Content
- Duodenal or stomach ulcer
- Views
- Stages and degrees
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Possible consequences and complications
- Hypertension
- Stages and degrees
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Possible consequences and complications
- Bronchial asthma
- Views
- Stages and degrees
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Possible consequences and complications
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Views
- Stages and degrees
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Possible consequences and complications
- Bowel inflammation
- Views
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Possible consequences and complications
- Hyperthyroidism
- Views
- Stages and degrees
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Possible consequences and complications
- Atopic dermatitis
- Views
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Possible consequences and complications
- Video about psychosomatic diseases
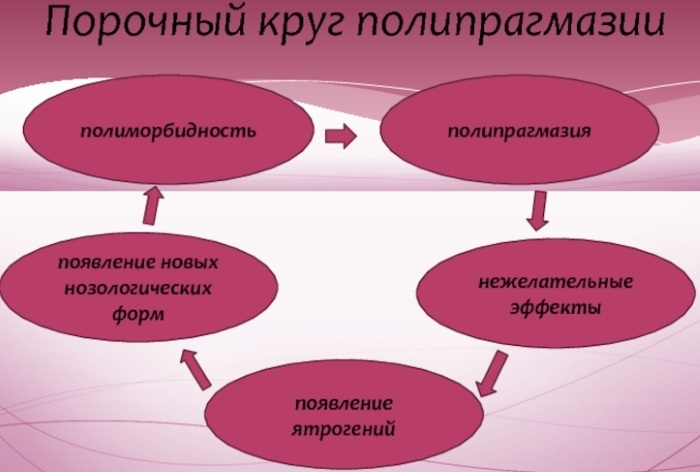
Psychosomatic problemsarising on the physical level - this is a consequence of the transferred emotional events. Experts distinguish seven such diseases, called Chicago, since this concept appeared in America in the 30s of the twentieth century.
Duodenal or stomach ulcer
An ulcer of the stomach and duodenum develops due to the accumulated resentment, aggression towards others, anger that occurs at those moments when a person is in dire need of understanding and care.
Views
The disease is usually classified according to:
- form (acute and chronic);
- flow (latent, mild disease, moderate or severe);
- sizes (small, diameter - no more than 0.5 cm, medium (0.5 - 1 cm), large (1 - 3 cm) and giant (more than 3 cm);
- complications (with bleeding, perforation, kaleznaya and penetrating).
The acute form is diagnosed at the initial detection of the disease, after which it becomes chronic and makes itself felt from time to time.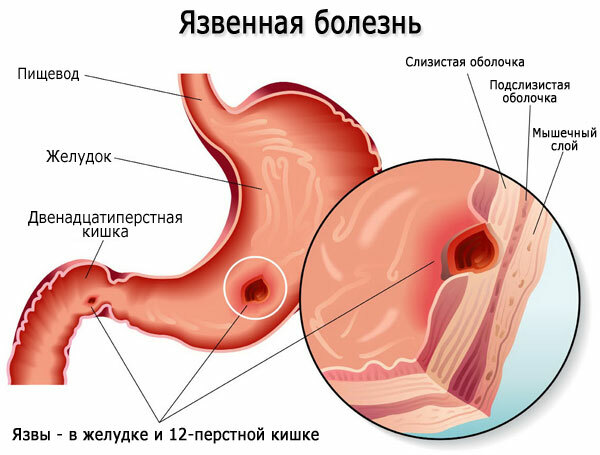
The severity of the disease is determined depending on the frequency of its manifestation and the presence / absence of complications. It can be in a latent form (latent), rarely appear (mild illness), 1 - 2 times a year (moderate) or more than 3 times a year (severe).
Stages and degrees
The development of an ulcer takes place in several stages:
- Acute stage. On the mucous membrane, there are places of inflammation of a round or oval shape with hyperemic edges and swelling.
- Reducing inflammation and edema.
- Scarring. The ulcer decreases, acquires a slit-like shape with slight hyperemia.
- Scarring stage ("red" scar). Initially, the scar is red, the relief of the mucous membrane is disturbed.
Sometimes an ulcer does not form a visible scar. At the site of the inflamed area, connective tissue appears (stage of the "white" scar).
Symptoms and Signs
The development of an ulcer is proved by the following symptoms:
- pain;
- nausea;
- vomiting (sometimes);
- heartburn (at night and in the morning);
- heaviness in the abdomen after eating;
- belching with air, bitter or sour taste in the mouth;
- increased gas formation.
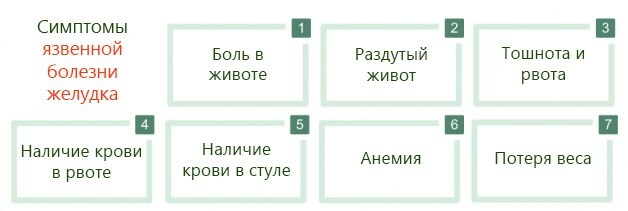 Sometimes patients complain of constipation. There are also atypical signs: sweating of the palms, pain when pressing on the abdomen, white bloom on the tongue. There is also a lack of symptoms.
Sometimes patients complain of constipation. There are also atypical signs: sweating of the palms, pain when pressing on the abdomen, white bloom on the tongue. There is also a lack of symptoms.
Causes
The causes of ulcers include the action of Helicobacter pylori bacteria in the stomach and duodenum, as well as inaccuracies in nutrition and metabolic disorders.
The risk of developing this disease is increased in those who abuse alcohol and smoke, especially on an empty stomach, or take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The predisposition to ulcers can be transmitted genetically. A common cause of damage to the stomach and duodenum is stress and emotional stress (worries, resentments).
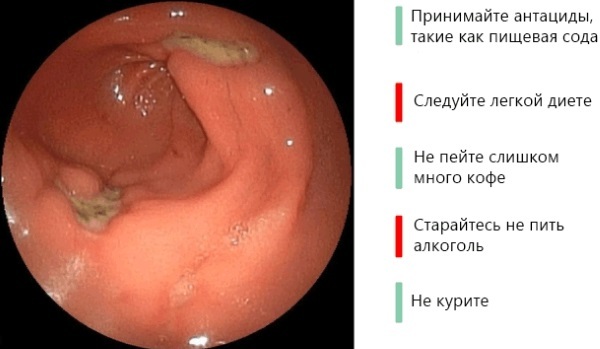
Treatment methods
For the treatment of ulcers, patients are recommended:
- exclusion from the diet of fried, smoked foods and products, as well as carbonated drinks;
- body weight correction;
- quitting alcohol and smoking;
- eating small amounts.
Among the medications for the treatment of stomach and duodenal ulcers are used:
- prokinetics that accelerate the movement of food into the stomach (Itoprid, Motilak, Motilium);
- drugs that suppress the production of hydrochloric acid (Omeprazole, Rabeprazole, Pantoprazole, Lansoprazole);
- drugs that neutralize hydrochloric acid in the stomach (antacids) (Almagel, Alumag, Gaviskon, Gastal, Maalukol, Altacid).
The treatment regimen for each individual patient takes into account comorbidities.
In especially severe cases (with bleeding, perforation, gross deformities of the stomach, etc.), an operation is indicated.
Among the traditional methods of treatment are used aloe and potato juice, sea buckthorn, as well as beekeeping products (honey, royal jelly, propolis). They have antiseptic properties, soothe pain and relieve inflammation and irritation of the mucous membrane.
Possible consequences and complications
In the absence of proper treatment, the disease can lead to serious complications: perforation, bleeding, and the growth of a malignant tumor. To minimize or completely eliminate this condition, you should listen to your body and consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Hypertension
The Chicago 7 psychosomatic illnesses include hypertension, or hypertension, a common a disease that is a malfunction of the heart due to blockage of the blood vessels supplying his.
Stages and degrees
Specialists distinguish 3 stages of the development of the disease and, depending on this, determine the degree of hypertension:
- 1st degree - preclinical stage. In the initial stage, the pressure rises to 140 - 159/90 - 99 mm Hg. Art. At the same time, the patient feels a headache, often gets tired, his working capacity decreases. In a calm environment, the pressure usually returns to normal.
-
2nd degree: pressure reaches 160 - 179/100 - 109 mm Hg. Art., atherosclerotic plaques are formed, left ventricular hypertrophy is determined, pathologies of the retina of the eye appear, problems in the work of the kidneys (increased creatinine).
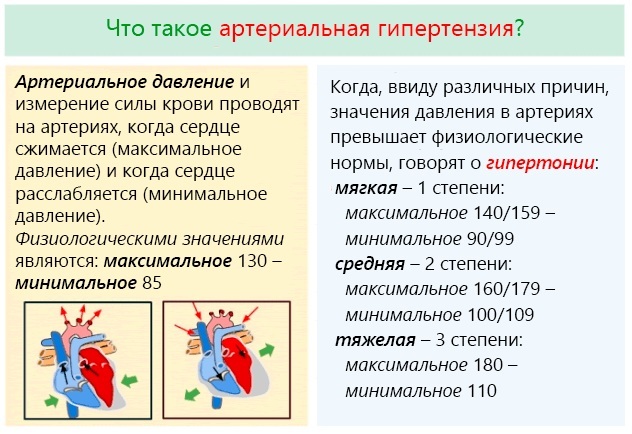
- Grade 3: pressure 180 or more / 110 or more mm Hg. Art. This increases the risk of angina pectoris, acute myocardial infarction, postinfarction cardiosclerosis, encephalopathy and renal failure, blindness.
Symptoms and Signs
Symptoms of hypertension include:
- prolonged headaches;
- noise in ears;
- fast heartbeat;
- "Midges" before the eyes;
- numbness of hands and feet;
- hyperemia of the face;
- sweating;
- chills.
In addition, the patient periodically feels dizzy, he has problems with memory, irritability, anxiety.
Causes
Arterial sclerosis, as well as stress and bad habits, lead to hypertension. During stress, adrenaline is released into the bloodstream, which leads to increased work of the heart muscle.
The causes of heart pathologies include excess weight, since the concentration of calcium and sodium in the blood increases, and the activity of the kidneys is disrupted.
The risk of hypertension increases with age. This is also influenced by genetics and a sedentary lifestyle, since the metabolism slows down and the work of many organs and systems is weakened.
Treatment methods
At the first stage, you need to adhere to a healthy lifestyle (eat right, normalize drinking regimen, moving more, getting rid of bad habits, balancing work time and recreation).
Medication therapy - drugs that normalize blood pressure, and subsequently maintain it within normal limits.
For hypertension, it is recommended to take:
- diuretics - diuretics that reduce puffiness and dilate blood vessels: hydrochlorothiazide, indapamide, furosemide;
- beta-blockers that reduce the production of normadrenaline (stress hormone) in the blood: Bisoprolol, Metoprolol, Corvedilol, Propranolol;
- calcium antagonists that reduce myocardial contractility and block the flow of calcium into vascular cells: Nifedipine, Diltiazem, Verapamil;
- ACE inhibitors that reduce blood pressure: Captopril, Ramipril, Lisinopril, Enalapril;
- angiotensin receptor blockers that relax the blood vessels: Candesar, Valsartan, Eprosartan.
Among the folk remedies for the treatment of hypertension, the most common are beet juice with honey, a decoction of plantain leaves, tea with mint, lemon with honey and garlic, pomegranate juice, normal water mode.
Possible consequences and complications
Untreated hypertension can lead to angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, serious disorders of the heart muscle (failure and arrhythmias).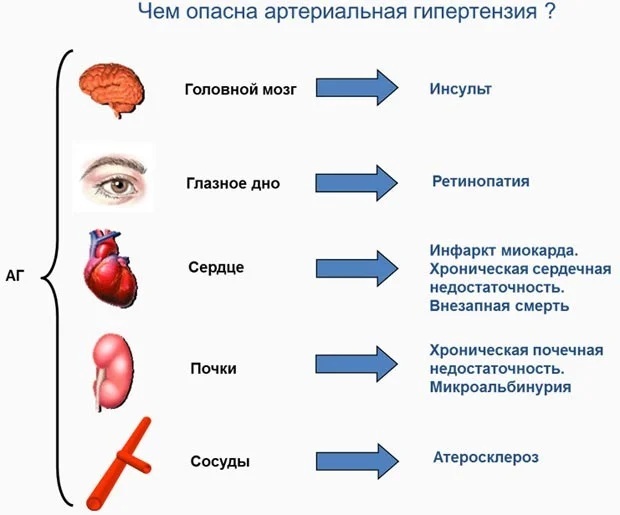 The most dangerous consequence of hypertension can be a stroke, which can rupture or block your arteries.
The most dangerous consequence of hypertension can be a stroke, which can rupture or block your arteries.
Bronchial asthma
The Chicago 7 psychosomatic illnesses are illnesses that are caused by frequent negative emotional states. Such pathologies include bronchial asthma.
Views
The types of asthma (phenotypes) depend on the manifestations of the disease.
According to this criterion, asthma is distinguished:
- neutrophilic, which is characterized by an increase in neutrophils in the sputum;
- eosinophilic, in which the concentration of eosinophils is increased in the sputum;
- mixed (with an increased content of eosinophils and neutrophils);
- low-granulocytic (with a low content of these leukocytes).
Clinical phenotypes include the following types of asthma:
- allergic, in the appearance of which heredity plays an important role;
- infectious-dependent (arising from viral or bacterial diseases);
- mixed.
Allocate aspirin, autoimmune (human lung tissue is an allergen) and hormone-dependent asthma.
Stages and degrees
The development of bronchial asthma includes 3 stages:
- Stage 1. Obstruction increases, the viscosity of the secreted secretion is increased, the cough increases, while the amount of sputum decreases. Choking increases, wheezing appears.
- Stage 2 ("silent" lung). Noisy breathing with a whistling sound, but no wheezing in the lungs, weakened breathing. Arrhythmia, tachycardia, pallor of the skin.
- Stage 3 - coma. Oxygen starvation, an increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide. Cyanosis, delirium, disorientation in time and place, heart rhythm failure, decreased blood pressure.
Symptoms and Signs
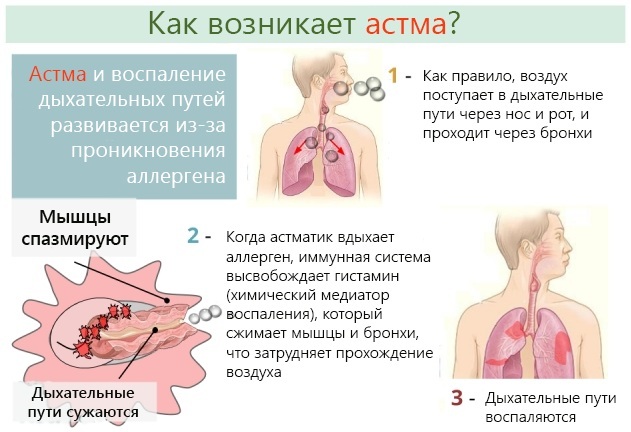
The main symptom of bronchial asthma is a cough with wheezing and subsequent sputum production, shortness of breath. The patient during an attack feels short of breath, especially at night. Before this, a runny nose, discomfort in the nose are possible.
The phlegm is usually viscous and transparent, the pulse is quickened, and sweating increases.
The time of the attack is 2 hours or more.
Causes
There are several causes of asthma. Among them are strong and frequent stress, which contributes to the difficulty of breathing, a decrease in the supply of oxygen to the blood and a disturbance in the rhythm of the heart.
In addition, heredity plays an important role, as well as nutrition (eating foods containing allergens for a particular person).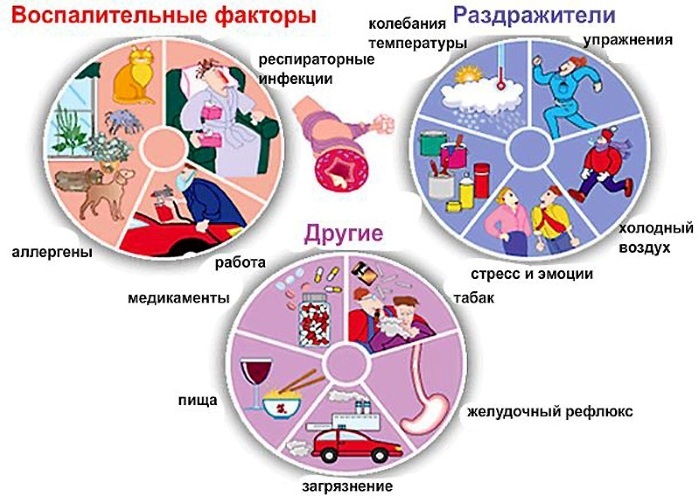
The development of asthma can be triggered by professional activities, in particular by working in a hazardous chemical industry, or by using detergents.
The infectious-allergic nature of asthma is influenced by fungi, viruses and bacteria, as well as harmful vapors in the air.
Treatment methods
First of all, you should exclude a possible allergen (switch to a hypoallergenic diet, remove carpets with pile, exclude contact with animals).
Allergen-specific immunotherapy has a good effect on the condition of patients, the purpose of which is to reduce sensitivity to allergens. This is done through vaccination.
Drug therapy includes taking cromones (Nedocromil sodium and Cromoglycate sodium), the use of inhalers with glucocorticosteroids, monoclonal antibodies.
To relieve an attack, use Euphyllin, Salbutamol, Fenoterol.
One of the effective methods of treating this disease is speleotherapy - the patient's stay in a special room (caves, grottoes, salt mines) with high ionization and the presence of highly dispersed aerosols, as well as halotherapy, when the patient is in an artificially created climate resembling salt caves.
Possible consequences and complications
Complications include pulmonary emphysema (impaired gas exchange), infectious bronchitis. If the disease is protracted, then the possibility of developing cor pulmonale increases (change in the right ventricle of the heart - thickening and expansion). The increasing lack of oxygen can be life-threatening.
Rheumatoid arthritis
This disease is associated with damage to the joints, leading to the destruction of their structures. 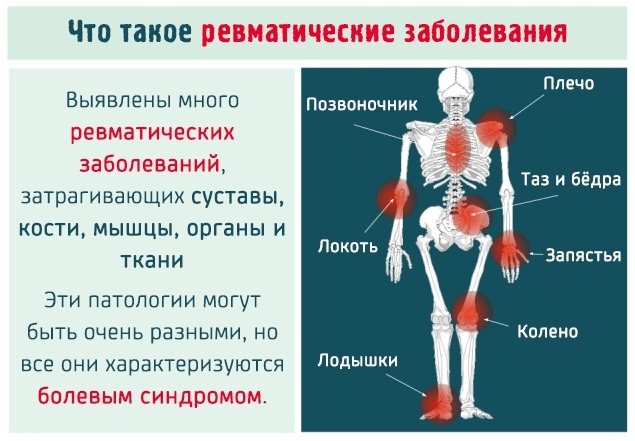 Its psychosomatics consists in the fact that the sick person is inflexible, stubborn and does not accept what should happen.
Its psychosomatics consists in the fact that the sick person is inflexible, stubborn and does not accept what should happen.
Views
There are such types of rheumatoid arthritis:
- seropositive (with the presence in the blood of antibodies to immunoglobulins that have changed due to infection);
- seronegative (without the presence of RF in the blood);
- juvenile (youthful), when joints are destroyed in children from 4 to 16 years old and growth retardation and pathology of internal organs occur;
- systemic (with damage to internal organs).
The rarest type of rheumatoid arthritis is Still's disease (with fever and damage to internal organs). It appears unexpectedly and also disappears.
Stages and degrees
This disease has a long course, during which the following stages are distinguished:
- very early (up to six months): the development of osteoporosis around the joint;
- early (from six months to a year): the joint space narrows;
- deployed (more than 1 year) with typical symptoms, erosions, subluxation of the joints;
- late (more than 2 years): bone immobility (ankylosis).
With each subsequent stage, the patient's mobility and self-care is increasingly limited.
Symptoms and Signs
The Chicago 7 psychosomatic illnesses have one common basis - emotional stress. Stress, severe emotional states lead to joint pathology.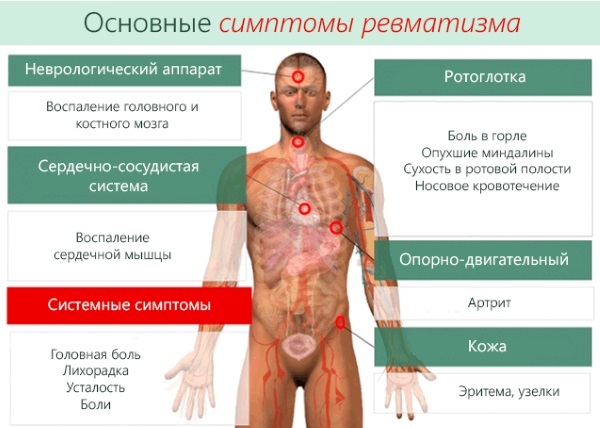
With rheumatoid arthritis, the pain is localized in the extremities. At first, it worries in the morning, then worsens with palpation. With the development of the disease, the mobility of the limbs in the affected areas decreases, redness and swelling are observed.
Rheumatoid nodules appear, under the skin - dense areas. Patients complain of fatigue and decreased performance. Sometimes the disease is accompanied by pathology of internal organs.
Causes
Arthritis is caused by the action of hepatitis B, measles, herpes or mumps viruses, which cause the production of antibodies. The disease provokes a prolonged stay in the cold or in direct sunlight, metabolic problems. This affects the functioning of the immune system and makes the infection easier to penetrate. In this case, heredity also plays an important role.
Treatment methods
For treatment, anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal drugs are used: Diclofenac, Napraxen, Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, etc., antineoplastic agents (Methotrexate, Endoxan, Cyclosporin). In addition, glucocorticoids are used in the form of tablets, ointments or injections: Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone, Betamethasone acetate, Triamcinolone hexacetonide.
The therapy of arthrosis includes monoclonal antibodies, physiotherapy, therapeutic exercises, and sometimes surgery. And folk medicine advises making various compresses: from raw potatoes, vinegar solution, bay leaf decoction, etc.
Possible consequences and complications
Prolonged rheumatoid arthritis can lead to pathologies of the heart, lungs, renal failure, visceral amyloidosis (accumulation of amyloid in tissues, leading to damage to many organs).
Bowel inflammation
This disease is caused by the development of an inflammatory process in one or more parts of the intestine.
Views
The types of this disease are ulcerative colitis (damage to the mucous membrane of the colon), and Crohn's disease (the formation of abscesses, ulcers and fistulas of unknown etiology).
Symptoms and Signs
Signs of intestinal inflammation are:
- cramping abdominal pain;
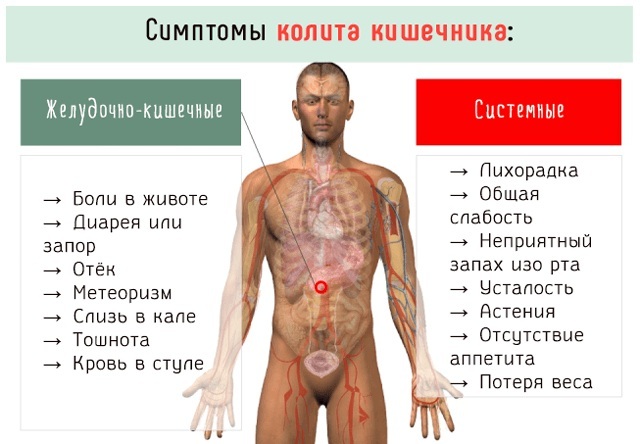
- chronic diarrhea with blood and mucus;
- bleeding;
- false urge to defecate;
- anal fissures;
- fistulas.
The patient feels weak, his temperature rises, anemia develops.
Causes
The true causes of the development of the disease have not been identified, but it has been established that it is influenced by immune disorders that contribute to the production of antibodies to its own cells, and genetics. In addition, stress and unbalanced diets also contribute to inflammation in the gut.
Treatment methods
Treatment is carried out in stages. Hungry pauses are helpful in the beginning.

At this time, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed: Mesalamine, Salofalk, Sodium olsalazine, Prednisolone, Metronidazole. In case of intestinal inflammation, enzymes Mezim, Creon, sorbents Polysorb or Smecta, as well as immunomodulators Viferon, Immunal, etc. are useful. Surgery is sometimes recommended. Among folk remedies, decoctions of chamomile, plantain, yarrow, milk thistle help.
Possible consequences and complications
Running inflammation can lead to bleeding, inflammation in the peritoneum, and even oncology.
Hyperthyroidism
The Chicago 7 psychosomatic illnesses include hyperthyroidism, a condition in which the thyroid gland produces excess hormones, which impairs a person's quality of life.
Views
Distinguish between primary hyperthyroidism, when pathology is determined, secondary - with damage to the pituitary gland and tertiary, when pathological processes affect the hypothalamus.
Stages and degrees
In addition, there are 3 stages of the disease:
- mild (subclinical form), in which the level of triiodothyronine decreases;
- medium (manifest), when the first symptoms are noticeable, the level of triiodothyronine is reduced;
- severe (complicated): heart failure is observed, heart rhythm is disturbed, psychosis appears.
At the first sign, you need to visit an endocrinologist and keep hormone levels under control.
Symptoms and Signs
You can distinguish hyperthyroidism by the following features:
- excessive sweating;
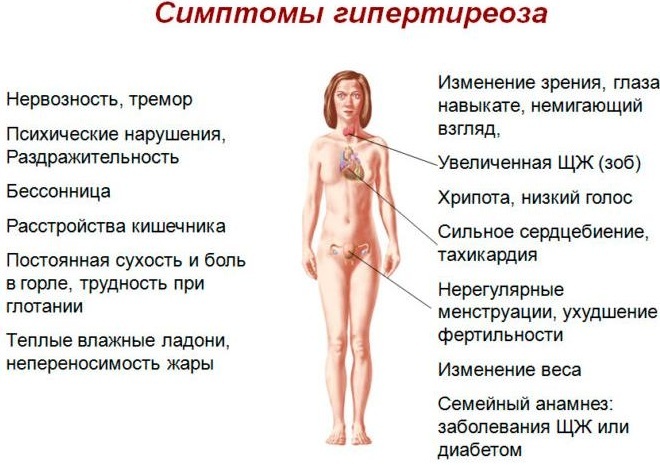
- frequent pulse (120 or more beats / min.);
- drastic weight loss;
- frequent bowel movements and urination;
- irritability, fatigue;
- poor sleep;
- increased blood sugar;
- bulging eyes;
- violation of the menstrual cycle.
With hyperthyroidism, symptoms may be subtle, especially in the elderly.
Causes
Lead to the development of hyperthyroidism: Graves' disease (antibodies are produced that stimulate excessive production of T4), nodular goiter (with the formation of benign nodes), thyroiditis (destruction of gland cells), as well as hereditary predisposition and stress.
Treatment methods
For treatment, drugs of radioactive iodine, Tiamazole, Propylthiouracil, lithium carbonate are used. For symptomatic treatment, medications are prescribed to normalize blood pressure and heart rate. In the presence of neoplasms and severe course, surgery is indicated.
Possible consequences and complications
The disease can lead to problems in the work of the heart, brittle bones, and blurred vision. The patient may develop skin problems (redness and swelling), and develop a thyrotoxic crisis (fever, tachycardia, mental disorders).
Atopic dermatitis
The Chicago 7 psychosomatic diseases include atopic dermatitis, which is common in children, but it can continue into adulthood.
Views
Infant (up to 2 years old): facial flushing, swelling and peeling. Sometimes - bubbles and crusts.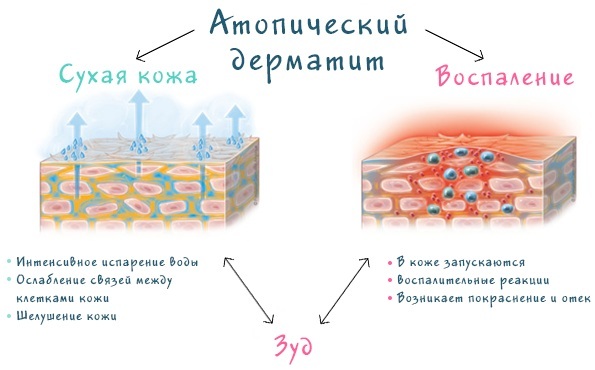
Children (2 - 12 years old): rashes, peeling on the elbows, under the knees, on the back of the neck.
Adult (over 12 years old): stable remission, but sometimes itching, vesicles, nodules, hyperemia appear.
Symptoms and Signs
Signs of the disease are severe itching, dry skin, rashes, redness, causing great discomfort.
Causes
It was not possible to establish the exact causes of atopic dermatitis, but it is known that there is a genetic predisposition to it.
Treatment methods
First, it is important to eliminate the factors that provoke the development of the disease. The administration of antihistamines (Sanaflan, Fenkarol), anti-inflammatory drugs (Advantan, Akriderm genta) is shown.
In severe forms - glucocorticosteroids (Hydrocortisone, Corticosterone), antibiotics (Fusidic acid, Erythromycin, Tetracycline), antifungal agents (Orungal), aqueous and alcoholic solutions.
Possible consequences and complications
The development of atopic dermatitis leads to pustular lesions (impetigo). And also to the development of inflammation on the eyelids (blepharitis) and on the mucous membrane of the eyes (conjunctivitis).
The described Chicago seven diseases, which develop as a result of many problems, have a psychosomatic basis. Therefore, it is important to learn how to keep your emotions under control, not to be stressed and worried, and to see a doctor in a timely manner.
Video about psychosomatic diseases
Psychosomatic diseases: