Content
- Types of bronchitis and causes of development in adults
- Acute and chronic bronchitis
- Catarrhal and purulent
- Obstructive and non-obstructive
- Symptoms of bronchial inflammation
- In acute course
- With chronic course
- Is there always a cough with inflammation of the bronchi?
- Is there always a temperature?
- Features of the course of the disease without fever
- Diagnosis of the disease
- Physical examination
- Clinical blood test with expanded leukocyte count
- X-ray
- Bronchoscopy
- Sputum examination
- Methods for the treatment of inflammatory processes in the bronchi
- Antibacterial therapy
- Suppression of the mechanisms of development of the disease
- Symptomatic therapy
- Physiotherapy
- Groups of drugs for home treatment, dosage regimens
- Expectorants
- Mucolytics
- Antipyretic
- Antiviral
- Antibiotics
- Features and treatment regimens for bronchitis in adults
- Acute bronchitis treatment
- Chronic bronchitis treatment
- Asthmatic bronchitis treatment
- Obstructive bronchitis treatment
- Complications of bronchitis
- Videos about bronchitis
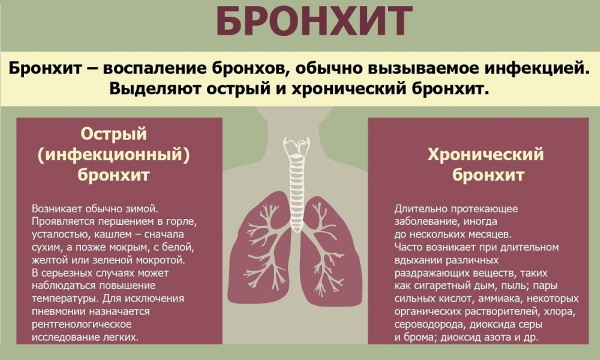
Inflammation of the bronchi
- a disease of the respiratory system, often developing in adults. Pathology is accompanied by an inflammatory process of the tissues of the organ. Symptoms appear in patients with an acute or chronic form of the disease, which depends on the characteristics of its course and the presence of complications.Types of bronchitis and causes of development in adults
Bronchitis is an inflammatory disease of the bronchi that develops as a result of exposure to external and internal factors, accompanied by various negative manifestations of the respiratory systems. There are many reasons for the development of pathology. Depending on the type of disease, provoking factors may differ.
Acute and chronic bronchitis
An acute condition develops suddenly, is accompanied by pronounced disorders of the bronchi, worsens the general condition. The chronic form of the pathological condition develops in the absence of therapy in the acute stage. At the same time, all symptoms appear in a mild form, many of them are absent.
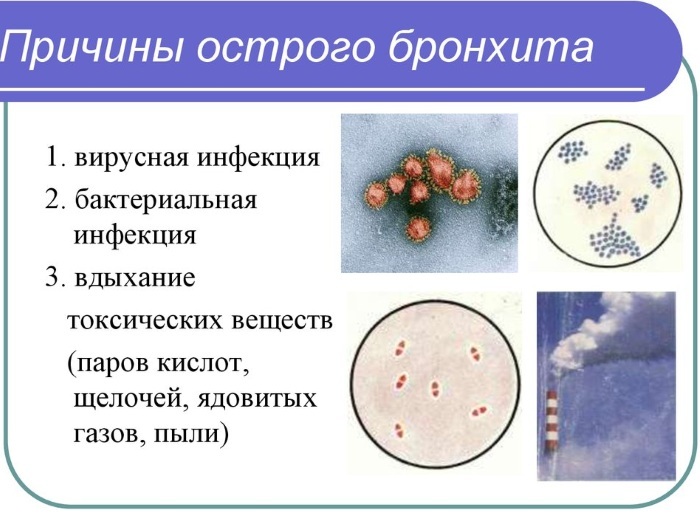
The main reasons for the development of acute and chronic forms of bronchitis:
- Frequent hypothermia of the body.
- Decreased immunity.
- Colds and viral pathologies that develop in the patient more often than usual.
- Unbalanced diet with a deficiency of vitamins and minerals.
- Smoking for many years.
- Poisoning of the body with toxic substances.
- The presence of chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract.
- Professional activity in which the patient is forced to regularly inhale dust.
 These and some other factors can provoke an acute pathology, and the lack of therapy or frequent recurrence of the disease leads to a chronic course of the inflammatory process.
These and some other factors can provoke an acute pathology, and the lack of therapy or frequent recurrence of the disease leads to a chronic course of the inflammatory process.
Catarrhal and purulent
Inflammation of the bronchi (symptoms in adults may not appear immediately after the development of an inflammatory process) in a catarrhal form is accompanied by acute tissue damage, but the absence of bacterial process. The main cause of such inflammation is considered to be the penetration of viruses into tissues, as well as their spread over large areas.
The purulent form of bronchitis in most cases is provoked by pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate the respiratory tract. They multiply on the surface of tissues and lead to the formation of a large amount of pus. This condition is usually accompanied by severe disturbances from other organs. Concomitant provoking factors are considered to be colds, as well as a weakening of the immune system.
Obstructive and non-obstructive
Obstructive bronchitis develops when there is a change in the tissues of the bronchi and a narrowing of the lumen. The main reason for this type of violation is the lack of timely treatment of an acute condition. This leads to tissue changes. The presence of other chronic pathologies of the respiratory system, for example, bronchial asthma, is considered a predisposing factor. The non-obstructive form of the disorder is not accompanied by tissue changes and narrowing of the lumen.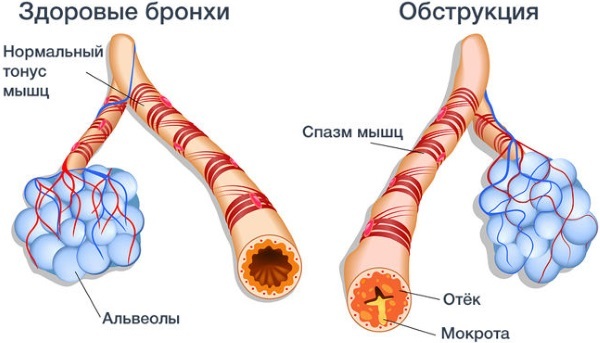
The reason may be:
- cold;
- viral lesion;
- penetration of bacteria.
The absence of obstructive changes can shorten the recovery period.
Symptoms of bronchial inflammation
In different patients, the pathological condition manifests itself in different symptoms. Depending on the type of disease, the clinical picture may differ.
In acute course
The acute course of the disorder is accompanied by various symptoms that affect not only the respiratory system.
The most common manifestations are:
- Increase in body temperature to high levels. Fever can persist for a long period of time.
- Joint and muscle pain, especially when moving.
- Disturbed night sleep, severe weakness and decreased performance.
- Deterioration or complete lack of appetite.
- Cough of various forms. Patients may be disturbed by dry or wet cough, which does not depend on the form of the pathological process.
- Sweating, discoloration of the skin. The skin becomes pale and moist to the touch, sweating is especially pronounced at night.
- Great thirst and dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth.
- Upset digestion and stool. These symptoms do not always appear, but they can be observed in patients with a tendency to such complications.
- Chest pain, shortness of breath and cough on exertion.

Cough is the main symptom of bronchial inflammation.
In the acute stage, the patient's mobility is significantly reduced. Most of the time, he is held in a horizontal position, refuses food, takes a lot of fluids. Despite this, urination becomes rare, which is associated with increased work of the sweat glands.
With chronic course
Inflammation of the bronchi in a chronic form may be less pronounced. Symptoms of this type of disorder in adults may not appear immediately, but several days after the onset of the pathological process.
The body temperature rises slightly, the cough is mild or absent. The patient retains appetite, but worsens somewhat. Thirst is not the main symptom. Since fever is not observed, there are no complications from the musculoskeletal system in the form of pain and severe weakness.
For a long period, the patient can lead a normal lifestyle, which only aggravates the condition and leads to the spread of the focus of inflammation to healthy tissues. Cough in the chronic course of the disease can be rare, without phlegm. The skin changes slightly, but dark circles under the eyes often appear.
Is there always a cough with inflammation of the bronchi?
When diagnosing the inflammatory process of bronchial tissue, cough does not always develop in patients, but in most cases. For several days or even 2 weeks after the onset of the development of pathology, such a symptom may be absent. However, with the aggravation of the symptoms, a cough necessarily appears, since sputum accumulates in different quantities on the inner surface of the bronchi.
Is there always a temperature?
In the acute course of the violation, an increase in temperature is always observed. The degree of increase differs in different patients, depending on the characteristics of the course of the inflammatory process.
With a chronic, obstructive and non-obstructive type of lesion, the absence of hyperthermia is possible, which only complicates the diagnosis.
Features of the course of the disease without fever
If the patient does not have an elevated body temperature, the diagnosis of the disease is complicated. The disease is more easily tolerated, there is no pain in muscles and joints, but there is severe weakness.
The patient does not go to the doctor as there are no symptoms of fever. Appetite may be slightly impaired, there is thirst, coughing and chest discomfort during breathing and exertion. The cough can be dry or moist. The patient can be treated in a hospital, since there are no acute symptoms and complications in most cases.
Diagnosis of the disease
Inflammation of the bronchi (symptoms in adults can significantly worsen the general condition) in some cases manifests itself in a fine-tuned form, therefore, several diagnostic methods are required.
Physical examination
This type of diagnosis includes a set of special measures that involve listening to the patient's complaints, examining the skin. A mandatory stage of the examination is listening to the bronchi and lungs to determine the degree of tissue damage.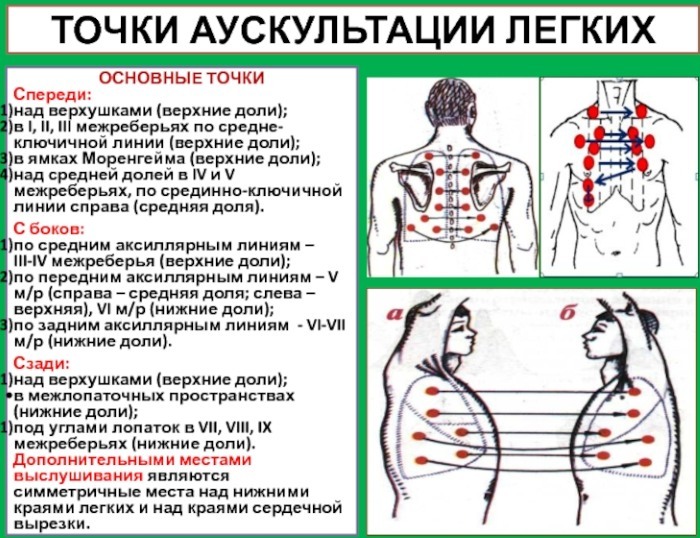
The specialist may note hard breathing or even wheezing if the condition is severe. This diagnosis is considered an important step. Based on the data obtained during it, a scheme for further examination is determined.
Clinical blood test with expanded leukocyte count
Another standard and one of the most important methods for diagnosing the inflammatory process, involving the collection of blood from the patient from a vein or finger, followed by poisoning it in a laboratory for research.
With standard diagnostics, only the number of erythrocytes, platelets and the total number of leukocytes is determined. But with a detailed diagnosis, it is required to determine the number of different types of leukocytes, that is, neutrophils and other cells. Changing the level of a particular cell type helps determine the type of inflammatory process.
X-ray
An effective method that involves studying the patient's bronchi using an X-ray machine. The picture shows pathological changes, the degree of their distribution and the presence of concomitant complications.
The procedure does not require special preparation, it is carried out quickly, and the result can be obtained within 1 hour.
Bronchoscopy
A minimally invasive diagnostic method, in which pathological changes in the tissues of the bronchi can be seen with the help of a special bronchoscope device. The procedure does not require special preparation, it is quite painful, so it is possible to use sprays with anesthetic properties.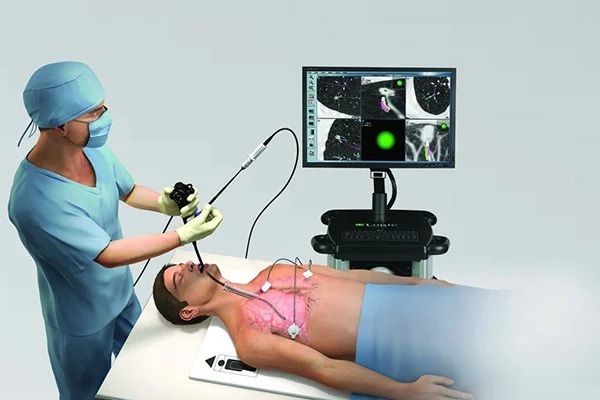
The manipulation is performed on an outpatient basis or in a hospital, depending on the course of the patient's pathology. During bronchoscopy, it is possible to collect a small amount of tissue for histological examination. But this is not always done, only if there is evidence.
Sputum examination
An additional diagnostic method, in which the patient collects sputum, which is released when coughing, into a special sterile container. In laboratory conditions, a specialist determines the causative agent of the inflammatory process in order to choose the most effective treatment.
Thanks to this method, you can quickly eliminate the symptoms of the violation. The use of drugs without identifying the type of pathogen only aggravates the symptoms.
Methods for the treatment of inflammatory processes in the bronchi
Inflammation of the bronchi (symptoms in adults are often accompanied by various complications) is often treated with medication.
Antibacterial therapy
Today, antibiotic therapy is considered the most effective way to eliminate the signs of an acute inflammatory process. But antibiotics are used only when the bacterial origin of the disease is confirmed during the diagnosis.
With a viral infection, the funds are ineffective, but often aggravate the symptoms of the condition. In severe obstructive or chronic inflammation, antibiotics can also be used, but strictly as directed, if other methods do not help improve the condition. Most often, patients are prescribed cephalosporins, drugs from the new generation penicillin group.
Suppression of the mechanisms of development of the disease
To suppress the mechanism of development of the pathological process, it is important to identify the root cause. It can be bacterial, viral, toxic. Depending on the provoking factor, suppression will require the appointment of antiviral, antibacterial, mucolytic drugs.
Without preliminary examination, the use of any medication can only worsen the patient's condition.
Symptomatic therapy
Symptomatic therapy is considered a prerequisite for therapy. It involves the appointment of expectorants for coughing, antipyretic for fever. The use of drugs to improve the condition of the digestive tract is often required.
The scheme of symptomatic treatment is also determined individually, since additional symptoms may be different in patients.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy treatment is usually carried out with a chronic form of pathology. In the acute stage, manipulations are not carried out, since the condition may worsen, but after the relief of acute manifestations, various methods can be used.
| Method | Peculiarities |
| Electrophoresis | Usually, in therapy, not only an electrophoresis device is used, but also medicinal solutions. They are selected individually for patients and help to speed up the process of tissue repair. |
| Inhalation | Inhalation is carried out in a hospital using a nebulizer. Patients are prescribed procedures with bronchodilators and even hormonal medications |
| UHF therapy | The use of a device with special radiation also has a positive effect on the condition of the bronchi and accelerates their recovery. |
Physiotherapy is carried out over a long period, but the number of manipulations for each patient may be different.
Groups of drugs for home treatment, dosage regimens
Despite the different course of the pathological process in patients, almost always doctors prescribe drugs from certain groups.
Expectorants
Drugs with expectorant properties help to improve the condition of patients and prevent the aggravation of the symptoms of the disease.
The most effective medications are:
-
Pertussin is a syrup based on thyme extract. It has expectorant properties. Syrup is taken orally in a dosage prescribed by a specialist. Usually, the drug is taken in courses of 10-14 days with daily use of 15 ml of syrup 3 times a day.

- Linkas available as an oral syrup. It is taken orally, 10 ml 2-3 times a day, and the therapeutic course lasts at least 7 days.
- Codelac Broncho with thyme is also available as a syrup for oral administration. The drug has expectorant properties. The remedy is taken in courses of 10-14 days. The dosage for the patient is 10 ml, the syrup is taken 3-4 times a day, depending on the severity of the manifestations.
The drugs are used only as directed, combined with other agents to increase the effectiveness of treatment.
Mucolytics
Means from the group of mucolytics are also considered effective, but they help not only to improve sputum discharge, but also lead to its liquefaction, which has a positive effect on the course of the disease and prevents the development of stagnation in bronchi.
Most effective mucolytics:
- Ambroxol in the form of tablets are taken in courses of 7-10 days. The tool has mucolytic properties. The daily dosage for the patient ranges from 3-6 tablets, is determined individually, depending on the severity of manifestations.
- Bromhexine in tablet form, they are also used in courses of 10 days. The product contains the active ingredient of the same name and helps to significantly improve the condition. Tablets are taken 1-2 pieces 2-3 times a day.
- Mucolic is a mucolytic agent based on carbocysteine. It is produced in the form of a syrup and is considered effective. Take it in courses of 5-10 days. A single dosage for a patient is 15 ml, it is taken 3 times a day.
- Lazolvan is considered the most popular mucolytic agent with pronounced properties. For adults, it is prescribed in pill form. A single dosage is 1-2 tablets, and they are taken 2-3 times a day. The therapy lasts up to 10 days.
Any mucolytic agent should be prescribed by a doctor after examination.
Antipyretic
Inflammation of the bronchi (symptoms in adults can be accompanied by a significant increase in body temperature) in an acute form requires the appointment of antipyretic medications. Most often in this case, Paracetamol and Ibuprofen are prescribed.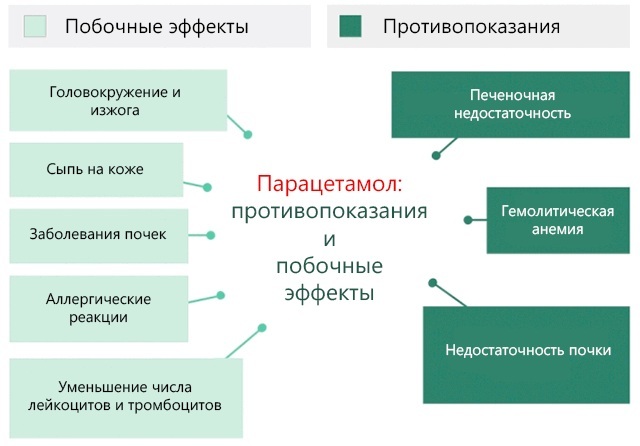
Paracetamol is taken 1 time in 4-6 hours, a single dosage for the patient is 500 mg. Ibuprofen is considered more effective, it acts for a long time, therefore, the reception is prescribed 1 time in 8 hours. A single dosage of the drug ranges from 1-2 tablets, depending on the patient's body.
Drugs from this group are allowed to be taken no longer than 3 days, but according to individual indications, therapy can be extended.
Antiviral
Antiviral medicines for bronchitis are prescribed only if the disease is provoked by viruses and the doctor established this during the diagnosis.
Most popular remedies:
- Kagocel has antiviral properties and is available in tablet form. Take it for 4 days. The first 2 days, take 2 tablets 3 times a day, for the next 2 days, the daily rate is 3 tablets, which are taken 1 piece during the day.
- Anaferon often prescribed due to high efficiency. Tablets are consumed in 3-6 pieces in bitches, depending on the neglect of the disease. The standard course duration does not exceed 7 days.
- Arbidol in tablet form is taken for 5-10 days. The daily dosage for an adult is 200 mg.
In the absence of symptoms of a viral disease, drugs from this group are not used.
Antibiotics
In the absence of complications, experts prescribe tableted antibacterial drugs; in case of a severe course of the disease, injections are indicated.
Most often, the following medications are used for bronchitis:
-
Augmentin prescribed as intravenous injection. The therapy regimen involves the introduction of 1 dose of the drug 2 times a day for 7-10 days.
- Ceftriaxone is considered more effective and is prescribed for severe violations. The daily dosage of the drug is 2-4 g. The agent is administered intravenously or intramuscularly 2 times a day after preliminary dissolution.
- Amoxicillin is also considered effective and can be used at home. The daily dosage is usually 2 tablets, and the duration of the course is 10-14 days.
Antibacterial drugs are selected strictly individually.
Features and treatment regimens for bronchitis in adults
Depending on the cause of the pathology and the presence of concomitant abnormalities in the patient, different treatment regimens can be used.
Acute bronchitis treatment
The acute form of bronchitis of bacterial origin requires the use of funds from different groups.
The standard therapy regimen involves the appointment of such medications:
- Ceftriaxone 1 g 2 times a day intravenously.
- Lazolvan 2 ml 2 times a day intravenously.
- Linex 1 capsule 2 times a day.
- Ibuprofen 1 tablet 2 times a day.
Depending on the accompanying symptoms, the doctor may add other agents to therapy.
Chronic bronchitis treatment
Therapy for this form of disorder differs little from the treatment regimen for acute inflammation. But antibiotics are prescribed less often, only when complications develop.
In addition to the treatment of chronic bronchitis, glucocorticosteroids, for example, Dexamethasone, may be added. The dosage is 4 mg, the solution is injected intramuscularly 2 times a day. In each case, the drugs and their dosage may vary.
Asthmatic bronchitis treatment
This form of pathology also requires the use of funds from different groups, but inhalations are considered the basis of therapy.
Standard scheme:
- Lazolvan - 2 ml intravenously 2 times a day.
- Paracetamol - 500 mg 2-4 times a day.
- Inhalation with Berodual 1-2 times a day for 10 minutes.
- Inhalation with Pulmicort 1-2 times a day.
For inhalation, a nebulizer is used, and treatment is usually carried out in a hospital.
Obstructive bronchitis treatment
Therapy for obstructive bronchitis is carried out according to the standard scheme, which is used in the treatment of acute inflammation. In addition to the main treatment, inhalation is done with the use of a nebulizer and drugs to expand the bronchi.
The most popular remedy is Berodual. In each case, the seme of the treatment of the disease may be different.
Complications of bronchitis
If untreated, the disease can become chronic, which is considered the most common complication.
Other consequences are possible:
- Purulent tissue inflammation.
- The transition of the inflammatory process to the lung tissue.
- Development of an abscess.
- Respiratory tissue damage.
- Indomitable cough.
- Bronchial asthma.
Complications can be prevented by timely treatment. Inflammation of the bronchi is today considered a common respiratory disease. Symptoms of pathology in adults differ depending on the type of inflammation and the presence of concomitant abnormalities.
Videos about bronchitis
How to distinguish bronchitis from a common cough: