Content
- Causes
- Views
- Stages and degrees
- Symptoms and manifestations
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Non-drug methods
- Lifestyle change
- Nutrition correction
- Folk remedies
- Physiotherapy procedures
- Drug treatment
- Surgery
- Possible consequences and complications
- Video about cardia and gatekeeper insufficiency
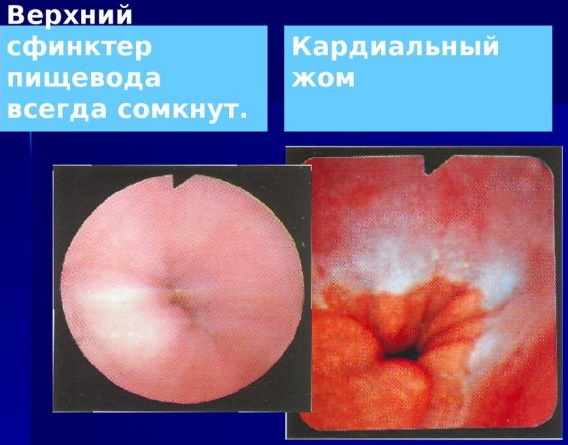
The cardia and pylorus are circular muscles (sphincters, valves) located at the junction of the esophagus to the stomach and stomach to the duodenum. The main function of the sphincters is to control the movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). Normally, when they contract, they close tightly, and when relaxed, they form holes for pushing food further along the digestive system. In case of violations in the processes of contraction and relaxation of muscle rings, they speak of insufficiency of the cardia and the pylorus of the stomach.
Insufficiency of the cardia and pylorus are pathological conditions in which the sphincters do not close or do not close completely. With weakness of the cardia, a mixture of food and gastric juice flows back into the esophagus. This pathology is called
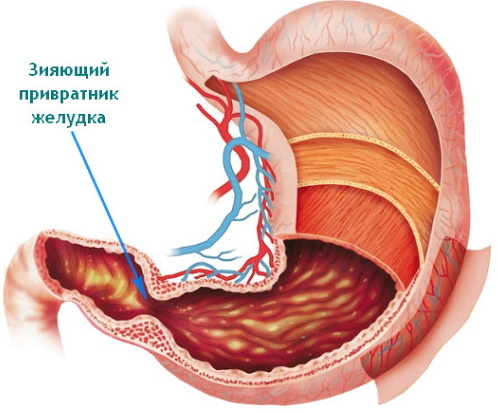
gastroesophageal reflux disease (reflux esophagitis, GERD).This is one of the most common diseases of the digestive system. In case of disturbances in the work of the gatekeeper, half-digested food and bile are thrown from the duodenum into the stomach cavity. In medicine, this process is called duodeno-gastric reflux. In most cases, it is combined with other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and only in 30% of cases is an independent pathology.
Causes
Failure of the cardia and pylorus develops under the influence of organic and functional factors. Organic causes are not associated with impaired sphincter function.
These include:
- binge eating;
- overweight and obesity;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm;
- acute and chronic stomach pathology.
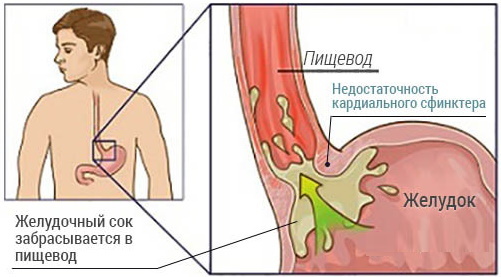
Lack of cardia and gatekeeper
Functional causes are associated with the malfunctioning of the sphincters themselves.
Which occur under the following conditions:
- increased intra-abdominal pressure (with the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, physical overstrain);
- in old age with atrophic changes in all muscles of the body;
- when hormonal metabolism changes in pregnant women;
- as a congenital pathology with malformations;
- after operations to excision of part of the stomach or intestines, removal of the gallbladder;
- diseases of the autonomic nervous system;
- taking a number of medications (tranquilizers, antipsychotics, nitrates, and others);
- malignant tumors in the digestive organs.
Weakness of the cardia and pylorus can also be observed in healthy people. But with proper functioning, the mucous layer of the esophagus and stomach has a protective barrier. This barrier prevents the aggressive action of digestive juices, in the case of minor damage, it contributes to the rapid restoration of the cellular composition.
Views
There are primary and secondary sphincter insufficiency:
- Primary during the first months of life is observed in newborns, is a variant of the norm, passes on its own by six months.
- Secondary is considered as an independent adult pathology.
Stages and degrees
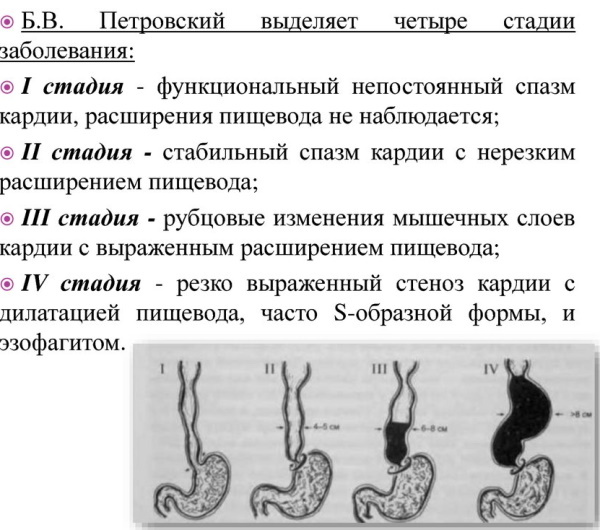
As a result of the damaging action of gastric juice on the walls of the esophagus, an inflammatory process occurs in the mucous membrane (reflux esophagitis). The stages of cardia weakness and the severity of reflux esophagitis are determined during fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS).
| Stage | What is observed during FGDS | Mucosal changes | The nature of the symptoms |
| 1 | Partial closure of the muscle ring. There is an area of free space next to the endoscope. During rotation and movement of the apparatus, this area does not disappear. | No visible changes | Periodic, occur after eating food. |
| 2 | The slit reaches up to 1/2 the diameter of the circle. | The mucous membrane of the stomach forms folds that move towards the esophagus. | They appear regardless of meals. |
| 3 | The valve does not close completely. The edges of the hole hardly touch the endoscope. When rotating, the apparatus always touches the mucous membrane. | Reveals areas of inflammation, erosion and ulcerative defects. | Persistent, have a severe course. |
| 4 | The free positioning of the endoscope in the hole is characteristic. When rotating, the walls of the apparatus do not touch the mucous membranes. | Extensive erosions and multiple ulcers are found. | There is a high risk of complications. |
 The degree of pyloric insufficiency is determined by the amount of bile in different parts of the stomach:
The degree of pyloric insufficiency is determined by the amount of bile in different parts of the stomach:
- 1 degree. It is characterized by an insignificant volume of bile in the pyloric region of the stomach.
- 2nd degree. Bile is located in the antrum and fundus.
- 3 degree. Bile reaches the fundus of the stomach up to the cardiac sphincter.
The throwing of bile into the stomach leads to damage to the protective barrier of the walls, and also activates the synthesis of special substances that further increase the acidity of gastric juice. Thus, the weakness of the gatekeeper provokes the onset of reflux gastritis.
There are forms of reflux gastritis that are established when performing EGD:
- catarrhal (simple) - there is swelling and redness of the mucous membrane;
- atrophic - a decrease in the height of the mucous layer due to the disappearance of the gastric glands;
- mixed - areas of an inflamed, reddened surface are combined with grayish zones of atrophy of the gastric glands;
- hyperplastic - overgrowth of the gastric mucosa and the appearance of cysts and polyps.
Determination of staging is carried out for the further choice of rational tactics for treating the patient.
Symptoms and manifestations
Failure of the cardia and pylorus has a characteristic clinical picture. The most common symptom is heartburn (a burning sensation in the lower chest that rises upward). Occurs some time after eating. Strengthens in a horizontal position, with physical exertion, torso bending. Often accompanied by a feeling of nausea and vomiting with an admixture of bile.
The following manifestations are common:
- pain when swallowing, hoarseness, feeling of a lump in the throat;
- the release of a large amount of saliva during sleep;
- belching with a sour or bitter taste in the mouth;
- cough, possible bronchitis due to ingestion of gastric contents into the respiratory tract;
- bad breath, caries, damage to the enamel of the teeth;
- pain in the chest, upper abdomen;
- heaviness and bloating after eating.
With a long course, a number of symptoms may join:
- constipation or diarrhea (frequent loose stools);
- yellow coating on the tongue, cracks in the corners of the lips, dry skin;
- general weakness, loss of appetite, weight loss.
Reflux gastritis and reflux esophagitis may be asymptomatic or mild, and only one symptom may appear, such as heartburn. Asymptomatic forms pose a particular danger in terms of the development of severe complications.
Diagnostics
Insufficiency of the cardia and the gatekeeper has no specific signs, so making a diagnosis in consultation with a doctor can be difficult. A gastroenterologist deals with diagnostics and treatment. Suspicion may arise when analyzing the patient's complaints.
To clarify the diagnosis, instrumental examination methods are used:
- X-ray using barium contrast agent. A series of images of the upper digestive system are taken, showing abnormalities in the esophagus and stomach. When an ulcer occurs, the contrast agent flows into its crater. Also, narrowing of the esophagus, diaphragmatic hernias are detected. The average cost of a study is 5000-7000 rubles.
- FGDS. The most effective method for detecting weakness of the sphincters, determining the severity, stages and lesions on the walls of the esophagus and stomach. The cost, for example, in the invitro is 4300 rubles.
- Daily ambulatory intragastric pH-metry. Fluctuations in gastric acidity are recorded. To obtain reliable results, the study of the pH of gastric juice is carried out at night. The cost in invitro is 1200 rubles.
- Biopsy. In the process of EGD, a special tool is used to pinch off pathologically altered sections of the walls of the esophagus and stomach. The histologist then examines this tissue under a microscope. This method allows you to determine the activity of the pathological process, precancerous and cancerous conditions. The cost in invitro is 2490 rubles.
- Electrogastroenterography. Allows you to assess the contractile activity of the muscles of the stomach and duodenum. A rare study carried out in specialized clinics.
-
Ultrasoundorgans of the abdominal cavity. Used to identify concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (pancreatitis, cholecystitis, cholangitis). Price in invitro 2500 rubles.
An appointment with an otolaryngologist in cases of cough and hoarseness to identify pathological changes in the larynx and pharynx. The examinations required for making a diagnosis are included in the list of compulsory medical insurance. They are carried out in outpatient and inpatient conditions of paid and free clinics.
Treatment
Treatment of cardia and pylorus insufficiency includes non-drug, medical and surgical methods.
Non-drug methods
This is primarily a change in lifestyle, nutritional correction, physiotherapy procedures and folk remedies.
Lifestyle change
- If overweight is the cause of valve weakness, then a weight loss diet is necessary.
- Quitting bad habits (smoking).
- It is recommended to sleep with the upper body and head raised.
- Excessive physical activity must be excluded.
Nutrition correction
Fractional meals are recommended. Frequent meals up to 10 times a day, in small portions 100-250 gr. After eating, you can not take a horizontal position for 2 hours.

Prohibited Products:
- spicy and fried foods;
- fatty types of meat and fish, smoked meats;
- alcohol and carbonated drinks;
- coffee, strong tea, chocolate;
- garlic, onions, tomatoes.
Healthy foods:
- vegetable oils;
- porridge on the water;
- bananas, apples and mangoes.
Folk remedies
Home remedies can only be done after consulting a doctor.
The following traditional medicine recipes are used:
- The juice from the leaves of the plantain is drunk in 1 tsp. before meals in the stage of exacerbation of pathology.

- A mixture (20 g of each plant) of chamomile, yarrow, motherwort, calendula, St. John's wort and flax is poured into 2 liters of boiling water. It is necessary to take 50 g, 20 minutes before meals, for a course of 10 days.
- Tea from raspberry leaves, juice from raw potatoes or cabbage helps with heartburn.
- Infusion from forest marshmallow. 2 tbsp herbs pour 500 ml of boiling water, insist 6-8 hours. Drink in small sips several times a day. Used to suppress nausea.
- 1 tbsp collection from sage, calamus root and angelica are poured with boiling water, insisted for 20 minutes. The infusion is taken 3 times a day after meals.
Physiotherapy procedures
The following physiotherapy procedures are prescribed:
- electrophoresis or phonophoresis with drugs to eliminate pain;
- amplipulse therapy to restore muscle motility;
- acupuncture to normalize the functioning of the digestive organs;
- UHF therapy (ultra high frequency) to improve blood circulation, relieve pain.
Physiotherapeutic treatment is contraindicated in cases of extensive erosions, ulcers, precancerous pathologies and the presence of tumors.
Drug treatment
Drug therapy is aimed at normalizing the sphincters and eliminating symptoms.
The course of treatment lasts 5-8 weeks (sometimes it reaches 3-6 months). The following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Means for stimulating the motility of the digestive system (prokinetics): Domperidone and Metoclopramide. Domperidone increases the tone of the sphincters and speeds up gastric emptying. Dosage: one or two 10 mg tablets 3-4 times a day. Metoclopramide has a pronounced antiemetic effect. It is taken 10 mg 3 times a day.
- Antacids - neutralize hydrochloric acid, reduce heartburn. Combinations of aluminum and magnesium hydroxide with various additives (Almagel, Alumag) are popular. Almagel take 1 tsp. in 30 minutes before meals.
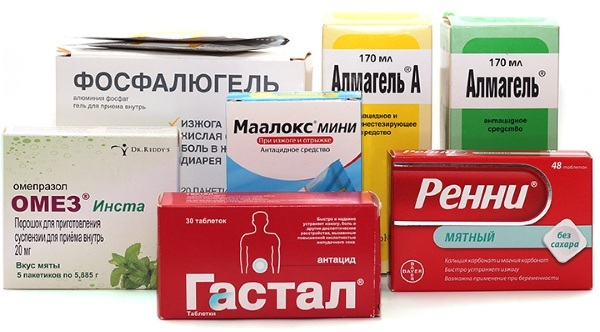
- Drugs that reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid. These include: proton pump blockers (Omeprazole, Pantoprazole), H2 blockers (Ranitidine), and M-anticholinergics (Pirenzepine). The most commonly used proton pump blockers. For example, Omeprazole is drunk 1 tablet (20 or 40 mg) 2 times a day.
- Medicines that promote healing of damaged areas of the walls of the esophagus and stomach. The best known are bismuth salts (De-nol), Sucralfat and Misoprostol.
- Enzyme medicines are used for concomitant pathology of the pancreas (Creon, Festal).
- Bile acid inhibitors (Ursosan). Reduces the irritating effect of bile. Standard dose: 10 mg per 1 kg of body weight 1-2 times a day.
Surgery
In the absence of the effect of drug therapy, the appearance of complications or to eliminate the cause of the disease (diaphragmatic hernia), surgical intervention is performed. The type and scope of the operation is determined by the attending surgeon, depending on the cause, form, stage of the disease, the presence or absence of complications.
The following types of surgical operations are used:
- radiofrequency ablation of the esophagus (the muscle layer of the sphincters is damaged to reduce casting);
- gastrocardiopexy (suturing the esophagus and upper stomach to the greater omentum or round ligament of the liver);
- laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication (the fundus of the stomach is wrapped around the esophagus, thereby forming a cuff that prevents reflux);
- implantation of valve prostheses.
Possible consequences and complications
At 3-4 stages of cardia weakness, acute and chronic ulcers form on the walls of the esophagus. The most dangerous complication of ulcers is profuse bleeding, which requires emergency medical attention. When mucosal lesions heal, scars (strictures) remain, which can narrow the lumen of the esophagus. Strictures reduce the passage of solid food into the esophagus and swallowing disorders (dysphagia) occur.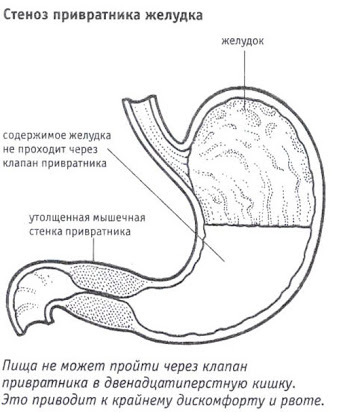
Long-term reflux leads to the replacement of the esophageal epithelium with the gastric epithelium. This process is considered a precancerous disease and is called Barrett's syndrome. In 2-5% of cases, the modified epithelium is transformed into esophageal cancer.
The consequences of gatekeeper failure include extensive erosions and ulcers that can cause profuse bleeding. Also dangerous are the stages of development of atrophic and hyperplastic changes in the mucous membrane, since they are considered precancerous conditions.
With scarring of ulcers, narrowing of the pyloric lumen is possible, which disrupts the movement of food from the stomach into the duodenum. This pathology is called pyloric stenosis. In severe cases of pyloric stenosis, signs of malnutrition (weight loss) appear and dehydration of the body may occur.
It can be concluded that with untimely treatment of cardia and gatekeeper insufficiency, life-threatening complications arise. When the first symptoms appear, you need to contact a gastroenterologist, go through the necessary list of examinations, and get treatment. During therapy, punctual intake of all prescribed medications, lifestyle changes and dietary changes are required. With the timely implementation of the recommendations, the outcome of the disease is favorable.
Video about cardia and gatekeeper insufficiency
What is cardiac insufficiency of the stomach:



