Contents of the page
- 1 Coagulogram: what is it? Who is being prescribed coagulogram analysis?
- 3 Coagulogram indices
- 4 Decoding of blood coagulogram
- 5 Coagulogram in pregnancy
- 6 Rules for preparation for coagulogram
- 7 How is blood taken?
- 8 Where can I do the analysis?
Any doctor starts treatment of a patient only after collecting an anamnesis and a number of laboratory studies that allow you to make the correct diagnosis. Today, let's talk about a coagulogram - what kind of analysis is this, and in what cases is it prescribed? Coagulation is an important laboratory blood test that gives an idea of the development of the disease, allows you to make an accurate diagnosis and choose the best method of treatment.
Coagulogram: what is it?
Coagulogram( gemostaziogramma) is a special study that allows to determine the parameters of blood coagulability. In simple terms, it is an analysis that shows blood flowing well or badly. This study gives an idea of the state of hemostasis, and allows you to identify such conditions as hypo - or hypercoagulation.
Hypercoagulation( increased blood coagulability) indicates a risk of thrombus formation and development of such dangerous pathologies as thromboembolism or thrombosis.
These indicators are very important to consider when preparing for surgery and other medical manipulations. The result of the coagulogram helps to determine how the operation or process of delivery will pass, whether it will be possible to stop bleeding and save the patient in emergency situations, when the time count goes for seconds.
To whom is the coagulogram analysis assigned?

Doctors advise doing a clotting test before any surgery, but the coagulogram in pregnancy becomes especially important. For women bearing a child, this analysis is mandatory, during pregnancy, it is taken three times, which allows you to identify and eliminate a variety of problems in a timely manner, including a dangerous condition, such as placental abruption. In addition, indications for conducting a study on blood coagulability are the following conditions:
- severe course of gestosis in a pregnant woman;
- preparation for surgical interventions( including cesarean delivery and delivery);
- varicose veins and high risk of thrombosis;
- taking certain medications( hormones, anabolic, oral contraceptives) that affect blood coagulability;
- severe liver damage( cirrhosis);
- inflammatory processes in the body, taking place in an acute form;
- cardiovascular pathology, accompanied by a high risk of thrombosis( ischemic disease, atrial fibrillation);
A coagulogram is often prescribed to assess the general state of hemostasis, and is also used to monitor a patient's condition during therapy with anticoagulants - blood thinning medications.
About coagulogram it is worth considering with such anxious signs as bleeding, which is difficult to stop or frequent appearance on the body of hematomas, formed even in the absence of bruises. In addition, a coagulogram is recommended to be done if you plan to resort to such an alternative method as hirudotherapy( treatment with leeches).
Coagulogram indices
In the expanded form, the adult coagulation assay includes many indicators. Therefore, in practice, the study identifies the optimal set, which can be used to judge the coagulation properties of the blood.
- Coagulogram of PTI or prothrombin index. Just like PTV( prothrombin time), this value indicates for what period of time the blood clot forms at the injury site.
- Coagulogram of APTT( activated partial thrombin time) is an indicator by which one determines how quickly a fibrin clot appears. This is one of the most accurate and sensitive indicators, allowing to judge how effectively the plasma blood factors work. At the same time, shortening the APTT value will indicate an increase in coagulability and a risk of thrombosis, and lengthening - about hypocoagulation and the probability of bleeding.
- Plasma fibrinogen. This is a special protein, which at the final stage of coagulation of the blood plasma is converted into fibrin and provokes the formation of blood clots.
- Thrombin time( TB) - This indicates how much fibrin is formed from fibrinogen.
In addition, there are a number of advanced coagulogram indicators that help to pinpoint which part of the blood clotting system has failed. These include factors such as prothrombin time, bleeding time, antithrombin, plasma recalcification time, RFMK and other values.
In medical practice, resort to two types of coagulograms - basic and deployed. In the first, basic version, the study allows you to identify abnormalities in hemostasis, while an extended analysis gives an idea of the causes of such abnormalities, helps to make an accurate diagnosis and differentiate the disease from other pathologies with similar symptoms.
Decoding of blood coagulogram

A blood test for a coagulogram needs to be able to correctly read and analyze. Not every doctor knows the skills of decoding the indicators, only a highly qualified specialist can correctly assess and interpret these or other parameters of the hemostasiogram. The interpretation of the analysis consists in comparing the values obtained with the norm of the blood coagulogram.
So, when determining the time of blood coagulation, the normal value is up to 15 minutes. Exceeding this value indicates a deficiency of prothrombin and fibrinogen and is an expected consequence of the administration of anticoagulants.
The prothrombin index( PTI) is from 12 to 20 seconds. Elongation of this time indicates a failure in the synthesis of prothrombinase, prothrombin and fibrinogen. Such changes are accompanied by avitaminosis, chronic liver pathologies, impaired absorption processes in the intestine or are the result of the use of indirect anticoagulants. The indicator is expressed as a percentage. In a healthy person, it is at the level of 97-107%
. When determining APTT - the normal value is from 38 to 55 seconds. A decrease in this value indicates a risk of developing thrombosis, and lengthening indicates a congenital deficiency of clotting factors( hemophilia) or is observed with heparin therapy.
Fibrinogen - this enzyme is synthesized in the liver. A decrease in this indicator indicates the presence of such pathologies as avitaminosis, toxicosis of pregnant women, liver damage( hepatitis, cirrhosis).An increase in the value is observed at the initial stage of myocardial infarction, with inflammatory and infectious processes in the body, hypothyroidism or tissue necrosis.
Here's how the table looks like with the coagulogram indicators:
| Indicator name | Norm |
| Blood clotting time: · Mass and Margot norm; · the rule by Lee-White. | · from 8 to 12 minutes; · from 5 to 10 minutes. |
| Bleeding time: · Shichikova norm; · Duke norm; · Ivey rate. | · no more than 4 minutes; · from 2 to 4 minutes; · no more than 8 min. |
| International Normalized Ratio( INR or INR) | 0.82-1.18 |
| Thrombin time( TB) | 14-21 sec. |
| Prothrombin Index( PTI) | 73-122% |
| D-dimer | 250.10-500.55 ng / ml * |
| Prothrombin time( AS) | 11-15 seconds. |
| ACTTV | 22,5-35,5 sec. |
| Fibrinogen | 2,7-4,013 g / l |
In this case, the doctor must take into account that the coagulogram indicators in children and adults differ. Thus, the prothrombin time for preterm infants is 14 to 19 seconds, for full-term infants - 13 to 17 seconds, and in healthy older children 12 to 16 seconds.
The indices of antithrombin III( physiological anticoagulant) also depend on age. So, if the value of 40-80% is considered normal in newborn children, then in adolescents this figure should be between 80 and 120%, and in adults it should be between 75 and 125%.
For a full assessment of clotting factors, a specialist should study at least 13 indicators, including taking into account the expanded components of the coagulogram. Additional indicators allow you to more accurately see the picture of the disease, put the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Coagulogram in pregnancy

During pregnancy, the woman's body is reconstructed, preparing for the upcoming maternity. The changes concern the system of hemostasis, which is caused by hormonal reorganization and the appearance of an additional uterine-placental circle of blood circulation.
During this period, coagulogram results usually show an increase in the activity of clotting factors and an increase in the fibrinogen index. At the same time fragments of fibrin are deposited on the walls of vessels of an additional circle of blood circulation, and suppression of fibrinolysis processes occurs, which prevents the formation of thrombi and placental abruption. Due to these changes, the woman's body is safe from the risk of developing uterine bleeding and miscarriage.
In pathological pregnancy and manifestations of gestosis, there is a violation of the regulation of blood coagulability. If you do not start timely treatment, it is possible to develop a dangerous complication - ICE - a syndrome. Its development is accompanied by the formation of many small thrombi and a violation of the blood supply to the fetus. In severe cases, uterine bleeding occurs, which leads to fetal death and threatens the life of a woman.
Rules for preparation for the coagulogram
It is necessary to prepare correctly for the delivery of an important analysis. The basic rules of training should be explained by the attending physician. They are included in the following:
- on the eve of the test, it is necessary to refuse to take heavy, fatty foods, to exclude any alcoholic beverages;
- in the evening allowed a light dinner, for example, stewed vegetables with a piece of boiled dietary meat;
- blood for analysis is taken in the morning, on an empty stomach;
- Do not smoke, drink tea or coffee before taking the material;
- for 20 minutes before entering the treatment room you can drink 200ml of ordinary drinking water;
If the patient is being treated with anticoagulants, before taking the test, stop taking them to avoid distortion of the results of the hemostasiogram. In cases where the reception of such drugs is a vital necessity, it is necessary to warn the lab technician about this, who will perform the analysis.
H should donate blood on the background of overwork, stressful situations. A few days before the material is withdrawn it is necessary to refrain from taking any medications. With intolerance of the type of blood, severe dizziness, fainting, you need to warn the lab technician about it. In this case, when taking blood, the patient is placed on the couch.
How is blood taken?
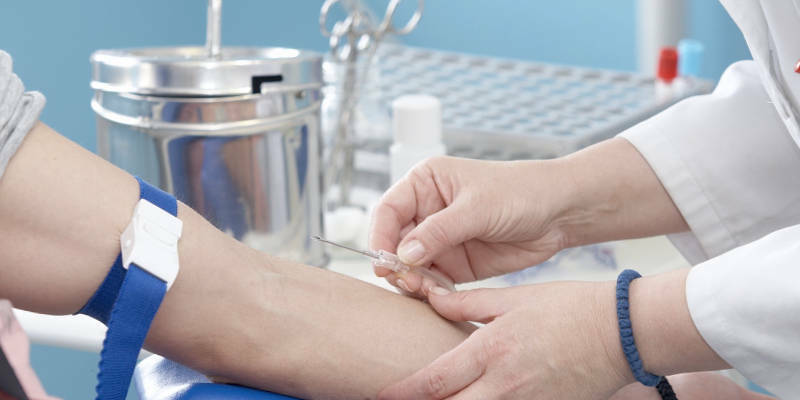
The material for analysis is taken from the vein, with a dry sterile syringe without harness. The syringe should be equipped with a needle with a wide opening. The puncture of the vein should be as less as possible traumatic, otherwise a pre-prepared tube with a special coagulant will get a lot of tissue thromboplastin, which can eventually distort the result of the coagulogram. After blood sampling, the laboratory worker fills 2 tubes with a material and sends one of them to the study.
Where can I do the analysis?
A standard analysis can be done at any state polyclinic, the laboratory of which has the necessary reagents for the study. Extended coagulogram in most cases can be done only in paid medical centers. This is a rather complex research, requiring highly qualified laboratory technicians. As a rule, the results of the analysis will be ready for two days.
The price to be paid for the study largely depends on the number of parameters that need to be determined when carrying out hemostasiograms, and varies from 2000 to 3500 rubles.