Diabetes mellitus is a complex and formidable disease. Every year more and more patients are registered, who suffer from this ailment. It is statistically proven that every 10-12 years there is an increase in the number of patients by 20% worldwide. The main danger is a sharp "rejuvenation" of the problem. Compared with the last century, the number of children who have insulin deficiency has increased by about 45%.Such a picture forces doctors and patients to seriously think about the possibility of preventing the disease, over timely diagnosis and adequate treatment.
Features of the disease course in children

Everything in this world is moving and developing. This is true for man. After all, it is completely natural that the body of an elderly man will function differently than the organism of a one-year-old child. If we talk about the pancreas, the norm of sugar in the blood in children, which directly depends on the activity of insulin, also varies depending on how old the baby is.
The main reasons that affect the difference in the amount of sugar in a child are:
- Physiological immaturity of the hormonally active organ. This is especially true for newborns. Since the pancreas at the beginning of life is not a critically vital organ( in comparison with the heart, brain, lungs and liver), in the first year of the existence of the small person, it undergoes the ripening process;Active phases of development. For children aged 6-8 and 10-12 years, so-called "growth spikes" are characteristic. They represent a powerful release of growth hormone, which causes all structures of the human body to increase in size. Because of this activation, physiological changes in the sugar level are sometimes observed. The pancreas should work harder and be a source of additional insulin;
Normal glucose values depending on the age of the
It is worth noting that in different periods of a child's life the sugar levels in the blood test may not be the same. Up to 10-12 years, there is a trend towards a decrease in the basic indicators. They may differ from those in adults and do not require medical intervention. For better perception, it is customary to demonstrate them in tabular form:
| Age | Adequate serum glucose level |
| Up to 1 year | 2.78-4.4 mmol / L |
| 2-6 years | 3.3-5.0 mmol / l |
| 10-12 years and older | 3.3-5.5 mmol, l |
These constants are currently used by endocrinologists around the world and are the basis for diagnosing the disease.
Why does the analysis change in the direction of hyperglycemia?
It is very important in time to suspect the pathology of the child and begin adequate treatment. Almost 100% of children under 12 years old can only have type 1 diabetes mellitus, caused by absolute or partial insufficiency of the hormone insulin, which has hypoglycemic effects. There are publications of some scientists describing the disease of the 2nd type in boys of 12 years. They connect this phenomenon with obesity of the child and the emergence of resistance of peripheral tissues to the action of insulin. But with the help of laboratory tests it is proved that such unhealthy children have organic and functional damage to the pancreatic parenchyma with a decrease in the production of the corresponding hormone, which indicates the combination of the disease.
The main reasons that can lead to changes in the blood sugar level of a newborn or schoolboy 10-12 years old are as follows:
- Heredity. If the 2 nd parents of the child suffer from the disease, then with a chance of about 25%, their child will be ill. When only one person in the family is diabetic, then the risk of developing the problem is 10-12%;
- Tumor neoplasm in the gland;
- Hormonal problems with other endocrine organs( pituitary, hypothalamus, adrenal glands, thyroid gland);
- Incorrect power. The predominance in the diet of light carbohydrates and fats leads to obesity and the development of hyperglycemia;
- Severe infectious diseases;
- Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and glucocorticoids;
- Incorrect analysis technique;
All these situations can cause a significant effect on blood sugar levels and lead to the development of diabetes.
Decrease in glucose values

As the child in most cases behaves very actively, it provokes an increased use of glycogen stores by the body. Therefore, there may be times when hypoglycemia is observed. These include:
- Excessive physical activity without adequate energy replenishment;
- Prolonged fasting;
- Disorders in the metabolic processes of the body;
- Diseases of the nervous system( tumors and trauma);
- Sarcoidosis;
- Constant stress conditions.
Similar problems are relatively rare, but they must be taken into account when interpreting the results of analyzes.
How to determine the glycemic index correctly?
Since, depending on the child's age, there is a certain variation in the level of sugar in the serum, it is absolutely necessary to properly deliver blood for analysis. This will help prevent diagnostic errors and pinpoint the presence or absence of the disease.
The correct procedure for taking the test involves abstinence from eating 10-12 hours before the blood sampling .You can drink still water.
During the procedure with the help of a lancet, first a puncture of an anonymous finger is made, a drop of blood is applied to a special piece of paper. It is entered into the glucometer, after a few seconds you can see the result.
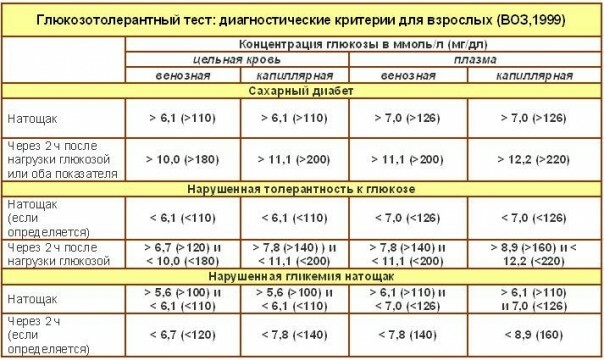
Abnormal values of the analysis are values greater than 5.5 mmol / l in fasting. But it does not always have to be an excuse for panic. To more accurately establish the diagnosis of an additional glucose tolerance test:
- The child is given to drink 75 g of glucose, diluted in water;
- After 2 hours, the blood sugar level is again analyzed;
- Rri values above 7.7 mmol / l with a certain accuracy can be said about the presence of diabetes.
It should be noted that the children's body has the ability to reduce glycemia compared with the adult body. This is due to the greater functional activity of the hormone, which, in turn, makes boys and girls more susceptible to all negative factors of the environment. A person who is more than 18 years old can only be considered a diabetic if his sugar value in the serum analysis is greater than 11.0 mmol / l ( 10.0 mmol / L for some individual publications) after carrying out a glucose tolerance test.
The organism of toddlers still remains in some way a mystery for doctors and scientists. It is possible that in a few years new ways of fighting the disease will be invented and the acceptable level of glycemia, which is topical at the moment, will be changed. The main task of parents - in time to suspect the possibility of developing ailment and seek medical help. With diabetes you can live for years, you only need to learn this.