Content
- List of indicators of a general blood test, their definition and meaning
- Table of norms of KLA indicators by age in children, reference values
- Deciphering indicators, reasons for deviations from the norm
- Hemoglobin
- Erythrocytes
- Leukocytes
- Color index
- Neutrophils
- Eosinophils
- Monocytes
- Basophils
- Lymphocytes
- Platelets
- What do violations of norms signal in the analysis of a child, what indicators confirm the diagnosis
- Leukemia
- Allergic manifestations
- Thrombocytosis
- Helminthic invasions
- Atypical leukocytes
- Hypochromic anemia
- Mononucleosis
- Roseola
- Video about KLA in children
UAC (complete blood count) is a medical study, aimed at studying the properties and characteristics of blood in children and helping to identify the presence of various diseases in time with correct decoding.
List of indicators of a general blood test, their definition and meaning
When examining blood, many different indicators are taken into account, which are taken into account when making a diagnosis.
List:
- Hemoglobin is a protein that distributes iron throughout the body. The study helps determine the level of hemoglobin in the blood.
- Red blood cells are red blood cells, oxygenated blood cells that distribute oxygen throughout the body. The analysis allows you to determine the concentration of cells in the blood volume.
- Leukocytes are "white" blood cells that perform a protective function and are responsible for immunity.
- The color indicator is the quantitative content of hemoglobin in 1 unit of erythrocyte.
- Neutrophils are a large group of representatives of "white" blood, whose function is to fight various bacteria, fungi and protozoa.
- Eosinophils are a type of white blood cell that prevents the development of allergic reactions caused by various pathogenic microorganisms.
- Monocytes are cells of innate immunity that take part in phagocytosis.
- Basophils are a subspecies of leukocytes that are involved in the development of allergic reactions. Components are one of the main indicators of the leukocyte formula.
- Lymphocytes are the main representatives of the immune system, which are responsible for the internal defenses of the body.
- Platelets are blood cells responsible for blood clotting and preventing bleeding.
The diagnosis and determination of deviations is established by the totality of the data obtained.
Table of norms of KLA indicators by age in children, reference values
UAC in children (decoding the analysis takes no more than 1-3 days) is carried out even in the absence of indications, since the study is mandatory for newborns and children under 3 years of age age.
There are certain norms of indicators in children and adults. A deviation from the norm may indicate the development of various pathological processes. At the same time, the permissible deviation rates can vary within 5%.
All indicators are calculated based on the quantitative content of cells per 1 liter of blood:
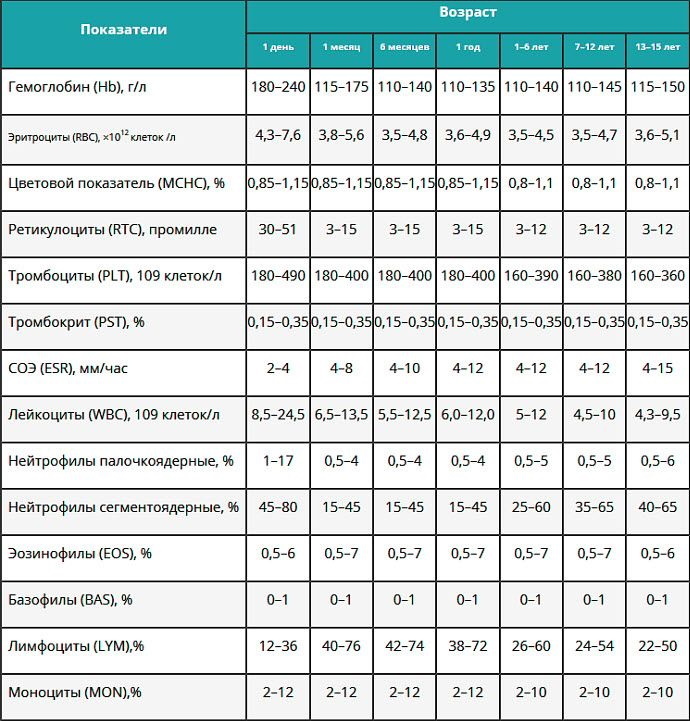
| Index | Child's age | Reference values |
| Hemoglobin | Newborns up to 1 month | 107-198 g / l |
| 1 month to 1 year | 94-141 g / l | |
| 1-5 years old | 110-140 g / l | |
| 5 to 10 years old | 115-145 g / l | |
| 10 to 18 years old | 117-166 g / l | |
| Erythrocytes | Newborns up to 1 month | 3,3-5,9×1012 l |
| 1 month to 1 year | 3,5-5,3×1012 l | |
| 1-6 years old | 3,7-4,9×1012 l | |
| 6 to 12 years old | 3,8-5,1×1012 l | |
| 12-18 years old | 3,8-56×1012 l | |
| Leukocytes | Children under 2 years old | 6-17,5×109 l |
| 2-6 years old | 5-15,5×109 l | |
| 6-16 years old | 4,5-13,5×109 l | |
| Over 16 years old | 4-10×109 l | |
| Color index | Newborns up to 1 month | 0,85-1% |
| 1-15 years old | 0,8-1% | |
| Neutrophils | Children under 4 years old | 1,5-8,55×109 l |
| From 4 to 16 years old | 1,5-8×109 l | |
| Over 16 years old | 1,8-7,7×109 l | |
| Eosinophils | Newborns up to 12 months | 0,05-0,4×109 l |
| 1 to 6 years old | 0,02-0,3×109 l | |
| Over 6 years old | 0,02-0,5×109 l | |
| Monocytes | Newborn 12 months | 0,5-1,1×109 l |
| 1 to 16 years old | 0,5-0,6×109 l | |
| Over 16 years old | 0,05-0,82×109 l | |
| Basophils | Up to 1 year | 16-45% |
| 1-6 years old | 28-58% | |
| 6-16 years old | 38-60% | |
| Over 16 years old | 47-72% | |
| Lymphocytes | Children under 12 months | 45-75% |
| 1-2 years | 37-60% | |
| 2 to 6 years old | 33-55% | |
| 6-16 years old | 30-50% | |
| Over 16 years old | 19-37% | |
| Platelets | Newborns up to 10 days | 99-421×109 l |
| 10 days to 1 month | 150-400×109 l | |
| 1 month to 5 years | 150-400×109 l | |
| 5-15 years old | 150-450×109 l | |
| Over 15 years old | 150-400×109 l |
Deciphering indicators, reasons for deviations from the norm
Deviation of indicators from the norm may indicate various diseases and disorders occurring in the body. Moreover, each disease has its own characteristics of changes in the quantitative content of blood corpuscles.
Hemoglobin
Low or high hemoglobin levels indicate various disorders developing in the body. Thus, an increased concentration of the indicator indicates an insufficient fluid content in the body. A similar condition occurs as a result of increased sweating or when taking diuretics. Pathology can develop against the background of diarrhea, with vomiting.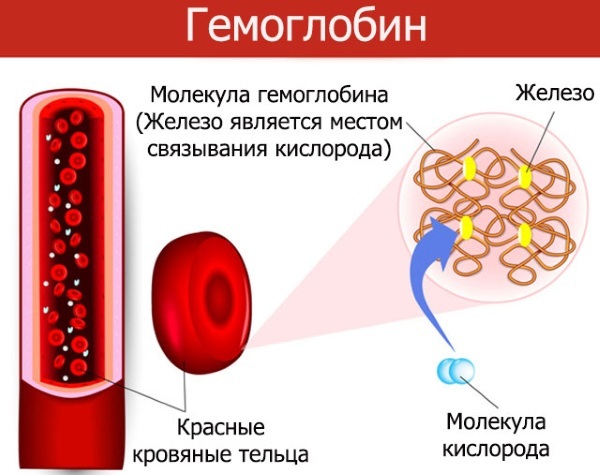
Possible diseases with increased hemoglobin:
- hereditary congenital diseases of the cardiovascular system or lungs (including lung or heart failure);
- kidney pathology - the presence of benign formations, stenosis;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system.
A lack of hemoglobin is otherwise called anemia, which is also one of the reasons.
Other possible violations:
- deficiency of vitamins;
- various forms of leukemia;
- lack of iron;
- general depletion of the body;
- congenital blood diseases.
Also, a lack of hemoglobin can be due to profuse blood loss.
Erythrocytes
UAC in children (interpretation of the results should be carried out only by a qualified specialist) can be prescribed for any suspicion of the development of diseases. An increased number of red blood cells in the blood may indicate a lack of fluid in the body, caused by various factors.
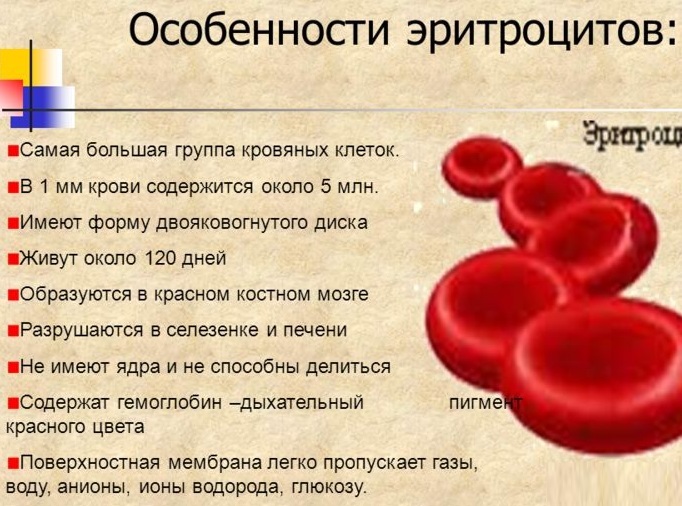
Also, the reason for their high level may be the following diseases:
- renal artery stenosis;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- malfunctions of the heart, leading to the development of organ or lung failure.
Causes of low red blood cell concentration:
- violation of dietary rules - deficiency of vitamins and proteins from food;
- profuse bleeding;
- various forms of leukemia;
- diseases leading to a violation of enzymes;
- hemolysis.
An accurate diagnosis is possible after decoding all the data received.
Leukocytes
There are many different factors that lead to a decrease in the level of white blood cells.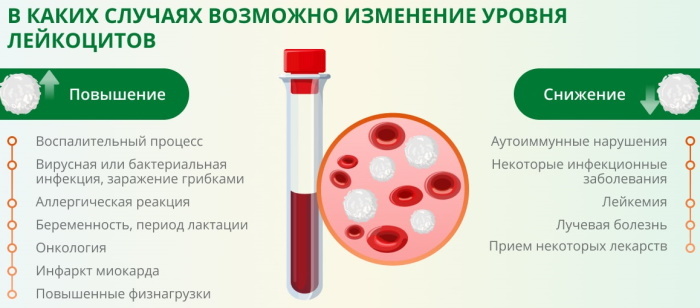
Most often, the development of pathology is due to physiological reasons:
- eating food;
- high physical activity;
- inflammatory processes;
- vaccination;
- surgical interventions;
- rheumatic pains;
- burn conditions and other soft tissue injuries;
- purulent-inflammatory diseases;
- cancers (leukemias).
Factors causing a decrease in the concentration of leukocytes:
- radiation sickness;
- viral or infectious damage to the body;
- lack of vitamins;
- rheumatism;
- some types of leukemia;
- anticancer therapy (while taking specific drugs).
Also, an increase or decrease in the concentration of formed elements can be influenced by psychoemotional disorders.
Color index
The color index may decrease as a result of anemic diseases. And also against the background of renal failure.
Reasons for the increase:
- blood diseases (erythremia);
- failure of the heart or respiratory system;
- dehydration of the body due to various factors;
- burn conditions.
Diabetes mellitus may be the cause of high color indices.
Neutrophils
UAC in most cases is prescribed for a comprehensive study of the child. At the same time, only the specialist who appointed them should deal with the deciphering of the analyzes. High levels of neutrophils in the blood are called neutrophilia.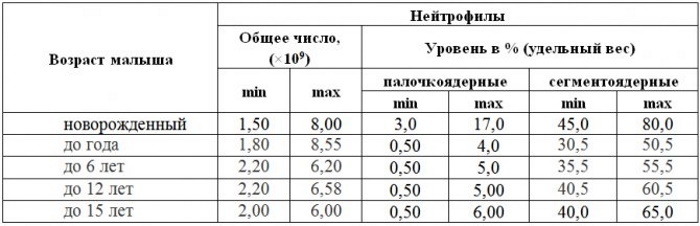
Its main reasons are:
- infectious damage to the body;
- inflammatory processes in the internal organs;
- malignant neoplasms;
- heart attack of various organs;
- metabolic disorders (chronic forms);
- abuse of immunostimulating drugs, vaccination.
Decreased concentration of neutrophils - neutropenia.
Causes of pathology:
- infections;
- blood diseases;
- hereditary predisposition;
- hyperthyroidism;
- complications caused by radio or chemotherapy;
Also, the development of a violation can lead to the intake of certain medications - antibiotics, antiviral and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Eosinophils
A high concentration of eosinophils in most cases indicates the development of various allergic processes in the body.
Also, pathology can be caused by the following disorders:
- parasitic infestations;
- malignant neoplasms;
- infectious diseases;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- rheumatic pathologies.
Factors leading to a decrease in blood corpuscles:
- the onset of the development of inflammatory diseases;
- toxic damage to the body caused by heavy metal poisoning.
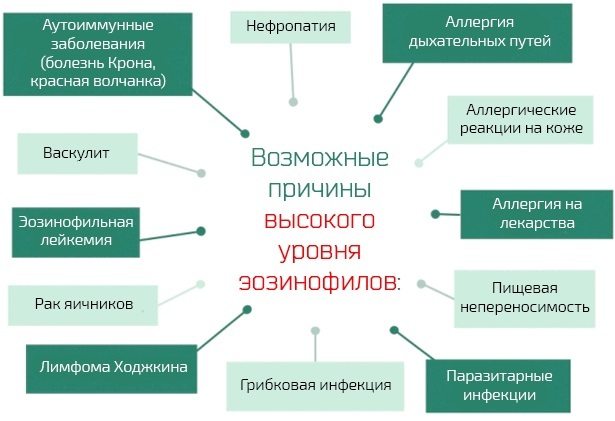
A low level of eosinophils can be caused by the occurrence of purulent and septic processes.
Monocytes
An increase in the number of monocytes is otherwise called mornocytosis.
The reasons leading to its development are:
- parasitic, fungal and viral infections;
- rehabilitation after postponed inflammatory diseases;
- rheumatic pathologies;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- intoxication of the body with acetylene tetrachloride or phosphorus;
- other specific diseases: tuberculosis, syphilis, brucellosis, sarcoidosis, ulcerative colitis.
Factors of reducing the number of monocytes (monocytopenia):
- period after surgery;
- development of purulent processes;
- leukemia (hairy cell disorder);
- aplastic type of anemia.
In rare cases, pathology can occur against the background of the use of steroid drugs.
Basophils
An increased number of basophils in the blood is called basophilia. A violation can occur for a number of different reasons.
Most often, the following diseases lead to its development:
- hypothyroidism;
- CML (chronic myeloid leukemia);
- ulcerative colitis;
- allergic reactions caused by drugs or food;
- chicken pox;
- prolapse of the kidneys (nephrosis);
- the period after the surgical removal of the spleen;
- anemia (hemolytic form of the disease);
- Hodgkin's lymphoma;
- taking hormonal drugs.
Reasons for basopenia (low basophil count):
- hyperthyroidism;
- allergic reactions;
Also, the condition can be observed with an infectious lesion of the body.
Lymphocytes
UAC in children (decoding of diagnostics should be carried out only in a hospital with the use of special skills) helps to identify the primary signs of infectious and inflammatory diseases at the initial stage of their development. A high concentration of lymphocytes in the blood is called lymphocytosis.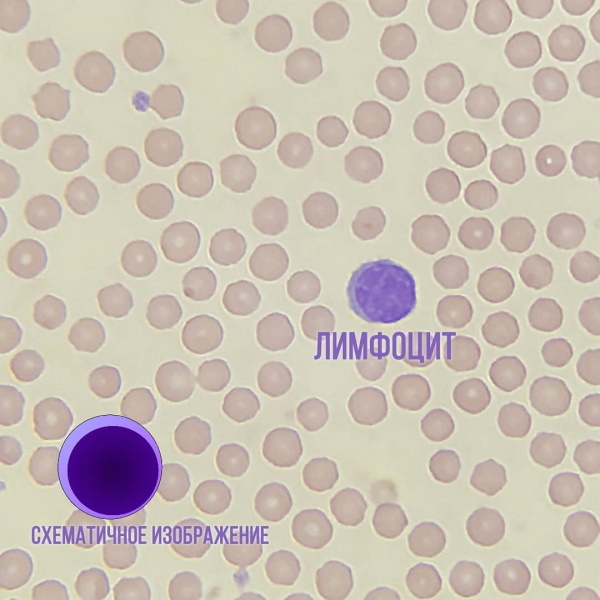
Violation may indicate the presence of the following processes:
- colds;
- viral infections;
- blood diseases;
- parasitic disease (toxoplasmosis);
- poisoning with substances such as lead, arsenic, carbon disulfide, tetrachloroethane;
- the use of certain medications.
Factors provoking a decrease in the level of lymphocytes (lymphopenia):
- anemia (aplastic form of the disease);
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- tuberculosis;
- Hodgkin's lymphoma;
- kidney failure;
- AIDS;
- conducting radio or chemotherapy;
- taking glucocorticoids.
In some cases, the condition can be caused by the formation of malignant tumors.
Platelets
A quantitative increase in platelets can occur with the following disorders:
- a condition caused by surgical interventions (especially after removal of the spleen);
- tumors regardless of their location;
- various forms of anemia;
- physical stress and fatigue;
- development of erythremia.
Reasons for a decrease in platelets (thrombocytopenia):
- hereditary blood diseases (hemophilia);
- taking certain medications;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- DIC syndrome;
- various types of infections;
- aplastic form of anemia;
- conditions associated with blood transfusion;
- prematurity (including hemolytic disorders);
- APG;
- the formation of blood clots in the region of the renal veins.
Often, pathology develops against the background of heart failure.
What do violations of norms signal in the analysis of a child, what indicators confirm the diagnosis
UAC in children (decoding of the study in emergency cases can be carried out within 1-3 hours) is carried out for the purpose of timely detection of diseases dangerous for the condition of the child, especially newborn children.
It is possible to determine the presence of a particular disease after a complete decoding of the analysis performed. In this case, for the diagnosis, it is necessary to take into account the totality of indicators.
Leukemia
Pathology develops against the background of infectious and inflammatory diseases. In this case, an increased content of young neutrophils is found in the blood.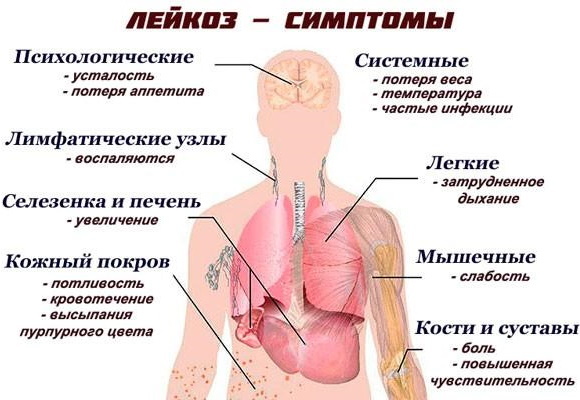
To make a diagnosis, first of all, the leukocyte formula is assessed. With the development of the disease, an increased content of immature leukocytes is observed in the child's blood. With an acute course of pathology, an increase in the level of mature leukocytes occurs.
Allergic manifestations
When an allergy occurs in a child, an increase in the level of leukocytes occurs. At the same time, they increase slightly, in contrast to the infectious process. The main increase is noted in the quantitative content of eosinophils. There is also an increase in ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate).
Thrombocytosis
The pathological process develops against the background of a sharp increase in the concentration of platelets in the blood. Moreover, their number can vary from 700 thousand. up to 1 million and more. The main causes of the disorder are malignant neoplasms, infectious and inflammatory processes, or rare genetic mutations. The disease is characterized by a change in the indicators of formed elements (leukocytes, erythrocytes).
Helminthic invasions
With parasitic invasions, an increase in the level of leukocytes and a decrease in hemoglobin are noted. At the same time, there is an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and an increase in eosinophils. To confirm the diagnosis, additional tests for immunoglobulin and the presence of antibodies are required.
Atypical leukocytes
A study for the presence of atypical cells is mandatory. Their content in the blood may indicate the development of diseases of a viral nature of origin. The most commonly detected Epstein-Barr virus.
Hypochromic anemia
With the disease, there is a decrease in the color index below 0.8%. As a result, a decrease in the level of hemoglobin (less than 110 g / l) is also observed.
To confirm the diagnosis, a biochemical blood test and laboratory tests for transferrin are prescribed.
Mononucleosis
Mononucleosis is characterized by an increase in the level of leukocytes, monocytes and lymphocytes. In this case, in most cases, atypical mononuclear cells are detected.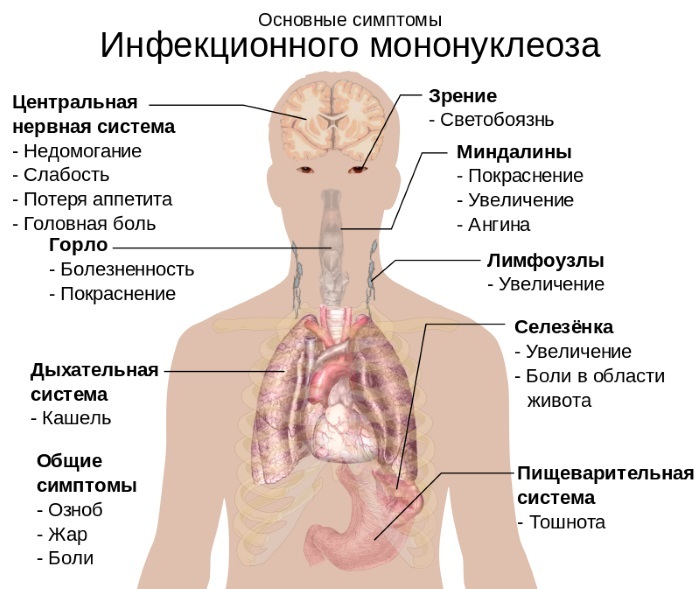
At the initial stages, the concentration of leukocytes may be normal or slightly reduced.
Roseola
Pathology has an infectious nature of origin and arises against the background of infection with herpesvirus types 6 and 7.
With the development of the disease, there is a decrease in leukocytes and neutrophils. In this case, the level of platelets, on the contrary, increases. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate also increases.
KLA is a standard and mandatory study in children. In this case, diagnostics is carried out starting from the first days of a child's life in order to monitor the condition of the newborn. Only a specialist should decipher the analysis.
Video about KLA in children
How to decipher a child's blood test: