Content
- Causes of facial nerve neuritis, risk factors
- Development mechanism
- Types, symptoms and signs
- Degrees of defeat
- Diagnostics of the causes of facial nerve neuritis
- Medication treatment
- Physiotherapy
- Is it possible to warm the facial nerve in case of inflammation?
- Consequences of neuritis of the facial nerve, prognosis
- Video about inflammation of the facial nerve
Inflammation of the facial nerve in medicine it is called neuritis or Bell's palsy. The disease is characterized by damage to the cranial nerve. It is accompanied by severe clinical symptoms and requires complex treatment.
Causes of facial nerve neuritis, risk factors
Inflammation of the facial nerve lasts a long time, it is difficult to treat. Most of the patients are in the hospital for 20-30 days. Full recovery will take six months. In 5% of cases, it is impossible to resume the functioning of the nerves. This is due to the development of a malignant tumor or traumatic brain injury.
There are the following factors that provoke the development of the inflammatory process:
| Name | Description |
| Herpes virus | The causative agents of viral infection are in every human body, but they are not active. The development of pathogenic flora occurs under the influence of numerous negative factors, as a result of which immunity decreases. Herpes causative agents often affect nerve fibers. Due to their activity, inflammation develops and edema appears. |
| Hypothermia | Being in the cold for a long time, a person runs the risk of local hypothermia. In this situation, a spasm of blood vessels and muscles occurs, immunity decreases, the nutrition of the nerve is disturbed, as a result of which an inflammatory process develops. |
| Bad habits | Ethyl alcohol, which alcoholic beverages contain, negatively affects the entire central nervous system of the human body. |
| High blood pressure | Increased intracranial pressure negatively affects the nuclei of the facial nerves. Hypertension provokes a stroke, which results in tissue hemorrhage. If the facial nerve is near, it will also be affected. |
| Pregnancy | During the period of gestation, the female body undergoes numerous hormonal changes, which negatively affects the functioning of the entire central nervous system. |
| A brain tumor | A malignant neoplasm grows and presses on the nerves, pinching them and disrupting sensitivity, impulse transmission. A rare cause of neuritis, but dangerous. |
| Traumatic brain injury | As a result of mechanical stress, a nerve rupture occurs. Inflammation develops due to the accumulation of fluid in the pathological focus. Soft tissues swell and disrupt the functioning of nerve fibers. |
| Colds | SARS, otitis media, sinusitis and other ENT pathologies can give complications, resulting in damage to the facial nerve. |
| Atherosclerosis | The small blood vessels that feed the nerve become clogged with cholesterol plaques. As the pathological processes progress, the affected nerve dies. |
| Diabetes | A pathological condition in which material metabolism is disturbed, and separate inflammatory foci appear. |
An unsuccessful trip to the dentist or severe stress, experiences can also end up with inflammation of the facial nerve. The same applies to multiple sclerosis, infectious pathologies, neuroinfections. At risk are people with a hereditary predisposition to neuritis.
Development mechanism
Facial nerves are more often affected due to anatomical features. They pass through the narrow channels of the facial bones, therefore they are easily subject to various influences. Even a slight inflammation provokes a clamping of the nerve, resulting in oxygen starvation and the development of pathological processes. In most cases, neuritis affects the nerves on one side of the face, as evidenced by decreased muscle sensitivity.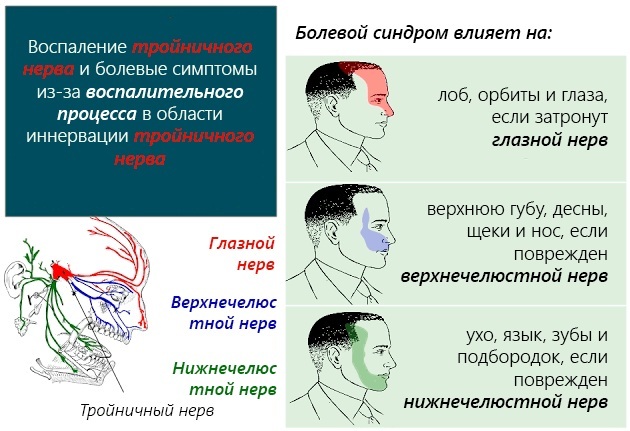
Under the influence of provoking factors, a spasm of blood vessels occurs. They shrink. Blood accumulates in them and their forced expansion occurs. Some components of the blood penetrate the walls of the capillaries and provoke edema of adjacent tissues. As a result, nerve endings are compressed.
As the pathological processes progress, blood circulation is impaired. Nerves suffer from this, they do not receive proper nutrition. The nerve trunk swells, impulse transmission is disrupted. The brain does not receive signals and does not respond. For this reason, all the clinical symptoms of neuritis are manifested.
Types, symptoms and signs
Inflammation of the facial nerve (symptoms and treatment require medical examination) is accompanied by bright signs that will help the specialized doctor determine the degree of fiber damage and the area of localization of the pathological hearth. Clinical manifestations also depend on the provoking factor.

| Name | Symptoms |
| Nerve damage |
|
| Damage to motor fibers |
|
| Infectious lesion |
|
| Common signs |
|
As the inflammatory process progresses, the clinical symptoms of neuritis intensify and provoke persistent degenerative changes that cannot be eliminated.
Inflammation of the facial nerve (a neurologist will help determine symptoms and treatment with a medical examination) depending on the manifestations of pathological processes, they are classified as follows:
| Name | Description |
| Gombo's neuritis | The disease is characterized by the destruction of the myelin sheath, which is located around the nerve. |
| Dejerine-Sott's hypertrophic neuritis | The inflammatory process is accompanied by hypertrophy of the sheath of nerve endings. At first, the fibers are compressed, then gradually collapse. |
| Rossolimo's neuritis | A type of Dejerine-Sott's neuritis, which is characterized by periodic recessions and exacerbations. The disease is more often diagnosed in children. |

Given the provoking factors, the disease is distinguished as follows:
| Name | Description |
| Primary neuritis | In most cases, the inflammatory process provokes a cold. At the time of hypothermia, the blood vessels on the face narrow, blood circulation and nutrition are disturbed. |
| Secondary | The disease provokes serious pathological changes in the human body (infection, tumors, inflammation). |
| Traumatic | The inflammatory process provokes nerve damage. |
| Professional | The disease occurs in people who are professionally in contact with provoking factors. |
| Infectious | Inflammation develops against the background of an infectious lesion of the human body. |
| Alcoholic | With the abuse of alcoholic beverages, not only does the central nervous system suffer, the vitamin of group B is also washed out from the human body. It is necessary for nerve fibers to function properly. In addition, nerve cells die from alcoholic beverages. |
In any situation, a person develops characteristic clinical symptoms, with which it is important to immediately go to the hospital. Lack of therapy will lead to the progression of the disease and the emergence of serious complications.
Degrees of defeat
To determine the severity of facial nerve neuritis, a special House-Brackman scale allows:
| Name | Description |
| Norm | All nerve endings function unchanged. |
| Mild severity | The disease is characterized by mild weakness and minor disturbances. The eyes are closed with effort, there is a slight asymmetry in the mouth. |
| Moderate | Pathological processes are accompanied by an obvious asymmetry, but not disfiguring a person's face. |
| Moderate degree | There is obvious weakness, and the asymmetry is markedly noticeable. There are no movements on the forehead, the eyes are not completely closed. |
| Severe damage | The facial muscles hardly move. Facial asymmetry is observed even in complete rest. |
| Total degree | Movement is completely absent. |
 In most cases, a specific branch of the facial nerve is affected, more often the lower one, which is slowly restored.
In most cases, a specific branch of the facial nerve is affected, more often the lower one, which is slowly restored.
Diagnostics of the causes of facial nerve neuritis
Inflammation of the facial nerve (symptoms and treatment will help to determine the profile specialist after the examination) requires a comprehensive diagnosis. A neurologist can immediately determine the disease by external signs, but it is necessary to accurately differentiate the pathology and establish the provoking factor.
For this purpose, the patient is assigned an instrumental and laboratory examination:
| Name | Description |
| General blood analysis | The results of the study will show the change in blood parameters that occurs during the development of the inflammatory process in the human body. |
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | The most informative examination method that will help to accurately determine the area of localization of pathological foci and the degree of damage to the facial nerve. |
| Computed tomogram (CT) | The specialist examines the brain tissue to identify malignant processes. |
| Electroneurography | The speed of transmission of nerve impulses and the functioning of the facial nerve are assessed. |
| Electromyography | A diagnostic method by which the doctor detects voluntary electrical impulses in the muscles. |

Comprehensive diagnostics for neuritis is necessary not only for making an accurate diagnosis. The results obtained are taken into account by a neurologist when drawing up an effective treatment regimen. In addition, the patient may be assigned a consultation with other specialized specialists, taking into account the provoking cause of the disease.
Medication treatment
Inflammation of the facial nerve (symptoms and treatment must be determined with a neurologist, you can harm your health on your own) manifests itself with acute symptoms and requires urgent medical attention. The therapy is carried out using complex methods after the examination and on the basis of the results obtained.
Patients are primarily prescribed drugs to reduce inflammation and associated symptoms of the disease. It is important to adhere strictly to the dosage, since the wrong use of drugs can provoke complications.
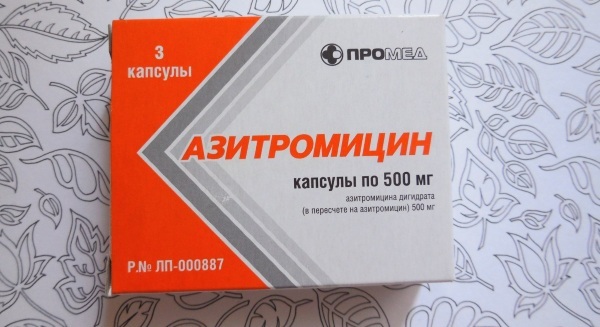
| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Antibiotics | Azithromycin, Doxycycline | The medicine is taken before meals 1 hour or after meals 2 hours later. The tablets should be swallowed whole, not chewed and washed down with water. Adult patients are usually prescribed 500 mg 1 time per day. The course of treatment lasts 3 days. |
| Glucocorticosteroids, NSAIDs | Nise, Dexamethasone | Medicines reduce inflammation and pain. Adults should take 1 tablet 2 times a day after meals. |
| Antispasmodics, analgesics | No-Shpa, Spazmol | Medicines relax the smooth muscles of the capillary walls, expanding them and improving blood circulation. Adult patients should take 1-2 tablets 2-3 times a day. The duration of therapy is 1-2 days. |
| Diuretic drugs | Furosemide, Furon | The drugs remove excess fluid from the human body, after which the swelling decreases. The dosage of the drug depends on the patient's condition and is 20-80 mg 2-3 times a day. |
| Vasodilators | Pentoxifylline, Cavinton | Medicines stimulate blood circulation in the area of development of the pathological focus, thereby improving tissue nutrition. The therapeutic dosage for an adult is 600 mg 2-3 times a day. The duration of therapy is 2-3 weeks. |
| Neurometabolitics | Actovegin, Solcoseryl | The drugs activate metabolic processes and promote the regeneration of damaged tissues. The tablets should be taken orally, not chewed and washed down with a small amount of liquid. The dosage of the drug for an adult patient depends on the condition of the person. Patients are prescribed 1-2 tablets 3 times a day. Treatment lasts 4-6 weeks. |
| Antiviral agents | Acyclovir, Zovirax | Medicines slow down the multiplication process of a viral infection. The drug should be taken with meals and washed down with plenty of water. The therapeutic dosage for adult patients is 200 mg 5 times a day or every 4 hours, except at night. The course of treatment lasts 5 days. |
| Anticholinesterase drugs | Neuromidin, Axamon | The drugs improve the transmission of nerve impulses, eliminate the paralysis of the facial muscles. The dosage of the drug depends on the patient's condition and is 10-30 mg 1-3 times a day. The course of treatment lasts 1-2 months, sometimes up to six months. |
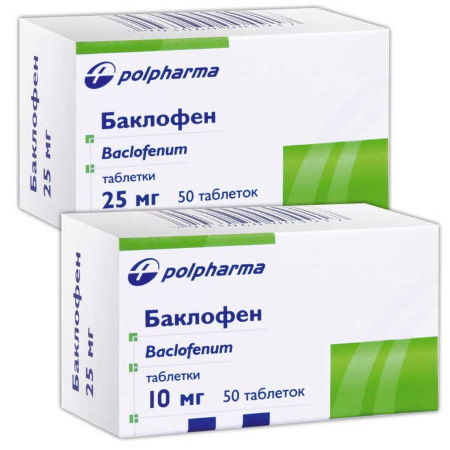
| Muscle relaxants | Mydocalm, Baclofen | Medications are prescribed to patients with chronic neuritis to relax the muscles and relieve spasms. Adult patients are prescribed 50 mg orally 2-3 times a day. If necessary, the dosage is gradually increased to 150 mg. |
 In addition, vitamin complexes are prescribed to patients with neuritis to improve functioning. central nervous system and protect nerve fibers from the negative effects of toxins (Thiamin, Riboflavin). In most cases, patients are selected drugs in tablets. Sometimes it is recommended to use topical ointments and gels in a complex manner. In difficult situations, drugs are administered intramuscularly.
In addition, vitamin complexes are prescribed to patients with neuritis to improve functioning. central nervous system and protect nerve fibers from the negative effects of toxins (Thiamin, Riboflavin). In most cases, patients are selected drugs in tablets. Sometimes it is recommended to use topical ointments and gels in a complex manner. In difficult situations, drugs are administered intramuscularly.
Physiotherapy
Treatment of inflammation of the facial nerve involves attending physiotherapy procedures by patients. A neurologist selects sessions, taking into account the individual characteristics of the human body, symptoms and the established diagnosis. In most cases, physical therapy procedures can be attended 7-10 days after the start of drug therapy.
| Name | Description |
| UHF therapy | Treatment involves the use of an ultra-high frequency electric field. Charged particles that penetrate the cells of the body, improve metabolic processes, eliminate edema, and enhance tissue nutrition. |
| Ultraviolet irradiation (UFO) | The rays used during therapy stimulate the production of certain hormones, increase the body's defenses, and activate the immune system. UFO has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. |
| Decimeter therapy | Electromagnetic microwave decimeter waves, due to an increase in local temperature, activate metabolic processes in the development of the inflammatory process. The blood vessels expand, against which the blood circulation improves. As a result, the normal functioning of the affected nerve is restored. |
| Medicinal electrophoresis | Electric current of low strength and voltage slows down the inflammatory process, eliminates edema, reduces pain and has a calming effect. Additionally, a specially selected preparation is used. Thanks to the electric current, the active components penetrate into the inflammation focus. |
| Diadynamic currents | During the session, pulsed direct currents are used, which penetrate the area of inflammation and cause contraction of muscle fibers. Diadynamic therapy improves metabolic processes, activates the regeneration of damaged tissues. |
 Patients are also advised to do paraffin and ozocerite applications, due to which the process of regeneration of damaged tissues is enhanced. The risk of complications is also reduced.
Patients are also advised to do paraffin and ozocerite applications, due to which the process of regeneration of damaged tissues is enhanced. The risk of complications is also reduced.
Is it possible to warm the facial nerve in case of inflammation?
Neuritis of the facial nerve requires medical advice. It is impossible to treat the disease on your own, since complications can be provoked. The diagnosis is established by a neurologist and a specialized specialist also prescribes therapy. It is possible to warm up the facial nerve, but 7-10 days after the onset of the disease. In this case, it is important to consult a neurologist.
Consequences of neuritis of the facial nerve, prognosis
Inflammation of the facial nerve (symptoms and treatment require the advice of a specialized specialist) does not go away without complications, especially if the patient ignores all the recommendations of the attending physician. After therapy, the nerve endings recover very slowly and easily succumb to any negative effects (hypothermia, stress).
In the absence of timely treatment or non-compliance with the prescriptions of a neurologist, the risk of the following complications increases:
| Name | Description |
| Muscle atrophy | The musculature on the face weakens and decreases in volume, since tissue nutrition is impaired. In most cases, the complication manifests itself one year after the illness. Muscle atrophy can be prevented by constantly kneading the skin on the face, doing exercises, massage and using special creams. |
| Synkinesia | A pathological condition in which the isolation of electrical impulses in the nerve endings is disturbed. Excitation of one nerve provokes the propagation of the signal to other fibers. |
| Conjunctivitis, keratitis | Inflammation of the inner lining of the eyelids and the cornea occurs, since a person cannot close his eyes tightly. |
A complication of neuritis is also a contracture of facial muscles, involuntary twitching on the face. With the appearance of degenerative changes, even surgery will not help to cope with pathological processes.
Inflammation of the facial nerve manifests itself acutely and it is impossible not to notice the disease. As soon as the first symptoms appear, it is important to immediately visit a neurologist and undergo an examination. A correctly selected treatment regimen will help not only stop the progression of the disease, but also prevent dangerous consequences.
Video about inflammation of the facial nerve
Facial nerve neuritis: