Content
- Possible reasons
- Non-pathological causes
- Pathological causes
- Treatment methods
- Caries prevention
- Eating a diet and drinking enough water
- Drug treatment
- Pilocarpine
- Cevimelin
- Physostegmine
- Application of stimulants
- Using oral sprays
- Mouth rinses
- Sage
- Calendula
- Vegetable oil
- Humidifier
- Possible consequences and complications
- Dry mouth videos
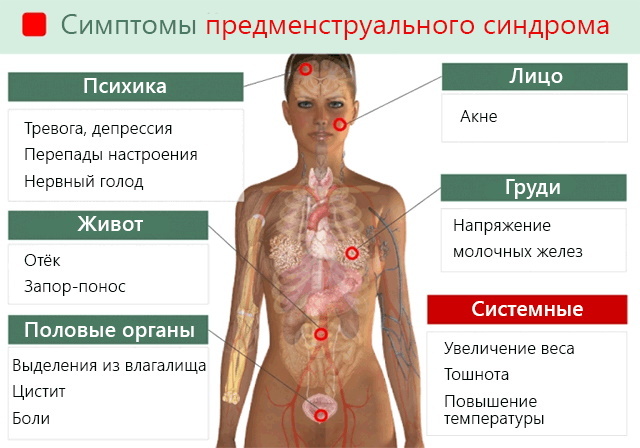
In an elderly person, metabolic processes in the body change every year and gradually dry mouth may appear. This harmless symptom - feeling of dryness in the mouth (xerostomia), in most cases is natural.
With the sudden appearance of xerostomia, it may indicate a serious health disorder and pathologies that need to be paid close attention. Insufficient production of saliva not only serves as an indicator of health in old age, but also creates discomfort for a person. He has difficulty swallowing and speaking. With increased dryness, a person begins to smell unpleasant from the mouth, which affects communication and circle of acquaintances.
Possible reasons
It dries up in the mouth of an elderly person for various reasons that affect the work of various organs and systems, general health, external factors. The main causes of dry mouth include:
Non-pathological causes
Non-pathological causes are not associated with disease and chronic changes. They are often natural or temporary and include:
- age-related changes;
With age, a person's salivary glands begin to work less intensely, which affects the amount of fluid they release. An older person's mouth may feel mildly dry at different times throughout the day, as the salivary glands always work differently. Such attacks of dryness depend on the time of year, the person's diet, and can be intermittent.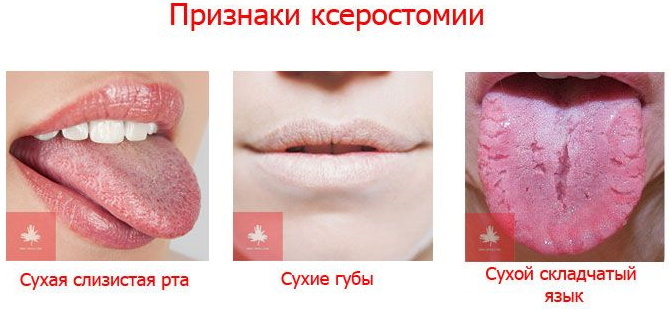
- drug treatment;
Many drugs have a depressing effect on the work of the salivary glands. Such changes are indicated in the side effects in the instructions and are not always encountered. A decrease in the production of salivary fluid may appear after taking pills, ampoules, or injections of drugs. Most often, drugs for edema, antiallergic drugs and antidepressants have this effect.
Chemotherapy also affects some cancer patients, as well as physiotherapy with drugs on selected elderly patients. All these changes depend on the individual characteristics of the organism and stop after the completion of the course of treatment.
- stress;
Strong nervous shocks and stressful situations disrupt the work of the whole organism. As a result, the functions of the salivary glands are disrupted, provoking dry mouth even in a healthy person. This manifestation can persist for 1-2 days after stress.
- nasal congestion;
Due to the narrowing of the nasal passage for pathological and non-pathological reasons (palips, curvature of the septum, inflammation of the mucous membrane with ARVI), a person loses the ability to breathe through the nose to the fullest. Mouth breathing causes dry mouth and throat, mouth discomfort and dry lips. This change is temporary and easily removable.
- dehydration;
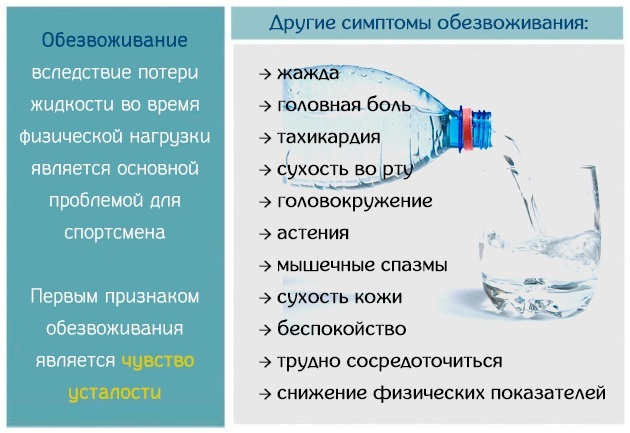
Water imbalance in the body due to lack of drink or diarrhea affects the work of the salivary glands. The body begins to secrete a little fluid, therefore, in older people, when dehydrated, first of all, it dries up in the mouth.
- avitaminosis;
A severe lack of vitamins, especially iron, can provoke insufficient functioning of the salivary glands.
- alcohol and smoking.
Intoxication with alcohol abuse, as well as constant smoking, provoke a disruption in the work of the whole organism, including the nervous and cardiovascular systems, of the processes of saliva secretion. The epithelium in the mouth is constantly irritated by the influence of cigarette tar, the surface of the mucous membrane is dried, which is especially noticeable in adulthood. With the rejection of bad habits, the work of the salivary glands is restored gradually and can return to normal.
Pathological causes
Pathological causes always require treatment and are associated with serious disorders in the functioning of the body. These include:
- diseases of the gallbladder and ducts;
With damage to the gallbladder and ducts, the salivary glands do not work to their full extent. Often, poor bile flow is associated with an enlarged thyroid gland and vascular dystonia, which affect the functioning of other glands. In this case, the secretion of secretions from the salivary glands becomes limited. The saliva becomes thick and bitter, with a taste of bile.
- HIV infection;
AIDS disrupts the body's immune system, and also manifests itself as disturbances in the work of the lacrimal and salivary glands. 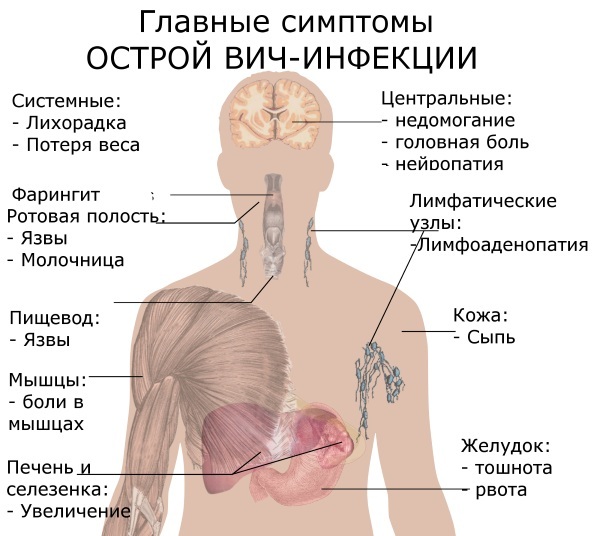 As the disease progresses, the amount of saliva is produced in a person less and less, causing severe dry mouth.
As the disease progresses, the amount of saliva is produced in a person less and less, causing severe dry mouth.
- endocrine diseases;
Violation of the ability to absorb glucose in diabetes associated with thyroid damage, provokes an increased blood sugar level. With diabetes mellitus, it is more difficult to remove fluid from the body, the patient periodically has a feeling of dry mouth and a desire to drink a lot.
- autoimmune diseases;
Diseases associated with impaired immune function (Sjogren's syndrome, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma) cause damage to the secret glands in varying degrees produced by the body by autoimmune cells. These changes affect the suppression of the salivary glands. The salivary glands become inflamed and secrete a limited amount of secretion.
- sialoadenitis;
Inflammation of the salivary glands or sialoadenitis can occur on one or both sides of the mouth. In the area of the salivary glands, the tissues swell and swell greatly, when the mouth is opened in a person, soreness appears, and the secretion of secretion from the affected gland stops almost completely. Most often, elderly people after an infectious disease are susceptible to this disease.
- stomatitis;
With stomatitis, the mucous surface of the mouth becomes inflamed. The mouth is dry, odorless, and the gums may bleed. Stomatitis can be bacterial or allergic. 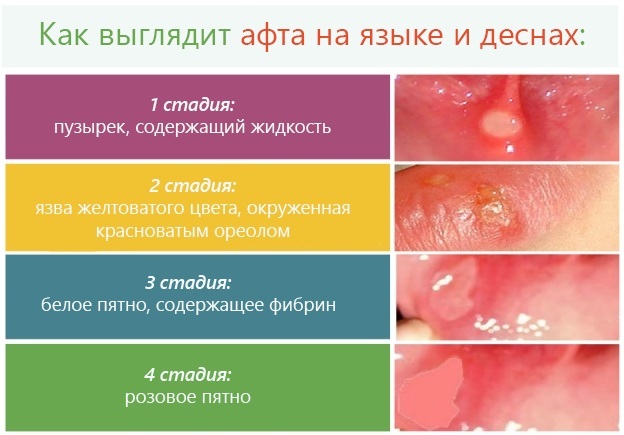 The disease develops on the surface of the mucous membrane and, if untreated, causes severe discomfort.
The disease develops on the surface of the mucous membrane and, if untreated, causes severe discomfort.
- candidiasis;
When the oral mucosa is affected by candida fungi, a dense white bloom appears on the surface of the epithelium. As a result, the person experiences severe dryness and burning sensation in the mouth.
- viral infections;
Viral diseases (lymphotropic virus, brucellosis, cytomegalovirus, hepatitis C) cause an imbalance in the body's water balance up to dehydration. An additional symptom of such infectious diseases is always dry mouth, weakness and dizziness.
- neurological dystrophy;
The lack of coordination in the work of the nervous system provokes a disruption in the connection of the brain with the root structures of the nerve endings, which are located on the surface of the mucous membrane. The affected nerve connections partially lose sensitivity in the mouth, which makes it possible to adequately assess the state of the mucous membrane. As a result, the person produces less saliva than is required. These symptoms are most often observed in older people with neurological diseases, panic attacks, and after a stroke.
- gastroenterological disorders;
It dries in the mouth of an elderly person very partly due to a violation of the process of digesting food. Dry mouth often occurs with heartburn or pancreatic involvement. 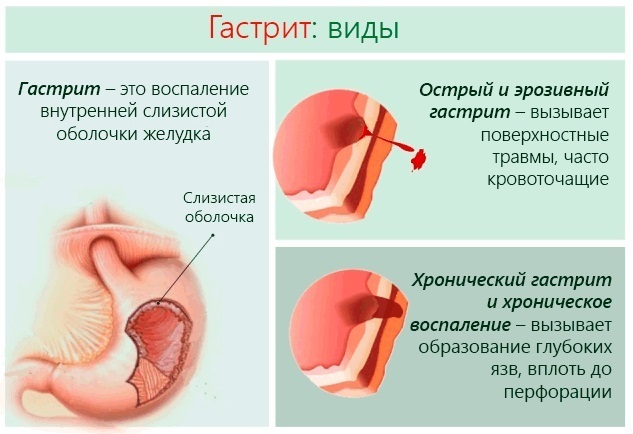 Pancreatitis and chronic gastritis are always associated with constipation, diarrhea, nausea. Any changes in the process of digestion provoke an imbalance in the water balance in the body, which is manifested by increased dry mouth. In the body of an elderly person, secretion stagnates and the amount of fluid secreted by the glands decreases sharply. A bitter sensation may appear in the mouth.
Pancreatitis and chronic gastritis are always associated with constipation, diarrhea, nausea. Any changes in the process of digestion provoke an imbalance in the water balance in the body, which is manifested by increased dry mouth. In the body of an elderly person, secretion stagnates and the amount of fluid secreted by the glands decreases sharply. A bitter sensation may appear in the mouth.
- urological diseases;
Inflammatory processes in the kidneys disrupt the process of fluid removal and blood purification. The body's water balance changes and the salivary glands begin to produce less fluid. Dry mouth also occurs with polyuria or renal colic, when renal failure occurs.
- oncological diseases;
In old age, dry mouth often accompanies cancer. Malignant formations in the glands, on the mucous membrane, as well as blood diseases provoke changes in the work of the salivary glands.
- bleeding;
With internal and external bleeding due to injuries or diseases, the body loses fluid, the water-electrolyte balance is disturbed. With such a violation, the body stops any secretions, so dry mouth occurs.
- cardiovascular diseases.
Disturbances in the work of the heart of a pathological nature (heart attack, angina pectoris, hypertension) are accompanied by headaches, impaired consciousness, dry mouth and decreased vision.
Treatment methods
Dries in the mouth of an elderly person always differently during the day. During the day, the salivary glands secrete more fluid than at night. However, in any case, xerostomia causes severe discomfort, therefore it is important to conduct a general examination of an elderly person in order to identify the main reasons for the change, diagnose and prescribe treatment for the underlying disease. The rate of recovery of the mucous membrane depends on the effectiveness of the treatment of the underlying disease.
In order to relieve the symptom of dry mouth, the following methods are often used in old age:
Caries prevention
It is recommended in old age to treat carious itching and to install, if necessary, prostheses to maintain the condition of the oral mucosa in normal condition.
Eating a diet and drinking enough water
In old age, it is especially important to drink enough water every day, since all body tissues lose their elasticity and change their properties. It is important to follow a dietary diet, exclude salty and smoked foods, and be more often in the fresh air. The amount of water you drink must be at least 1 liter. taking into account chronic diseases and health conditions.
Drug treatment
It dries up in the mouth of an elderly person if there are reasons for this all the time. However, in the presence of insignificant production of saliva by the glands, the level of secretion production can be regulated with the help of drugs. There is a group of medicines that stimulate the salivary glands. These include:
Pilocarpine
Pilocarpine is an antiglocoma drug that interferes with the functionality of the salivary glands. The composition of the product includes alkaloids of plant origin.
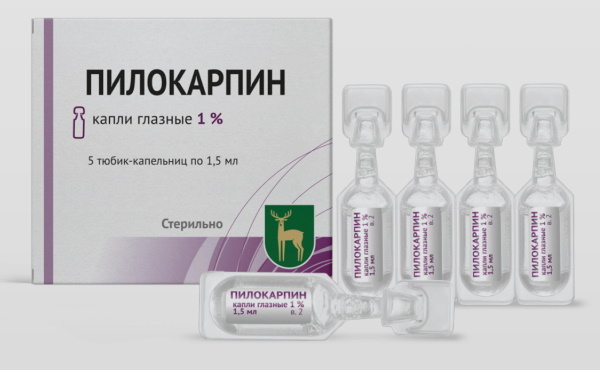
The agent is prescribed in a dose of 4 mg. to be taken 3 times a day in the elderly for 2-3 months.
Cevimelin
The drug cevimelin effectively relieves dry mouth and is a parasympathomimetic agent that stimulates the salivary glands. The drug is taken 1 tab. 3 times a day for 2-4 months.
Physostegmine
Physostegmine is used to treat the eyes, but it effectively helps stimulate the small glands on the surface of the oral mucosa. The drug is prescribed to restore salivation in 1 tab. 2-3 times a day. The course of treatment is 2 months.
Application of stimulants
Saliva production by the glands can be stimulated at any age. It is produced in greater quantities during sucking and chewing movements, as well as through:
Using oral sprays
There are many sprays that contain substances that increase the production of saliva in the mouth (xerostom, dental, dentaid). They need to be sprayed on the oral mucosa up to 4-6 times a day.
Mouth rinses
Rinsing the mouth with broths helps to restore the mucous membrane of the mouth for 1-2 hours. For rinsing, decoctions from medicinal herbs are most often used, namely:
Sage
Sage has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties, it restores the condition of the oral mucosa and promotes the healing of microcracks. Sage helps to restore mucous membranes in case of infectious diseases and fungal infections.

- For the preparation of the broth 1 tbsp. sage must be combined with the same amount of chamomile and calendula.
- The mixture is stirred and filled with 350 ml of boiling water.
- The infusions are left warm until they cool, and then filtered.
- The resulting mixture should be rinsed out your mouth 3-4 times a day for 2-4 months.
Calendula
Calendula helps to maintain the moisture level in the mouth, it has a disinfectant and wound healing effect. With continued use, calendula can help reduce the development of tooth decay.
- To prepare a mixture in 1 tbsp. boiled warm water, you need to add 1 tsp. tincture of calendula.
- The mixture is thoroughly mixed and used for rinsing the mouth 3-5 times a day in courses of 1.5 months.
Vegetable oil
Vegetable or olive oil is actively used for rinsing with dry mouth. Vegetable oil tightly envelops the mucous membrane of the mouth and reduces moisture loss by 2-3 hours. For the procedure, you need to put a small amount of oil in your mouth. Then rinse your mouth thoroughly for a few minutes and spit it out. It is recommended to do such rinses no more than 2 times a day.
Humidifier
A standard humidifier is capable of maintaining a humidity of 35-40%. This is especially important in summer or during the winter heating season. With this humidity, water from the body evaporates much more slowly, which means that dry mouth will not feel so much.
Possible consequences and complications
Dry mouth as a harmless symptom in an elderly person with sudden onset in most cases is an indicator of a pathological disorder in the body. In the absence of examination and treatment, these people may develop complications over time.
Namely:
- chronic dryness of the mucous membrane;
- weakness;
- lesions of the oral mucosa;
- purulent eruptions around the mouth;
- decreased appetite;
- trouble swallowing food;
- digestive disorders;
- fainting;
- bleeding of teeth and gums;
- progressive development of concomitant chronic diseases.
An older person may have dry mouth as a standard age-related change. To exclude possible complications during the period when a feeling of constant dry mouth appears, it is important for an elderly person to undergo a complete examination. When a pathology is detected, it is enough to use the standard treatment of the underlying disease, which will completely restore well-being and return the comfort of the oral mucosa for a long time.
Dry mouth videos
Malysheva. Three tests for dry mouth: