Content
- By frequency
- Increased
- Slow motion
- By the depth of breathing movements
- In-depth
- Superficial
- By the ratio of inhalation and exhalation
- Normal
- Pathology
- By types
- Pectoral
- Abdominal (diaphragmatic)
- Mixed
- Pathology
- Cheyne-Stokes
- Biota
- Interrupted by deep breaths
- Grokko
- Kussmaul
- Dissociated
- Apnea and weakened during sleep
- Chaotic
- Cluster (periodic group)
- Atonal (gasping)
- Stridoroznoe
- Video about the types of respiration in humans
Respiration in animals and humans consist of alternating inhalation and exhalation. But humans are divided into many types. They differ in frequency, depth, and the ratio of exhalation and inhalation. Separately, abnormal breathing is considered, which has arisen against the background of certain diseases or disorders of the brain, central nervous system.
By frequency
The types of breathing in humans are determined depending on the frequency of inhalation and exhalation. With full breathing, the entire volume of the sternum is used, the air is constantly renewed, which does not allow pathogenic microorganisms to linger in the lungs. Then a person takes about 15 breaths per minute, the norm is no more than 20.
However, it also depends on age:
- in newborns, the frequency of respiratory movements is 40-55;
- from 1 to 2 years old - 30-40;
- in men it is less than in women by 2-4;
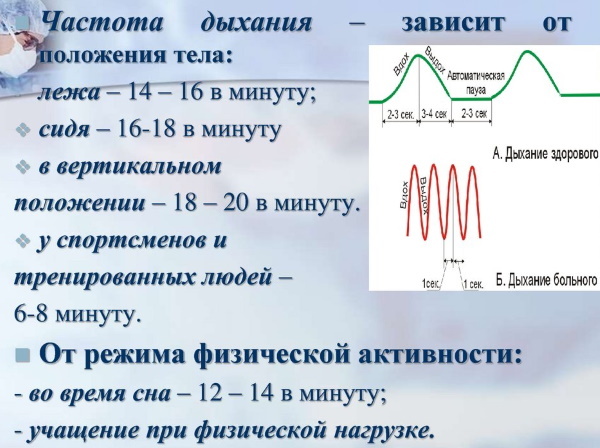
- in the "lying" position - 14-16;
- "Sitting" - 16-18;
- "Standing" - 18-20.
However, the frequency is influenced by many factors - external and internal.
Increased
Breathing quickens during exercise. Also, the frequency is influenced by stimuli, the signals of which enter the brain through muscles, nerves and airways. When stopping, rhythmic pressing on the sternum and artificial respiration help to restore breathing.
Varieties:
-
Tachypnea - very rapid breathing, over 24 cycles / min. Most often appears with febrile conditions, lung damage, blood diseases. But usually the reason lies in the irritation of the center of breathing with carbon dioxide. Tachypnea can even be caused artificially - by an effort of will. For example, in hysterics, the frequency reaches up to 80 cycles per minute.

- Polypnea - the frequency of sighing increases in people with high fever, during pregnancy, after physical exertion, against the background of certain diseases.
- Hypernea - deep, fast, arising against the background of diseases. But such breathing cannot be fully attributed to pathological. It can occur due to the acceleration of metabolism. Then the body needs more oxygen as a catalyst in metabolic processes. Hypernea most often occurs with high emotional and physical stress. If the cause was a pathological condition, then more often - fever or thyrotoxicosis.
Rapid breathing occurs with hysteria. At this moment, it can reach up to 60-80 / min. Otherwise, this state is called "the breath of a hunted animal." An increase in temperature, strong feelings, pain leads to an increase.
Slow motion
In athletes, the resting frequency can be 6-8 breaths / min. Also, breathing slows down during sleep. Shortness of breath accompanies dyspnea. This violates the frequency, rhythm, depth. The person does not have enough air.
The same happens with shortness of breath:
- inspiratory (shortness of breath);
- expiratory (difficult to exhale);
- mixed (breathing in and out is difficult).

Also, a slowdown occurs with the Cheyne-Stokes type, Kussmaul, in patients with diabetes mellitus or in a coma. During breathing of Biota, rhythmic periods with pauses alternate. Bradypnea - a person takes less than 12 breaths and exhalations (full cycle) per minute. Such breathing occurs in diseases of the brain, pathological conditions of its membranes, inflammation. Also, the cause can be severe intoxication, vascular rupture, fluid accumulation.
The excitability of the nerve centers of the spinal cord decreases with toxic shock, increased blood levels of acetone, insulin, uric acid or poisons. Bradypnea is diagnosed if up to 12 months a child takes less than 30 breaths, up to 12 years old - less than 20, over 50 years old - no more than 12.
By the depth of breathing movements
The types of breathing in humans depend not only on the frequency of contractions, but also on the depth of movement. With frequent, superficial, the lungs are ventilated only partially. As a result, a favorable environment for pathogenic bacteria is created. With full breathing, all parts of the lungs work.
The result is good ventilation. The depth of breathing is determined by the volume of circulating air. In adults, this value is from 300 to 900 ml. Based on these numbers, they distinguish between shallow and deep breathing.
In-depth
This species includes the breath of Biota. It is characterized by deep movements that alternate with long pauses.

This is observed during agony, in patients with impaired blood circulation in the brain, with meningitis. Cheyne-Stokes breathing is characterized by shallow breathing, the depth of which increases rapidly.
Superficial
Shallow breathing is clavicular, designed for measured and calm inhalation and exhalation. Or pathological, with a small volume of circulating air. For example, Cheyne-Stokes breathing is initially characterized by shallow breathing. This group includes Grokko (wavy). It is also accompanied by periods of weak breathing.
By the ratio of inhalation and exhalation
The type of breathing is also determined by the ratio of inhalations and exhalations. In a healthy person, it is the same. It can change for a short time due to stress, physical activity, shortness of breath, nervous overexcitation. For example, after running, the ratio of inhalation and exhalation is disturbed. But in a short time, breathing returns to normal. If this does not happen, then the person has one of the pathological options.
Normal
Normally, the number of inhalations and exhalations is the same - 15-20 per minute. But this value can change depending on age, gender, physical activity. For example, for athletes, a value of 8 at rest would be normal.
Pathology
Respiratory depression can be caused by many reasons. Gasping - indicates deep hypoxia, hypercapnia. At the same time, 10-20 seconds pass between rare breaths before exhalation. Such breathing accompanies serious pathological conditions. It can lead to a complete stop and can only be normalized with the help of resuscitation measures.
By types
During normal breathing, they breathe quietly, evenly. Inhalation, exhalation - uniform. There is no need to breathe through your mouth.
There are three types, which differ in the direction of the change in the size of the chest.
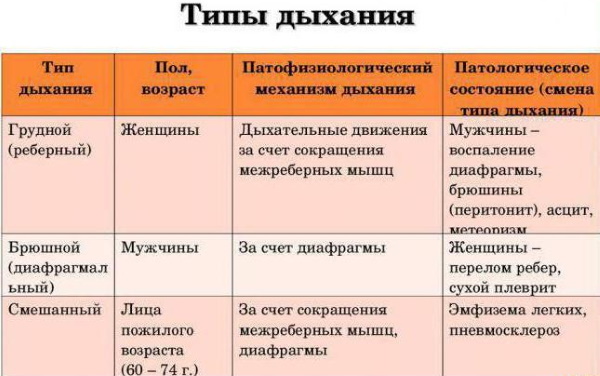
Pectoral
Chest breathing is more common in women. In this form, only the upper region of the lungs takes part in the process. Chest breathing is divided into costal and clavicular, depending on the part involved. In the first case, the process is carried out using the intercostal muscles. They help to expand the chest to the desired volume. On exhalation, they contract, pushing air out. The ribs are also involved in the process, which are distinguished by their mobility and can be displaced.
Clavicular breathing is more common in older people, as lung performance deteriorates or in preschoolers. On inhalation, together with the sternum, the clavicle rises, and down on exhalation.
Abdominal (diaphragmatic)
In a healthy person, inhalation and exhalation are performed at the expense of the intercostal, abdominal and diaphragmatic muscles. Such breathing is considered complete, since the supply of oxygen to tissues and organs is improved. Most of the lungs are involved in the process. Breathing is facilitated by the diaphragm (the septum between the chest and abdominal cavity). It is made up of muscles and can contract strongly. On inhalation, it goes down, pressing on the peritoneum, on exhalation, it rises, and the abdominal muscles relax.
Diaphragmatic breathing is more common in men, singers, athletes, and children. If it is not given by nature, then it can be learned. There are special exercises for this. Diaphragmatic breathing helps to maximize oxygenation of all tissues with a minimum amount of muscle contractions. At the same time, there is a natural massage of the chest and abdominal organs, digestion is improved.
Mixed
The type of respiration in a person is not always only one, there are mixed ones, if the abdominal and thoracic regions are involved in one cycle. Then not only the diaphragm works, but also the ribs. The rib cage expands in different directions. As a result, all parts of the lungs are ventilated.
Pathology
Respiration disorders cause deterioration of metabolic processes in cells. Then the toxins are not completely eliminated, which contributes to the development of various diseases. Some functions of gas exchange affect the skin, and it fades, dermatological pathologies appear. With insufficient ventilation of the lungs, harmful and dangerous microorganisms remain in them, due to which infectious and viral diseases arise.
Pathological breathing is divided into three types:
-
Obstructive, when the patency of the air channels is disrupted and insufficient oxygen enters the body. More often the cause is brain damage. This type includes breathing of Kussmaul, Cheyne-Stokes, Bioto, apneistic. And also chaotic, cluster, atonal (gasping) and stridorous.
- Restrictive, developing due to incomplete expansion of the lungs. Then they function at the limit, gas exchange and ventilation are disrupted. A person, even if he wants to, cannot hold his breath for a long time, take a large amount of oxygen into his lungs. It's hard to do active sports. The provoking factors of the disorder can be intra- and extrapulmonary.
- Mixed - with the reasons of the first two types.
The process when normal lung function alternates with a temporary stop is called periodic breathing. It is divided into two varieties - Biota and Cheyne-Stokes. Pathological types of breathing are characterized by periodic stops and rare / frequent breaths.
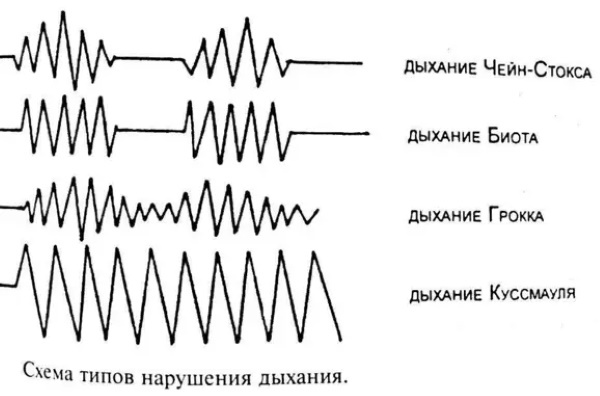
Cheyne-Stokes
It is characterized by deep breathing movements, gradually decreasing (with an interval of 5-10 seconds) until a complete stop. The pauses between inhalation and exhalation can last up to a minute. In this case, brief silent stops appear. The duration of the pauses increases gradually, breathing becomes more noisy. By the eighth breath, the stop reaches the maximum time interval. Then the process is repeated in reverse order.
With Cheyne-Stokes breathing, the movements of the chest gradually increase. Then there is an extinction of intensity until a complete short-term stop. Then breathing is restored and the cycle repeats. Most often, the Cheyne-Stokes species appears as a result of poisoning, brain hypoxia or hemorrhage into it. This can be caused by uremia or injury.

With this type of disorder, there is clouding or loss of consciousness, a change in the rhythm of the heart, paroxysmal shortness of breath. When breathing is restored, the nutrition of the brain is normalized, negative symptoms disappear, patients come to their senses, consciousness clears up. For babies, the Cheyne-Stokes variant is considered a physiological norm.
Biota
With this breathing, the cycles are full, normal, alternating with a complete stop. Violation is periodic, the duration of apnea can reach up to 1.5 minutes. Breath Biota appears in case of brain lesions, shock conditions, infectious diseases of the respiratory system. Also, problems with the central nervous system can lead to it. With this type of breathing, serious disturbances in the work of the heart occur.
Interrupted by deep breaths
The apneistic look is a long inhalation, a hold, a sharp exhalation. In this case, the chest expands, although it is on inhalation. Then the body cannot regulate respiratory movements. This type of breathing occurs with strong toxic effects, brain trauma, ischemic stroke.
Or with severe meningitis or hypoglycemic coma. This view can lead to a complete stop. An apneastic appearance often accompanies the dying process. However, with proper resuscitation, breathing can be restored.
Grokko
The types of respiration in humans are included in the Grokko list, which is otherwise called wavy. It is similar to the Cheyne-Stokes view, with pauses replacing shallow, weak breaths in and out.

Then the depth of breathing increases and gradually decreases. The Grokko species often passes into the Chain Stokes and comes back again.
Kussmaul
If a breathing disorder has caused irreversible changes, then over time, a complete stop occurs. For example, Kussmaul is noisy and deep. It appears during hypoxia, toxin poisoning, uremic and diabetic coma. The breathing of Kussmaul is characterized by convulsive noisy breaths, alternating with rare, deep breaths - up to a complete stop. This type belongs to the terminal types, more often such patients are in a coma.
The differences in the listed four types are more clearly visible in the table:
| Sign | Breath type | |||
| Kussmaul | Biotta | Grokko | Cheyne Stokes | |
| Breath | Rare, noisy, deep | Sudden termination and recovery | Noisy | With a gradually increasing noise |
| Stop | – | + | – | + |
These types of breathing can be caused by colds, meningitis, paralysis, and other pathological conditions.
Dissociated
It occurs when the medulla oblongata is damaged. This condition is characterized by "ugly" breathing. Dissociated - with paradoxical movements of the diaphragmatic muscles, asymmetry when lifting different sides of the chest.
Apnea and weakened during sleep
Types of breathing in humans are sometimes accompanied by temporary or reflex cessation of breathing (apnea). This is provoked by a decrease in the excitability of the center due to necrosis or brain damage, poisoning. Most often, sleep apnea occurs during childhood. There is a "false" one that occurs when the skin is severely irritated.
An example is when a body is immersed in ice water. Obstructive sleep apnea is isolated, when the upper airways are sagging. Such breathing is most often characteristic of snoring people and with the development of cardiovascular insufficiency.
Chaotic
It is an erratic process, characterized by apnea attacks and short-term complete stops. The cause can be cerebral hemorrhage, tumors, head injuries and various diseases.
Cluster (periodic group)
It is characterized by irregular pauses between entrances and exhalations. The most common cause is Shai-Drager disease.
Atonal (gasping)
The rhythm is rare, with convulsive breaths. More often this occurs with brain damage or hypoxia. There is a risk of stopping completely, especially after taking sedatives or narcotic drugs.
Stridoroznoe
With it, the lumen of the larynx and trachea narrows. As a result, the person begins to make hissing and hissing sounds. The cause may be traumatic brain injury, diphtheria croup, goiter, or allergic laryngeal edema.

There are many types of respiration in humans. The best option is complete. But when disorders appear, it helps in the diagnosis of diseases. In some cases, there is not partial, but complete cessation of breathing. Then resuscitation can save.
Video about the types of respiration in humans
How to breathe in a person: