What is it? Bradycardia is not considered a separate disease - it is the manifestation of various cardiac function disorders, a nonspecific symptom that can develop in pathologies of both the heart and other systems or organs. Therefore, in order to identify the exact cause of bradycardia, a thorough examination is required.
Contents
- 1 Sinus bradycardia of the heart - what is it?
- 1.1 Causes of bradycardia, risk factors
- 2 Symptoms of bradycardia, classification of
- 3 Diagnosis of bradycardia
- 4 Treatment of bradycardia, drugs
- 4.1 Preventative measures
Sinus bradycardia of the heart - what is it?
Normally, the heart rhythm is uniform and has a certain number of beats per minute - from 60 to 100. And sinus bradycardia of the heart is a phenomenon in which heart rate - the number of heartbeats is less than 60, it is a kind of arrhythmia. A healthy rhythm of the heart acts as one of the factors of the normal functioning of the body, so its disturbance requires careful analysis and correction.
Often moderate bradycardia does not refer to the symptoms of any pathology and is a physiological feature. Normally, the reduction in the frequency of heart attacks occurs in athletes, trained people, as well as in people who have strong muscle walls from birth.
The opposite of bradycardia is tachycardia, in which the pulse, on the contrary, is faster than normal.
Causes of bradycardia, risk factors
Pathological bradycardia occurs for various reasons that are divided into intracardial and extracardiac. The first include:
- cardiosclerosis - scarring of the heart tissue - it is postinfarction and atherosclerotic;
- myocardial infarction;
- myocarditis and endocarditis( inflammatory process in the muscle or outer layer of the heart wall);
- age-related organ changes;
- is ischemic heart disease.
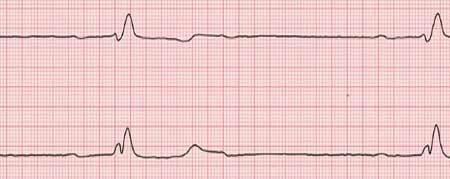
Causes of bradycardia, photo of ECG
Extracardial factors are considered pathologies of other organs other than the heart:
- high intracranial pressure;
- bruises of the brain, concussions;
- meningitis;
- hypothyroidism( decreased thyroid function);
- cerebral edema;
- uremia( high presence of urea in the blood);
- hemorrhage in the brain;
- peptic ulcer disease;
- obstructive jaundice;
- tumor of the diaphragm, esophagus, lung;
- hypertension;
- Ménière syndrome;
- meager food, starvation;
- renal colic;
- infectious diseases - influenza, sepsis, hepatitis and others;
- decreased body temperature( hypothermia);
- intubation of the trachea or bronchi( the introduction of a respiratory tube for life support, for example, with anesthesia);
- poisoning with organic substances with a phosphorus content;
- high concentration of calcium in the blood( hypercalcemia).
Symptoms of bradycardia, classification of

Clinical signs are complaints about the general condition, with bradycardia, there are often such phenomena as:
- palpable palpitation;
- lowering of blood pressure;
- weakness and fatigue;
- swelling;
- problem with concentration;
- sensation of lack of air, shortness of breath;
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- dizziness;
- fainting and convulsions( with a pulse below 30 strokes);
- discomfort in the heart;
- short-term intermittent reduction in visual acuity.
These signs are expressed in individuals in different degrees, it can be as a complex of several symptoms, and one or two of the listed. The lower the pulse, the stronger the symptomatology.
Often a person does not pay attention to the appearance of shortness of breath or fatigue, not suspecting the presence of a bradycardia and the disease that caused it.
With severe bradycardia, the symptoms are severe enough, for example, loss of consciousness, or Morgagni-Adams-Stokes attack, which requires emergency medical attention, otherwise breathing and death may occur.
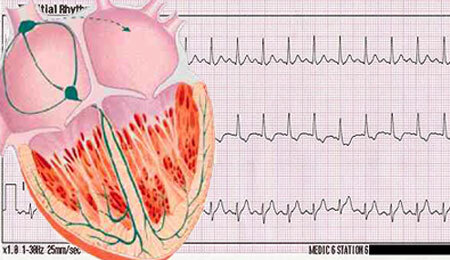
Objective signs of bradycardia are pulse rate( less than 60 per minute) and electrocardiogram readings. The ECG shows an increased P-Q( R) interval( 0.15-0.20 s), the P tooth does not change compared to the norm.
If the bradycardia is nonsinus, then on the cardiogram there is a negative T-tooth, an elongation in comparison with the normal Q-T interval, extended QRS-teeth.
There are two types of bradycardia:
- sinus bradycardia - occurs due to a decrease in activity of the sinus node;
- non-sinus bradycardia - due to the difficult conduct of electrical impulses between cardiac nodes.
The manifestations in both of these forms are the same, and this classification of bradycardia is mainly important for the specialist choosing the treatment. Also, the reduced heart rate is of three types, depending on the factor that triggered it:
- medication, or pharmacological, bradycardia - develops as a consequence of taking certain medications;
- physiological - appears without the presence of pathology, in healthy trained people;
- pathological - is a symptom of a disease.
The latter can be chronic or acute, depending on the nature of the disorders in the body. For example, acute bradycardia, which develops sharply, spontaneously, can cause a heart attack, myocarditis, poisoning. Chronic is present for many months and years, accompanying the course of the underlying disease.
By the degree of manifestation, a decrease in heart rate below the norm is easy( 50-60 strokes), moderate( 40-50) and severe( less than 40).In the first two cases, there is no disturbance of blood circulation, since the heart is still capable of pushing blood with the necessary force.
But in the case of severe bradycardia it occurs, and more often in the area of intracranial arteries, while the skin and mucous membranes pale, cramps and loss of consciousness are possible.
Diagnosis of bradycardia
Different types of arrhythmia, and bradycardia including, are diagnosed using the following methods:
- pulse measurement;
- ECG( electrocardiography);
- auscultation;
- phonocardiography.
In the ECG, bioelectric pulses in the heart are studied using an artificially created electric field. The procedure is painless and fast, this is the most effective and common method for assessing cardiac activity. Auscultation is listening to heart sounds using a stethophonendoscope.
The method gives approximate data on the work of the organ. Phonocardiography makes it possible to investigate heart sounds and sounds, this is a more accurate method than auscultation - its results are recorded as a graph.
In the diagnosis of bradycardia, it is important to determine whether the decrease in heart rate is a physiological norm, a feature of the body or a manifestation of the disease. Therefore, in addition to the above methods, a number of additional tests are assigned to accurately reflect the functional and structural changes in the heart, blood vessels and other systems.
Specifying methods are:
- general and biochemical analyzes of urine and blood;
- blood test for hormones;
- bacteriological study of liquids and secretions( urine, blood, feces);
- echocardiography.
Treatment of bradycardia, preparations
Physiological bradycardia, in which there are no clinical symptoms, does not require therapy. Methods of treatment of bradycardia and drugs are prescribed for heart failure, fainting, low blood pressure and other obvious signs after a thorough diagnosis. Specific drugs and methods are selected depending on the disease.
In case of cardiac causes of bradycardia, the pacemaker installation is most often indicated. When extracardiacal therapy is carried out the main pathology, for example, elimination of cerebral edema, treatment of peptic ulcer, correction of thyroid function.
Along with this, a symptomatic increase in heart rate is necessary by intravenous administration of Atropine, Iazrin, administration of Zelenin drops with moderate bradycardia. Efillin is considered to be effective - in the treatment of bradycardia tablets are taken once a day at a dosage of 600 mg, and if it is injections, then 240-480 mg;
All these drugs only temporarily stabilize the heart rate and are used exclusively as an emergency measure. To completely get rid of bradycardia, therapy of the underlying disease is necessary.
An effective addition to the main treatment of bradycardia are folk remedies - walnuts, a mixture of honey, garlic and lemon, a yarrow broth, and a healthy lifestyle.
In the diet should be a minimum of fats and high-calorie dishes, alcohol intake should be limited, from cigarettes to refuse and do not forget about regular moderate physical exertion.
Prognosis for bradycardia
The risk of serious complications with a decrease in heart rate is low, but still present. In addition to lowering blood pressure in bradycardia, heart failure may develop, chronic attacks of slowing the pulse, sometimes clots are formed.
With a physiological, mild or moderate form and with the timely elimination of the causes, the prognosis for cure is satisfactory.
Preventive measures
In the prevention of bradycardia are important:
- timely treatment of heart and vessel pathologies of any nature;
- elimination of other diseases that indirectly affect the heart rhythm;
- refusal of self-treatment and selection of preparations only with the help of a specialist;
- adherence to a healthy lifestyle.