Lactose monohydrate - a biochemical substance, the molecular components of which consist of residual compounds of galactose and glucose. In the products of the medical and digestive industry, this component can be found under such names as lactobiose, milk sugar, and tablettose.
Record content:
- 1 What is Lactose Monohydrate?
- 2 Chemical composition and properties
- 3 Biological role
- 4 Breakdown in the body
- 5 Views
- 6 Benefit
- 7 Harm
- 8 Daily intake of lactose
-
9 Where is lactose monohydrate used?
- 9.1 Food industry
- 9.2 Pharmaceuticals and Medicine
- 9.3 Other industries
-
10 Lactose intolerance
- 10.1 Causes
- 10.2 Influence on the body
- 10.3 Infancy and lactase deficiency
- 10.4 Symptoms in adults, children
- 10.5 Diagnostics
- 10.6 Treatment principles
- 11 Milk sugar allergy
- 12 Diet therapy. How to avoid lactose?
- 13 Milk sugar for weight loss: benefit or harm?
- 14 How to consume lactose monohydrate for health benefits?
- 15 Analogs of lactose monohydrate
- 16 Video about lactose
What is Lactose Monohydrate?
Lactose monohydrate is a complex carbohydrate that belongs to the category of disaccharides, and its greatest amount is found in milk and all types of dairy products. This biochemical substance has a wide range of applications in the production of pharmaceuticals and food products.
Lactose monohydrate has many positive properties, which are beneficial influence on the work of the gastrointestinal tract, providing the body with an additional source of complex carbohydrates. This substance can only be harmful if a person has an individual lactose intolerance.
Chemical composition and properties
Lactose monohydrate is actually a type of sugar that is completely natural in origin. This substance is obtained from whey, which is a by-product after the main stage of milk processing. Lactose monohydrate is a crystalline substance with a rich white color, which has an extremely dense structure.

The melting point of milk sugar is +203 degrees Celsius. When this chemical is boiled with the addition of low concentration acids, a chemical reaction occurs with the formation of lactose hydrolysis.
When interacting with compounds based on alkali solutions, lactose monohydrate is able to oxidize with the formation of the final product in the form of saccharin acids. The solubility of milk sugar is in the range of 21.6 g per 100 ml of ordinary water at room temperature.
You can also highlight the following properties of lactose monohydrate:
- is a natural preservative;
- acts as an additional source of food energy;
- provides a breeding ground for the production of antibacterial drugs;
- prevents the development of dysbiosis and constipation (provided that initially the human gastrointestinal tract is lactose tolerant).
Lactose monohydrate can be used as an intermediate for the production of other milk sugar-based chemicals. In most cases, these are drugs, the release form of which is tablets and capsules.
Biological role
Lactose monohydrate is a carbohydrate, the biological role of which is to provide the human body with a sufficient amount of energy reserves. At the same time, the assimilation of milk sugar occurs with less stress on the organs of the digestive system and the tissues of the pancreas.
Lactose promotes better absorption of calcium, which is present in dairy products.
This substance acts as a natural substrate for the active development of beneficial lactobacilli, which are an integral part of the beneficial intestinal microflora. Due to the beneficial effects of lactose, the stable work of all organs of the gastrointestinal tract is ensured, and the maximum amount of nutrients is extracted from the milk used.
Breakdown in the body
The breakdown of lactose takes place in the small intestine. Under the influence of a digestive enzyme called lactase, milk sugar is hydrolyzed to form the final chemical products in the form of galactose and glucose.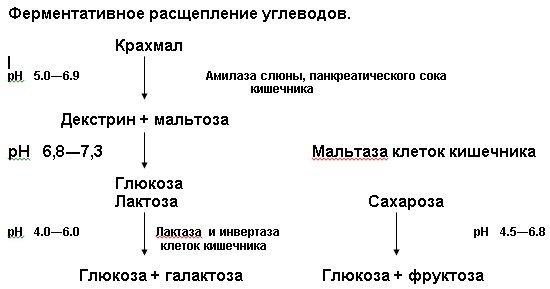
These components are absorbed into the intestinal wall as nutrients that provide the body with an additional source of energy. After entering the blood glucose, milk sugar nourishes the cells of the internal organs and brain tissue. In people with lactose intolerance, the above chemical reactions do not occur.
Views
Lactose monohydrate is a biochemical substance of organic origin. The table below lists the main types of this milk sugar, as well as describes their distinguishing features.
| Types of lactose | Distinctive features of the chemical |
| Natural | It is a natural carbohydrate that is present in milk, sour cream, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese, kefir. In this case, lactose is part of the food product, and its assimilation occurs along with other constituent components. |
| Industrial | It is a concentrated chemical that is obtained by long-term evaporation of whey. The industrially extracted lactose is sent to the pharmaceutical and food industries. This substance is not used in its pure form due to its high concentration and unpleasant taste. |
Most people experience the first type of lactose when they consume dairy products, as well as other milk-based foods (pastries and baked goods). Lactose monohydrate, obtained industrially, is found in medicines, canned meat, sausages, cocoa powder, and culinary spices.
Benefit
Lactose monohydrate is a disaccharide whose main benefits are related to its chemical properties.
Milk sugar has the following effects on the human body:
- regulates the work of the gastrointestinal tract;
- improves the protective function of the immune system, which is expressed in the body's resistance to bacterial, viral and fungal microorganisms, the frequency of colds decreases;
- normalizes the functioning of cells of the central and peripheral nervous system;
- saturates the body with an additional amount of calcium, which has a positive effect on the condition of bones, skin, hair, joints, nails and teeth;
- reduces the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases;
- improves the absorption of vitamins E and PP;
- maintains an optimal energy balance within the cells of muscle fibers (this useful property of lactose is especially in demand among people involved in strength sports).
In moderation, lactose monohydrate can be eaten by people with diabetes. This substance does not create an additional load on the pancreas, but at the same time provides the body with food energy.
Harm
Lactose monohydrate can really be harmful to adults and children, whose body has an innate or acquired intolerance to this substance. Also in medical practice, there are cases when, after entering the gastrointestinal tract, milk sugar became the cause of an allergic reaction.
People who have these health problems should study in detail the composition of drugs and food that they purchase for personal consumption.
Daily intake of lactose
In order for the child to be able to replenish the daily intake of lactose, he needs to drink 2 glasses of milk daily, with a capacity of 250 ml each. Adults should drink 2 times more of this product.
Also, milk can be replaced with kefir, natural yogurt, sour cream, fermented baked milk, yogurt. At the same time, do not worry if, due to various circumstances, it is not possible to get the daily norm of milk sugar. A sufficient amount of carbohydrates is present in bakery, pasta, confectionery and cereals.
Where is lactose monohydrate used?
Lactose monohydrate is used in the manufacture of food products, agricultural and pharmaceutical industries.
Food industry
In the food industry, lactose monohydrate is used as a substitute for milk powder, since this substance is cheaper and increases the profitability of production.
Milk sugar is a component of the following foods:
- cookies, pastries, cakes, sweets, chocolate;
- sausages and sausages (lactose monohydrate improves the fermentation process of meat at the stage of its industrial processing);
- infant formula, which are used as an analogue of breastfeeding (this food industry product contains up to 85% milk sugar);
- potato chips;
- muesli and instant soups;
- all types of waffles;
- instant coffee;
- margarine and spreads based on combined vegetable fats;
- sugar substitutes.
Lactose monohydrate is also used in the production of alcoholic beverages, sauces and condiments. Depending on the industrial technology used in a particular enterprise, milk sugar can be added to other types of food products.
Pharmaceuticals and Medicine
In the pharmaceutical industry, lactose monohydrate is used as an excipient in the production of pharmaceuticals. In the composition of tablets and capsules, milk sugar acts as a cheap, safe and natural preservative, which prolongs the shelf life of the medicine.
During the manufacture of penicillin, lactose is a nutrient medium, allowing the production of a drug with excellent antibacterial properties. Lactulose is produced on the basis of milk sugar.
This is a substance that is included in the composition of medicines intended for the treatment of dysbiosis, constipation, flatulence, inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract. Also, milk sugar can be found in sports nutrition preparations designed for faster muscle gain.
Other industries
Lactose monohydrate is used in the production of animal feed and biologically active additives for faster fattening of livestock. Milk sugar accelerates the growth of farm animals, gaining fat and muscle mass.
The inclusion of lactose in the diet of cattle allows you to increase milk yield, as well as get higher quality milk. Young livestock of animals take a good starting development, are less susceptible to bacterial and viral diseases.
Lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance is a negative reaction of the body to milk sugar entering the cavity of the gastrointestinal tract. In Russia and neighboring Slavic countries, about 20% of the population is lactose intolerant.
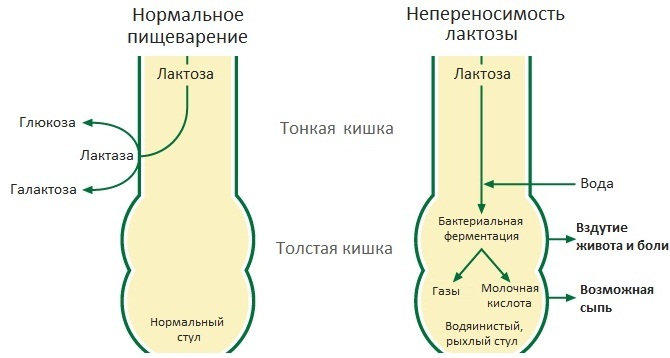
After consuming this substance, symptoms appear that resemble an acute intestinal upset. Lactose intolerance practically does not occur in the indigenous people of Sweden and Denmark (found in only 3% of people). At the same time, 100% of the population of Africa, Southeast Asia, Latin America, the gastrointestinal tract is not able to assimilate milk sugar.
Causes
The main cause of lactase deficiency is a deficiency in a digestive enzyme called lactase. The absence of this substance may be associated with an innate feature of the body, or milk sugar intolerance is acquired in the process of independent life. In the latter case, a deficiency of a digestive enzyme can cause diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and the endocrine system.
Influence on the body
Lactose intolerance does not cause any deterioration in well-being as long as a person does not consume foods that contain milk sugar. People who cannot digest milk sugar need to take care of their diet in advance, excluding the lactose monohydrate substance from it.
Infancy and lactase deficiency
Most infants are lactose-tolerant and their main source of nutrition is breast milk. If the child has a congenital intolerance to milk sugar, then pediatricians recommend to carry out the correct organization of breastfeeding.
To do this, the following rules must be followed:
- express a small amount of milk before starting feeding, since the first portion contains the highest concentration of lactose;
- feed the baby with the same breast;
- do not exclude night feeding;
- avoid eating foods containing a high amount of carbohydrates.
In the diet of a child with lactase deficiency, they try to include the first complementary foods as early as possible, which are completely free of lactose. In case of urgent need, artificial mixtures without milk sugar can be used.
Symptoms in adults, children
Signs of lactase deficiency appear in the first 1-2 hours after drinking milk or other products containing lactose.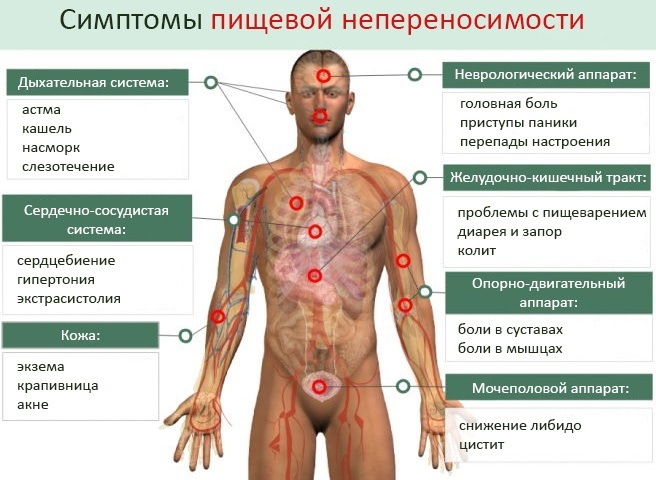
In adults and children, the following symptoms occur:
- bloating and gas production;
- an upset bowel movement, which is most often accompanied by diarrhea (in young children, foamy stools with an unpleasant sour smell are observed);
- loss of appetite;
- cramping pain in the central abdomen;
- nausea;
- discharge of vomit;
- feeling of constant rumbling inside the abdomen;
- slow weight gain in children of the younger age group;
- in adults, there is a rapid decrease in body weight.
The main reason for the appearance of the above symptoms is that after entering the gastrointestinal tract, lactose is not cleaved by lactase. Milk sugar binds water inside the intestines. In this regard, the work of this organ is disrupted, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and other painful signs begin.
Diagnostics
To determine lactase deficiency, you will need to pass the following types of tests, the results of which reflect an objective the reaction of the gastrointestinal tract to the action of lactose monohydrate:
- samples of feces, the composition of which is examined for non-degraded milk sugar compounds;
- capillary blood to determine general indicators and glucose levels;
- tests for allergic lactose intolerance.
If there is a suspicion of lactase deficiency of congenital etiology, the method of genetic research is used. Capillary or venous blood is used as a biological material.
The purpose of the diagnosis is to detect the gene that causes lactose intolerance. The genetic form of lactase deficiency can be inherited from both parents. At risk are people who have blood relatives with a similar gastrointestinal disease.
Treatment principles
Treatment of lactase deficiency is reduced to adherence to a strict diet that restricts the use of all types of foods with added milk sugar. Diet therapy is the most effective method to maintain a stable gastrointestinal tract.
Milk sugar allergy
A distinctive feature of milk sugar allergy is that the patient's body produces sufficient the amount of the enzyme lactase, but the cells of his immune system identify lactose as a dangerous biochemical connections.
For this reason, a person has an intestinal disorder, nausea, vomiting, itching and rashes of the skin surface, edema of mucous tissues, urticaria, and signs of dysbiosis are present.
Milk sugar allergy therapy involves adherence to a therapeutic diet that does not contain foods with lactose, as well as taking drugs with antihistaminic properties (Suprastin, Aleron, Loratadin, Citrine).
Diet therapy. How to avoid lactose?
People suffering from lactase deficiency should only eat foods that are free of natural and industrial lactose. Before buying food, you need to pay attention to what ingredients are contained in a particular type of product.
In this case, the following food can be completely excluded from the diet:
- bakery and confectionery products;
- milk and fermented milk products;
- sausages, sausages, canned meat;
- cottage cheese and hard cheeses of all sorts
- chocolate;
- cocoa powder;
- sauces;
- margarine;
- noodles and instant soups.
Before buying medicines, you should carefully study their chemical composition, since in most tablets and capsules of lactose, monohydrate acts as an excipient. Taking these medications is contraindicated.
Milk sugar for weight loss: benefit or harm?
The amount of milk sugar that enters the human body along with food does not have a significant effect on gaining excess body weight or losing weight too quickly.
How to consume lactose monohydrate for health benefits?
In order for the use of lactose to be extremely beneficial, it is necessary to include in your diet only natural products containing milk sugar in their composition. The best option would be to daily drink fresh milk, kefir, yogurt or fermented baked milk in an amount of 0.5 to 1 liter.

In this case, the human body will receive the required amount of milk sugar, ensure high-quality assimilation of calcium and other nutrients, and normalize the intestinal microflora. It is recommended to refuse the use of industrial lactose monohydrate, which is found in other food products as a food additive.
Analogs of lactose monohydrate
Milk sugar is a unique biochemical compound that has no analogues. This applies to natural lactose, which is found in milk and its by-products, as well as an industrial substance extracted from whey.
Lactose monohydrate is a complex milk carbohydrate that is broken down in the human gastrointestinal tract under the influence of the digestive enzyme galactase.
As a result of this process, glucose is formed, which is absorbed into the walls of the small intestine, and then spreads throughout the body as a nutrient. The highest concentration of lactose is found in fresh milk, kefir, yoghurts, cottage cheese, sour cream, and hard cheese.
Commercially, lactose monohydrate is obtained from whey. This substance is actively used in the food, pharmaceutical and agricultural sectors. For people suffering from lactase deficiency, the use of milk sugar is contraindicated. Limitations are associated with the risk of dysfunction of the digestive system.
Video about lactose
Composition, application and benefits of lactose:
