Content
- Reasons for the development of liver steatohepatosis
- Risk factors
- Classification of the disease
- Symptoms of pathology
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of the disease with drugs
- Folk remedies
- Rosehip infusion
- Lemon infusion
- Pumpkin with honey
- Immortelle
- Milk thistle
- Diet therapy
- An example of a daily menu
- Prognosis and complications
- Video about steatohepatosis
Liver steatohepatosis is a serious condition, in which there is a degeneration of hepatocytes. The second name of pathology in medicine is fatty degeneration. Degenerative changes in the liver are often asymptomatic. The diagnosis and treatment of steatohepatosis is carried out by a hepatologist. Additionally, patients are advised to adhere to a special diet. Lack of timely therapy will lead to serious complications.
Reasons for the development of liver steatohepatosis
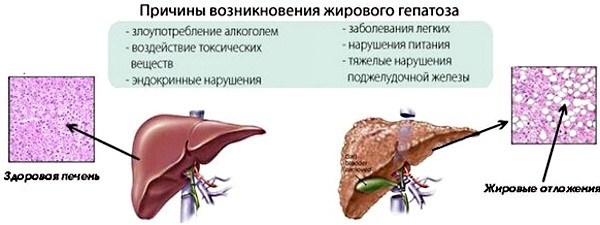
The main provoking cause of steatohepatosis is chronic alcohol dependence. Ethanol has a detrimental effect on liver cells (hepatocytes). They die, and connective tissue forms in their place. The gradual progression of pathological processes leads to the fact that the liver does not receive enough oxygen. The level of protein decreases, and a large amount of fluid accumulates in the cells. Ultimately, the functioning of the organ is disrupted.
There are also other reasons that provoke the degeneration of liver cells:
- hereditary predisposition;
- viral liver damage;
- insufficient amount of protein in the human body;
- surgical intervention on the organ;
- toxic effects of toxic substances;
- problems with carbohydrate and fat metabolism;
- long-term treatment with certain drugs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hormonal drugs, antibacterial drugs);
- inflammatory or infectious liver disease;
- parasitic infection with helminths;
- genetic diseases;
- mechanical trauma to the abdominal cavity.
An inactive lifestyle also provokes the development of steatohepatosis. A person moves little, body weight increases, as a result of which metabolism is disturbed. Fat accumulates in the cells of the internal organs. Pathological processes trigger diseases of the biliary tract and pancreas.
Risk factors
There are many provoking factors against which pathological processes are triggered. At risk are mainly people who abuse alcohol. Non-alcoholic steatohepatosis is more common in women over 45 years of age or hypertensive patients.
The following people are also at risk:
- patients with diabetes mellitus;
- patients with obesity of varying degrees;
- people with atherosclerosis;
- workers of hazardous production.
Some hereditary diseases provoke fatty degeneration of hepatocytes. The same goes for poor nutrition. Rarely, the disease is detected in people who have undergone complex operations on the organs of the digestive system.
Classification of the disease
Liver steatohepatosis (treatment and diet for patients are prescribed by a specialized specialist on an individual basis), depending on the provoking factor in medicine, it differs in several types:
| Name | Description |
| Alcoholic steatohepatosis | When drinking alcoholic beverages, the liver of the human body feels a strong load, since it is responsible for the processing of ethanol. The end result is the formation of a toxin (acetaldehyde), which contributes to the development of liver steatohepatosis. Due to its accumulation, the cells of the organ increase and secrete a large amount of fatty acids. Progressive pathological processes provoke the development of alcoholic steatohepatosis. |
| Non-alcoholic | In this situation, the disease is provoked by other reasons, as a result of which fat cells accumulate and the functioning of the liver is disrupted. |
 It is impossible to diagnose pathological changes in the liver at an early stage of development, since the organ does not have nerve endings. A preventive medical examination and examination will help identify problems.
It is impossible to diagnose pathological changes in the liver at an early stage of development, since the organ does not have nerve endings. A preventive medical examination and examination will help identify problems.
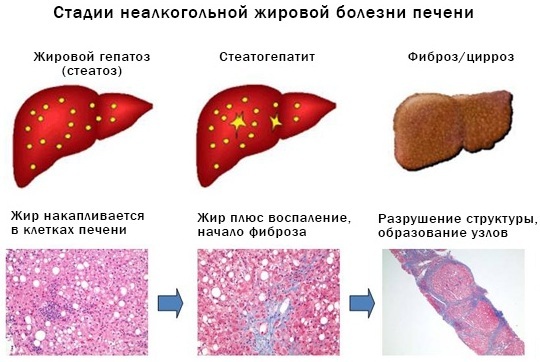
Due to the gradual development of steatohepatosis, the following stages of the disease are distinguished in medicine:
| Name | Description |
| Stage I | The disease is characterized by small accumulations of fat with a certain distance between the lesions. Abnormalities in the liver and characteristic clinical symptoms are absent. |
| Stage II | Pathological foci increase and merge with each other. There is a failure in the functioning of the liver, and the first symptoms of steatohepatosis appear. |
| Stage III | Severe stage of the disease, in which the number of properly functioning liver cells is rapidly decreasing. Fatty foci increase, connective tissue is formed. The liver cannot perform its functions in full. In this situation, the patient is shown surgery, which involves an organ transplant. |
Given the progression of pathological processes, the following degrees of hepatic steatohepatosis are distinguished in medicine:
- Focal. The disease is accompanied by separate pathological foci on the renal parenchyma. Fat accumulates only inside the cells of the organ.
- Diffuse. Pathological processes affect the entire gland and provoke its enlargement. Diffuse hepatic steatohepatosis in most cases is a hereditary disease. If the parents are diagnosed with pathological changes, it is highly likely that the child will also have the disease.
- Focal. Steatohepatosis is accompanied by the formation of benign tumors in the liver.
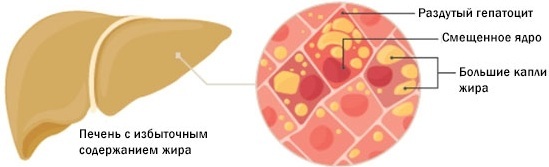 As the disease progresses, the cells of the organ die and are replaced by connective tissue, which leads to serious malfunctions of the gland. Therefore, it is necessary to consult with a hepatologist and undergo an examination, especially if the person is at risk.
As the disease progresses, the cells of the organ die and are replaced by connective tissue, which leads to serious malfunctions of the gland. Therefore, it is necessary to consult with a hepatologist and undergo an examination, especially if the person is at risk.
Symptoms of pathology
Liver steatohepatosis (treatment and diet are selected for the patient, taking into account all the individual characteristics of the body), as it progresses, causes characteristic symptoms in the patient. The clinical picture will help the specialized specialist to determine the stage and type of the disease, and also to establish the degree of organ damage. At an early stage in the development of pathological processes, characteristic symptoms rarely occur.
As steatohepatosis progresses, the patient has the following symptoms:
- general weakness in the body;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- severity and pain in the right side, where the liver is located;
- rashes on the body, which are accompanied by intense itching;
- periodic vomiting for no apparent reason;
- rapid weight loss (anorexia);
- stool disorders (diarrhea);
- bloating;
- disturbed by strong painful sensations on the right side under the ribs;
- immunity decreases;
- the skin and mucous membranes turn yellow.
Differential diagnosis will help to establish an accurate diagnosis, since many liver pathologies are accompanied by similar clinical symptoms. It is important to immediately consult a hepatologist, undergo an examination and start treatment in order to prevent serious complications. The severity of clinical signs depends on the degree of organ damage. Therefore, it is important not to miss the first signs of steatohepatosis.
Diagnostics
The specialized doctor prescribes comprehensive diagnostics after the examination and on the basis of the patient's complaints. Preventive examination will reveal steatohepatosis at an early stage of development, when pathological processes can still be stopped and eliminated. In the later stages of the disease, comprehensive diagnostics will allow you to choose a treatment to slow down the destruction of the liver in humans.
Patients are assigned the following diagnostic measures: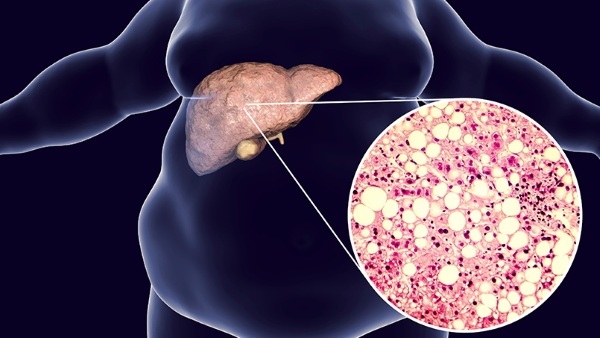
| Name | Description |
| Laboratory research |
|
| Hardware diagnostics |
|
It is important to differentiate the disease and, during therapy, additionally undergo a comprehensive examination in order to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment. In some situations, patients additionally require consultation with other specialized doctors (nutritionist, cardiologist, endocrinologist).
Treatment of the disease with drugs
Treatment of hepatic steatohepatosis is selected by a physician hepatologist individually for each patient. The profile specialist is also guided by the results of the comprehensive examination and the clinical symptoms present. Patients are prescribed medications, the use of folk remedies is allowed, if there are no medical contraindications. It is also important to stick to a strict diet.
The scheme of drug therapy is drawn up taking into account all the characteristics of the patient's body. It is important to adhere strictly to your prescriptions to reduce the likelihood of side effects.
| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Hepatoprotectors | Carsil, Galstena |
 Medicines have a powerful effect on liver cells to help repair them. They also increase their protection from external factors. Adult patients are prescribed a dosage of the drug, depending on the condition of the person. The standard dosage is 1-4 tablets 3 times a day. The course of treatment lasts at least 3 months. Medicines have a powerful effect on liver cells to help repair them. They also increase their protection from external factors. Adult patients are prescribed a dosage of the drug, depending on the condition of the person. The standard dosage is 1-4 tablets 3 times a day. The course of treatment lasts at least 3 months. |
| Antioxidants | Mexidol, Cytoflavin | Medicines remove toxins from the patient's body. The drug is administered intramuscularly or intravenously through a dropper. The dosage is selected individually in each case. Intramuscularly injected at 100-200 mg 2-3 times a day. The maximum dosage per day is 800 mg. |
| Insulin Sensitizers | Metformin, Siofor | The drugs help liver cells to better absorb insulin in order to prevent the development of diabetes mellitus. The tablets are swallowed and not chewed, washed down with a sufficient amount of liquid, preferably after meals. Adult patients are prescribed 300-500 mg 2-3 times a day. The course of treatment lasts at least 2 weeks. |
| Lipid-lowering drugs | Atorvastatin, Hemofibrate | The initial dosage of the drug for an adult patient is 10 mg 1 time per day. It is gradually increased to 80 mg. The course of treatment lasts 2-4 weeks. |
| Antihypoxants | Carnitine, Actovegin | The drugs increase the resistance of liver tissue to oxygen starvation. The medicine is administered by intravenous drip. The preparation is preliminarily diluted with sodium chloride solution. The dosage of the drug for adult patients depends on the condition of the person and is 0.5-1 g per day for a week. Take a break for 10-12 days and repeat the treatment. |
Fatty hepatosis in most cases is easily amenable to drug therapy, therefore, surgery is rarely prescribed to patients. The indications for surgical treatment are portal hypertension, severe bleeding, ascites.
Folk remedies
Liver steatohepatosis (treatment and diet must be selected for patients based on examination results) allows the use of non-traditional methods. The recipes of healers and healers are used in complex therapy and strictly after consultation with a specialized doctor.
It is necessary to take into account the fact that even safe natural ingredients can provoke an allergic reaction or individual sensitivity. Folk remedies help not only to slow down the process of tissue degeneration, but also to reduce the unpleasant symptoms of the disease.
Rosehip infusion
It is necessary to pour 50 g of dry rose hips with hot water (2 tbsp.). Leave for 10 hours and strain. It is advisable to infuse the broth in a thermos.  The resulting solution is recommended to be taken orally throughout the day in small portions. The course of treatment with rosehip decoction lasts 3 days. Then the patient should take a short break and continue therapy.
The resulting solution is recommended to be taken orally throughout the day in small portions. The course of treatment with rosehip decoction lasts 3 days. Then the patient should take a short break and continue therapy.
Lemon infusion
Wash well and chop 3 medium lemons with a blender. Add hot water (500 ml) to the resulting mass. Mix all components well until a homogeneous consistency is obtained. The finished broth must be kept for 10 hours and filtered. It is recommended to drink lemon tincture in small sips a day. The course of treatment lasts 3 days. Then it is recommended to take a short break, since lemon juice negatively affects the gastric mucosa.
Pumpkin with honey
A small pumpkin is washed well, the top is cut off and all seeds are removed. It is necessary to pour natural honey inside the pumpkin, preheated a little. From above it is necessary to cover the hole with the cut part. It is recommended to keep the pumpkin in this state for 2 weeks in a dark, cool place. The finished honey must be poured into a glass container. The resulting product should be taken every day 3 times for 1 tbsp.
Immortelle
The plant has a choleretic effect, helps to restore metabolism in the liver. It is necessary to fill the flowers of the plant with warm water (200 ml). Put the resulting mass in a water bath and heat for another 30 minutes. Then remove the solution from heat, leave for 10 minutes and strain. It is recommended to dilute the resulting broth with warm water to obtain 200 ml. The finished product must be taken in 1-2 tbsp. 3-4 times a day before meals for 15 minutes.
Milk thistle
The plant is a natural hepatoprotector that has an antioxidant effect. Milk thistle protects liver cells from the negative effects of the oxidative process.
The herb also increases the defenses of the organ's cells so that they can independently cope with provoking factors. Milk thistle seeds must be poured with boiling water (200 ml). Leave for 1 hour and strain. The finished broth should be taken orally. The recommended dosage for an adult is 1/3 tbsp. 3 times a day. The broth should be taken before meals 30 minutes in advance.
Diet therapy
Liver steatohepatosis (treatment and diet are individually selected for patients after medical diagnosis) requires the patient to comply with proper nutrition without fail. The patient's diet consists of low-calorie foods.
| Prohibited foods | Allowed Products |
|
|

You should eat in small portions throughout the day. Cook food in water, steam, bake or simmer. Patients should consume a minimum of 1.5 liters of clean fluid every day to restore water balance in the body. A properly formulated diet will help to reduce the load not only on the liver, but also on the gastrointestinal tract, as well as restore the amount of fats and carbohydrates.
An example of a daily menu
The correct menu for steatohepatosis will be helped by a dietitian doctor, taking into account the diagnosis and the patient's complaints. It is important to adhere to a dietary diet throughout the entire period of treatment of the disease in order to reduce its progression and reduce the burden on the affected liver.
Approximate daily menu:
| Meal time | Dishes |
| First breakfast | Oatmeal, cooked in water with the addition of a small amount of milk. Low-fat cottage cheese and green tea. |
| Lunch | Dried fruits, apples, prunes. |
| Dinner | Vegetable soup with the addition of vegetable oil. Buckwheat and compote. |
| Afternoon snack | Bread, unsweetened biscuits and rosehip decoction. |
| Dinner | Mashed potatoes, steamed fish. Beet salad, low-fat kefir. |
In most cases, the diet will have to be followed not only during the treatment of steatohepatosis. The patient is advised to radically change his lifestyle forever. Additionally, in order to achieve the most positive therapeutic result, patients should engage in minor sports activities. Swim, do yoga exercises, ride a bike, and walk more outdoors.
Prognosis and complications
Liver steatohepatosis (treatment and diet are selected by a narrow-profile specialist, taking into account the results of medical examinations) without timely therapy progresses and at later stages provokes dangerous complications for the patient. There is a degeneration of the affected tissues of the organ, against the background of which oncology or cirrhosis develops. Timely and early diagnosis increases the chances of a favorable prognosis.
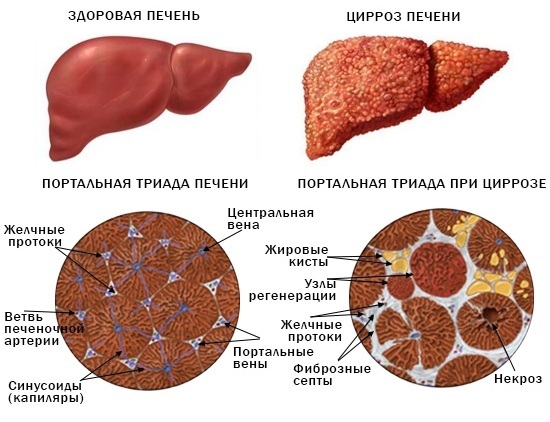
Complications of steatohepatosis:
| Name | Description |
| Fibrosis | The disease is characterized by the proliferation of connective tissue in the liver due to chronic pathological processes. The changes significantly reduce the functioning of the liver. The tissues of the organ become denser, scars form at the site of pathological foci. |
| Cirrhosis | Severe chronic pathology, against the background of which liver cells die. They are destroyed, and connective tissue is formed in their place. The pathological condition is characterized not only by impaired liver function, but also by the development of portal hypertension. |
Pathological processes at an early stage progress without therapy, especially against the background of numerous negative factors. If a person has concomitant diseases or continues to abuse alcohol, the condition deteriorates rapidly.
Liver steatohepatosis provokes irreversible fatty degeneration of organ tissues. The progression of pathological processes can be established if you go to the hospital at an early stage of the development of the disease. Treatment and diet are essential steps in the fight against steatohepatosis. Otherwise, irreversible consequences and complications await a person.
Video about steatohepatosis
Liver steatohepatosis: