Content
- Indications
- Contraindications
- Possible complications
- Training
- Procedure step by step
- Care procedures after
- Efficiency
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Where do
- Video about the GHA
Hysterosalpingography evaluates the shape of the uterus and checks if the fallopian tubes are open. HCV is also used to investigate the risks of miscarriages due to problems with the uterus. Many of the patients who passed the test experienced mild spasms. But judging by the reviews, the fear of upcoming pain was much stronger than the discomfort they experienced during the study.
Indications
After ovulation, the egg moves into the fallopian tubes, meets with the sperm, where conception is carried out. The fertilized egg then continues to move through the fallopian tubes until it reaches the uterus and is implanted into its lining.
As she advances, she should not meet any obstacles in the area of the fallopian tube. A hysterosalpingogram is usually offered to patients who have difficulty conceiving. In this case, the openness of the fallopian tubes, the correctness of the shape of the uterus are assessed. The test makes sure that the cavity is not affected by fibroids, polyps, or scar tissue.
GHA of the fallopian tubes (it is better to study reviews of the procedure before the start of the test) is an X-ray monitoring of the uterus and fallopian tubes, which is used mainly in the study of infertility.

Other indications for HCV include the assessment of women:
- with a history of repeated miscarriages;
- postoperative, when ligation or reversal of the fallopian tubes was performed;
- before myomectomy.
Testing allows you to investigate the causes of recurrent miscarriages caused by congenital or acquired uterine problems, such as:
- myoma;
- polyps of the endometrium (uterus);
- adhesions;
- congenital problems (abnormalities of the uterus);
- tumors.
A hysterosalpingogram (HSG) is performed in women who do not have a history of injuries or infections of the pelvic organs
Contraindications
GST allows you to see only the inside of the uterus and fallopian tubes. To identify problems with the ovaries, uterine wall and other structures of the small pelvis, MRI or ultrasound is prescribed, and the GST cannot evaluate infertility problems due to low or abnormal sperm count or inability to implant a fertilized egg into uterus.
The GHA has contraindications:
- Pregnancy.
- Acute pelvic inflammatory disease.
- Recent dilatation and curettage, abortion, or testing just after menstruation.
- Contrast sensitivity.
Possible complications
Sometimes some complications arise during the test, the two most common of which are:
- Bleeding. The patient should be aware that she may have mild spotting after the procedure, usually lasting less than 24 hours, especially if the catheter balloon irritates the endocervical canal or is pulled to traction the uterus.
-
Infections. The use of sterile instruments only minimizes the risk of infection. Patients are advised to monitor the development of fever or foul-smelling vaginal discharge for 2–4 days after the procedure.

There are a number of side effects of testing:
- Patients usually experience cramping when the catheter balloon is inflated in the endocervical canal or when the uterus is severely distended with the contrast medium being inflated. Spasms often occur with obstruction of the fallopian tubes. They are usually mild, transient, and well tolerated by most women.
- Some patients may experience severe pain leading to premature termination of the procedure or, in in rare cases, to a vasovagal reaction (fainting, as a response of the body to physical and emotional overvoltage)
- There is a possibility of a reaction to contrast material, but such a reaction is very rare with the currently available low-osmolarity non-ionic contrast agents.
- Perforation of the uterus or fallopian tubes is another extremely rare complication.
- Finally, there is the possibility of radiation exposure in early, unexpected pregnancies. An appropriate examination time and a negative pregnancy test in questionable circumstances should minimize this potential risk.
Training
GHA fallopian tubes (reviews of the procedure prove the effectiveness and relative safety) does not require preliminary special preparation of the patient. The procedure is performed while awake and does not require general anesthesia. There is no need to fast the day before or in the evening.
Some doctors prescribe antibiotics to reduce the risk of infection. Since patients may experience seizures during the examination, women are advised to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs 1 hour before the procedure.
The examination is scheduled for 7-12 days of the menstrual cycle (day 1 is the first day of menstrual bleeding). During this proliferative phase, the endometrium is thin, which facilitates the interpretation of images and also ensures that there is no pregnancy. The patient should be instructed to abstain from sexual intercourse from the end of menstrual bleeding until the day of the study to avoid potential pregnancy.
Examination before the procedure:
| General analysis of blood and urine. | |
| Blood chemistry. | |
| A smear for cleanliness of the vagina. | |
| The level of human serum β-chorionic gonadotropin is assessed | If the patient has an irregular menstrual cycle or is likely to become pregnant. |
| erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) | To check for an active pelvic infection that is causing the ESR to rise. |
| Negative cultures for gonorrhea and chlamydia | In patients with concomitant inflammatory disease (eg, arthritis, sarcoidosis, collagen vascular disease) that can lead to an increase in ESR. |
The decision on the prophylactic use of antibiotics in patients with a history of pelvic inflammatory disease is made by the attending physician. Usually no prior prophylactic antibiotic treatment is required in patients with medical conditions history: arthritis, sarcoidosis, collagen vascular disease), which can lead to an increase ESR.
Procedure step by step
Fluoroscopy uses a continuous or pulsed X-ray beam to create a sequence of images that are projected onto a fluorescent screen or television monitor.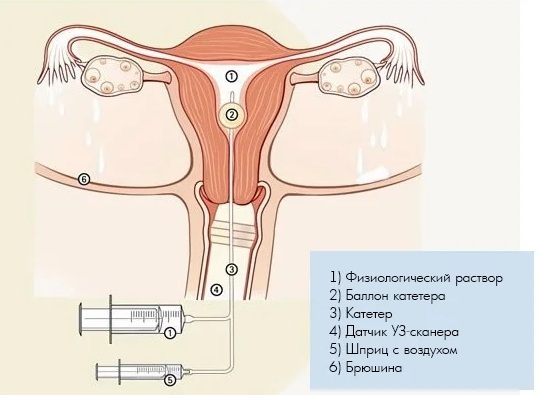
When using a test with a contrast material that clearly defines the area of interest, making it dark (or by electronic change the contrast of the image to white), this special X-ray technique allows the doctor to see the joints or internal organs in movement. Still images are also recorded and stored electronically on a computer.
Most X-ray images are digital files stored electronically. These saved images are readily available for diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
GST or fluoroscopy, which converts X-rays into video images, is used to monitor and guide the procedure for examining the fallopian tubes. The video is created by an X-ray machine and a detector suspended above the table on which the patient lies. The survey is carried out on an outpatient basis and, according to women, it is better to conduct it under the guidance of a competent specialist.
The equipment commonly used for this examination consists of an X-ray table, one or two X-ray tubes, and a television monitor that is located in the examination room.
- The patient is placed with his back on the fluoroscopy table in the position for lithotomy or modified lithotomy (placing the feet above or at the same level with the thighs).
- The perineum is treated with a povidone-iodine solution and a two-handed gynecological examination is performed.
- The speculum is then inserted into the vagina.
- The cervix is localized and cleaned with a povidone-iodine solution.
- The catheter is placed in the cervical canal.
- The balloon is fully inflated (or to the extent that the patient can tolerate, as this maneuver can cause spasms).
- A metal marker is placed on one side of the pelvis to indicate the patient's right or left side.
- Before the contrast medium is injected, a Scout (digital image) radiograph of the pelvis with the catheter in place is taken.
- A water-soluble contrast material is then slowly instilled through the catheter and fluoroscopic images are obtained.
- The first image is taken during early filling of the uterus and is used to assess any defect or contour anomaly.
- The second image is obtained with the uterus fully distended. At this stage, the shape of the uterus is best assessed, although small filling defects may be hidden when the uterus is well darkened.
- The third image is taken to demonstrate and evaluate the fallopian tubes.
- The fourth image shows free intraperitoneal spillage of the contrast agent.
- At the end of the procedure, the doctor removes the catheter and invites the patient to sit down.
HSG fallopian tubes
Additional spot x-rays can be used to document any observed abnormalities. If necessary, you can get a view of the fallopian tubes at an angle or displacement of superimposed structures. An x-ray is usually done at the end of a deflated study to assess the lower segment of the uterus, if the balloon has obstructed this area after initial placement or moved into this area during research.
The procedure usually takes about 30 minutes.
Care procedures after
During the X-ray process, mild convulsions may occur. Pain relievers taken before the procedure often help with cramps. If GST was performed under local anesthesia, then after the procedure the woman may experience slight dizziness and nausea.
After the test, the woman can resume her normal activities. Some doctors advise to refrain from sexual intercourse for several days after the examination.
Although mild cramps are normal, if the discomfort increases in the following days or the temperature rises, you should see a doctor. There is a rare risk of infection after GST. Intensifying pain can be a sign of infection.
Efficiency
The GHA fallopian tubes (expert reviews are unambiguously positive) helps the doctor check 2 important factors:
- Are the fallopian tubes open? If the oviducts are blocked, the egg cannot meet with the sperm and conception is impossible. In this case, there are several possible causes and appropriate treatments.
- Is the shape of the uterus normal? In some women with recurrent miscarriage, an irregular uterus is to blame. The test may show fibroids or polyps that interfere with implantation or embryo growth. Some uterine abnormalities are treated with surgery.
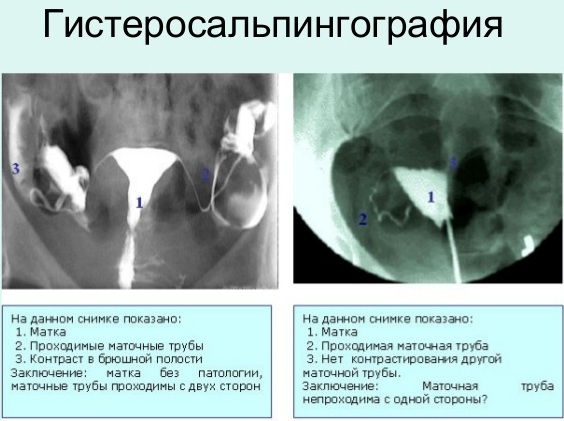 If the x-ray shows the normal shape of the uterus, and the injected dye flows freely from the ends of the fallopian tube, then the analysis results are considered normal. However, this does not always mean that a woman has normal fertility. The hormonal causes of infertility will not be found. Not all uterine fertility problems can be visualized with GST.
If the x-ray shows the normal shape of the uterus, and the injected dye flows freely from the ends of the fallopian tube, then the analysis results are considered normal. However, this does not always mean that a woman has normal fertility. The hormonal causes of infertility will not be found. Not all uterine fertility problems can be visualized with GST.
In addition, endometriosis cannot be diagnosed with GST. Only exploratory laparoscopy can rule out or diagnose endometriosis.
If the dye shows an irregular uterus or does not flow freely from the fallopian tubes, this indicates a problem in this area. Sometimes the dye does not pass through the uterus into the tubes. The blockage may be located exactly where the fallopian tube and uterus meet. In this case, the doctor prescribes an additional examination, including diagnostic laparoscopy or hysteroscopy.
GST can detect abnormalities in the uterus or fallopian tubes that impair fertility. Since diseases of the oviducts, such as adhesions or scar tissue, cause about 20% of cases of infertility, HSG should be performed in the early stages of fertility examination.
In addition, some studies demonstrate an increased pregnancy rate in patients undergoing normal HSH. This may simply be because when contrast is injected into the area through a catheter, the flow of dye sometimes displaces anything that is blocking the fallopian tubes, such as lesions of endometriosis.
Often doctors advise a patient who is about to start fertility treatment with clomid or hCG (gonadotropin), get GST first, especially if she has a history of endometriosis or other problems with pipes.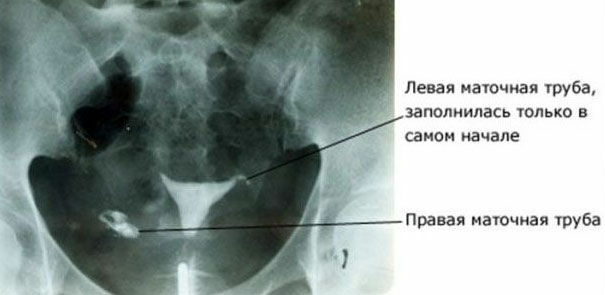
Before ovulation is induced, the doctor must see a good, dynamic, open flow called tubal patency. The examination can be helpful in the diagnostic process, but the first step towards making an accurate diagnosis is to schedule a consultation with a fertility specialist.
Advantages and disadvantages
GHA fallopian tubes (reviews indicate the usefulness and information content of the procedure) has many positive aspects:
- The procedure is minimally invasive with rare complications.
- Provides valuable information about problems with pregnancy or bearing a fetus.
- Potentially blocked fallopian tubes open, allowing future pregnancies.
- After an X-ray examination, no radiation remains in the patient's body.
- X-rays usually have no side effects in the typical diagnostic range for this test.
 There is always a small chance of cancer due to excessive exposure to radiation. However, the benefits of an accurate diagnosis far outweigh the risks.
There is always a small chance of cancer due to excessive exposure to radiation. However, the benefits of an accurate diagnosis far outweigh the risks.
- The effective dose of radiation for this procedure varies.
- Modern X-ray systems have controlled X-rays and dose control techniques to minimize spurious (scattered) radiation. This ensures that those parts of the patient's body that are not visualized receive minimal radiation exposure.
- Always tell your doctor if you have a pelvic infection, inflammatory condition, or untreated STDs. This will help keep the infection from worsening.
- Women should always tell their doctor or radiologist if they are likely to be pregnant.
Where do
The average cost of hysterosalpingography (the price of the GHA procedure itself) is 4600 rubles.
Where can the procedure be carried out:
| Region | City | Clinic | Price |
| Federal cities | Moscow | Invitro | 8 thous. rub. |
| Mother and child | 12 thous. rub. | ||
| Best Clinic | 12 thousand 500 rubles. | ||
| WITH. Petersburg | Medica | 6 thousand 500 rubles. | |
| Family Planning and Reproduction Center | 4 thousand 800 rubles. | ||
| Northwestern Federal District | Vologda | Vita | 3 thousand 300 rubles. |
| Department hospital at the station. Vologda Russian Railways | 1 thousand 200 rubles. | ||
| Southern Federal District | Volgograd | Demeter | 3 thous. rub. |
| Panacea | 3 thous. 650 RUB | ||
| Siberian Federal District | Novosibirsk | Avicenna | 5 thous. RUB 100 |
| Ural Federal District | Ekaterinburg | Health 365 | 5 thous. RUB 400 |
| Tyumen | Clinic them. E. M. Niginsky | 1 thous. RUB 200 | |
| Volga Federal District | Ufa | Department clinical hospital at Ufa station | RUB 500 |
| North Caucasian Federal District | Makhachkala | Center for Medicine of High Technologies named after I.Sh. Ismailova | 2 thous. rub. |
The procedure is also available in other large regional cities at the bases of various clinics, hospitals, and family planning medical centers. When choosing a location for the study, one should be guided by a well-known diagnostic center in the city, and not go to the first gynecological hospital, where they offer such a study.
The HTS is a valuable tool for assessing the condition of the uterus and fallopian tubes. This is one of the important procedures for a woman, and although, according to patients' reviews, it is not always pleasant, you should not be afraid of it.
Video about the GHA
GHA hurt or not: