Content
- General characteristics of the disease
- Reasons for the appearance
- Provoking factors
- Symptoms and Signs
- Infected or not
- Anatomy and Mechanism of Cavern Formation
- Varieties and classification
- The clinical picture of the development of cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis
- Diagnostic measures
- Basic principles of treatment
- Physiotherapy
- Surgical intervention
- Chemotherapy
- Medicines and drugs
- ethnoscience
- Recovery Predictions
- Rehabilitation and features of the body's recovery
- Consequences and possible complications
- Prevention methods
Cavernous tuberculosis is a form of the disease characterized by destructive changes in the lung tissues. Pathological cavities appear, and perifocal inflammation and bronchogenic elimination are absent. In order to recognize the disease in time, you need to know the reasons for its development, varieties and possible complications.

General characteristics of the disease
The disease is a progressive stage of pulmonary tuberculosis. It proceeds with the formation of cavities, but there are no inflammatory fibrotic changes. Adults are at risk. Children with tuberculosis VHLH and PTC are less susceptible to the disease. Their cavities are much less common.
In more than 50% of cases of morbidity, cavernous tuberculosis is a complication of the infiltrative. In the remaining 50%, we are talking about focal and disseminated disease. If there is no treatment or it is incorrect, tuberculosis becomes fibro-cavernous. The walls of the pathological cavities and the parenchyma grow.
Many foci of seeding are formed.
When the cavernous or fibrous-cavernous form is detected for the first time, they account for 5-6% of the total incidence of tuberculosis infection. Further development of the disease can provoke its last stage - cirrhotic. It is characterized by wrinkling of the lung, tk. connective tissue grows strongly.
Reasons for the appearance
The disease appears for various reasons. The main ones are:
- primary tuberculosis;
- damage to the lungs with another infectious disease;
- bad habits - smoking;
- hypersensitivity to pathogens;
- illiterate treatment of the main form of tuberculosis.
In rare cases, the disease develops with primary infection. However, more often it appears against the background of existing tuberculosis.
The disease can arise from a frivolous attitude towards health. Sometimes it develops if a wrong diagnosis has been made earlier. Therefore, it is necessary to do fluorography annually. Then it is possible to timely identify pathological changes in the lung tissues.
Any sign of tuberculosis should see a doctor immediately.
Provoking factors
The number of mycobacteria that cause the disease is about 75,000 species. They live in soil, water and among animals. The most dangerous species for humans is Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
The main features of the bacteria are pathogenicity and virulence. It adapts well to changes associated with environmental factors.
The villagers are threatened by another pathogen. In addition to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium bovis is also common. Otherwise, it is called bullish. Cavernous tuberculosis is a transitional stage between other types of the disease. The destructive stage occurs when decaying tissue appears. Further, the fibrous-cavernous form develops.
Symptoms and Signs
The insidiousness of the disease lies in its asymptomatic course. It occurs 3-4 months after ineffective treatment of other types of tuberculosis.

The localization of the disease is one-sided. Its main features are as follows:
- wet cough and hemoptysis;
- the presence of wet wheezing;
- asthenia and constant feeling of fatigue;
- subfebrile body temperature that occurs periodically;
- decreased appetite;
- weight loss.
Important information: The clinical picture of the course of fibrocavernous pulmonary tuberculosis
Pulmonary bleeding indicates a hidden pathological process. It appears suddenly, even if a person considers himself healthy. Profuse bleeding occurs due to the entry into the cavity of the terminal arteries of the lungs. This condition is called Rasmussen's aneurysm.
It is possible to develop cavity aspergillosis - an infection caused by mold spores entering the lungs.
Infected or not
The disease in question is contagious. Patients serve as a source of distribution of mycobacteria, being their reservoir. Therefore, they need to be isolated from others to avoid infection.
Anatomy and Mechanism of Cavern Formation
The trigger for the appearance of cavities in the lung is caseosis, which forms at the site of the focus of tuberculosis. Its masses are necrotic tissue. At the initial stage, it has a dry residue.
Later, the caseous masses are liquefied. The tissues are rejected by the bronchial passages. Caverns appear in their places.
The cavity wall consists of several layers:
- internal - the remains of caseous formations;
- middle - specific granulations;
- external - fibrous tissue.
The caverns have an average size of 2-4 cm. Large cavities (4-6 cm) are rare. Giant ones reach a size of 6 cm, but they are rarely found.
Varieties and classification
There are several types of caverns. Formative occurs in the process of tissue decay. Such a cavity has no distinct boundaries.
The fresh cavity is characterized by a two-layer shell. There are some cavernous formations inside.
A capsule with a three-layer shell and clear contours - a formed cavity. Inside there are fibrous tissues that appear with fibrous-cavernous tuberculosis.
Sanitized cavities - voids that arise when cavernous masses move away. They are formed after treatment.
The clinical picture of the development of cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis
The disease has an undulating course, as well as erased symptoms. The hallmarks of the described form of tuberculosis are hemoptysis and severe shortness of breath.
Long periods of remission are followed by relapses. An exacerbation can occur when another infection is attached. Then the dimensions of the cavities increase or new ones appear.

A focus of inflammation occurs around the cavities. Relapses are accompanied by increased body temperature and intoxication of the body. The patient's condition worsens, tk. he is tormented by coughing and shortness of breath. The secretion separated by the bronchi becomes purulent. The phlegm has an unpleasant odor.
The risk of pulmonary bleeding increases. With exacerbations, Koch's sticks can enter the respiratory tract. As a source of infection, the patient poses a threat to others.
The patient's appearance deteriorates. He is losing weight dramatically due to poor appetite. The skin darkens and dries, and the back muscles atrophy.
Diagnostic measures
Before the detection of the disease, patients are most often already registered with a phthisiatrician. The anamnesis contains information about tuberculosis. Sometimes the disease is detected after fluorography, carried out for prophylaxis.
If there is a suspicion of tuberculosis infection, an additional examination is prescribed. The person is sent for a lung x-ray. In the presence of localized shadows, cavernous tuberculosis is diagnosed. They are round or oval in shape.
Important information: Features of the treatment of different forms of disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis
Subsequent diagnostic measures are necessary to clarify the diagnosis.
It is worth differentiating the disease from:
- lung cancer;
- abscess;
- bullous emphysema;
- echinococcosis, etc.
Further, the research results are obtained. Most often, general and biochemical blood tests are performed. Bronchial secretion is taken for bacterial culture and cytology. An analysis is required for the sensitivity of mycobacteria to anti-tuberculosis drugs.
With a weak separation of the secret, difficulties arise. Therefore, a bronchoscopy may be prescribed, which allows you to take sputum for research and see changes in the bronchi. They prevent the caverns from closing.
According to doctors, tests may not give an accurate result. For example, such as tuberculin tests.
Basic principles of treatment
To cure cavernous tuberculosis, a number of recommendations must be followed. We must not forget about them both in the period of exacerbation and improvement.
Recommendations:
- Give up smoking.
- Engage in therapeutic and respiratory gymnastics.
- Take the prescribed medications, observing the time intervals.
- Walk more in the fresh air.
- Follow all the doctor's instructions regarding the treatment of the disease.
Physiotherapy
These procedures are in addition to the main treatment.
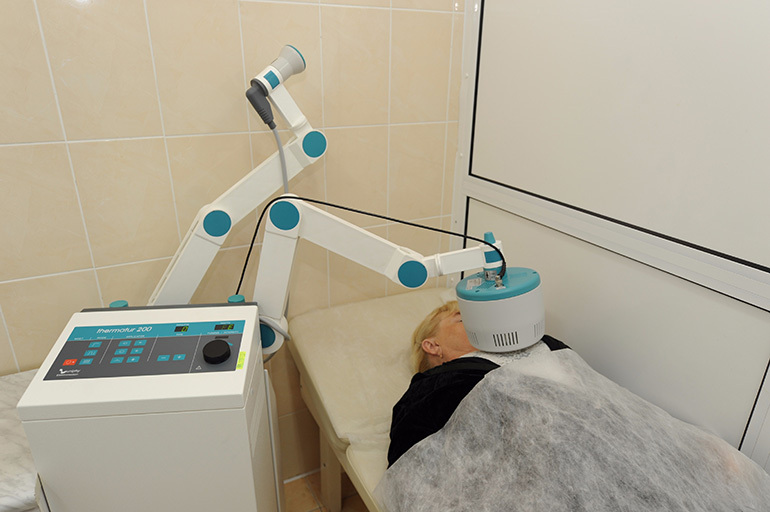
Inductothermy is a method of electrotherapy using a high-frequency alternating magnetic field. Its energy contributes to the appearance of vortex flows that turn into heat. The procedure has a powerful bacteriostatic effect.
Laser therapy is the use of the optical range. Its source is laser radiation. The luminous flux is characterized by a fixed wavelength. The effect of a laser on the body is the interaction of quantum particles and cellular biostructures.
Ultrasound - application of mechanical vibrations with a frequency of 20 kHz. The method has an anti-inflammatory and resorption effect, provides tissue micromassage. The procedure helps to increase immunity and detoxify the body.
Surgical intervention
If after 4-5 months conservative treatment does not help, surgery will be required. The abnormal cavity or part of the lung affected by tuberculosis is removed.
The radical method is resorted to in the absence of positive dynamics in the patient.
Chemotherapy
Special chemotherapy drugs with anti-tuberculosis action are prescribed. The most popular drugs are Ethambutol, Streptomycin, Rifampicin, and Isoniazid.
The duration of therapy is approximately 5-6 months. If the outcome is favorable, the caseous masses disappear. The caverns are closed, and the bacterial excretion stops.
Medicines and drugs
Tuberculosis is treated in a hospital. The therapy regimen depends on the neglect of the disease. At the initial stage, several drugs are used simultaneously.
To ensure the maximum concentration of the drug, it can be injected into the cavity itself, into the bronchi or intravenously. Medicines and their combination are selected by the doctor, based on the test results.
ethnoscience
Folk remedies cannot replace conservative treatment. They are just an addition. Due to tuberculosis, the human body is weakened. He needs more vitamins than a healthy one. It is advisable to regularly eat black currants, cranberries, viburnum, onions, cabbage and carrots.

Recovery Predictions
Most often, the disease responds well to treatment. Thanks to tuberculostatic therapy, small cavities are closed and scarred. If the caverns have rigid walls, after a while they are again filled with caseous formations. As a result, pseudotuberculoma develops.
Important information: The clinical picture of the development of tuberculous pleurisy in humans
A poor prognosis is rare. However, with inadequate treatment, there is a risk of suppuration, progression of tuberculosis and aspergillosis.
Rehabilitation and features of the body's recovery
Physical activity is important for accelerated recovery of the body. Walking long distances and outdoor work are especially helpful. It is necessary to increase the load on the body gradually.

It is necessary to take care of good nutrition after an infection. The diet should have enough vitamins and minerals. To improve immunity, it is recommended to use bee products. They help to comprehensively restore the body.
Consequences and possible complications
Initially, complications appear in the presence of concomitant diseases: bronchitis, other forms of tuberculosis and AIDS. Negative consequences are possible with weakened immunity and the presence of superinfection.
They are like this:
- Pulmonary hemorrhage is the most dangerous complication. If a cavity forms near a large blood vessel, it may even burst. The decaying tissues of the organ involve its wall in the process, and it becomes thinner. With a strong cough, the vessel bursts. Its size and location affect the severity of the condition.
- Pleural empyema is a complication associated with the proximity of the cavity to the lung. With the progression of the disease, the wall of the cavity collapses, and the contents enter the pleura. It is advisable not to allow such a serious condition.
- Tuberculous cachexia - irreversible exhaustion with advanced disease. Often fraught with death.
- Respiratory failure is a common cause of death. Develops in the later stages.
- Spontaneous pneumothorax is an increase in intrathoracic pressure that causes rupture of the pleura: an acute condition can lead to death. Urgent medical attention required.
- Pulmonary bronchiectasis - the occurrence of adhesions in the bronchi. They make it difficult to separate phlegm and breathe.
- Atelectasis is the cessation of the flow of oxygen from the bronchus to the lung. Part of the organ ceases to participate in gas exchange. Various microbes actively multiply in the affected segment.
- Amyloidosis is the deposition of protein compounds in blood vessels and between tissues of internal organs. Amyloid is not destroyed even by alkalis and acids.
Mycobacteria can end up in the stomach. With lymphatic or hematogenous spread, eye lesions occur. Weakened immunity increases the risk of fungal infections. Periodically, there are several complications at once, which complicate treatment.
Prevention methods
Knowing the causes of the disease, you can minimize the risk of its development.
Preventive measures:
- Do fluorography annually to identify pathological processes in the lungs.
- You should be attentive to your health and contact a phthisiatrician in the presence of the above signs.
- Vaccinate newborns in the first month of life.
- Isolate patients if they live in an apartment building or dormitory.
Prevention of a dangerous disease almost always brings a positive result. You cannot ignore the manifestations of the disease without consulting a doctor. It becomes chronic with the wrong treatment.