive analysis, according to the results of which blood clotting is determined. Using a coagulogram, you can assess the risk of bleeding and thrombus formation. Usually, the analysis is prescribed for diseases of the cardiovascular system (heart attack, stroke, ischemia). And also in case of bleeding, increased likelihood of thrombosis. Additionally, it is recommended to take a coagulogram in case of impaired liver function, heavy menstruation, and nasal bleeding.
- Coprogram. The procedure involves a study of feces. The result sheet indicates the color, smell, consistency of the biomaterial. As well as the content of eggs, worms and other parasites. Additionally, the change in the intestinal microflora is indicated. Coprogram is prescribed for suspected gastrointestinal diseases, including liver disease.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the liver. The procedure is recommended if a person is worried about pain in the right side. Ultrasound does not cause discomfort. The person is asked to lie on a couch, then a transducer that emits ultrasonic waves is guided through the abdominal cavity. The device is preliminarily lubricated with a special gel for better visualization. The image is displayed on the monitor in real time. With an ultrasound scan, a specialist may ask you to hold your breath, roll over to the other side. Thanks to ultrasound examination, it is possible to determine the size of the liver, seals in the organ.
- X-ray. Based on the results of the procedure, a snapshot of the organ is issued. To improve visualization, a contrast agent can be used, which is injected before the X-ray.
- Biopsy. A small piece of tissue is taken from the liver with a needle, then it is sent to a laboratory for research. A biopsy is prescribed when the liver is enlarged for unknown reasons, in the case of diseases (hepatitis, cirrhosis). And also the procedure is recommended to be done if a person has yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes. Additionally, a biopsy is needed to determine whether the tumor is benign or malignant. It is not recommended to carry out the procedure in case of purulent-inflammatory changes in the abdomen or the liver itself, a large amount of fluid, coma.
-
Computer (CT) or magnetic resonance (MRI) tomography. During a CT scan, the body is exposed to X-rays. Compared to X-rays, the radiation exposure is lower with computed tomography. And with an MRI, electromagnetic radiation is affected.
The cost of diagnostics is different. It all depends on the list of procedures, city, organization. Therefore, the price must be found out in a specific clinic.
When to see a doctor
Toxic hepatitis is a disease that requires a visit to a specialist. A person alone will not be able to determine the method of therapy. Treatment of toxic hepatitis is in the competence of a gastroenterologist or hepatologist. The first specialist deals with the entire gastrointestinal tract, and the second - the liver. Therefore, you can contact any of these doctors.
Before the diagnosis, the specialist examines the patient, pays attention to the color of the skin and the whites of the eyes. Additionally, they can change the temperature, pressure, pulse. Next, a survey is carried out, during which it is necessary to tell about all the symptoms.
If a person does not know where to turn, it is allowed to visit a therapist or pediatrician (for children). These are general specialists who deal with the treatment of all diseases. If necessary, after the examination, the doctor will write a referral to a gastroenterologist or hepatologist.
There are symptoms in which you need to call an ambulance or a doctor at home.
Namely:
- pain in the right side that cannot be tolerated;
- frequent vomiting (more than 2 times in 10 minutes);
- severe diarrhea;
- rapid deterioration in a person's well-being;
- coma.
Prophylaxis
Toxic hepatitis is a pathology, the likelihood of which can be avoided. For this, preventive measures must be followed.
They include the following rules:
- exclude contact with toxic substances;
- take medications as directed by a doctor and strictly follow the recommended dosage;
- exclude bad habits - alcoholic beverages, smoking, drugs;

- bring body weight back to normal;
- change the place of work if the activity is related to hazardous production or carefully adhere to safety rules;
- not picking unfamiliar mushrooms or plants;
- restrict children's access to drugs, alcoholic beverages and chemicals - the item prevents the emergence of toxic hepatitis in a child;
- timely treat various diseases;
- undergo a routine examination by a therapist once every 6 months;
- undergo a complete examination of the body 1 time in 12 months.
Treatment methods
Toxic hepatitis is a disease that must be treated. For this, drugs, folk remedies and other methods are used.
Medications
Medicines help eliminate the symptoms of the disease and alleviate the person's condition. The table lists popular medications that are prescribed for toxic hepatitis.
| Group of drugs | Action | List of funds |
| Detoxification infusion solutions | Under the influence of drugs, the volume of circulating blood increases, excess fluid is excreted through the urinary organs. With the help of medicines, you can get rid of 95% of poisons. | Acesol, Trisol, Ringer's solution |
| Antiemetic | The group of drugs eliminates the release of vomit. | Domperidone, Motilium, Metoclopramide |
| Antidiarrheal | Medication relieves diarrhea. | Imodium, Lopedium, Loperamide |
| Laxatives | The drugs soften the feces and promote their excretion from the body. Laxatives are recommended for constipation. | Guttalax, Senade, Duphalac |
| Rehydration | Medication replaces fluid loss if severe vomiting or diarrhea occurs. | Regidron |
| Enterosorbents | The drugs remove toxic substances from the digestive tract. | Smecta, Enterosgel, Polysorb |
| Sedatives | Medicines normalize the emotional background of a person. | Novo-Passit, Afobazol, Tenoten |
| Hepatoprotectors | The drugs restore the structure of the liver and protect it from negative factors. | Essentiale Forte N, Phosphogliv, Heptral |
| Combined (hepatoprotectors and choleretic) | Medicines have properties similar to hepatoprotective agents. But they additionally accelerate the excretion of bile from the bladder. Part of the toxins are removed from the liver along with the fluid. | Ursosan, Ursofalk, Livedexa |
| Enzymes | The drugs improve digestion, eliminate diarrhea. | Mezim, Pancreatin, Creon |
| Antihistamines | Medicines relieve itching on the skin. | Claritin, Zodak, Erius |
| Vitamin complexes | Means restore the lack of vitamins and minerals. | Vitrum, Supradin, Complivit |
In addition, the doctor may prescribe other medications. Or not to prescribe medication at all. For example, if toxic hepatitis appears due to the influence of drugs. When the drugs that caused the disease are canceled, the person's well-being returns to normal and the symptoms disappear.
Traditional methods
Herbal recipes have a low likelihood of side effects. Therefore, the use of folk remedies for toxic hepatitis is allowed. High efficiency of treatment can be achieved when prescriptions are used in conjunction with other methods of therapy (medicines, proper nutrition, etc.).
With toxic hepatitis, the following folk remedies are allowed:
- Infusion of chicory. For cooking, you need to take 1 tbsp. dry component and 250 ml of hot water. Leave the mixture for 20 minutes, add 1 tbsp. liquid honey. Mix thoroughly, for ease of use, you can filter the solution through cheesecloth. Take 0.5 cups 2 times a day. It is necessary to consume the mixture in 30 minutes. before meals. The course of application is 10 days.
- Pumpkin juice. To prepare the product, you must purchase a fresh product. Next, squeeze the juice out of its pulp. Take 0.5 cups per day. It is best to use the recipe after 60 minutes. after meal. The course is 10 days.
-
Hypericum infusion. For cooking, you need to take 1 tbsp. dry component and 400 ml of hot water. Leave for 40 minutes, filter through cheesecloth. Take 150 ml up to 2 times a day. It is better to do this in 15 - 30 minutes. before meals. The course of use is 14 days.

- Dandelion decoction. To prepare a recipe, you need to take 1 tbsp. crushed component and 1 glass of pure non-carbonated water. Simmer for 60 minutes. Filter through cheesecloth, take 1 tbsp. up to 3 times a day. It is better to use the solution in 15 - 30 minutes. before meals. The course is from 5 to 10 days.
Other methods
In addition to medicines and folk methods, disease therapy includes additional measures. Details are shown in the table.
| The name of the therapy method | Description |
| Proper nutrition | In case of toxic hepatitis, it is recommended to stick to a diet. It includes the following rules:
Do not forget about the drinking regimen. The recommended amount of clean non-carbonated water per day is at least 1.5 liters. Additionally, you can drink rosehip broth, weak tea or coffee. |
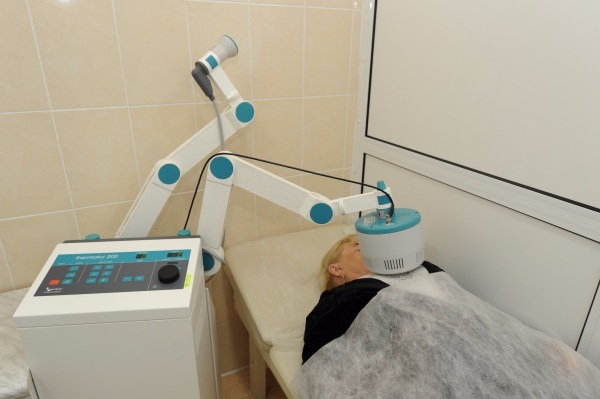
| Physiotherapy | The method restores the functionality of the liver and gallbladder. Additionally, the immune defense is improved. Physiotherapy is not recommended for acute illness, as well as in case of complications. Types of treatment: 1. Diathermy. The area of the affected organ is heated using a high-frequency electric current; 2. Inductothermy. Exposure to high frequency electromagnetic current; 3. Electrophoresis. Medicines are injected into the body, which accumulate in the skin depot. Then they are absorbed into the bloodstream, then affect the liver. The effect of medications is enhanced by the action of the current. 4. UHF - therapy. The affected organ is affected by an ultra-high frequency electromagnetic field. 5. Paraffin therapy. The tissues of the affected organ are warmed up with medical wax. 6. Magnetotherapy. The liver is affected by a magnetic field. 7. Laser therapy. The effect of a laser on an organ. When penetrating through the skin, the rays warm up the liver. As a result, the healing of organ cells is accelerated. |
| Bed rest | The method helps to restrict the patient's movement in order to reduce the oxygen demand of the cells. Additionally, the horizontal position eliminates pain. Bed rest helps to restore the body's strength. |
| Gastric lavage | This method of therapy must be carried out with toxic hepatitis. Gastric lavage is performed by medical personnel. |
Possible complications
Most often, complications occur in the absence of treatment for toxic hepatitis.
Possible consequences:
- liver failure;
- damage to the central nervous system - as a result, a person has convulsions, and also there is a loss of consciousness;
- cirrhosis of the liver - parenchymal tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue;
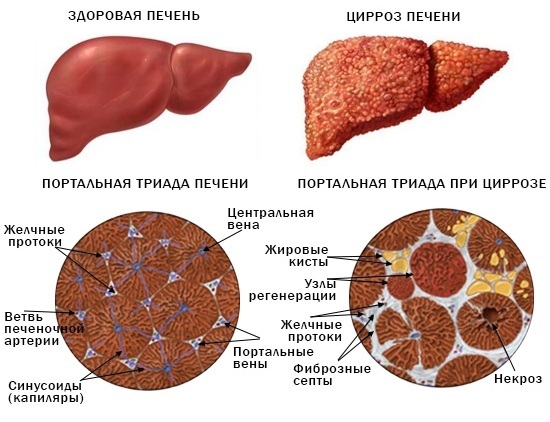
Cirrhosis of the liver - death.
If toxic hepatitis occurs in a pregnant woman, spontaneous miscarriage can be distinguished among the consequences. Therefore, when a disease is detected, an abortion is most often performed. In pregnant women, toxic hepatitis is rare, but not excluded.
The prognosis for recovery is favorable if the disease is mild or moderate. The liver is able to regenerate up to 75%. An unfavorable outcome is associated with acute injury or delayed treatment.
A disease called toxic hepatitis can occur when exposed to harmful substances. Most often these are drugs, herbal or industrial poisons. Symptoms include pain in the right side, fever, problems with stools (diarrhea, constipation).
Additionally, there is vomiting, nausea. As a treatment, it is recommended to use medicines, folk remedies. And also other methods are prescribed (proper nutrition, physiotherapy, bed rest). It is important to see a doctor promptly to reduce the likelihood of complications.
Toxic hepatitis video
Symptoms and treatment of toxic hepatitis: