Content
- The essence of the analysis
- What can it show?
- Indications for research
- During the period of bearing a child
- How many days does the analysis take?
- How long is the analysis valid?
- Preparation for analysis
- How is the procedure carried out
- Probability of error in results
- Decoding
- Positive Wasserman reaction
- Wasserman's false positive reaction
- Negative Wasserman reaction
- What tests do patients take additionally?
- Video about the Wasserman reaction
In 1906 g. immunologist and microbiologist of German origin A. NS. von Wassermann in collaboration with A. L. WITH. Neisser developed a test for diagnosis of syphilis. This is a reaction that detects the presence of antibodies to the causative agent of the disease. Currently, the classical research approach is little used, but all methods aimed at identifying the disease are named after its creator.
The essence of the analysis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease of an infectious nature. It is caused by pale treponema and is characterized by a periodic course, damage to the mucous membranes, skin, musculoskeletal system and internal organs.
It has the following transmission paths:
- Sexual: is the most common.
- Contact-household: children from parents with syphilis become infected in this way.
- Transfusion: after transfusion of blood and its components from a donor with a causative agent in the body.
- Transplacental: transmitted to the fetus through the placenta from the mother during pregnancy.
- Professional: medical personnel become infected when performing manipulations with persons infected with pale treponema: surgeons, obstetricians-gynecologists, dentists.

The causative agent of the disease remains active in fresh secretions of the infected person, such as saliva, urine and other physiological fluids.
By its form, syphilis is divided into:
- Primary. It occurs after infection with pale treponema. The incubation period is 6-8 weeks from the moment of infection. It is characterized by ulcerative formation at the site of the introduction of the pathogen, an increase in the submandibular or inguinal lymph nodes. A positive reaction is diagnosed in 8 out of 10 cases.
- Secondary. Characterized by a pale rash all over the body, including the palmar and plantar surface, symptoms of intoxication, characteristic of a respiratory infection. It is detected in almost 100% of cases.
- Tertiary. In 1/3 of patients, the RW test gives a negative result. In a sick person, the bone skeleton is affected, causing its deformation, internal organs and the nervous system.
- Carrier bacteria. A person becomes infected with pale treponema, a strong immune reaction of the body suppresses its active reproduction, but cannot completely destroy the infection. In this case, there are no symptoms of the disease, but the carrier is dangerous to people with whom he contacts.
The Wasserman reaction is a serological study that is carried out by an express method. Its other name: blood test for RW. The study of material for syphilis is based on the identification of specific antibodies that are produced the immune system of the human body in response to the invasion of foreign antigens into the bloodstream, causing them death.
The causative agent of the disease contains a nonspecific protein called cardiolipin. The medical industry gets it from the hearts of cattle and releases it ready-made with instructions. When carrying out a study in a test tube containing biological material (serum), this antigen, forming strong bonds between antibodies and proteins of innate immunity (complement) of the blood the patient. Then the composition is subjected to hemolysis, after which the results are evaluated.
The analysis for RW indicates and fixes the autoimmune process that was triggered in the human body by treponema pallidum.
Blood for research is taken only from a venous vessel in the amount of 5-10 ml. The manipulation is carried out in the conditions of the treatment room of the polyclinic, diagnostic center or hospital.
What can it show?
The RW assay is based on the complement binding response. Its purpose: to identify antibodies to the causative agent of the disease.
Syphilis testing helps:
- To establish a diagnosis of the disease at its first stage.
- Determine the duration of the infection.
- Reveal infection in the latent (latent) course of the disease.
- Monitor the treatment.
- Examine people who have contact with a sick person for the carrier of the pathogen.
Indications for research
The Wasserman reaction is a blood test that is performed for diagnosis and examination of the following groups of people:
- Medical professionals and hospital staff.
- People associated with food (growing, selling, processing): working in preschool and school institutions.
- Persons who, by profession, have contact with contaminated material.
- Donors of physiological materials of the body.
- HIV-infected, drug addicts and leading an asocial lifestyle.
- Patients undergoing treatment in a hospital, as well as those who are prescribed an operation.
- With prolonged fever of unknown origin.
- Holders of sanatorium vouchers.
- Pregnant women are examined several times throughout the entire period.
- Newborn children to identify congenital syphilis.
- After intercourse with a casual acquaintance without the use of protective equipment (condom).
- If you suspect infection with treponema: ulcers in the genital area, enlarged lymph nodes, skin rashes.
- When undergoing an annual medical examination.
- For patients undergoing treatment for syphilis, to track the dynamics of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment for its timely correction.
During the period of bearing a child
Pregnant women are prescribed a blood test for RW 3 times:
- When you first apply for pregnancy and registration.
- At 13 weeks of gestation.
- Upon admission to the hospital.
A woman who has had syphilis should refrain from conceiving a child for 5 years. You should know that the Wasserman reaction when carrying a fetus in 1.5 out of 100 pregnant women is false positive. Therefore, the doctor prescribes a second analysis. Upon confirmation of infection with treponema, the patient needs treatment in order to protect the fetus from infection and prevent intrauterine death.
How many days does the analysis take?
The Wasserman reaction is a method related to express diagnostics to identify the causative agent of syphilis. The study in the classical way is carried out during the day, after which the doctor receives the analysis data. The exception is the district polyclinics. Due to their remoteness from the laboratories of the dermatovenous dispensary, the analysis will have to wait up to 2 weeks (this is due to the fact that the material is transported and the results are delivered on set days).
Nowadays, the PCR method (polymerase chain reaction) is widely used. It is an accurate study to identify the causative agent of the disease. Its reliability reaches almost 100%. The result is known after 5 hours. after taking biological material. Disadvantage: high price. Therefore, analysis is available to private clinics.
How long is the analysis valid?
The duration of the reliability of the results for the RW reaction does not exceed 3 months. Most often, the analysis is carried out during a preventive medical examination once a year. It should be noted that during the incubation period, the pathogen cannot be detected, since the blood contains a very small amount of antibodies. A positive test is possible 4 weeks after the penetration of pale treponema into the human body.
Preparation for analysis
The Wasserman reaction is one of the laboratory research methods and requires the fulfillment of the necessary conditions in preparation for the collection of biomaterial. This is necessary to eliminate errors that affect the result.
Before testing blood for RW, the following factors should be considered:
- Blood is taken in the first half of the day strictly on an empty stomach or abstinence from eating should be within 6 hours, since the reliability is influenced by the enzymes of the digestive system.
- The day before the examination, you must not consume: coffee and caffeinated drinks, fruit juices, fatty foods, alcohol. You must refrain from tobacco immediately before taking blood.
- It is not recommended to take medications for 24 hours, especially those containing digitalis, and antibiotics. The doctor should be notified about vital drugs so that he can take this into account when decoding the result.
- On the eve of taking an analysis, one must refrain from physical, emotional stress.
- You can drink still water or boiled water.
How is the procedure carried out
To check a person for the presence of the pathogen of pale treponema in his body, blood taken from a vein is needed.
Sequencing:
- During the collection of material, the patient should lie or sit.
- A medical tourniquet is pulled over his arm above the elbow.
- The site of the future puncture is treated with a napkin soaked in 70% alcohol.
- A needle is inserted into the venous vessel and connected to a vacuum tube. With the help of a vacuum, 5-10 ml of blood is drawn.
- After the injection, the wound is pressed with an alcohol-containing material. To prevent bleeding, the arm is bent at the elbow for a few minutes, or a tight fixation bandage is applied by the nurse.
- When taking an analysis in children under one year old, veins on the child's head are used.
- A test tube with a blood mass is sent to the laboratory for testing for antibodies to the pathogen. Storage is carried out in a refrigerator for no more than 48 hours.
Research technique:
- Serum is separated from the taken blood by centrifugation.
- It is divided into 3 portions, one of which is the control, and the other 2 are injected with the cardiolipin antigen. Then the test tubes are placed in a thermostat with a temperature of + 37 ° C for 1 hour, during which strong bonds are created in the biological material between the antibodies and the injected drug.
- The composition undergoes hemolysis by means of chemicals. After 30-60 minutes. assess: a negative result is evidenced by the destruction and hemolysis of erythrocytes. The absence or slowing down of the reaction in comparison with the control sample indicates the occurrence of a reaction of binding of antibodies to the antigen. The stage of the disease is assessed by the delay time.
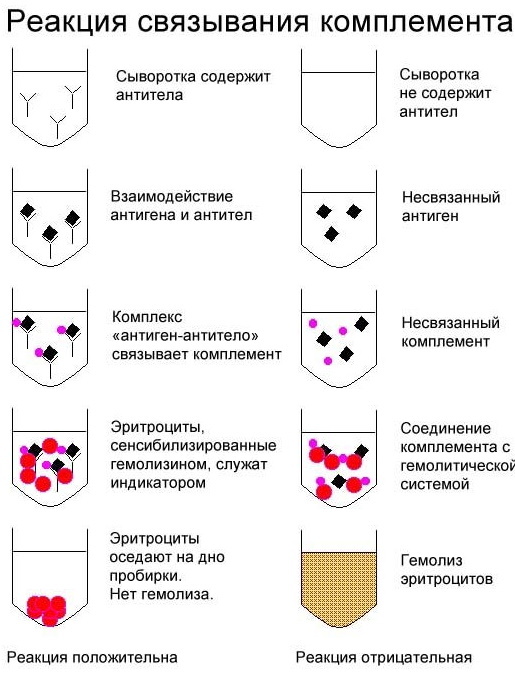
Wasserman reaction (RW).
The results of the analysis are sent to the doctor who prescribed the examination or are handed out to the patient when they independently go to the medical laboratory.
Probability of error in results
The error reaches 10-20% of cases.
It's connected with:
- The presence of somatic diseases that affect the composition of the blood.
- The characteristics of the human body.
- The presence of a latent course of syphilis, which is combined with another pathology.
- Patient neglect of recommendations before sampling.
- Insufficient qualification of laboratory assistants: erroneous actions when taking blood, storing and transporting it.
- Use of reagents that have expired.
- Uneven distribution of antigen in a test tube, non-use of control blood samples in the study of material.
The distortion of the results can also be influenced by diseases of an infectious nature: leptospirosis, relapsing fever, borreliosis caused by a tick bite, some tropical diseases of Latin America, Africa (pint, bejel). Their pathogens are similar in antigens to treponema pallidum. In the study, they give a false positive reaction.
Decoding
The Wasserman reaction is a technique for detecting pale treponema in the human body, based on the response of its immune system to the invasion of a protein similar in composition to the antigen of the causative agent of syphilis. A negative result (negative) indicates the absence of bacteria in the patient's blood and is indicated by a “-” (minus) sign. A positive one is written with a "+" (plus) sign.
Positive Wasserman reaction
A positive RW indicates that cardiolipin, a treponema antigen, was found in human blood serum.
This is possible under the following conditions:
- The patient is sick with syphilis.
- The test gave a false positive reaction.
- With antiphospholipid syndrome.
- Within a year after the treatment of syphilis.
In this case, a re-examination is always assigned to detect antibodies to the pathogen and other diagnostic methods.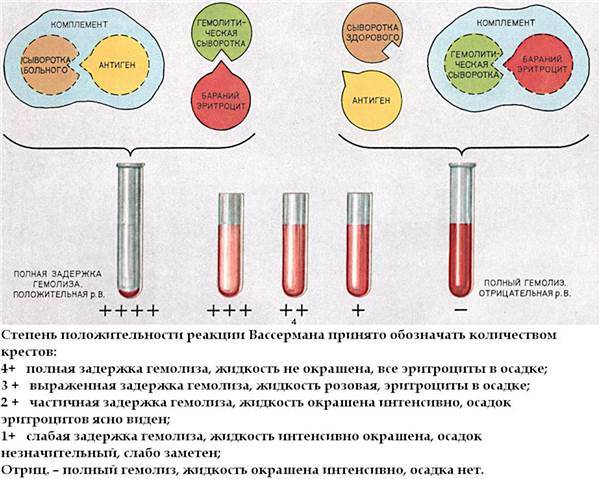
Depending on the delay time of the hemolysis reaction, the test result is interpreted as follows:
| Quantity "+" | Reaction | Hemolysis of erythrocytes in time | Number of pathogen |
| ++++ | Strongly positive | There were no signs | Very big |
| +++ | Positive | Significant delay | Significant |
| ++ | Weakly positive | Partial | Small |
| + | Dubious | Insignificant | Very little or the result is wrong |
The patient is removed from the register after three consecutive studies for the presence of the pathogen, analysis of cerebrospinal fluid and examination by doctors: an ophthalmologist, a neurologist and an otolaryngologist.
Wasserman's false positive reaction
False positive RW can be triggered by disruption of the endocrine and immune systems, the presence of severe somatic diseases.
It manifests itself in the following infections and conditions:
- Tuberculosis of the bronchopulmonary system.
- Connective tissue diseases.
- Infectious diseases: chickenpox, mononucleosis, mumps, measles.
- During the period of convalescence and after vaccination.
- Oncology: lymphoma, myeloma.
- Hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, HIV infection.
- Diabetes.
- Rheumatic and autoimmune diseases: systemic lupus erythematosus, leprosy.
- After a recent stroke, heart attack.
- In case of poisoning and intoxication.
- With brucellosis.
- In women during menstruation, pregnancy, within 2 weeks before and after childbirth.
- In infants in the first 10 days of birth.
- After eating fatty foods, alcoholic beverages, smoking.
Also, the inaccuracy of the result is influenced by the patient's elderly age (80+), the frequency of transfusion of blood components in hemophilia, leukemia, and drugs injected.
In case of a false positive result up to "++", a second blood test of the patient is required. It is carried out after a few weeks or other diagnostic methods based on modern laboratory tools are used.
Negative Wasserman reaction
It characterizes a healthy person (this applies only to sexually transmitted diseases and does not apply to somatic diseases), who has not been infected with syphilis.
It should be noted that in the first 3 weeks after infection with treponema pale, the Wasserman reaction shows a negative result. This is due to the small amount of antibodies in the patient's blood. After 1.5 months, a positive test is shown in 25% of patients. Only at the height of the disease does the reliability approach 80-90%.
False negative RW is possible during the period of the gray-negative window at any stage of the disease, as well as when capillary blood is taken from a finger.
What tests do patients take additionally?
The criterion for the correct diagnosis of syphilis is the isolation of the causative agent of the disease or the presence of antibodies to it.
Direct research methods include:
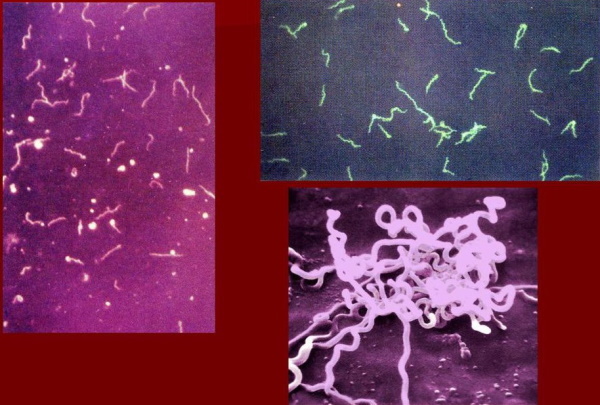
- TMP - dark-field microscopy. The most reliable diagnostic approach. The material is the discharge from the ulcer, erosion, the contents taken during the puncture of the lymph node. In a dark field under a microscope, pale treponema appears in the form of a spiral. Differentiation from other similar pathogens is made by the morphology of the bacterium and its characteristic movements. Based on this, a diagnosis is made.
- Mutual fund - direct immunofluorescence. It is used to study discharge from the area of lesions of the oral mucosa, rectum, material obtained during autopsy, biopsy. The technique of analysis consists in placing the samples on a glass slide; during fluorescence microscopy, a laboratory doctor observes a glow of bright green light.
- PCR - polymerase chain reaction. The technology is based on the detection of the pathogen's DNA. The source is spinal, tissue, amniotic, seminal fluid, blood.
Also used are such reactions and examinations as:
- RIF - immunofluorescence.
- RPHA - passive hemagglutination.
- RIBT - immobilization of pale treponemas.
- ELISA - enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
- Immunoblotting.
In the XX century. Wasserman's reaction was the only way to diagnose and monitor treatment in syphilis patients. This is an inexpensive and fast analysis with a high percentage of accuracy. Currently, new research technologies have been developed that give fewer unreliable results. But some laboratories are still using this technology because of its availability.
Video about the Wasserman reaction
RW blood test: