Content
- Indications for the purpose of the study
- How to collect and pass a general urine test correctly?
- Preparation for analysis
- Collection of material
- Hygiene rules for women when collecting material for OAM
- Norm and interpretation of results, table
- Diagnostics of possible pathologies
- Urine staining
- Transparency
- Density
- Acidity
- Protein
- Glucose
- Bilirubin
- Ketone bodies
- Epithelial cells
- Erythrocytes
- Leukocytes
- Hemoglobin
- Slime
- Cylinders
- Salt
- Bacteria and fungi
- Video about the analysis of OAM, the norm in women
OAM in women is an important laboratory test, which is prescribed by doctors to diagnose many diseases. The results obtained usually come in the form of a table, which presents the values of a particular patient and their comparison with the norm.
Indications for the purpose of the study
This analysis is mandatory for the doctor's prescription in cases where the patient complains of symptoms such as:
- weakness, malaise for no apparent reason;
- discoloration of urine (darkening or, conversely, discoloration);
- frequent or rare urge to urinate;
- inability to fully urinate (the bladder does not empty completely);
- a painful or burning sensation when going to the toilet or at any other time;
- aching pain in the lower abdomen, in the lower back or in the pubic area;
- frequent thirst, drinking too much fluids;
- clouding of urine, the detection of suspensions or turbidity in it;
- swelling of the limbs and face, which a woman can notice not only in the morning, but also at any other time of the day.

OAM, the norm in women (the table is presented according to the results of the study) is compared with the actual indicators with in order to exclude infectious diseases and any other abnormalities in the functioning of the urinary system. The study of the results obtained and their comparison with the normative figures can only be carried out by a specialist (therapist, urologist, nephrologist, gynecologist).
With the help of this urinalysis, diseases such as:
- diabetes of any nature of origin (sugar and non-sugar);
- urolithiasis disease;
- bacterial blood poisoning (sepsis);
- benign and malignant diseases of the urinary system;
- functional impairment of the kidneys (renal failure);
- deviations in the work of the digestive system (pancreatitis, cirrhosis);
- infectious processes (urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis).
Particular attention should be paid to the fact that no doctor will make a diagnosis based on the results of the general analysis of urine and their abnormalities. OAM is the first step in diagnosis. For an accurate diagnosis, further examination of the patient is required. A urinalysis can guide the specialist, indicate in which direction to move.
How to collect and pass a general urine test correctly?
A general urinalysis is an important diagnostic measure, but the results can be incorrect. This often happens with improper preparation for the delivery of biological fluid.
Preparation for analysis
Urine is a sterile environment. It is easy to change this if the urine collection is not accurate enough or if the preparation rules are violated.
To avoid this, save your time and nerves, it is better to study the following algorithm in advance:
- 24 hours before collecting the material, products such as svela, carrots, seasonings and spices, spicy and salty foods, marinades, and herbs should be excluded from the diet. They can change the color of urine, which will make it difficult to diagnose pathologies.
- It is unacceptable to consume coffee and coffee drinks. Caffeine increases urine output, which will influence the results obtained.
- Refuse to take certain medications. For example, antibiotics, vitamins, laxatives can distort test results. Therefore, when undergoing a course of treatment with one of the listed means, a doctor should be warned about this. As a rule, the drug is canceled for a day. If this is not possible, then the fact of using the drug will be taken into account when obtaining the results.
- Diuretic use greatly affects urinalysis. Therefore, the doctor needs to be informed in advance about taking such a remedy.
- Quit smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages in any quantity.
- You cannot take a hot bath, visit the solarium, spa, sauna or steam bath. This is done in order to exclude thermal effects on the patient's body.
- Strong stress or intense physical activity should be avoided.
- The day before urine collection, it is important to exclude sexual intercourse. Otherwise, it can lead to inflated results about the bacteria in the urine, which can get there.
- If the patient is menstruating, it is necessary to refuse to collect the analysis and postpone the procedure for a week.
- If a woman underwent a cytoscopy procedure, urine analysis is postponed for 5-7 days.
Collection of material
OAM requires not only compliance with the rules of preparation, but also a thorough collection of material.
It consists of several stages:
- It is necessary to take a sterile transparent container with a volume of 100-200 ml. For convenience, it is better to buy a special container at the pharmacy. It costs about 30 rubles. and very easy to use. The container has a fairly wide neck and a plastic screw cap. In addition, the container does not need to be boiled as it is already sterile.
- All hygiene measures must first be carried out. They will be discussed below.
- You need to urinate immediately after waking up in the morning, before drinking water or food.
- The first portion of urine should be sent to the toilet, but not to a container. The first 20-30 liters of liquid contain a lot of epithelium, which makes the examination not very informative.
- Next, you need to urinate into the container. The amount of 100-150 ml will be more than enough for a full study.
- The rest of the urine should be directed back to the toilet.
- After that, the container must be tightly closed with clean hands, without touching its inner walls.
- Within the next 2 hours, it is necessary to deliver the sample to the laboratory. It is important to follow the transportation rules. The storage temperature should be between 5 ° C and 20 ° C.
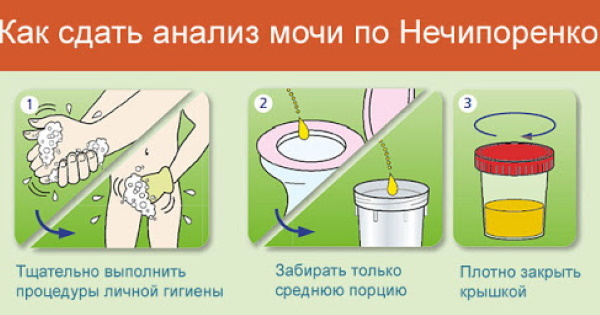
There are times when there is no way to send urine so quickly for analysis. Then it can be stored in a cool dark place for several hours.
Hygiene rules for women when collecting material for OAM
OAM, the norm in women (the table of the obtained values of this analysis will be reliable in the case when the patient previously carried out the necessary hygiene measures) may be violated as a result of poor-quality preparation for collection of biomaterial.
You will need a tampon that can be made from sterile medical cotton. It should be dipped in soapy water and wiped off the external genitals, then rinsed with water and dried with a clean paper towel.
Norm and interpretation of results, table
Before studying the tabular values of normal urine parameters, it should be noted that they do not differ for patients of any age. OAM is carried out with the aim of comparing the actual results with the norms established for women.
The results are presented in a tabular form with the following content:
| Designation | Indicator name | Reference values (norm) |
| COLOR | Colour | Straw |
| CLA | Transparency | No |
| pH | Acidity | 5-7 |
| SG | Specific gravity | 1,010 – 1,025 |
| PRO | Protein | Less than 0.033 g / l |
| GLU | Glucose | Less than 1 mmol / L |
| KET | Ketone bodies | Less than 0.5 mmol / L |
| EPT | Epithelium | 0-4 in sight |
| CYL | Cylinders | No |
| HGB | Hemoglobin | No |
| BIL | Bilirubin | Less than 8.5 μmol / L |
| BLD | Erythrocytes | Less than 2 in f / z |
| LEU | Leukocytes | Less than 5 in f / z |
| BAC | Bacteria | No |
| FUN | Mushrooms | No |
| MUC | Slime | No |
| NIT | Salt | No |
When receiving the results, the doctor evaluates several indicators of urine:
- external characteristics (color, smell, transparency);
- physical and chemical (density, pH balance);
- biochemical (the presence of metabolites such as protein or ketone bodies, bile pigments such as bilirubin, and glucose);
- microbiological (cylinders, blood cells, fungi, bacteria, salts).
Even if the analysis indicates a deviation of one or more indicators from the norm, the patient should not worry. First you need to make sure that the algorithm for preparing for the procedure and collecting material has not been violated. In any case, the doctor should deal with the decoding of the result. If necessary, he can prescribe a second OAM or other urine tests (biochemical, bacteriological).
Diagnostics of possible pathologies
Any deviations from the norm in the results of a general urinalysis may indicate the development of certain pathologies. Therefore, to decipher it is not enough to know the norms, you also need to understand what deviations of a particular indicator may indicate. Therefore, it is so important not to engage in self-diagnosis and search for diseases in oneself, but to contact a competent specialist.
Urine staining
A change in the color of urine to a different shade may indicate a disease:
- A bright, intense yellow color indicates dehydration, edema, the use of B vitamins.
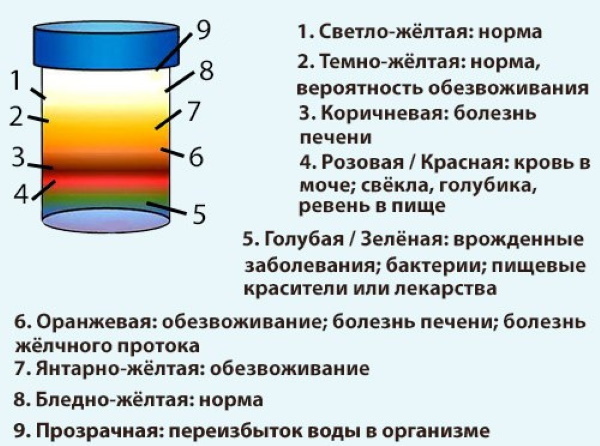
- A pale yellow color is observed with diuretics or diabetes insipidus.
- A pinkish tint is usually caused by eating red foods or drugs with a red pigment.
- A deep red color indicates renal colic, kidney infarction.
- Red-brown color can be with phenol poisoning, taking metronidazole or sulfonamides.
- The color of meat slops can be observed with glomerulonephritis in the acute stage.
- Green urine indicates mechanical jaundice.
- The milky appearance of urine indicates urinary tract infections.
Transparency
If the urine is not transparent, but cloudy, there is a suspension and sediment in it, this indicates the ingress of epithelial cells, bacteria, leukocytes and erythrocytes into it. This may be one of the signs of an acute infectious process.
Density
The density of the biological environment is affected by the presence of uric acid and urea, as well as electrolytes.

Exceeding the indicator may indicate diseases such as:
- glomerulonephritis;
- diabetes;
- dehydration of the body.
Low indices of urine density can be observed with:
- diabetes insipidus etiology;
- renal failure.
Acidity
Too alkaline environment of urine can be observed in the following cases:
- The patient prefers to eat food of plant and dairy origin, often refusing meat.
- The body is in a state of prolonged dehydration.
- An alkaline urine reaction is typical for infectious and malignant processes in the urinary tract, as well as for chronic renal failure.
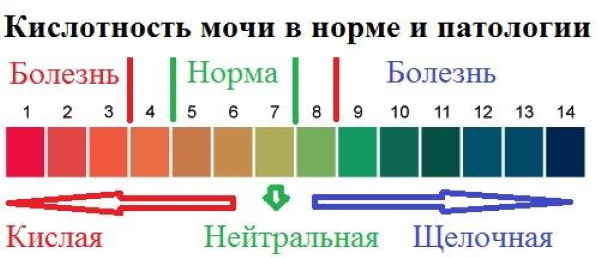
An acidic reaction of urine (pH less than 5) is observed under conditions such as:
- excessive consumption of meat products;
- fever.
Protein
OAM, the norm in women (the table of results also shows the content of protein structures in the urine) may slightly differentiate in terms of the protein component. The PRO value is one of the first points that a doctor pays attention to. Normally, its content should be zero or less than 0.033 g / l.
The detection of a protein is called proteinuria, it is a reason to suspect such pathologies as:
- glomerulonephritis;
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- benign and malignant tumors in the kidneys;
- nephrotic sclerosis.
The excretion of protein in the urine can be observed in adolescents, as well as with excessive cooling of the body or with prolonged stress.
Glucose
A healthy body does not excrete glucose in the urine. However, moderate glucosuria (up to 1 mmol / L) is often observed in patients with sugar abuse. Urinalysis for glucose is also helpful in people with diabetes. It reflects the stage of the disease.
A high glucose content in urine (above 1 mmol / L) can be in such cases as:
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- pregnancy, especially in the third trimester;
- Cushing's syndrome.
Bilirubin
Abnormalities (above 0) indicate that the liver is not coping with its functions.
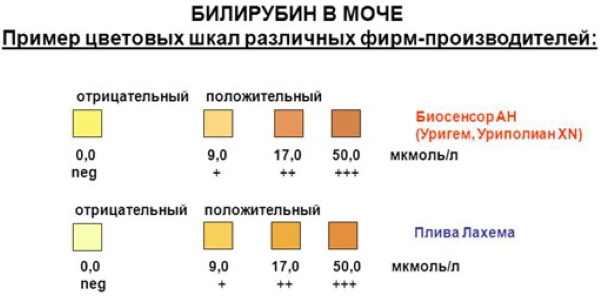
This fact will indicate processes such as:
- liver damage of any etiology;
- viral hepatitis;
- the presence of malignant metastases in the liver.
Ketone bodies
Normally, this indicator should be zero.
Any excess may indicate such changes in the body as:
- exacerbation of diabetes mellitus;
- the likelihood of a hypoklycemic coma;
- poisoning with ethyl alcohol;
- prolonged nutritional deficiencies;
- lack of carbohydrates in the diet;
- precom;
- eclampsia (it is especially important to check the level of ketone bodies in those patients who are carrying a child and are prone to developing edema and high blood pressure).
Epithelial cells
This component is constantly present in urine, but normally a small content of only some types of epithelium is allowed.

For example, the following values are valid:
- flat can be present in the amount of up to 5 objects in the field of view of the microscope;
- transitional - up to 1 cell in the field of view;
- but the renal epithelium should be completely absent.
If there is an excess of the presented norms, the doctor may suspect such pathologies as:
- infectious processes in the urinary tract (with an abundant content of squamous epithelium);
- Kidney stones and pyelonephritis develop with an increase in the number of transitional cells;
- severe toxicosis, glomerulonephritis, heavy metal poisoning are observed when renal epithelium appears in the sediment.
Erythrocytes
The BLD indicator can be exceeded for both physiological reasons (prolonged stay of the patient in a standing position, taking a long walk, regularly engaging in heavy sports, taking certain medications), and pathological reasons.
These include:
- arterial hypertension;
- urolithiasis disease;
- traumatic kidney damage;
- tumors of any etiology located in the organs of the excretory system.
Leukocytes
OAM, the norm in women (the table of results may indicate leukocyturia based on the excess of the LEU indicator) should be observed for all main indicators. If the values deviate significantly, medical attention is required.
An increase in the number of leukocytes of more than 5 cells in the field of view indicates that the patient has one of the following diseases:
- pyelonephritis;
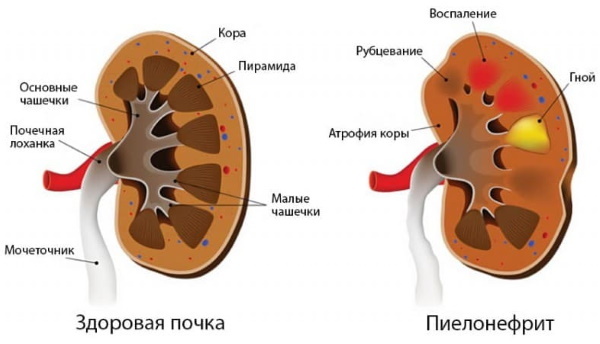
- glomerulonephritis;
- cystitis.
It is relevant to check this indicator in women who have been transplanted into the kidney, since a large number of leukocytes indicates its possible rejection.
Hemoglobin
If a certain concentration of hemoglobin is found in urine, this allows one to suspect the development of diseases such as:
- anemia;
- burns;
- blood poisoning (sepsis);
- poisoning with phenol or aniline.
Slime
If urinalysis reveals mucus in the urine, this confirms the chronic course of inflammatory processes in the kidneys, bladder, or excretory tract.
Cylinders
They are of several types, the excess of any of them indicates the presence of pathology.

For example, such:
- Hyaline casts can be detected when the body overheats, intense physical exertion, prolonged fever, high blood pressure, heart failure.
- Granular cylindrical structures indicate the presence of viral urinary tract infections.
- Waxy casts are present in chronic renal failure as well as in amyloidosis.
Salt
A healthy body does not excrete salt crystals in the urine. If this happens, there is a risk of kidney stones forming.
Exceeding the NIT indicator occurs in conditions such as:
- gout;
- dehydration of the body;
- chronic renal failure;
- pyelonephritis.
The presence in the patient's diet of a large amount of oxalic acid, which is found in sorrel, spinach, tomatoes, can also lead to the appearance of salts in the urine. The same applies to patients undergoing treatment with ampicillin or sulfonamides.
Bacteria and fungi
Detection of bacteria and fungi in urine in any quantity will confirm the presence of bacterial or fungal invasion in the organs of the excretory system. OAM in women is an analysis that is of paramount importance when examining a patient. Exceeding the norm in the table of the results obtained cannot be the reason for the final diagnosis and requires further examination.
Video about the analysis of OAM, the norm in women
General urine analysis (OAM): the norm of the main indicators: