Content
- Characteristics of the pathogen
- Stages and degrees
- Infection
- The development of chickenpox
- Final stage
- Pathogenesis and routes of infection
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Diagnostics
- Treatment methods
- Drug therapy
- Rinses
- Homeopathic treatment
- Traditional methods of treatment
- Possible consequences and complications
- Chickenpox video
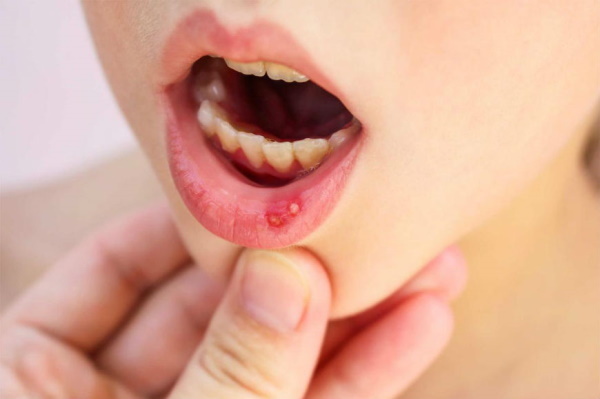
Infectious disease common in childhood chickenpox disease (in the common people - chickenpox) has a viral nature of occurrence. The pathological process is sometimes localized in the mouth, affecting the epithelial tissues. The photo clearly shows the characteristic bubble eruption.
Characteristics of the pathogen
With chickenpox, generalized intoxication of the body develops. The causative agent of the disease is Varicella-Zoster, classified as type III herpevirus. Chickenpox is considered the most common infectious pathology. The virus belongs to the category of DNA-containing.
It is characterized by low resistance to environmental conditions and the ability to replicate exclusively in the human body. The pathogenic agent is inactivated within 14-21 days.
The process is accelerated by:
- antiseptic treatment of the affected mucous membrane;
- exposure to sunlight;
- targeted ultraviolet irradiation;
- the effect of high temperature on viral particles;
- drying of exudate secreting in vesicle papules.
Chickenpox in the mouth, a photo of which allows you to consider the zones of an infectious lesion, is localized less often than on the surface of the skin of the body. About 70-90% of the world's population carries a viral disease before the age of 15.
Stages and degrees
The infectious agent that provokes chickenpox is highly contagious - the ability to be transmitted from an infected organism to a healthy one. Therefore, the incidence in large cities is higher than in small settlements and rural areas.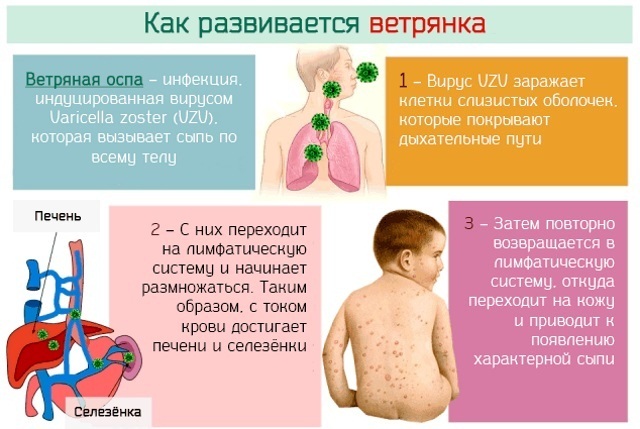
The peak of infection occurs in the autumn-winter season, when there is an increased activity of the Varicella-Zoster virus. The pathological process develops according to the standard scenario in all cases. The incubation period is divided into 3 stages, each with its own clinical characteristics.
Infection
The phase begins from the moment of close contact with the virus carrier. The infectious agent enters the respiratory tract and actively replicates, expanding the area of damage to the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and dental space.
Typical localization areas:
- surface of the tongue;
- inner side of the lips;
- soft tissues of the palate;
- gingival structures;
- inner planes of the cheeks;
- hard areas of the palatine surface.
At the stage of infection, some viral agents neutralize immunocompetent cells by phagocytosis - absorption and digestion of hostile elements. The amount of pathogenic particles eliminated depends on the state of the patient's defense mechanism.
The development of chickenpox
The stage is characterized by the adaptation of the pathogen, the activation of replication, the capture of new areas of the oral cavity. Bubble papules filled with pathological exudate are formed.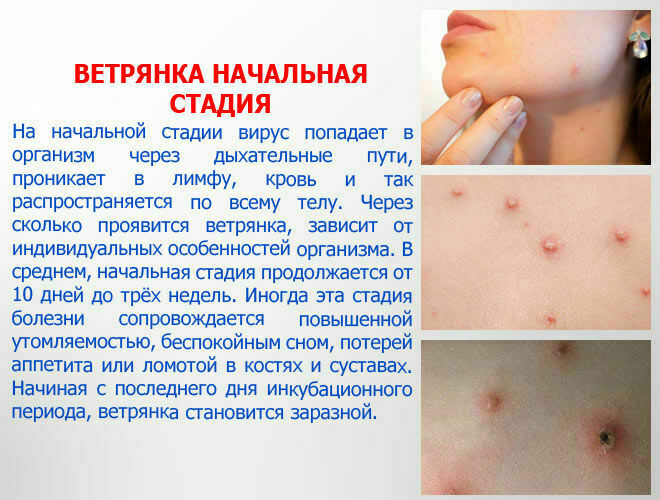
Their contents serve as a breeding ground for the herpes virus and accelerates its reproduction. There is an infectious lesion of the lymph nodes and the penetration of a pathogenic agent into the lower parts of the respiratory system.
Final stage
The herpetic virus moves along the bloodstream to the epithelial membranes and soft tissues of internal organs. A high concentration of disease-causing particles in them causes functional disorders of varying severity.
At this stage of the disease, the active production of antibodies by the immune system is recorded. The virus is spreading rapidly. Any close contact with other people leads to their infection.
In the final stage of the disease, a lifelong persistent immunity to chickenpox is formed. Re-infection cases are rare, their number is negligible.
Pathogenesis and routes of infection
The Varicella-Zoster virus enters the respiratory canals and concentrates in the epithelial cells of their walls. In the future, it spreads in the body through the systemic circulation with damage to the regional lymphatic plexus.
Ways of transmission of the pathogen of chickenpox:
- Aerosol, called airborne droplets. The most common way. Virions are released into the surrounding space with sneezing, coughing and respiratory microscopic suspension.
- Contact and household. Due to the low resistance of the pathogen to environmental conditions, this method of infection is difficult to implement and unlikely. The contact-household variant of infection provides for 2 ways of transmission - through intermediate surfaces and objects, or through direct bodily contact from burst papules. The likelihood of infection by both methods is negligible due to the special biological characteristics of the pathogen.
- Transplacental. In clinical practice, cases of infection of a pregnant woman carrying a fetus have been recorded. The ability of herpes viruses to cross the placental barrier has been proven. Such cases are not common. In the first 14 weeks, the probability of infection is 0.4% and rises to 1% by 5 months.
Chickenpox in the mouth (a photo of an infectious pathology makes it possible to consider papules in detail) is often observed due to the biological relationship of the pathogen to the epithelial tissues.
The introduction of pathogenic particles causes the death of the cellular structures of the mucous membrane. The dead elements are replaced by the characteristic vesicular papules filled with inflammatory exudate.
On the epithelial cover of dental tissues, vesicles rapidly progress to noticeable erosional destruction. There is a phenomenon of latent virus carriage, in which pathogenic particles are concentrated in nerve tissues and lymphatic plexuses.
Symptoms and Signs
A blistering rash in the mouth forms within 7 days after infection. Vesicles spread to the epithelial covering of the larynx, tonsils, and the inner surface of the cheeks.
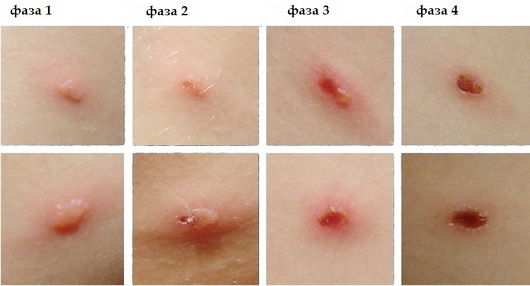
Papules have a distinctive appearance and are obvious visual signs of viral infection. Pathological formations filled with exudate are distinguished by a bright red color, characteristic of the inflammatory process.
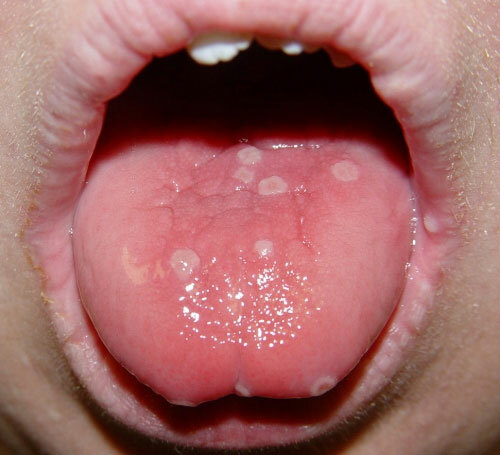
Numerous vesicles are covered with a thin film and are small in size.
Of the characteristic symptoms stand out:
- deterioration in general physical condition, which is due to suppression of the immune system;
- lethargy;
- apathetic behavior;
- lack of appetite;
- fever with high viral load;
- chills;
- hyperthermia;
- pain in the mouth and respiratory tract;
- difficult swallowing function.
Body temperature can rise to 38.5 ° C and be accompanied by headaches. With complicated chickenpox, antipyretic drugs do not always give the expected therapeutic effect.
Typical symptoms and noticeable external signs are determined by:
- the speed of the incubation period of the pathogen;
- the general state of the patient's immune system;
- the presence of concomitant diseases;
- physiological characteristics of the body.
Children are characterized by a weak severity or complete absence of prodromal phenomena - pathological events between infection and the active stage. Adults carry the disease more severely.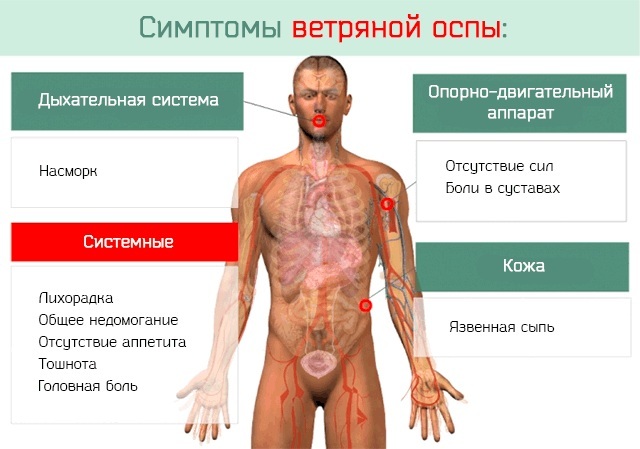
In adult patients, headaches of high intensity and duration, joint aches are possible. The general intoxication syndrome is manifested by nausea and activation of the gag reflex.
The epithelial covering around each vesicle is hyperemic, there is swelling of the soft tissues. After a few days of the infectious process, the color, consistency and chemical composition of the exudate change.
It takes on a yellowish tint. Vesicles do not have a clear distribution pattern in the oral cavity. The development of each can be at a different stage - some are bursting, others are just being formed.
Due to the high humidity and acidity in the oral cavity, seals do not appear, as on the skin. Eroded areas of the epithelium are quickly tightened with new tissues.
Causes
With an uncomplicated course of a viral disease, a bubble rash appears only on the skin. Localization of vesicles in the epithelial membrane of the dental zone is observed with increased aggressiveness of the pathogenic agent against the background of weakened immunity.
Chickenpox in the mouth appears with concomitant chronic diseases. A photo of patients with such anamnesis demonstrates multiple lesions of the mucous membrane. The etiological factors in adolescence include hormonal instability.
Vitamin starvation, deficiency of essential amino acids and trace elements increase the likelihood of infection of the oral cavity with herpes virus type 3.
Common causes are:
- dental infections of a fungal and bacterial nature;
- diabetes;
- hematological disorders;
- taking antibiotics, cytostatic drugs and glucocorticosteroid hormones.
The risk group includes patients with progressive carious pathology, anatomical destruction and chronic diseases of the upper respiratory system.
A specific cause of an infectious lesion of the oral cavity is the increased vulnerability of the mucous membrane in comparison with the skin. The epithelium is much thinner, equipped with a large number of nerve receptors and small blood vessels.
Diagnostics
Chickenpox is determined by visual examination. The characteristic clinical picture is difficult to confuse with the symptoms of another infectious disease. Additional diagnostics are not required in most cases.
The general laboratory hematological test for infection with the Varicella-Zoster virus is nonspecific. In the analysis of blood, an accelerated reaction of erythrocyte sedimentation is recorded, which is characteristic of any inflammatory process.
Therefore, it is impossible to associate a pathological change with chickenpox. Biochemical parameters of blood indicate general intoxication symptoms. In a particularly difficult clinical situation, a virological study of vesicular exudate is prescribed.
Such diagnostics provides for the detection of virions by an electromicroscopic method with silvering of the obtained biological material. Of retrospective significance is a serological study, which is carried out using the complement fixation reaction (CSC).
If you have a compulsory medical insurance policy, diagnostic measures in state medical institutions are carried out free of charge. In a private clinic or commercial laboratory in the Moscow region, a biochemical blood test will cost 900-1000 rubles. Virological and serological tests cost approximately 1300-1500 rubles.
Treatment methods
In the vast majority of cases, treatment of chickenpox is carried out on an outpatient basis. The disease does not require specific treatment. The patient is admitted to a hospital only when complications develop and an acute intoxication syndrome occurs.
There is no etiotropic therapy for infectious pathology. Treatment of vesicles localized in the oral cavity has an exclusively symptomatic focus and aims to reduce painful manifestations.
Drug therapy
When pustules appear (morphological rash with purulent contents), antibacterial medicines are used in a short course of administration in medium therapeutic doses. Patients with immune deficiency are prescribed antiviral drugs - Acyclovir, Vidarabin, Interferon and others.
The appointment of such drugs facilitates the course of the infectious process and reduces the likelihood of complications. Pregnant women are prescribed specific immunoglobulins that protect the embryo and reduce the general intoxication of the woman's body.
Chickenpox in the mouth, a photo of which allows you to notice inflammation of the tissues around the vesicles, is often associated with an increase in body temperature. It is advisable to use antipyretic drugs. Panadol is recommended for children - an effective and safe drug based on paracetamol.
The dosage is calculated according to the scheme of 20 mg of active substance per 1 kg of body weight. Panadol is taken as a tablet 3 times a day at regular intervals. The standard frequency of application for chickenpox is 3-5 days. For adults, you can take Nurofen, which can quickly reduce high fever.
Apply 1 tablet 3 times a day. It is strictly forbidden to give Aspirin to children. Its active component, acetylsalicylic acid, can lead to toxic damage to the hepatobiliary system. To reduce itching, sore throat and other unpleasant pathological effects, antihistamines are prescribed.
Fenistil, a drug based on dimethindene maleate, is suitable for children. The medicine is taken 5 drops 3 times a day. For adolescents and adults, Suprastin with the active ingredient chloropyramine is recommended. The regimen for chickenpox is 1/2 tablet 3 times a day for 5 days.
Rinses
When the oral cavity is infected with the Varicella-Zoster virus, an antiseptic treatment is necessary. Against the background of suppressed immunity, bacterial and fungal agents are added that provoke inflammation, suppuration, and swelling of the tissues of the nasopharynx.
Use collections of medicinal herbs, pharmacy solutions of the appropriate purpose, homeopathic remedies. The preparations recommended for rinsing are presented in the table.
| Medication solution | Pharmacological properties |
| Furacilin | Has a pronounced bactericidal effect. It is effective in the treatment of acute inflammatory lesions of the mucous membrane of the dental zone. |
| Miramistin | Cationic antiseptic used for herpes infections, stomatitis, caries. Suppresses inflammation, relieves swelling of soft tissues and hyperemia. Use a spray or rinse solution to treat the blistering rash. |
| Stomatofit | Plant-based antiseptic. The composition includes pharmacy chamomile, oak bark, arnica, calamus, peppermint. Has bactericidal and fungicidal properties, pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. |
| Chlorophyllipt | Medicinal solution based on eucalyptus leaf extract. Suitable for rinsing diluted with water and for lubricating vesicles with a cotton swab dipped in a concentrate. |
Rinsing is an effective way to reduce the severity of the infectious process in children and adults. Antiseptic solutions allow you to treat vesicles and foci of microbial lesions even in the most inaccessible areas of the dental zone and nasopharyngeal cavity.
Homeopathic treatment
Such drugs significantly facilitate the course of the infectious process and have an immunostimulating effect. Homeopathic treatment is aimed at shortening the duration of the disease, improving appetite, and eliminating general discomfort.
Effectively inhibit all types of herpes infection:
-
Ranunculus bulbozus. A homeopathic preparation based on a bulbous perennial herb that suppresses pain and itching.

- Natrium Muriaticum. A medicine containing sodium crystals similar to table salt. It has a tonic effect on the affected tissues, has anti-inflammatory and drying effects.
- Antimonium krudum. Neurological drug. Eliminates anxiety and moodiness in children caused by an infectious process.
- Pulsatilla. Homeopathic remedy, the pharmacological formula of which is designed on the basis of lumbago - a perennial herb of the buttercup family. Pulsatilla improves appetite, suppresses painful symptoms.
- Sulfur. Accelerates recovery, activates protein metabolism, eliminates neurological disorders. In homeopathic dosages, sulfur compounds have a wound-healing and regenerating effect.
Chickenpox in the mouth, a photo of which demonstrates numerous foci of infectious lesions, in severe cases requires complex supportive and immunomodulatory therapy. Homeopathy is used as an adjuvant.
Traditional methods of treatment
Homemade recipes serve as an effective additional component of complex therapy for herpetic lesions of the oral cavity. To eliminate unpleasant symptoms, rinse with herbal infusions is used.
Decoctions give a good therapeutic result:
- clover;
- dandelion, known for its anti-inflammatory properties;
- chamomile, which has a pronounced anti-edema effect;
- turns;
- yarrow;
- wormwood.
Infused with boiling water for 10-15 minutes. the broth is filtered through cheesecloth and the oral cavity is rinsed with chickenpox 3-4 times a day. Parsley root extract is effective.
It contains a large amount of ascorbic acid, which strengthens the immune system and suppresses inflammation. When the dental zone is infected with the Varicella-Zoster virus, such a tincture is taken in 1-2 tsp. 3 times a day.
Possible consequences and complications
Chickenpox is a benign infectious disease. Complications and negative consequences are recorded in less than 5% of clinical cases.
Among the registered delayed pathological manifestations, the leading ones are:
- diseases provoked by the addition of a secondary infection of a bacterial and fungal nature;
- strengthening of the general intoxication syndrome by pathogenic microflora;
- development of abscesses;
- phlegmon;
- sepsis due to the confluence of several unfavorable clinical factors.
A complication that is difficult to treat is viral pneumonia, which develops in less than 1% of cases of the total number of chickenpox diseases in the mouth. Infection of the mucous membranes with the Varicella-Zoster virus can theoretically cause encephalitis or nephritis. Numerous photos give a general idea of the appearance of the vesicles, which facilitates self-recognition of the disease.
Chickenpox video
Malysheva about chickenpox:

