Content
- What is hematocrit
- Norms of hematocrit
- How is this indicator determined
- What do deviations mean?
- Causes of increased hematocrit
- Causes of low hematocrit
- Signs of deviations
- With increased rates
- With reduced rates
- What to do with high hematocrit?
- What to do with low hematocrit?
- Consequences, complications
- Video about hematocrit
When examining a blood test, attention is often paid to the number of erythrocytes, their sedimentation rate, and the ratio of leukocytes. Hematocrit, along with other elements, is an important indicator, it can be increased or decreased. The different degree of deviation from the norm in women depends on a number of reasons and may affect the health of the unborn child.
What is hematocrit
Blood is a liquid connective tissue composed of plasma and corpuscles that perform main functions in the human body: protective (leukocytes), hemostatic (platelets) and transport (erythrocytes). The latter not only carry oxygen and carbon dioxide, but also participate in cellular respiration and the removal of processed substances. Make up 90% of the amount of all elements.
Hematocrit (HTC) refers to the number of red blood cells to the total blood volume in the human body, expressed as a percentage (or liter per liter). The index is measured during the study of a general blood test.
The hematocrit is increased in women (the reasons for this lie in a change in the number of red blood cells or the volume of circulating blood) in the presence of diseases or short-term conditions that provoke this phenomenon.
Norms of hematocrit
The average indicator is in direct proportion to age, gender, professional activity, place of residence.
The following numbers are taken as the norm:
| Age | Gender | Rate of indicator in percent | Value in liters |
| Newborn | 40-67 | 0,40-0,67 | |
| Up to 1 year | 33-45 | 0,33-0,45 | |
| 1 to 5 years old | 36-41 | 0,36-0,41 | |
| 6-11 | 33-41 | 0,33-0,41 | |
| 12-17 | Boys | 35-45 | 0,35-0,45 |
| Girls | 34-41 | 0,34-0,41 | |
| Adults | Men | 36-46 | 0,36-0,46 |
| Women | 40-48 | 0,40-0,48 |
The maximum level is observed in infants, which is understandable from the point of view of physiology. As they grow older, the child's body is in constant development, which affects the hematopoietic system. Therefore, the indicators of adults and children are different.
An increase in the index of more than 55% indicates an increase in the number of blood cells, which is the basis for re-analysis and the appointment of a comprehensive examination to find out the cause.
If a deviation of the HTC level from the norm is detected, examinations are prescribed:
- Blood test: general, biochemical, for hormones.
- Analysis of urine.
- Ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal organs, genitourinary system and adrenal glands.
- ECHO-KG, electrocardiography.
- Kidney scintigraphy.
- MRI, CT if a tumor is suspected.
- Consultation with a gemologist.
How is this indicator determined
A blood test for hematocrit is performed routinely during clinical examination and in the presence of symptoms indicating a disease that affects the hematopoietic function of the body.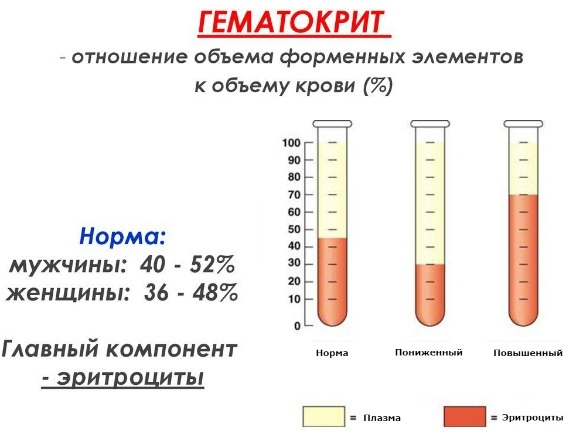
The study is carried out with:
- Diagnosis of anemia and polycythemia and assessment of the dynamics of treatment.
- Determination of the degree of dehydration.
- Deciding on the transfusion of blood components.
- Condition after blood transfusion.
- Infectious diseases in which it is important to prevent dehydration of the body.
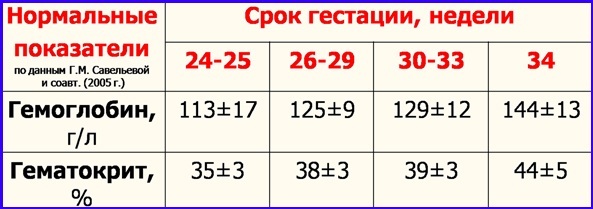
- Pregnancy. The hematocrit level is one of the main blood indicators during gestation and is determined in all three trimesters.
- Symptoms of rapid fatigue, weakness, dizziness, changes in skin and hair against the background of general health.
- Suspected latent bleeding.
When prescribing an analysis for hematocrit, the doctor takes into account the use of drugs that thin the blood (anticoagulants, non-steroidal analgesics).
You should refrain from analysis:
- During a viral illness or immediately after recovery.
- After menstruation or acute blood loss.
These conditions distort laboratory diagnostics.
Before taking an analysis, you should refrain from fast food and fatty foods, alcohol, exercise, stress for a day. The last meal should be 8-10 hours, and smoking should be 2 hours before the study.
The level of hematocrit is detected in a general blood test in the laboratory.
The process includes several stages:
- Taking biological material from the capillary of the third to fourth fingers of the hand or the ulnar vein.
- Placing it in sterile graduated tubes with the addition of an anticoagulant (heparin).
- Centrifugation for 1-2 hours.
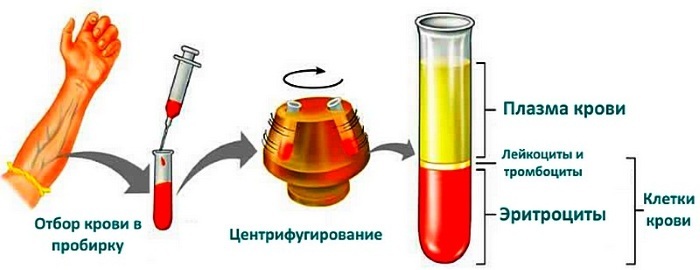 Under the action of centrifugal force, the blood settles in layers. Erythrocytes remain at the bottom, then a small layer of leukocytes and platelets, and the plasma is concentrated in the upper layer. The results of the study are interpreted by a hematologist. Then they are transferred to the attending physician. Nowadays, manual measurement is more often replaced by the use of an automatic analyzer.
Under the action of centrifugal force, the blood settles in layers. Erythrocytes remain at the bottom, then a small layer of leukocytes and platelets, and the plasma is concentrated in the upper layer. The results of the study are interpreted by a hematologist. Then they are transferred to the attending physician. Nowadays, manual measurement is more often replaced by the use of an automatic analyzer.
What do deviations mean?
With an increased hematocrit in the human body, there is an increase in the size of erythrocytes, their increased production in the cells of the red bone marrow. This is due to various factors that cause a malfunction in the compensatory reaction of the body.
The hematocrit is increased in women (the reasons may be of a physiological nature) and does not require specific treatment for short-term changes. Or, the reasons may be pathological in the presence of diseases that disrupt the work of the hematopoietic organs.
Causes of increased hematocrit
Abnormalities associated with physiological disorders:
- Dehydration of the body against the background of vomiting, diarrhea, prolonged exposure to the sun, increased sweating. In these conditions, the plasma from the vessels passes into the tissues, the volume of the formed elements increases. After eliminating the cause of the deviation, the blood composition is quickly restored.
- Diabetes. This disease is characterized by chronic tissue hypoxia, which stimulates the formation of red blood cells to provide additional oxygen to the body's cells and compensates for hypoxia.
- Smoking and staying at high altitude (mountaineering, rock climbing, frequent long flights, living in high mountain areas). In the first case, the consumption of oxygen by the tissues is reduced due to vasospasm under the influence of nicotine, in the second, the violation occurs due to the rarefaction of the air. The response mechanism of the hematopoietic system is the same as in diabetes.
- Professional sports. Increased loads affect the bronchopulmonary system, which causes a compensatory increase in the volume of shaped elements.
Diseases that cause disturbances in the ratio of blood cells to plasma are divided into 3 types:
- Contributing to a decrease in the amount of plasma:
- Inflammatory processes in the peritoneum: peritonitis.
- Burns affecting more than 15% of the body surface.
- Chronic impairment of pulmonary ventilation, bronchial asthma, pulmonary emphysema.
- Heart failure, decompensated defects.
- Ascites.
- Gestosis in the second half of pregnancy.
- Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
- Stimulating the formation of red blood cells:
- Diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands: tumors, hydronephrosis, polycystic.
- Anemia of various origins.
- Erythremia (Bakez's disease), in which the normal functioning of the bone marrow is impaired.
- Long-term treatment with glucocorticosteroids, diuretics.
- Poisoning with drugs.
- Malignant neoplasms of the circulatory system that cause an increase in cell formation: leukemia.
Other conditions:
- Erythrocytosis is characterized by an increase in hemoglobin levels up to 170 g / l and above.
- Internal bleeding.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Oncological diseases.
- Disruption of the endocrine system: increased androgen levels, climacteric syndrome.
- Age-related changes in the elderly.
- Profuse menses.
The hematocrit is increased in women (causes may be due to pregnancy) due to the following conditions:
- Failure in the digestive system.
- Frequent vomiting or diarrhea in the first trimester.
- Eating a lot of salty food.
- Abuse of iron supplements.
- Use of diuretics.
An increase in red blood cells leads to an increase in blood viscosity, a slowdown in blood flow, and a decrease in the supply of oxygen to tissues. Blood cells clump together, leading to the formation of blood clots.
In addition to weakness and fatigue, a pregnant woman complains about:
- Muscle pain.
- Bleeding gums.
- Hematomas.
- Cold limbs even in hot weather.
- Heaviness in the legs.
Causes of low hematocrit
A decrease in the percentage of formed elements below 25% is called erythropenia.
Diseases leading to this condition:
- Diseases in which the production of red blood cells is impaired: anemia, leukemia, renal paresis.
- Inflammation of the bladder: cystitis.
- Infectious pathology associated with intoxication of the body.
- Hemolysis in case of poisoning with plant poisons or chemical compounds.
- Hyperproteinemia in myeloma, Hodgkin's disease.
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to impaired absorption of iron.
- Damage to organs involved in the formation and purification of blood cells: bone marrow, liver, kidneys.
Other conditions:
- Fasting, adherence to diets lead to a deficiency of B vitamins and iron in the body, due to which erythropoiesis (the formation of red blood cells) slows down.
- Acute blood loss.
- Chronic bleeding with hemorrhoids.
- II and III trimester of pregnancy.
- Overhydration after intravenous infusion.
- Stay in immobility for a long time.
A decrease in the level of HTC is observed when protozoa are parasitized in the human intestine (Toxoplasma, dysentery amoeba) and helminths (opisthorchis, roundworm, echinococcus), which feed on blood and weaken erythrocytes. Sometimes a decrease in the index occurs after taking cytostatics and a course of chemotherapy.
In pregnant women, a decrease in hematocrit of up to 33% is observed, since there is an increase in the volume of fluid in the body by 35-50% due to the uteroplacental circle of blood circulation, while the number of formed elements increases by 15%. For a woman who is carrying a fetus, these values are the norm.
In addition, the decrease in the level of HTC is influenced by such factors as:
- Gestosis.
- Age under 18.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- The birth of children at a short interval.
- Anemia.
- Insufficient intake of iron from food.
A decrease in hematocrit below 30% contributes to the development of bleeding, premature birth and postpartum depression. This affects the formation of the fetus and leads to developmental pathologies.
Signs of deviations
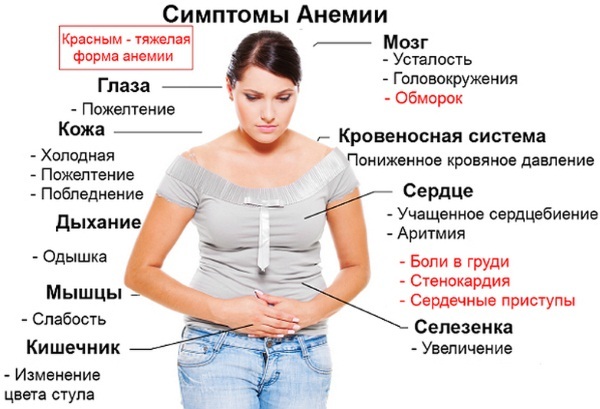
The cause of an increase in the level of hematocrit, as a rule, is a disease that affects the change in the composition of the blood. Some signs in women are specific, others are general (weakness, dizziness).
With increased rates
The following ailments are noted:
- Dizziness, headache.
- Weakness, fatigue.
- Deterioration of orientation in space.
- Feeling of numbness in the limbs and their swelling.
- Chest pain.
- The skin is pale, dry, itching is noted.
- Breathing is difficult.
- Thirst.
- Vomiting.
- Convulsive readiness.
- Decreased muscle tone.
With reduced rates
Symptoms manifest themselves:
- Dizziness.
- Shortness of breath.
- Tachycardia.
- Decreased performance.
- Constant headache.
- Hair loss, fragility, lack of shine.
Children tend to have faster progression of symptoms than adults.
What to do with high hematocrit?
Drug therapy is aimed at treating the underlying disease that caused the increase in hematocrit. It can be operational or conservative.

Additionally, the doctor prescribes:
- Medicines that thin the blood (anticoagulants) and prevent the adhesion of its elements (antiplatelet agents): cardiomagnet, aspirin, syncumar, courantil.
- Bloodletting up to 500 ml per day.
- Intravenous infusion with ringer, glucose, rheopolyglucin solutions.
Also contributes to the reduction:
- Avoiding drug abuse.
- Regular walks in the fresh air, ventilation of living and working spaces.
- Drinking enough fluids.
Increased hematocrit in women (causes are often corrected through dietary changes) is due to the use of inappropriate foods.
The daily menu should include foods that help thin the blood:
- Berries, fruits.
- Vegetables with red, orange, yellow fruits: tomatoes, zucchini, carrots, pumpkin.
- Fermented milk: kefir, cottage cheese, fermented baked milk.
- Vegetable oil: sunflower, corn, olive, sesame, linseed.
- Sunflower and pumpkin seeds.
- Nuts of any variety.
- Cereals: corn, millet, barley, rice, oats.
- Fatty fish: salmon, mackerel, tuna.
- Lean meat: turkey.
- Seafood and seaweed.
- Baking: rye bread.
- Sweets: honey.
- By-products: liver, kidneys.
- Drinks: decoctions of sage, hawthorn, water, juices.
It is not recommended to eat:
- Fruits: bananas, currants, mangoes.
- Dairy: whole milk, butter, cheese.
- Cereals: buckwheat.
- Legumes: peas, chickpeas, beans.
- Meat: goose, duck.
- Canned food, smoked meats.
- Mushrooms.
- Delicacies: caviar.
- Drinks: soda, coffee, black tea.
With care greens: parsley, dill, lettuce, spinach. All dishes are best prepared by boiling, stewing or steaming. Fried food is excluded from the diet.
What to do with low hematocrit?
When the level of hematocrit drops below 25%, a transfusion of blood or components is necessary in a hospital setting.
In the future, it is recommended:
- Identify the cause of the violation of the process of hematopoiesis.
- Eliminate the disease that led to the development of this condition.
- Take medications that promote the formation of erythrocytes: sorbifer durules, ferlatum fore, maltofer, gyno-tardiferon.
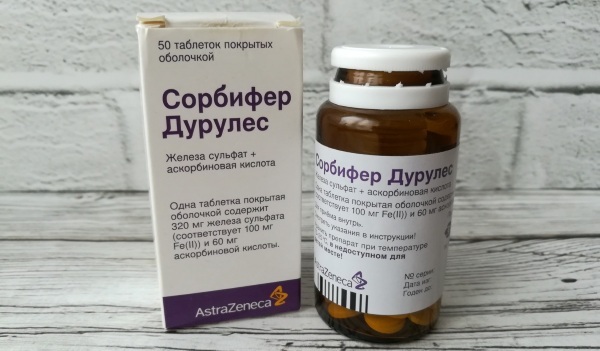
Sorbifer Durules - B vitamins: milgamma, folic acid.
- Control the amount of incoming and outgoing fluid.
- Normalize proper nutrition by including foods containing protein, iron and vitamin C.
- Exercise daily.
Treatment for mild to moderate disease can take place at home or in a day hospital. A severe course requires hospitalization.
The diet includes:
- Red meat and liver.
- Leafy vegetables: spinach, cabbage, parsley.
- Whole grain bran bread.
- Fish.
- Poultry meat.
- Chicken eggs.
- Legumes.
- Raisins, prunes, dried apricots, dates, apples.
- Sturgeon caviar.
- Vegetables and fruits rich in vitamin C: tomatoes, citrus fruits, broccoli.
Consequences, complications
An increase in hematocrit is a secondary manifestation of a malfunction of the body and signals diseases that can cause blood clots. With an index of 60-70%, there is a tendency to form blood clots.
This contributes to the development of:
- Heart attack.
- Ischemic stroke.
- Acute respiratory failure.
- Gangrene of the limb and its amputation.
When carrying a pregnancy, high levels lead to:
- Severe hypoxia, leading to fetal retention in the womb.
- Intrauterine fetal death.
After birth, the child has an increased excitability of his nervous system, disruption of the cardiovascular system.
A decrease in the number of red blood cells leads to a disruption in the supply of oxygen to the tissues of the body, especially the brain. This leads to a decrease in attention, memory impairment, and rapid fatigability. If this condition lasts long enough, it leads to diseases of the cardiovascular, excretory systems and disruption of the liver.
In pregnant women, low HTC levels lead to:
- Hypotension.
- Strengthening toxicosis.
- Weak labor.
The accumulation of carbon dioxide in the cells of a pregnant woman provokes:
- Miscarriage or missed pregnancy.
- Gestosis with edema, increased blood pressure, loss of protein in the urine, seizures and loss of consciousness.
- Fetoplacental insufficiency, leading to impaired placental circulation.
- Placental abruption.
- Premature birth.
Maternal anemia causes impaired fetal development and leads to:
- Intrauterine growth retardation.
- Weight loss.
- Underdevelopment of the cerebral cortex.
- Weak immunity.
For a balanced ratio of red blood cells in the total blood volume, it is necessary to adhere to some principles:
- Sports activities and an active lifestyle.
- Quitting smoking and alcohol.
- Balanced diet: the ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
- Drinking plenty of fluids and monitoring salt intake.
- Eliminating the influence of stress on the emotional state.
- Refusal of self-medication.
- Dispensary observation once a year.
Deviation of the hematocrit from normal values, both upward and downward, leads to the development of serious health complications in women and children. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of disturbances in the functioning of the hematopoietic system and changing lifestyle and nutrition. With the timely detection of pathology, the prognosis in most cases is favorable.
Video about hematocrit
What is hematocrit: