Record content:
- 1 Airborne droplet path. What is it, transmission of infection, infection
- 2 How is the transmission of the disease by airborne droplets
- 3 The concept and types of diseases transmitted by airborne droplets
- 4 The peculiarity of such diseases
- 5 Major infections and viruses transmitted by airborne droplets
- 6 Are pneumonia, tonsillitis, bronchitis, sinusitis, meningitis, herpes transmitted?
- 7 Video about airborne transmission
Airborne droplet path. What is it, transmission of infection, infection
There are more than 200 different types of viruses and bacteria in the world, many of which are transmitted via airborne droplets. These are, as a rule, acute seasonal viral infections, influenza virus and "childhood infections". Each of these infectious diseases has a number of characteristics and differences.
How is the transmission of the disease by airborne droplets
Airborne droplets are the transmission of the causative agent of an infectious disease through a person's discharge from his upper respiratory tract.
If a person is sick with an infectious disease, then pathogenic microorganisms multiply in his nasopharynx and respiratory tract. When a person coughs or sneezes, the virus can enter the mucous membranes of a healthy person, thereby causing them to become ill.
You can also get infected with respiratory infections when talking to a sick person or a virus carrier. In the latter case, the person is unaware that he is sick, but at the same time secretes the pathogen.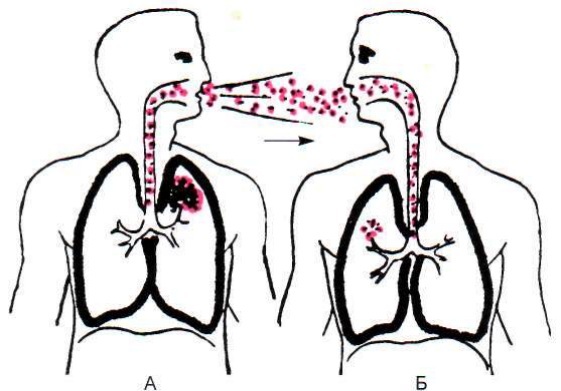
The airborne pathway is divided into several transmission mechanisms:
- Aerogenic.
- Air-dust.
The aerogenic mechanism consists in the transmission of the pathogen in the air. Some viruses can not only be transmitted through direct contact with a sick person, but also through ventilation openings. Highly contagious infections have this ability. For example, the varicella and variola virus, measles.
The air-dust transmission mechanism can be realized with a disease such as tuberculosis. Koch's bacillus settles on dust and when a person breathes in the remains of the dust, infection can occur.
Airborne droplets are the transmission of infection that directly depends on the environment. This means that many viruses or bacteria that are transmitted through the patient's excreta may be unstable to environmental factors. Some viruses die quickly in sunlight, while others are able to settle on surfaces in the form of the smallest particles.
The concept and types of diseases transmitted by airborne droplets
Respiratory infections are a broad group of diseases with an airborne transmission mechanism. These infections are very common in the human population, people are constantly faced with them.
All respiratory infections are divided into the following types:
- Bacterial.
- Viral.
Bacterial infections include meningococcal, pneumococcal, hemophilic infections, scarlet fever, tonsillitis, whooping cough.
Viral infections include ARVI (which have many pathogens), "childhood infections" (measles, rubella, chickenpox, mumps), especially dangerous infections (smallpox), as well as seasonal influenza viruses and parainfluenza.
The peculiarity of such diseases
All respiratory infections have a number of characteristics. Because of this, their course, treatment and diagnosis are very similar.
The main features of respiratory infectious diseases include:
- High contagiousness. Respiratory diseases are highly infectious. This is directly related to their transmission mechanism. Viral diseases are transmitted most rapidly in organized groups (schools, kindergartens). Infection often leads to outbreaks and even epidemics of seasonal illness.
- Pronounced seasonality. Respiratory diseases are characterized by their occurrence in the autumn-winter period and in the spring. This is due to a decrease in ambient temperature, as well as a general decrease in immunity.
- The defeat of the upper and lower respiratory tract. Many respiratory diseases are characterized by damage to the respiratory tract. Some affect the upper respiratory tract (ARVI, flu, tonsillitis), others are capable of affecting the lungs and provoking the development of pneumonia (pneumonia).
- Incubation period. Infections are characterized by the presence of a period during which it multiplies. Typically, the incubation period ranges from several hours to several days. In some cases, such as chickenpox, the incubation period takes from 10 days to 3 weeks.
- General susceptibility. Respiratory diseases affect people of all ages.
- More severe course in older people. This is due to the presence of chronic diseases in people of this age, as well as to a decrease in immunity.
- Similar symptoms. Diseases begin, as a rule, acutely and their course is characterized by the presence of a syndrome of general infectious intoxication and an increase in body temperature.
- Prolonged asthenia after recovery. This means that after a previous illness, weakness persists for 10-14 days.
- A similar pathogenesis (developmental mechanism). In case of respiratory diseases, the pathogen enters the respiratory tract, and then is absorbed through the mucous membranes, enters the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body.
- The presence of specific prophylaxis. For almost all respiratory diseases, there are vaccines that can prevent the development of the disease.
Major infections and viruses transmitted by airborne droplets
Airborne droplets are common in many diseases. This is observed with seasonal infections, as well as some others. The main list of diseases:
| Infection | Features and clinical picture |
| Flu | This is an acute respiratory disease that occurs with acute infectious intoxication, an increase body temperature up to + 39-40C, with dry (tracheal) cough, nasal congestion, nausea, vomiting and photophobia. Influenza is quite difficult, the most severe course is observed in children and the elderly. Influenza often causes massive epidemics, this is due to its ability to mutate. There are several types of flu: simple seasonal flu type. A, B, C, as well as "swine" and "bird" flu.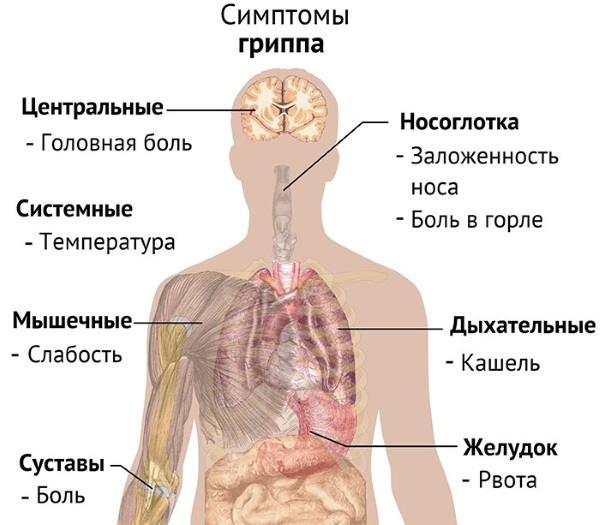
|
| Respiratory infection | This is ARVI (acute viral infections). They are characterized by a pronounced seasonality. ARVI includes: rhinovirus, adenovirus, coronavirus infection, as well as a number of others. These diseases are characterized by a milder course in comparison with the influenza virus. Mainly the upper respiratory tract is affected, proceeding with an increase in body temperature to 38. And also characterized by sore throat, redness of the back of the throat, severe rhinitis, conjunctivitis, abdominal pain and loose stools. Each infection has its own clinical manifestations. The treatment of these infectious diseases is symptomatic, since there are still no drugs for viral diseases. |
| Diphtheria | This is an acute bacterial disease that manifests itself in the form of damage to the oropharynx. Clinical manifestations are severe intoxication, an increase in body temperature to 40. In addition, there is a pronounced sore throat and an increase in the tonsils with the presence of plaque on them. Unlike sore throat, plaque adheres tightly to the tonsils, and when trying to remove it, bleeding occurs. Also, often there is a blockage of the lumen of the trachea with diphtheria films. Because of this, true croup develops. Asphyxiation can occur without treatment. Treatment is with an anti-diphtheria serum. |
| Rubella | This is a disease that occurs with the appearance of an elevated body temperature, a bright red rash on the body. Rubella is dangerous for its teratogenic effect on the fetus, in pregnant women it can cause fetal malformations (the classic triad is deafness, blindness and heart disease). In children, rubella proceeds, as a rule, favorably. The contagiousness of the infection persists for 10 days from the moment of illness. |
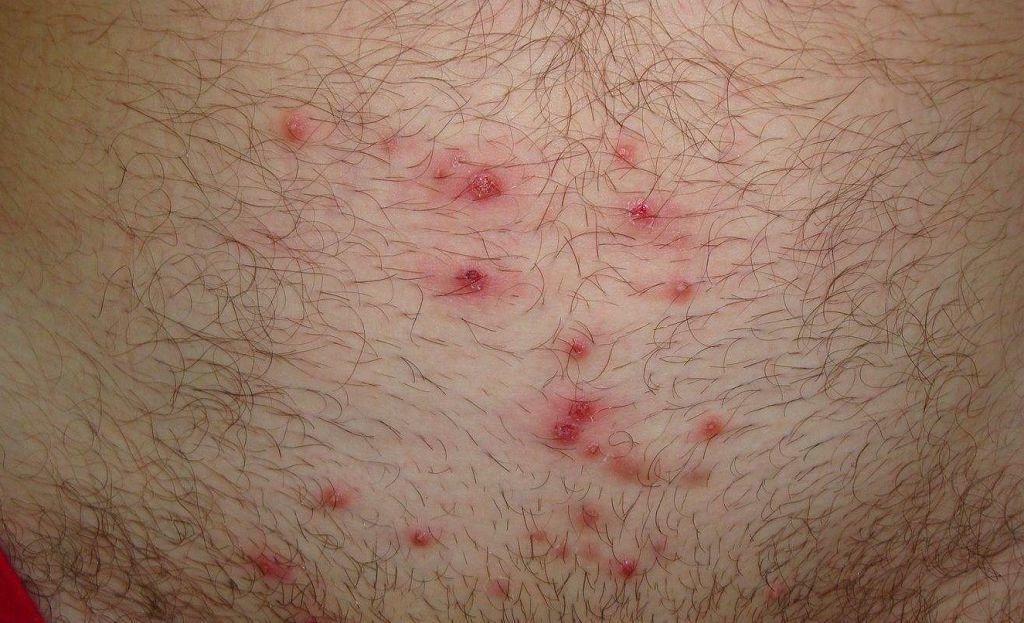
| Chicken pox | It is a highly contagious disease caused by the herpes simplex virus type 3. Most often found in children, a milder course is observed. It manifests itself in the form of an increase in body temperature, as well as a characteristic rash. The nature of the rash is vesiculopustular (there are nodules and pustules on the skin filled with serous contents). They do not appear at once, it is characterized by the constant "pouring" of new elements of the rash. Chickenpox is characterized by a long incubation period, at the end of which the patient becomes contagious to others. Treatment of chickenpox is symptomatic, but in older people, it is advisable to prescribe acyclovir. A person remains contagious until the last elements of the rash appear, plus 5 days.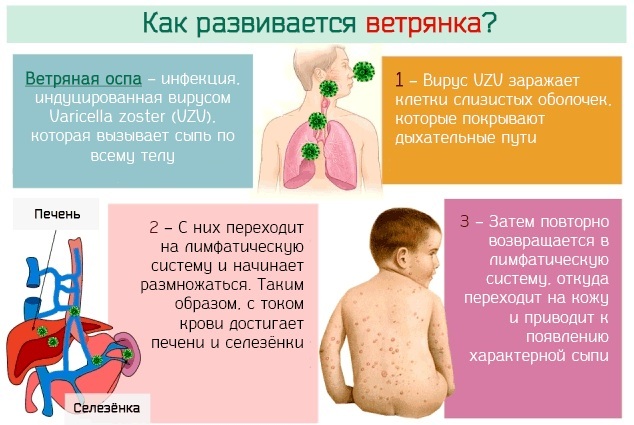 After the transferred disease, stable immunity is formed. But re-infection is possible in old age. In this case, there is a reactivation of the virus in the body and herpes zoster occurs. |
| Meningo-coccal infection | Meningococcus can cause meningococcal nasopharyngitis and meningitis (inflammation of the lining of the brain). Meningitis is characterized by the appearance of severe headaches, nausea and vomiting, as well as the appearance of meningeal symptoms (stiff neck, Brudzinsky symptom). The patient assumes a characteristic pose (the pose of a "pointing dog"). And also the body temperature rises. Meningitis is dangerous and, if untreated, leads to the death of the patient. And also another form of meningococcal infection is meningococcal sepsis. It is manifested by the formation of a "stellate" rash on the lower extremities, which gradually goes higher. Treatment of meningococcal infection consists in compulsory hospitalization and therapy with broad-spectrum antibiotics. |
| Whooping cough | This is a disease that manifests itself as a dry, tearful cough. It can stop breathing. Whooping cough is an extremely dangerous disease, especially for young children. Cough is often confused with bronchitis, so whooping cough can be difficult to diagnose. There is no specific treatment for the disease, therefore, vaccine prophylaxis is of great importance. |
| Scarlet fever | It is an infectious disease caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus. It is characterized by an acute onset with symptoms of infectious intoxication, as well as an increase in body temperature. In addition, there is acute tonsillitis (sore throat, enlarged tonsils), "raspberry" tongue, small-dot rash mainly in the groin and on the sides of the body. Peeling of the skin occurs 14 days after the onset of the disease. Treatment includes the use of antibiotics and symptomatic therapy. |
| Epidemic parotitis ("mumps") | It is a viral disease that affects the salivary glands, as well as other glandular organs (testes, ovaries, pancreas). It proceeds with severe symptoms of intoxication. Complications may develop. The development of meningitis is common. There is no specific treatment for mumps. Disease can be prevented only with the help of vaccine prophylaxis. |
Are pneumonia, tonsillitis, bronchitis, sinusitis, meningitis, herpes transmitted?
Airborne droplets are the most common person-to-person transmission of infection. But not all respiratory diseases are transmissible.
It all depends on the degree of contagiousness:
| Disease | The degree of contagiousness |
| Pneumonia | Pneumonia caused by viruses can spread from person to person.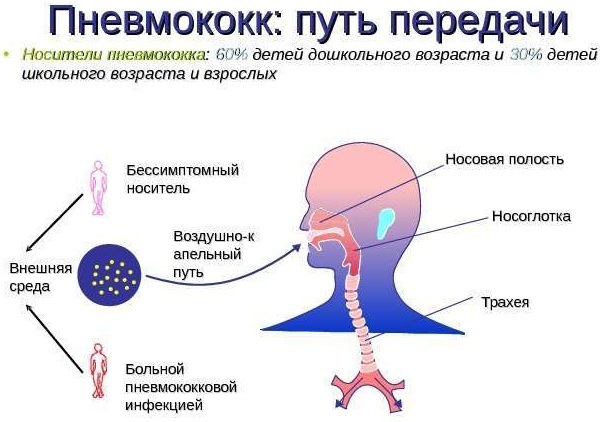
|
| Bronchitis | Acute bronchitis is contagious, chronic bronchitis is not. |
| Angina | Transmitted from person to person through close contact. |
| Sinusitis | It is not an infectious pathology, since sinusitis is a complication of rhinitis or sinusitis. |
| Meningitis | Meningitis can be transmitted if it is bacterial or viral in nature. |
| Herpes | It is transmitted from person to person by airborne droplets. Some herpes viruses cause infectious mononucleosis (kissing disease) and chickenpox (herpes simplex virus type 3). |
Diseases transmitted by airborne droplets can be dangerous in their complications. Therefore, at the first signs of respiratory pathology, it is necessary to seek medical help for diagnosis and treatment.
And also special attention should be paid to vaccination and timely vaccination against especially dangerous diseases. Such prevention will significantly reduce the risk of morbidity, which will avoid the development of dangerous complications.
Video about airborne transmission
On the transmission of airborne infections: