Content
- Types of dyspeptic stomach disorders
- Causes, what diseases cause indigestion
- Risk factors
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of dyspeptic disorders in adults
- Drugs
- Nutrition Basics
- Folk remedies
- Treatment of dyspepsia in children
- Safe medicines
- Traditional methods
- Features of nutrition for children of different ages
- Possible complications
- Forecasts, prevention
- Myths and dangerous misconceptions in the treatment of dyspepsia
- Stomach Dispensation Videos
Stomach dyspepsia occurs on the background pathologies of the digestive tract or in case of violations of the processes of food splitting. This clinical syndrome usually presents with acute pain. The characteristic symptoms of dyspepsia in the absence of drug treatment can persist for several months.
Types of dyspeptic stomach disorders
Dyspepsia of the stomach is a violation of the functional activity of the digestive organ. There are several main forms of the disorder:
| Type of violation | Description |
| Pancreatogenic | This type of disorder occurs in patients with cystic fibrosis, chronic pancreatitis, and pancreatic cancer. Dyspepsia of the hepatogenic type develops against the background of bile disorders. |
| Gastrogenic | Violation of functional activity occurs with achlorhydria, achilia, atrophic gastritis, stomach tumors. Endogenous dyspepsia is diagnosed in patients with celiac disease and chronic enteritis. |
| Functional | Indigestion against the background of achlorhydria, achilia, pancreatic cancer. It occurs when the processes of production of bile, intestinal and gastric juice slow down. Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract can cause the development of functional dyspepsia. |
| Fermentation | A functional disorder of the digestive system develops against the background of systematic abuse foods high in carbohydrates (fermented milk, drinks, fruits, cabbage, kvass, legumes, bread). With their excessive amount in the intestine, pathogenic microflora begins to multiply rapidly. |
| Intestinal | Functional impairment of this type is caused by the penetration of infection into the intestine. Most often, dyspepsia is diagnosed in people with salmonellosis or dysentery. |
| Soapy (fatty) | Disorder of functional activity is caused by the abuse of food, which contains a large amount of animal fats. They are slowly broken down and absorbed. Fats can provoke the development of putrefactive processes. Soapy dyspepsia can develop after eating meat that has not been stored properly. |
 In some cases, patients are diagnosed with enzymatic dyspepsia. Disruption of functional activity is caused by a slowdown in the synthesis of substances involved in the breakdown of food. In women, pathology occurs much more often than in men.
In some cases, patients are diagnosed with enzymatic dyspepsia. Disruption of functional activity is caused by a slowdown in the synthesis of substances involved in the breakdown of food. In women, pathology occurs much more often than in men.
Causes, what diseases cause indigestion
Pathology can occur as a result of a prolonged stressful situation. In this case, the functional activity of some parts of the intestine is disrupted.
In addition to psycho-emotional disorders, the reasons for the development of dyspepsia are considered:
- deficiency of vitamins C, B;
- slowed down the digestion of sugar;
- dyskinesia of the gastrointestinal tract;
- long-term use of gastroprotective agents;
- seeding the gastric mucosa with Helicobacter Pylori bacteria;
- acceleration of the processes of production of hydrochloric acid.
Regardless of the reasons for the development of dyspepsia, the stomach walls become more sensitive. After food enters the gastrointestinal tract, acute pain and other ailments occur.
Dyspeptic syndrome is characteristic of the following diseases:
- infections of the gastrointestinal tract;
- intestinal and stomach tumors;
- gatekeeper diseases (acquired or congenital);
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- cholecystectomy;
- acute cholecystitis;
- the presence of stones in the gallbladder;
- ulcerative lesions of the duodenum and stomach;
- violation of the processes of synthesis of hydrochloric acid (including complete);
- diaphragmatic hernia with displacement;
- reflux gastritis;
- food type allergy.
In children, dyspeptic disorders usually develop against the background of severe intoxication.
Risk factors
Stomach dyspepsia is a disorder that occurs for a number of reasons.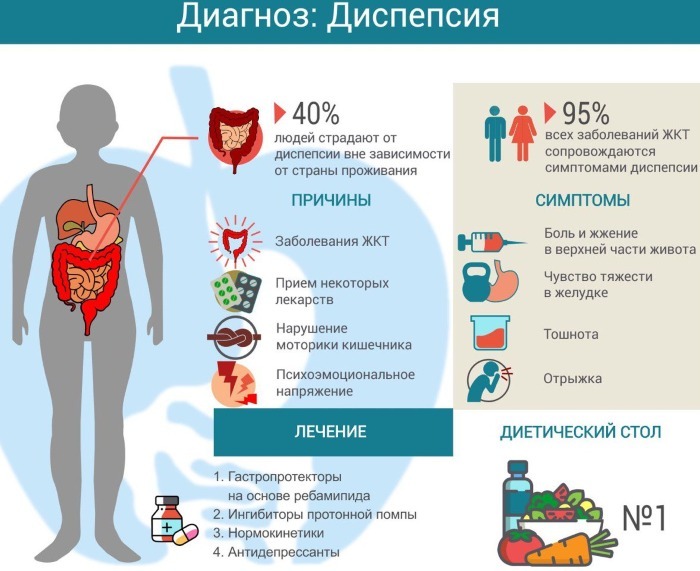
At risk are people:
- staying in stressful situations for a long time;
- suffering from psycho-emotional disorders;
- leading an inactive lifestyle;
- prone to allergic reactions;
- systematically abusing fatty foods;
- taking medications for a long time that irritate the gastric mucosa.
The risk group also includes people whose professional activities are related to hazardous production (electroplating chemists, metallurgists, pharmacists).
Symptoms
Dyspepsia of the stomach is a clinical syndrome, the development of which is indicated by a number of characteristic signs:
- bright taste of metal in the mouth;
- rapid fatigue;
- fatigue;
- heaviness in the stomach (especially after eating);
- refusal of food (complete or partial);
- heartburn;
- severe pain in the epigastric region;
- prolonged migraine;
- bouts of nausea;
- vomiting after eating;
- increased gas formation;
- diarrhea;
- the formation of fecal congestion;
- change in the color of feces (depending on the type of pathology).

Putrid dyspepsia is characterized by a change in stool from brown to almost black. With a soapy type of pathology, feces become yellow or white.
Often, the clinical syndrome is confused with ulcerative lesions of the stomach due to the similarity of the symptom complex:
- temperature jumps;
- vomit;
- weight loss;
- blood in feces or vomit;
- pain while swallowing.
Symptoms can vary depending on the type of pathology:
- Nonspecific dyspepsia is characterized by pain in the epigastric region, burning sensation, and temperature fluctuations.
- Reflux-like dyspepsia is accompanied by sour belching and severe heartburn.
- Dyskinetic dyspepsia is characterized by heaviness in the stomach after eating, bloating, vomiting, and nausea.
People suffering from ulcerative dyspepsia complain of heartburn, belching and severe pain, aggravated at night.
Diagnostics
The discomfort that occurs in the epigastric region after a meal is the reason for contacting the nearest medical facility. Only a gastroenterologist can make an accurate diagnosis. The specialist should listen carefully to the patient and ask him about possible complaints. The gastroenterologist examines and takes an anamnesis.
To confirm or refute dyspepsia, the patient is assigned the following laboratory tests:
- analysis of feces - in the feces, the nature, the percentage of undigested food, the presence or absence of fats, dietary fiber are determined;
- biochemical blood test - allows you to identify the inflammatory process;
- clinical analyzes of feces and blood - determine latent anemia caused by bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
If the preliminary diagnosis is confirmed, then the patient is prescribed:
- electrogastroenterography;
- manometry;
- CT scan of the digestive system;
- colonoscopy;
- radiography;
- Ultrasound; EFGDS.
To receive medication, the patient must revisit the gastroenterologist.
Treatment of dyspeptic disorders in adults
Drug therapy is selected depending on the patient's well-being, age and type of pathology. The patient should inform the specialist about possible allergic reactions to this or that drug. In combination with drug therapy, the patient is prescribed a diet. With the permission of the attending physician, traditional medicine is used.
Drugs
Stomach dyspepsia is a disorder that can be successfully treated with medication.
The following categories of drugs are included in the therapy:
- Antacids. Aktal, Gestal, Fosfalugel, Maalox are responsible for neutralizing hydrochloric acid, inhibiting the activity of gastric juice and adsorption of aggressive contents.
-
Proton pump blockers. Pantoprazole, Lansoprazole, Omeprazole, Rabeprazole slow down the process of transporting ions into parietal cells. The drugs relieve pain and heartburn.

- H2-blockers of histamine. Medicines are responsible for inhibiting the production of hydrochloric acid. For dyspepsia, Roxatidine, Nizatidine, Famotidine, Cimetidine are prescribed.
The composition of drug therapy can also include drugs that correct peristalsis. They are responsible for restoring natural bowel motility. Prokinetics prevent the development of constipation. For dyspepsia, Domperidone, Metoclopramide, Motoprid, Cisaprid are prescribed.
For drugs, a pronounced prokinetic effect is characteristic. The drugs Raglan and Cerucal will help get rid of vomiting. Antispasmodics Papaverine and Drotaverine eliminate muscle spasms and reduce the severity of pain. If dyspepsia is accompanied by diarrhea, then activated charcoal or Loperamide may be prescribed to the patient.
Nutrition Basics
With dyskinesia (regardless of type), therapeutic fasting is indicated for 24-48 hours. A person should only drink water. With fermentative dyspepsia, it is necessary to exclude from the menu all products that contain coarse fiber and carbohydrates (cucumbers, beets, cabbage, sweet fruits, legumes). The basis of the diet is veal, rabbit, chicken, turkey, cottage cheese.
Fresh fruits and vegetables can be consumed no earlier than 14 days after fasting. Putrid dyspepsia requires exclusion of protein-rich foods from the diet. The menu is based on crackers, white bread, oatmeal, semolina, apples, freshly squeezed juices. No more than 1 time a week, you can eat a little boiled fish, cottage cheese or chicken breast.
Dyspepsia of the fatty type requires rejection of products containing animal fats (smoked meats, pork, lamb, bacon, bacon). If necessary, your doctor can adjust your diet to include foods that reduce colic or bloating.
Food that is poorly digested must be completely discarded.
The following products are included in the approved list:
- natural yogurt;
- kefir;
- low-fat milk;
- pasta;
- White rice;
- millet;
- oatmeal and flakes;
- buckwheat grain;
- dried fruits;
- gooseberry;
- apples;
- peaches;
- bananas;
- apricots;
- plums;
- Cherry;
- beet;
- carrot;
- potato;
- zucchini.
2-3 times a week, you can eat 150 g of boiled rabbit or veal.
It is necessary to partially exclude from the diet:
- drinks containing sugar and alcohol;
- melon;
- watermelons;
- grape;
- raisin;
- black bread;
- confectionery;
- sugar;
- fatty dairy products;
- beans (beans, peas, corn);
- mushrooms;
- bell pepper;
- pumpkin;
- onion;
- cauliflower, Brussels sprouts;
- broccoli;
- turnips;
- radish.
The use of fatty meats (goose, duck, pork) is strictly prohibited. You also need to give up fast food and fast food.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine does not guarantee a complete cure for dyspepsia. They need to be prepared according to the recipe. It is strictly forbidden to change the proportions on your own. Decoctions, infusions based on medicinal plants are selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the organism.
With dyspepsia, you can take:
-
Celery infusion. The root of the plant (3-5 g) is crushed, poured with boiling water (1 l). The container with the infusion is removed to a warm, dark place for 8 hours. The cooled product is decanted. Take 50 ml 3-4 times a day on an empty stomach.

- Blackberry decoction. Plant roots (10 g) are thoroughly washed, placed in a saucepan and filled with water (500 ml). Simmer for 15-20 minutes over low heat. The broth is decanted, 150 ml of red wine is poured into it. Take 50 ml 4 times a day.
- Wild boar broth. Black poplar bark (1 tsp. l.) Pour boiling water (350 ml) and simmer over low heat for 3 minutes. Take 50 ml 2-3 times a day.
Dyspeptic disorders, characterized by heaviness in the stomach, pain, heartburn, are treated with decoctions based on dill, fennel and marjoram. To improve the taste, you can add 1-2 tsp to the product. l. natural honey.
Treatment of dyspepsia in children
Treatment of dyspepsia in children is carried out by several methods.
Non-drug therapy includes:
- diet;
- massage.
With the permission of the attending physician, you can take traditional medicine. Children can be prescribed medications that are responsible for reducing acidity, restoring the process of producing enzyme substances.
Safe medicines
Children under 3 years of age suffering from dyspeptic disorders are usually not prescribed medications. The mainstay of treatment is diet. Most drugs prescribed for violations of the functional activity of the stomach have age restrictions. For dyspepsia in children, drug therapy includes:
Enzymatic preparations. These include Micrasim, Panzinorm, Mezim, Creon. Medicines are responsible for supporting the digestive system and normalizing food breakdown processes.
- Antisecretory drugs (for example, Omez). The drugs restore the process of producing gastric juice in the amount necessary for the body. The medication is indicated for high acidity.
-
Antacids. Phosphalugel, Almagel, Rennie are prescribed for nonspecific or ulcer-like dyspepsia. The medicine is responsible for neutralizing gastric juices.

- Prokinetics. Cerucal, Domperidone, Motilium are usually prescribed for nonspecific dyspepsia. Medicines are responsible for the restoration of intestinal motility, eliminate vomiting.
Children with flatulence are prescribed Bobotik, Espumisan. If dyspepsia is caused by intoxication, then it is advisable to use sorbents (Enterosgel, Smecta). In case of acute pain, the child is prescribed antispasmodics (Papaverine, No-Shpa).
Traditional methods
For infants, traditional medicine is usually not prescribed due to the high risk of complications.
If the child does not have a tendency to allergic reactions, then he can be given decoctions and infusions based on:
- yarrow (leaves);
- licorice (root);
- anise (seeds);
- buckthorns (bark).
The decoction algorithm is approximately the same, only the ingredients differ:
- extracts of medicinal plants (1 tsp. l) pour warm water (500 ml);
- the container with the broth is put on a slow fire;
- the liquid is brought to a boil;
- the broth is cooled, filtered and given to the child, 50-100 ml 1-2 times a day.
The appearance of ailments against the background of taking traditional medicine are the reason for an immediate appeal to a medical institution.
Features of nutrition for children of different ages
Diet can be considered one of the main treatments for dyspepsia. Correction of the menu is required for dyspepsia of fermentative, putrefactive and ulcerative type. The list of permitted and prohibited products may vary depending on the type of pathology.
The basis of the diet for fermentative dyspepsia is:
- weak broths;
- poultry meat (chicken, turkey).
From the child's diet, you need to exclude foods rich in carbohydrates.
In case of putrefactive dyspepsia, the diet should include:
- zucchini;
- potato;
- wheat bread;
- fruits;
- low-fat river fish;
- crackers;
- porridge.
Butter and fatty meat are excluded from the diet. If dyspepsia has been diagnosed in a newborn child, then he is shown daily fasting. Within 24 hours the child cannot be fed. He is given a decoction of carrots, raisins, or sweetened tea every 25-30 minutes. A serving is no more than 20 ml. A day later, you can feed the newborn with mother's milk.
Diet table number 4 is shown to children of primary school age.
Permitted products include:
- eggs (in the form of a steamed omelet);
- decoctions of currants, blueberries, rose hips, quince;
- weak black tea;
- wheat rusks;
- turkey meat, chicken;
- fish (low-fat varieties), mostly boiled;
- fat-free cottage cheese;
- jelly and compotes from berries and fruits;
- buckwheat, rice, oat groats.
All other foods not included in the list are subject to complete exclusion from the diet.
Possible complications
Dyspepsia of the stomach, in the absence of adequate treatment, can transform into dysphagia. This is a psychosocial pathology characterized by an undulating course.
If the patient, with the appearance of characteristic symptoms of dyspepsia, did not apply to a medical institution in a timely manner, then the risk of developing subsequent complications is high:
- violation of the functional activity of the kidneys;
- convulsions;
- arrhythmia;
- violation of the water-salt balance;
- weight loss;
- haemorrhoids.
In some cases, dyspepsia is characterized by constipation. If left untreated, stool plugs can cause anal fissures or hemorrhoids. Diarrhea is accompanied by the loss of micro- and macroelements useful for the body. The human body begins to slowly absorb nutrients. Uncontrolled vomiting leads to electrolyte imbalance.
Forecasts, prevention
The drugs prescribed by a specialist relieve the symptom complex of dyspepsia and improve the patient's condition. With adequate therapy, the prognosis is good. Dyspepsia is characterized by a wave-like course. Experts recommend taking preventive measures to minimize the risk of developing the disorder. It is imperative to lead a healthy lifestyle.
Doctors recommend walking daily. Nutrition should be as balanced as possible. It is recommended to take food at the same time. The frequency of admission is 4-5 times a day. The diet should be varied. It is based on fresh vegetables, fruits, lean fish, meat. It is necessary to exclude completely gas-forming products, spicy, salty, smoked food.
Experts recommend giving up alcoholic beverages and tobacco products. Overeating should be avoided. When buying products, you must carefully study their composition and expiration date. It is impossible to neglect the basic rules of personal hygiene: after visiting public places, it is recommended to wash your hands with soap and water. Rinse fruits and vegetables with warm water before use. It is necessary to undergo an annual examination by a gastroenterologist.
Myths and dangerous misconceptions in the treatment of dyspepsia
Self-selection of medicines for dyspeptic disorders is strictly prohibited. There is no need to rely on the opinion and experience of friends or advertising. You cannot diagnose yourself on your own.
Many people mistakenly believe that bloating, heaviness in the stomach and bouts of nausea will eventually disappear on their own, and slight discomfort is not a reason to visit a medical facility. The majority opinion that enzyme preparations and antispasmodics eliminate heaviness in the stomach is also wrong. Spicy, acidic food does not eliminate heartburn and nausea.
It is impossible to treat dyspeptic disorders only with traditional medicine. They act as an auxiliary component. Traditional medicine has a gentle effect. To achieve a positive result, you need to take them continuously for several months.
The diet helps to restore the functional activity of the digestive tract. Vitamin-mineral complexes have no positive effect on the stomach. Drugs of this type help restore immunity.
Dyspepsia of the stomach, as a violation of the functional activity of the organ of the digestive tract, has pronounced symptoms. This clinical syndrome occurs against the background of malnutrition, pathologies of the pancreas, intestines. In addition to epigastric pain, heartburn and bloating, patients may complain of bad breath, a metallic taste in the mouth. Concomitant symptoms include rapid fatigue, insomnia, and decreased performance.
Stomach Dispensation Videos
Functional dispensation:



