Content
- General information
- Classification
- Causes in children
- Psychological reasons
- Symptoms in children
- Symptoms of true encopresis
- False encopresis symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Differential diagnosis
- Treatment
- Psychological support of the child
- Parental counseling
- Defecation mode
- Diet
- Drug treatment
- Complementary treatments
- Treatment of non-retention calomazone
- Forecast
- Video about kalomazaniya
The skill of controlling the selection process feces in humans develops gradually, in the period from 1 to 3 years. First, there is abstinence from defecation at night, then the child begins to consciously regulate this function during the day. Therefore, in the medical community, it is customary to talk about kalomazaniya at the age of not earlier than 4 years. The reasons for the different timing of the acquisition of this skill are the anatomical and functional features of the digestive system and differences in the upbringing of children.
General information
Kalomazaniya in children is a pathological condition that is manifested by involuntary defecation at the age of more than 4 years. Kalomazanie in medical terminology is also called encopresis or fecal incontinence. The prevalence of this pathology among children, according to various sources, is 0.3-8%, and it is more common in boys. Encopresis is characterized by a protracted or recurrent course, the cause of which is untimely treatment parents for medical help, so this disease remains an urgent problem in modern pediatrics.
Calomizing in children, the reasons for which are the absence or loss of the ability to control the excretion of feces or deliberate defecation in the wrong places, can be a separate pathology or be a symptom of a mental and / or behavioral disorder in child.
Classification
Depending on the time of occurrence, there are:
- Primary encopresis. Occurs when the skill of controlling defecation did not previously exist, that is, from birth, the child has no conditioned reflex.
- Secondary encopresis. It is formed when the skill of normal regulation of bowel movement was previously present, but there was a loss of it.
According to the severity, fecal incontinence is classified into:
- I degree. Only gas incontinence is observed.
- II degree. It is characterized by incontinence of gases and liquid feces.
- III degree. The child is unable to retain hard feces.
For reasons of occurrence, they are distinguished:
- Organic encopresis. It is observed against the background of various pathologies and diseases of organs involved in the regulation and implementation of defecation.
-
Functional encopresis. Occurs when it is not possible to identify the pathomorphological cause of the development of this condition.

Depending on the frequency of manifestation, encopresis is:
- frequent (1-3 times a day);
- moderate (up to several times a week);
- rare (appears several times a month);
- episodic (occurs no more than once a month).
Kalomazaniya in children, the causes of which are functional disorders, are divided into:
- Non-retentional (true). It is not associated with fecal retention and is characterized by a disruption in the work of the cerebral cortex, as a result of which involuntary emptying of the intestine occurs. It is rare.
- Retention (false). It is characterized by a delay in feces, observed in children who suffer from constipation and suppress the urge to defecate. It is a common form of this pathology.
- Mixed. Appears against the background of false calozing, as a secondary pathology.
Causes in children
Organic encopresis occurs as a result of congenital or acquired pathology of the anorectal region, as well as structures of the nervous system involved in the regulation of the act of defecation:
- congenital anomalies and malformations of the anus and rectum;
- conditions after surgical treatment of the intestines;
- developmental defects of the spinal cord, spinal cord cleft;
- tumor-like formations of the spinal cord;
- Cerebral palsy (infantile cerebral palsy);
- diseases characterized by damage to the muscles of the pelvic day and the external sphincter of the rectum;
- trauma to the anal sphincters, rectum, perineal muscles, spinal cord.

Physiological and psychological factors play a significant role in the development of functional kalomazaniya in children.
The physiological causes of encopresis include immaturity or damage to the fetal nervous system during pregnancy and childbirth as a result of:
- entanglement with the umbilical cord of the fetus;
- the development of severe forms of late gestosis;
- maternal anemia;
- birth trauma;
- polyhydramnios or low water;
- infectious pathology transferred by the mother;
- immaturity or prematurity of the fetus;
- post-term pregnancy;
- rapid childbirth;
- weakness or discoordination of labor.
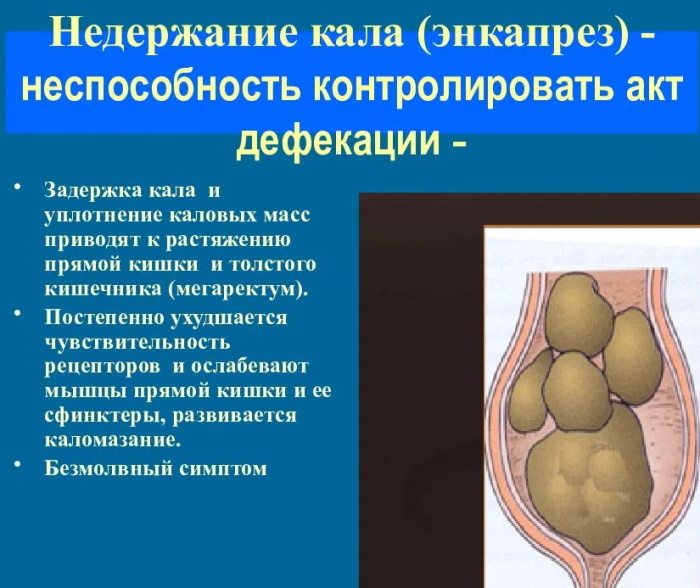
False calomination is manifested against the background of the following conditions:
- Chronic constipation, which is the main cause of the development of retention encopresis. Prolonged and frequent overflow of fecal masses of the rectum causes pressure on the sphincters, which leads to involuntary emptying of the intestine.
- Deliberate delay in feces, which can be associated with a number of psychological reasons.
Psychological reasons
Factors of a psychological nature that provoke the development of kalomazaniya include:
- improper potty training of a child, including excessive severity and persistence of parents in this matter;
- acute traumatic situations (loss of loved ones, severe fright, physical abuse, trauma or surgery);
- situations that constantly oppress the child's psyche (divorce of parents, parents suffering from drug addiction and alcoholism, the beginning of attending preschool institutions);
- excessive loads and stress (conflicts with peers and parents, school change, moving);
- psychological characteristics of the child (shyness, fearfulness, shyness);
- inability to carry out bowel emptying in a timely manner;
- sharp accustoming to an adult toilet;
- restraining bowel movements due to pain during bowel movements;
- fear of going to the toilet due to the inability to independently monitor hygiene after a bowel movement.



Kalomazaniya in children, the causes of which lie in the psychological state of the child, is called chronic neurotic encopresis.
Symptoms in children
The clinical picture of true and false kalomazaniya has some differences between themselves.
Symptoms of true encopresis
Non-retentional encopresis occurs with regular, daily bowel movements with normal stool volume and consistency. The main symptom of the disease is calorification, which occurs during physical or psycho-emotional stress, or for no reason. Mostly the pathology is characterized by a sluggish course, in rare cases it develops quickly.
With a prolonged course of the disease, voluntary defecation disappears. In a child with true encopresis, the perineum and underwear are constantly in the feces, as well as the skin around the anus is irritated. At the same time, the appetite is preserved, pain during bowel movements is rare. On objective examination, feces in the rectum are not palpable, the sphincter tone is preserved. Enuresis is a rare symptom. The combination of fecal incontinence and psychological problems occurs at the same level as with false encopresis.
False encopresis symptoms
Retentional calorification develops against the background of functional constipation.
Constipation in children over 4 years of age is diagnosed if 2 or more of the following symptoms are present within 1 month:
- The number of bowel movements in the toilet per week is less than or equal to 2.
- Kalomazaniya at least 1 time a week.
- Intentional containment of the act of defecation in the anamnesis.
- Detection of overflow of the rectum with feces during examination.
- Pain during bowel movements, emptying of the bowel with hard stools.
- Identification of large-diameter feces.

With false encopresis in children, stool incontinence is at first episodic in nature, with the progression of the disease, caloing is observed regularly. The child's appetite is reduced or absent. Daytime urinary incontinence and bedwetting are common.
With a digital examination, the doctor discovers an accumulation of a large amount of fecal masses in the rectum. Periodically, false diarrhea is observed, which occurs due to the fact that liquid stool from the outside flows around the hard feces and is released outside. When palpating the abdomen at the level of the intestine, accumulations of feces are palpated. Psychoemotional disorders are combined with false encopresis in 30-50% of children.
Comparative characteristics of retention and non-retention kalomazaniya:
| Sign | Retentional calorification | Non-retentional calorification |
| The prevalence of pathology | Frequent form | Rare form |
| Stool frequency | Rare | Daily |
| The volume of feces in the rectum | Large | Normal or absent |
| Pain during bowel movements | Often | Seldom |
| Soreness in the abdomen | Often | Seldom |
| Appetite | Reduced | Normal |
| Urinary incontinence | Often | Seldom |
| The combination of pathology with psychoemotional disorders | 30-50% | 30-50% |
| Laxative drug therapy | Effective | Ineffective |
Diagnostics
If parents suspect that their child has a calorification, then it is necessary to contact a pediatrician. To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor will conduct a comprehensive examination, if necessary, appoint additional consultations from specialists (neurologist, surgeon, gastroenterologist, psychiatrist).
The assessment of the condition of children is always carried out with the help of parents or other guardians. The diagnosis of encopresis is made on the basis of a detailed analysis of the anamnesis data, with the help of which it is possible to obtain essential information about the causes, type and nature of the disease.
During the initial consultation, the pediatrician pays special attention to the period before the onset of calomazation in children. Often at this time there was chronic constipation or diarrhea, combined with fecal retention. An important role is given to clarifying the psychological situation in the family, as well as the course and characteristics of pregnancy and childbirth in the mother.
During a physical examination, the doctor examines the perineal area, describes the structure of the spine, reflexes, also palpates the abdomen and digitally examines the rectum. The specialist prescribes general clinical blood and urine tests, bacteriological examination of feces.
The following instrumental examination methods are used to verify the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of kalomazaniya:
- transrectal ultrasound (determine the condition and diameter of the rectum, in children with constipation, the diameter is more than 25-30 mm);
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space;
- sigmoidoscopy (endoscopic research method to exclude organic pathology of the rectum: tumors, malformations, polyps);
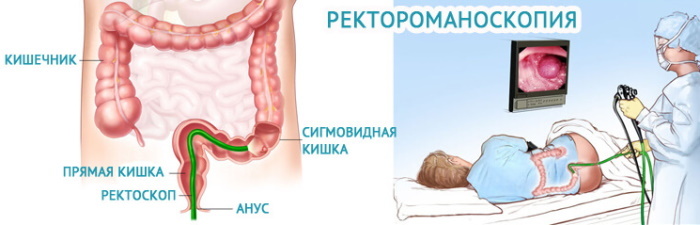
- magnetic resonance imaging (the most detailed examination technique);
- manometry (a method to determine the susceptibility of the rectum to various stimuli);
- proctography (X-ray examination using a barium contrast agent).
Invasive methods are used to diagnose encopresis in children in exceptional situations. Also, in most cases, a neurological and / or psychiatric examination of the child is performed.
Differential diagnosis
Kalomazaniya in children, the causes of which lie in somatic pathology, accounts for 5% of all cases. Therefore, to exclude organic causes, differential diagnosis of encopresis with a number of diseases is carried out.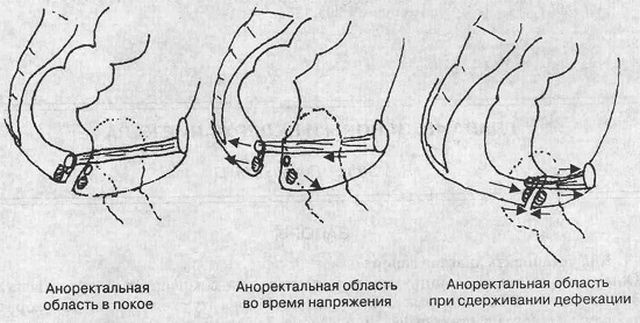
These include:
- pathology of the anorectal region (cracks in the anus, papillomas, abscesses, anal stenosis);
- metabolic disorders and endocrine diseases (cystic fibrosis, celiac disease, lactose intolerance, diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism);
- neurological problems (cerebral palsy, non-closure of the arches of the vertebrae and spinal hernia);
- stool retention caused by drugs;
- Hirschsprung's disease (pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, which is characterized by the absence of nerve ganglia in the end sections of the intestine).
Treatment
The basis of the treatment of false calomazone is to relieve the child of constipation. The main goal of constipation therapy is to restore stool consistency and normalize the frequency of bowel movements.
With a relatively recent kalomazaniya, the leading place in treatment is given to the formation of a rational regimen of the child's day, correction of nutrition and normalization of the amount of fluid consumed. If kalomazaniya exists for a long time, then the treatment takes place in 2 stages.
The first stage of therapy involves cleansing the rectum from fecal masses using cleansing enemas or the use of laxatives directly into the rectum. The size of the enema is determined individually, depending on the age of the child.
It is also possible to use rectal suppositories with glycerin. These suppositories irritate the rectal mucosa, thus increasing its contractility. Also, under the action of glycerin, the consistency of the stool softens. Suppositories with glycerin are contraindicated in inflammatory pathology in the rectum. The release of the end sections of the intestine from feces leads to the activation of intestinal motility.
The second stage of therapy includes several areas:
- psychological support for the child;
- counseling for parents;
- teaching children the skills of using a pot / toilet and forming a regime of trips to the toilet;
- diet;
- medication and complementary therapies.
Psychological support of the child
Psychological support of a child is carried out in conscience with a psychiatrist, psychotherapist or psychologist.
The specialist defines the following vectors of work:
- getting rid of fears and the consequences of trauma;
- teaching the child relaxation techniques;
- correction of relationships in the family and with peers;
- a course of psychotherapy that develops the child's ability to control their needs.
Parental counseling
Parents are given a number of recommendations for creating a favorable psychological climate for the child. In an everyday environment, stressful situations should be excluded, a clear daily routine should be established. It is recommended not to punish the child for mistakes; regulatory support methods can be used. For example, it can be games that relieve the fear of the toilet.
Defecation mode
Teaching your child to use a potty or toilet can significantly reduce anxiety and guilt and increase adherence to treatment. The main goal of training is the formation of skills that are aimed at performing a regular, voluntary act of defecation.
These skills include:
- training in the habit of going to the toilet (the child is asked to sit on the potty or toilet several times a day after eating);
- keeping a diary of bowel movements (by a child or by parents), where they indicate the time and place of bowel movement;
- correct potty / toilet training (it is necessary for the child to sit on the potty for about 5-10 minutes in a relaxed state, with his feet on a hard surface).
It is important that the learning process does not cause negative emotions in the child, therefore it is necessary to use encouraging productive sitting in the toilet with praise, as well as eliminating severity and criticism in this question.
Diet
A correct and balanced diet is of the utmost importance in the treatment of infantile calozoa. 4-5 meals a day are recommended.

Some foods should be excluded from the diet:
- pastries made from butter dough;
- fatty meats and fish;
- smoked meats and canned food;
- spicy and fried foods;
- chocolate;
It is also recommended to reduce consumption:
- cereals (semolina and rice);
- pasta;
- gas-forming products (cabbage, peas, beans, apple juice).
It is recommended to include in the diet foods high in fiber:
- bran;
- chia and flax seeds;
- cereals (buckwheat, quinoa);
- nuts;
- dried fruits (dried apricots, figs);
- vegetables (carrots, beets, zucchini, pumpkin);
- fruits (apples, grapefruits).
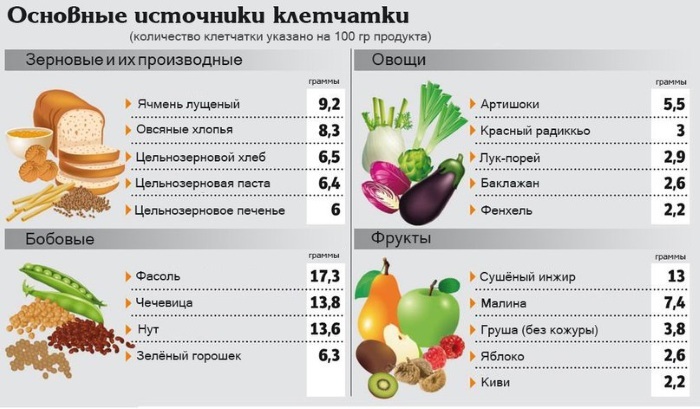
Vegetables and fruits should make up more than half of the daily diet. Fiber helps to loosen the stool and increase the frequency of bowel movements. It is also necessary to include in the menu fermented milk products that contain probitics and prebiotics. Probitics are microorganisms that normally inhabit the gastrointestinal system, and prebiotics are a breeding ground for these microbes.
Compliance with the drinking regime is an integral component of the treatment of retention encopresis. The volume of water required per day for a child weighing more than 20 kg is calculated by the formula: 600 ml + 20 ml / for each kg of weight over 20 kg.
Drug treatment
If a child suffers from false encopresis for a long time, then the appointment of drugs is indicated.
The following groups of medicines are usually used:
- laxatives;
- prokinetics (drugs that stimulate the intestinal muscles);
- probiotics and prebiotics;
- enzyme agents;
- choleretic drugs.
Laxatives are prescribed not only to stimulate bowel movement, but also to develop the habit of going to the toilet regularly.
The following groups of laxatives are distinguished:
- substances that increase the volume of feces (bran, synthetic drugs);
- compounds that soften the stool (petroleum jelly);
- substances that are irritating (castor oil);
- osmotic agents (magnesium salts);
- di- and polysaccharides (lactulose).
Lactulose preparations are recognized as a safe laxative in pediatrics. It is not absorbed in the small intestine. Under the influence of the microflora of the large intestine, lactulose is broken down into fatty acids, which increase the osmotic pressure in the intestine. The action of the drug begins 1-2 days after administration. When using this drug, side effects are extremely rare.
Complementary treatments
Additional methods of treatment include all non-drug technologies that are used for the therapy of retention calomassage:
- Exercise therapy;
- massage of the anterior abdominal wall;

- physiotherapy (sinusoidal modulated currents, diadynamic currents, drug electrophoresis);
- balneotherapy (use of natural and artificial mineral waters);
- reflexology (impact on biologically active points by physical methods).
Treatment of non-retention calomazone
Felting in children, the causes of which are not associated with constipation, is much less treatable. In this case, laxatives are ineffective and can worsen the course of the disease. Therefore, they use teaching the child the ability to use the toilet correctly, as well as psychotherapeutic techniques. In rare cases, the benefits of using prokinetics are noted.
Forecast
Both variants of fecal incontinence with prolonged course and no therapy have a poor prognosis. The kalomazanie can persist until adulthood. It should be remembered that after the end of treatment, supportive therapy is prescribed. Its duration ranges from 2-3 months to several years, in order to achieve a lasting result and avoid relapses of the disease. Seeing a doctor at the early stages of encopresis development significantly increases the chances of a favorable outcome of the pathology.
Kalomazaniya in children is a fairly common pathology, with the overwhelming majority of cases occurring in the retention form of the disease. Diagnosis and treatment of encopresis is carried out by a group of specialists: pediatrician, neurologist, psychiatrist and surgeon. The reasons due to which complications develop and the effectiveness of treatment decreases include untimely visits to the doctor and the somatic nature of encopresis. Getting rid of kalomazaniya improves the quality of life of the child and allows you to lead a full life.
Video about kalomazaniya
What to do if a child constantly gets his panties dirty: