Content
- Features of ocular tuberculosis
- How mycobacterium enters the eye tissue
- Classification of tuberculosis of the organs of vision
- Metastatic form
- Allergic form
- Disease risk group
- Contagiousness of eye tuberculosis
- Symptoms of the disease
- External manifestations of the disease (photo)
- Other symptoms according to the stages of the disease
- Who is involved in the treatment
- Differential diagnosis
- Difficulties in making a diagnosis
- Ocular tuberculosis in children
- Treatment of ocular tuberculosis
- Is it possible to treat at home
- Inpatient care
- Complications during and after illness
- General prognosis for patients
- Prevention of the development of eye tuberculosis
Tuberculosis of the eyes is a rare form of the disease in phthisiology, which is accompanied by damage to the adnexa, conjunctiva, choroid and other structures of the organ of vision. In most cases, a violation occurs with a strong decrease in immunity and generalization of the pathological process.
Features of ocular tuberculosis
For the first time, the possibility of infection of the structures of the organs of vision with mycobacteria was experimentally proved by the German doctor Yu. Congame in 1879 Ocular tuberculosis is secondary in most cases.
More often this form of the disease is diagnosed in young people from 25 to 35 years old. Women are more prone to the development of pathology.
The first signs of the disease can be easily confused with the manifestations of other infectious pathologies of the organs of vision. Mycobacterium lesion of the eyes is difficult to treat and often leads to the development of complications. Often, pathology becomes the cause of vision loss.
How mycobacterium enters the eye tissue
Most often, the infection of the structures of the visual apparatus occurs by the hematogenous route, i.e. from primary a focus located in the lungs or other organ, microorganisms enter the vessels and are brought into eyes.
However, primary infection is also possible if a person comes into contact with a patient suffering from an open form of tuberculosis and secreting Koch's bacillus into the environment when sneezing and coughing.
In this case, droplets of sputum infected with mycobacterium will help get onto the mucous membrane of the eyes. If the immune system is weakened, the body is not able to fight the pathogenic microflora, and its number is rapidly increasing. This leads to the appearance of characteristic symptoms of the disease.
Rubbing your eyes with dirty hands can also lead to infection. In rare cases, infection occurs when a sick person is used together with towels, eyelash care products, as well as during cosmetic procedures.
Children are more likely to become infected in utero. When transferring mycobacteria from mother to child, the likelihood of damage to the visual apparatus is high. In this case, the newborn immediately after childbirth shows signs of an inflammatory process in the structures of the eye tissues. Infection is also possible with trauma to the organs of vision.
Classification of tuberculosis of the organs of vision
Ocular tuberculosis is classified according to the location and type of tissue affected.
According to this principle, the following forms of pathology are distinguished:
- With damage to auxiliary elements (eye sockets, eyelids, lacrimal sac, eyelashes).
- With infection of the structures of the anterior section (retina, cornea, iris).
- With damage to the back of the eye (blood vessels, nerve endings, vitreous).
Important information: Features of the treatment of different forms of disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis
Depending on the symptoms and the nature of the changes in the tissues, metastatic and allergic varieties of the disease are distinguished.
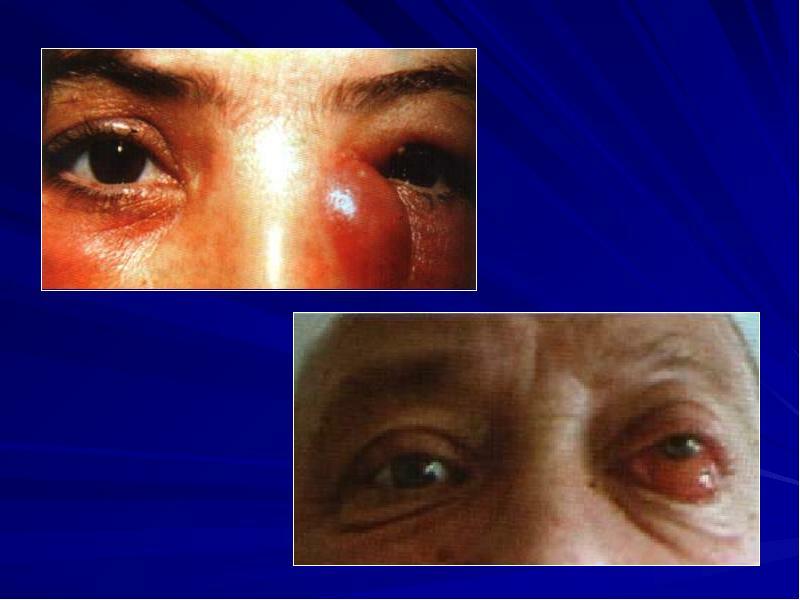
With a metastatic form, a granuloma grows on the surface of the mucous membrane of the eye. This defect is formed when mycobacteria enter the vessels of the visual apparatus with blood flow. As the granuloma forms, it thickens and acquires a shell. Calcification of the nodule is extremely rare.
The most common metastatic form of tuberculosis is observed in people with severe immunodeficiency.
The growing neoplasm compresses the surrounding healthy tissue, which often leads to severe visual impairment. With late detection, the defect can only be eliminated surgically.
Allergic form
The allergic form is more common. It has pronounced clinical manifestations. There are signs of inflammation caused by the activity of mycobacteria, as well as allergy symptoms provoked by an increased reaction of the body to tissue damage by bacilli.
The disease can occur both when Koch's bacillus enters the mucous membrane of the eye, and when pathogenic microflora enters the bloodstream.
Disease risk group
The risk of infection with mycobacteria is increased with frequent contact with patients suffering from an open form of tuberculosis. In this case, pathogenic bacilli will regularly enter the human body.
A special risk group for developing ocular tuberculosis includes people living in unfavorable sanitary conditions:
- people without a place of residence;
- refugees;
- migrants;
- prisoners;
- patients in drug addiction and psychiatric clinics;
- residents of nursing homes and shelters.
The medical factors that predispose to damage to the organs of vision by mycobacteria include:
- HIV infection;
- diabetes;
- malignant tumors;
- pathology of the genitourinary system;
- blood diseases;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland.
A special risk group for developing eye tuberculosis includes people with a long history of alcoholism and drug addiction.
Contagiousness of eye tuberculosis
When the visual apparatus is damaged, mycobacteria can be released onto the mucous membrane. When the eyes are rubbed, pathogenic microorganisms fall on the hands, and then on various objects.
In this case, there is a possibility of infection of other people with reduced immunity. The degree of infectiousness can be detected only after receiving the result of bacterial sowing.

Symptoms of the disease
The rate of increase in clinical manifestations largely depends on the form of the course of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient's body.
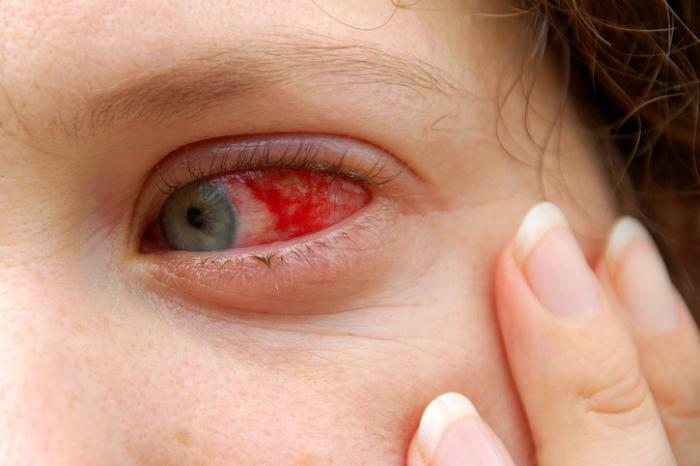
External manifestations of the disease (photo)
In adults and children, the following symptoms of eye tuberculosis are most often observed:
- redness:
- increased vascular pattern;
- tearing;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- purulent conjunctivitis;
- glaucomatous changes in the eye.
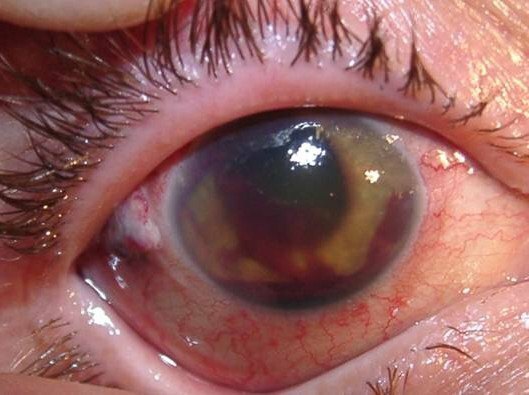
Other symptoms according to the stages of the disease
Clinical manifestations accompanying eye damage by mycobacteria depend on the degree of neglect of the process. After the penetration of Koch's bacillus into the tissues of the visual apparatus for a long time, there are no pronounced signs of tuberculosis. After the initial activation of the infection, the sclera of the eyes turn red.
There is a sensation of the presence of a foreign body in the eye. The person is worried about severe pain and cramps. The eyelids are swollen. Profuse lacrimation begins. Separation of purulent contents is possible.
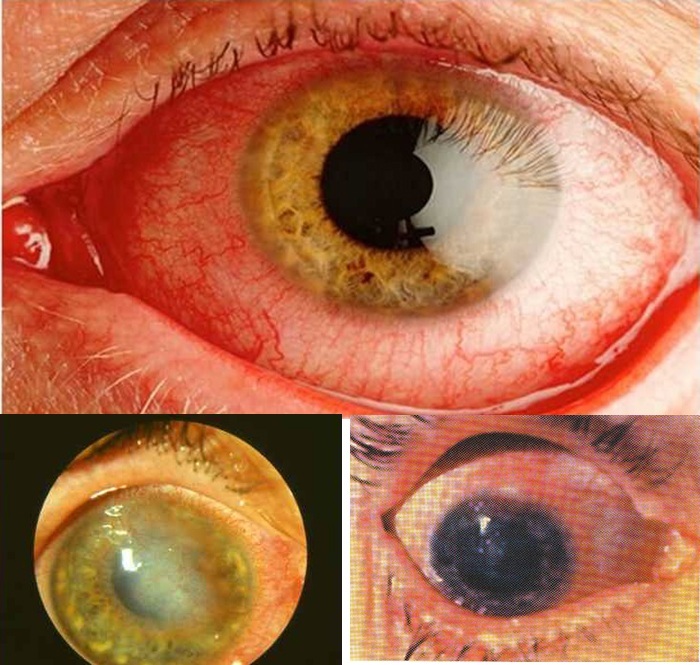
In the future, tuberculous keratitis develops, i.e. inflammatory lesion of the cornea. At the same time, the patient can see a veil or dark spots. Infected tissues die off, and mycobacteria multiply rapidly.
Important information: Basic principles of treatment of tuberculosis of the spine and bones in adults
White and gray-green defects form in the iris. Glaucoma develops. Scars form gradually. In the last stages of infection, visual acuity decreases.
In many people, against the background of eye damage by mycobacteria, an increase and softening of the tissues of regional lymph nodes is observed. After an exacerbation, the intensity of clinical manifestations decreases. For a while, the patient's condition improves, but the pathological process does not stop.
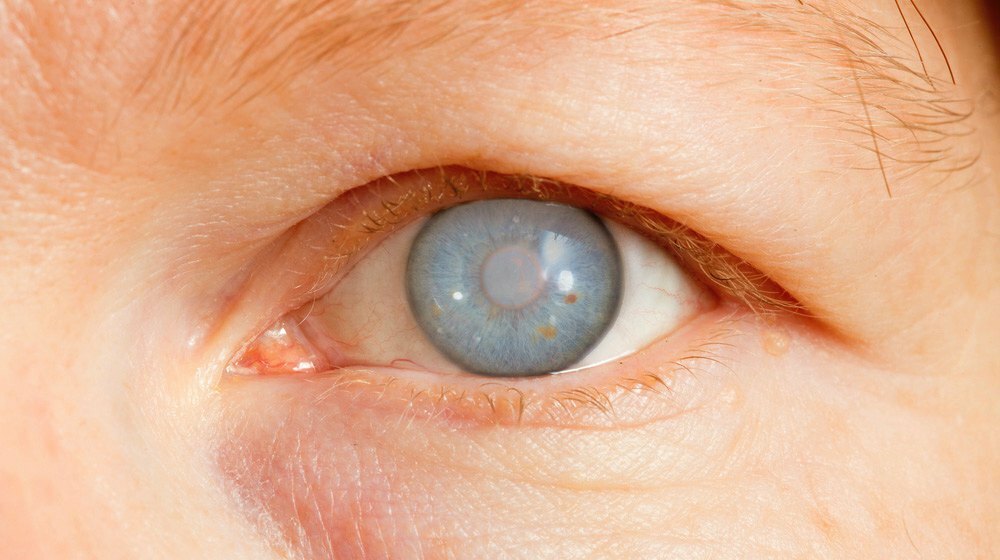
Who is involved in the treatment
When signs of damage to the visual apparatus by mycobacteria appear, the patient should immediately contact an ophthalmologist. After determining the type of pathogenic microflora that caused the destruction of the structures of the eye, the patient is referred for a consultation with a phthisiatrician.
Differential diagnosis
The clinical manifestations of eye tuberculosis are similar to the symptoms of many other diseases of the visual apparatus, therefore, a comprehensive differential diagnosis is required to confirm the diagnosis.
It should be excluded:
- uveitis caused by systemic pathologies and gonococcal infection;
- herpetic keratitis;
- retinal vein thrombosis;
- retinitis of Coats;
- pigmented nevus of the iris;
- sympathetic ophthalmia;
- retrobulbar neuritis;
- recurrent corneal erosion;
- iridociliary dystrophies, etc.
Difficulties in making a diagnosis
The similarity of the symptoms of ocular tuberculosis with the signs of many other pathologies complicates the diagnosis. First of all, studies are performed to identify the primary focus of infection in other organs, incl. X-ray, bacteriological analysis of sputum and immunodiagnostics.
After examination by an ophthalmologist and phthisiatrician, to determine the causes of damage to the structures of the eyes, appoint:
- visometry;
- biomicroscopy;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- tonometry.
If the pathological process affects the eyelids, a biopsy is performed. In rare cases, chorioretinal endobiopsy is performed. The obtained samples are subjected to histomorphological examination to determine the presence of mycobacteria.
As part of the diagnosis, iridectomy is often performed. During this procedure, the contents of the vitreous body or anterior chamber are aspirated.
The resulting material is sent to cytology. A comprehensive examination will help confirm the diagnosis and exclude other pathologies accompanied by similar symptoms.
Ocular tuberculosis in children
Children's immunity is immature, therefore, even if the child received the necessary vaccinations, the body's defense mechanisms cannot always cope with mycobacteria. In patients under 12 years of age, eye damage with Koch's stick occurs in an allergic form.
In most cases, tuberculosis of the organs of vision in children is secondary. In this case, the primary focus has pulmonary localization. Therapy should be carried out in a hospital setting.
The child's body quickly recovers, therefore, with a timely start of treatment, there is a high probability of overcoming the disease without consequences.

Treatment of ocular tuberculosis
Treatment of eye tuberculosis requires an integrated approach. Mycobacteria are highly resistant to antibiotics, therefore, drug combinations are used to suppress pathogenic microflora.
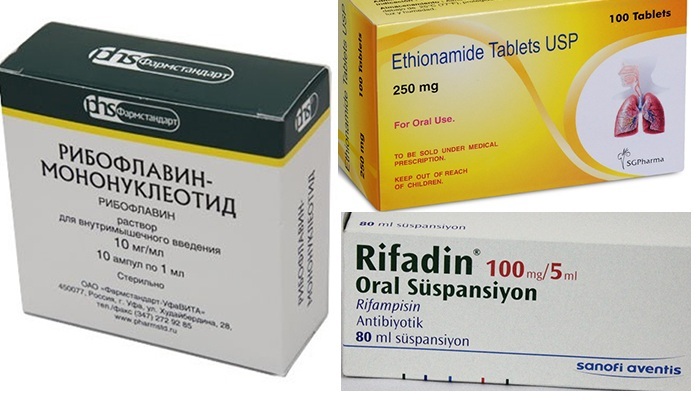
The following medicines are most often combined:
- Riboflavin.
- Ethionamide.
- Rifadin.
- Tubazid.
To suppress the inflammatory process, corticosteroids are prescribed:
- Ketalog-40.
- Dexamethasone.
- Hydrocortisone.
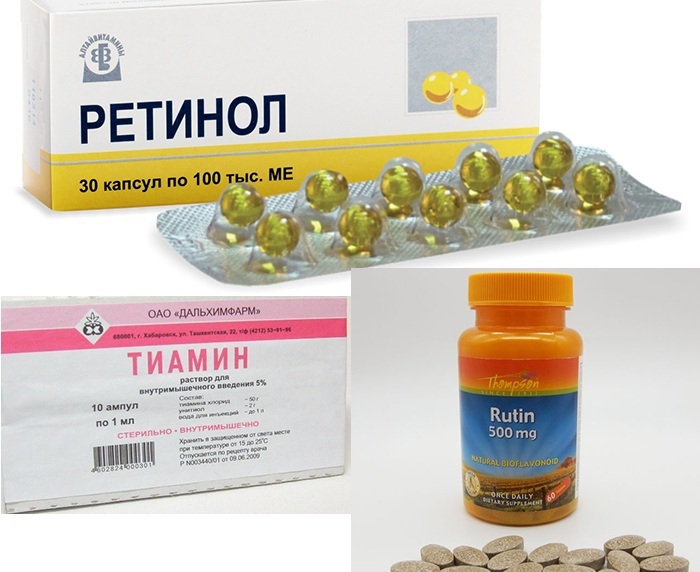
To improve the general condition and stimulate immunity, it is recommended to take vitamins.
Especially useful:
- Retinol.
- Ascorbic acid.
- Rutin.
- Thiamin.
- Alpha-tocopherol.
To reduce the severity of symptoms, eliminate edema, and accelerate tissue regeneration, eye drops are selected for the patient.
Important information: Features of the clinical development of renal tuberculosis in adults and children
Recommended use:
- Syntomycin.
- Tobradex.
- Albucida.
To protect the liver from the toxic effects of drugs, hepatoprotectors are prescribed:
- Carsil.
- Essentiale.
- Phosphogliv, etc.
With the ineffectiveness of drug therapy and severe visual impairment, a corneal transplant is required. To reduce intraocular pressure, paracentesis, iridectomy or other antiglaucomatous surgery is performed.
In addition, the patient is prescribed a sparing diet rich in protein of plant and animal origin, as well as vitamins and minerals that enhance the activity of the immune system.
Is it possible to treat at home
The possibility of home therapy depends on the severity of the clinical manifestations. If the symptoms are acute and growing rapidly, the patient should be treated in a hospital setting. However, with mild signs of pathology, therapy can be carried out on an outpatient basis.
Inpatient care
Inpatient treatment is considered more effective because the patient is under medical supervision. Specialists, if necessary, can quickly change the drug treatment regimen. In the hospital, patients take drugs strictly on schedule.
In addition, nursing care is provided for patients who experience discomfort due to decreased visual acuity. Patients are regularly treated with eyes and help with everyday problems.
When undergoing inpatient treatment, intrabulbar and subconjunctive injections of antibacterial drugs are often performed. In addition, therapy is often complemented by exercise therapy, water procedures.

Complications during and after illness
The disease often becomes recurrent.
The acute phase of eye tuberculosis is complicated by the following conditions:
- clouding of the cornea;
- retinal detachment;
- increased intraocular pressure, etc.
Even with a favorable course of the disease and the achievement of a stable remission in patients, vision is greatly impaired. After the attenuation of an acute infectious process, the development of pathologies such as glaucoma and cataracts is often observed. The most dangerous complication is irreversible loss of vision.
General prognosis for patients
More often, the organs of vision are affected against the background of a decrease in immunity, therefore, the prognosis in most cases is unfavorable. Pathology often leads to disability.
Patients with diagnosed ocular tuberculosis should be registered with a phthisiatrician and ophthalmologist and regularly undergo examinations for the timely detection and treatment of possible complications.
Proper nutrition, normalization of sanitary living conditions and comprehensive treatment help to improve the prognosis.
Prevention of the development of eye tuberculosis
Vaccination is essential to reduce the risk of contracting mycobacteria.
Non-specific methods of prevention include:
- compliance with the rules of healthy eating;
- taking multivitamins;
- avoiding contact of dirty hands with eyes;
- rejection of bad habits;
- hardening;
- regular walks in the fresh air, etc.
Avoid visiting crowded places, as well as communicating with persons suffering from open form of tuberculosis. It is necessary to regularly undergo preventive examinations and do fluorography. At the first signs of eye damage, you should immediately contact an ophthalmologist.