Epileptic status is a condition that is characterized by frequently recurring or continuous epileptic seizures with a duration of up to half an hour.
Epileptic status is a condition that is characterized by frequently recurring or continuous epileptic seizures with a duration of up to half an hour.
In this case, each new seizure occurs earlier than the patient has time to get out of the previous one. During the time between attacks, the consciousness remains unclear, and there are also signs of coma, for which there is a violation of blood flow through the vessels and an upset of respiratory function.
Epistatus is the most common neurological condition. The incidence of this pathology is approximately 20 cases per 100,000 people.
In half of cases, ES occurs in young children. Among people with epilepsy, this condition is more common in children than in adults( in the ratio of 15-25% to 5%).
About 7% of patients with epilepsy have a history of one to three EC attacks during their entire illness.
Contents of
- What is the provoking factor?
- Species and stages of the epistatus
- How it looks in real life
- First emergency aid - rules and advices
- Next steps
- Features of the condition in children
- Danger of the state
- For the prevention of
What is the provoking factor?
The main reason for the emergence of EC is the abolition of medications taken, the effect of which is directed to the suppression of epileptic seizures.
However, the status epilepticus can occur not only against the background of epilepsy, but also because of brain lesions, among which:
- head trauma;

- intoxication;
- intracranial malignancy;
- circulatory disturbance in the brain;
- infection;
- hydrocephalus( encephalopathy);
- withdrawal syndrome;
- complications of diabetes mellitus;
- of the hematoma.
Species and stages of the epistatus
The variability of the types of epileptic seizures causes the formation of various clinical forms of ES.They are divided into two main groups - convulsive and non-convulsive seizures.
The following types of epileptic status are distinguished by classification:
- Generalized ES - characterized by unfolded tonic-clonic seizures with unconsciousness.
- Not completely generalized ES - characterized by atypical muscle spasms with complete loss of consciousness.
 Tonic status is most common among children with Lennnox-Gastaut syndrome. Can be observed at different ages. Clonic status is observed with epilepsy in infants, as well as convulsions with a high temperature in small children. Myoclonic status is manifested by constant or episodic muscle twitching.
Tonic status is most common among children with Lennnox-Gastaut syndrome. Can be observed at different ages. Clonic status is observed with epilepsy in infants, as well as convulsions with a high temperature in small children. Myoclonic status is manifested by constant or episodic muscle twitching. - The status of focal paroxysms proceeds according to the type of Jackson epilepsy with muscular contraction of a certain localization, for example, only the muscles of the face, one limb or half of the body. In this case, loss of consciousness may not occur.
- Abscess or non-convulsive status of - accompanied by complete loss of consciousness without muscle contractions. Such seizures are characterized by the easiest course, but because of the absence of seizures, the diagnosis can be difficult.
- Partial status of is characterized by unconscious and automatic actions with complete or incomplete loss of consciousness.

Also the stages of the development of the epistatus are singled out:
- appears - lasts 1-10 minutes;
- initial - lasts from 10 minutes to half an hour;
- deployed - lasts from half an hour to an hour;
- refractory - lasts more than an hour.
How it looks in real life
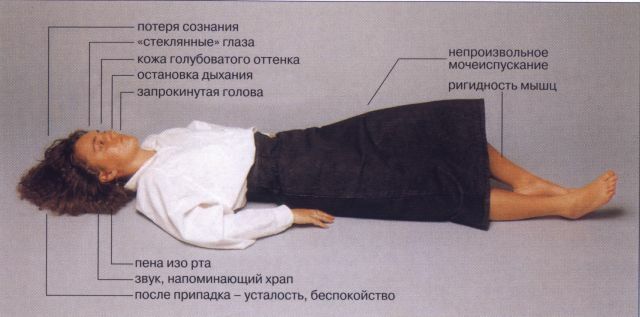
Symptoms of epileptic status are determined by severe disorders in the mind, respiratory system and hemodynamics, which are caused by a previous attack, the amount of seizures in an epistatus can be from 3 to 20 per hour.
Consciousness by the time of the next attack does not clear up and the person is in a state of stunning, numbness or coma.
With prolonged ES, the coma is exacerbated, becomes deeper, the cramps take on a tonic form, the increase in arterial pressure is replaced by a sharp decrease, and increased reflexivity is due to the lack of reactions. Disorders of hemodynamics and respiration become more pronounced.

Seizures may disappear, and then the stage of epileptic prostration occurs, for which external changes are characteristic:
- the size of pupils varies;
- the view becomes unconscious;
- mouth slightly ajar.
Epistatus always lasts more than half an hour. This condition should be differentiated from episodic seizures, between which there is a complete or almost complete clearing of consciousness, as well as a partial restoration of the physiological state of the patient.
The convulsion ES can be divided into two phases. At the first, compensatory changes take place to maintain circulation and metabolism.
This condition is characterized by: 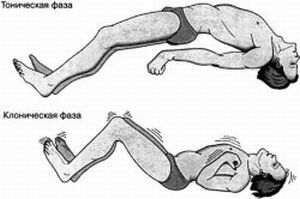
- tachycardia;
- high blood pressure;
- vomiting;
- involuntary urination;
- involuntary stool.
The second phase comes in half an hour or hour and is characterized by a breakdown of compensatory changes. In this state, such processes occur:
- lowering of blood pressure;
- arrhythmia;
- impairment of respiratory function;
- pulmonary artery thrombosis and its branches;
- acute renal and hepatic insufficiency.
An inconclusive epistatus is characterized by a variety of disorders of consciousness:
- feeling of detachment;
- immobilization.
In the case of ES complex partial seizures observe:
- deviation behavior;
- confusion;
- symptoms of psychosis.
Epileptic status from A to Z:
First emergency aid - rules and advice
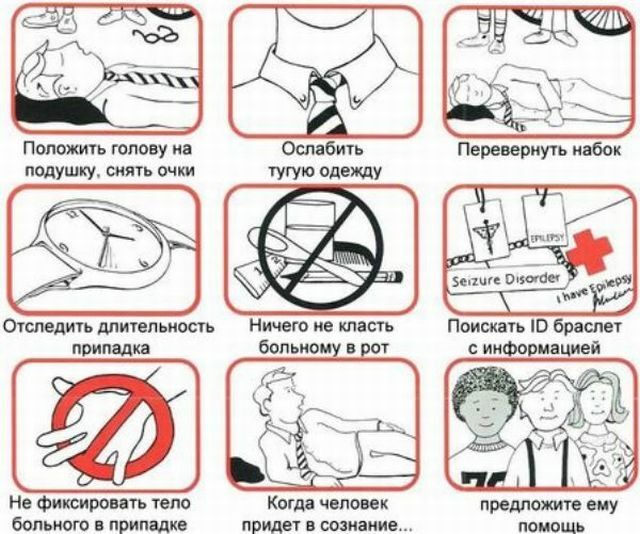
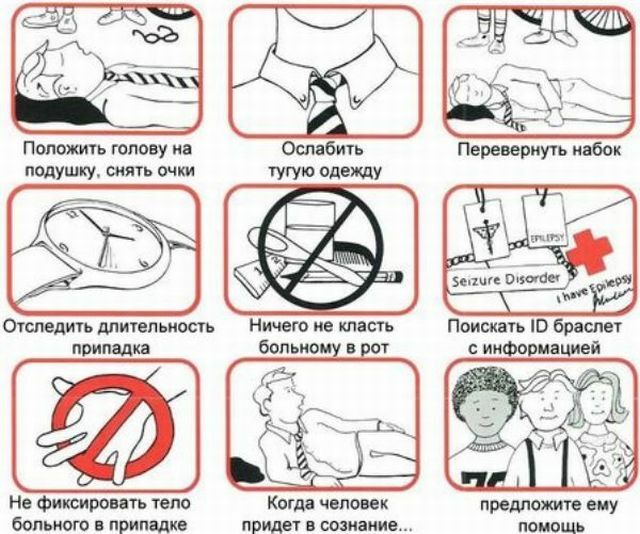
The main objective in the provision of first emergency care in case of an epistatitis before the arrival of doctors is to prevent injury and trauma to the patient.
What needs to be done at the time of the attack:
- put the person on a comfortable surface to reduce the traumatic risk;
- remove those garments that can cause discomfort( for example, tie, belt), unfasten the collar;
- lay under the head of twisted clothes;
- gently turn his head to one side so that the patient does not choke on his saliva;
- if the mouth is ajar, you need to put a handkerchief or any tissue between your teeth, but in no case is a sharp object to break your teeth;
- remove all dangerous items that are at the nearest distance to avoid injury;
- does not keep a person too much, otherwise the probability of bone fracture is high;
- does not open the teeth if they are compressed.
Next steps
The epileptic status is relieved by carrying out the following activities:
- providing airway patency;
- application of oxygen therapy;
- intravenous injection of Diazepam( maximum daily dose is 40 mg), a side effect of this drug may be respiratory depression.
Therapy is followed by the introduction of medications depending on the stage of epileptic status.
At the initial stage for the arrest of epileptic status, such drugs are used:
- Diazepam;
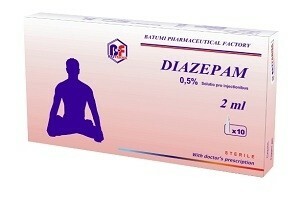
- Lorazepam;
- Depakin;
- Feniton;
- Oxytobutyrate.
Among the side effects of treatment can be identified following effects: arterial hypotension, acute toxic hepatitis, phlebosclerosis, hypokalemia.
At the advanced stage of ES apply:
- Diazepam;
- Lorazepam;
- Phenobarbital;
- Thiopental sodium.
At the refractory stage of ES the following measures are carried out:
- Intubation, correction of electrolyte disturbances, transfer to artificial ventilation of the lungs - to maintain the vital functions of the body.
- Barbiturate Anesthesia - intravenous injection of Thiopental sodium for 20 sec.100-250 mg of the drug is administered. If the patient's condition does not improve, a dose of 50 mg is given every few minutes until the seizure ceases. Barbituric anesthesia can last from 12 hours to 24 hours.
- Injections of Dexamethasone and Mannitol are administered to prevent cerebral edema.
- Infusion dehydration therapy is conducted with the purpose of elimination of disturbances of liquorodynamics and metabolic process. For this apply: Magenzia, Lasix, Cordiamin, Eufillin, Korglikon.
Features of the state in children
 Very often, the epistatus that occurs in children is a sign of the onset of epilepsy, but it happens that convulsive attacks appear already in the late stages of the course of the disease.
Very often, the epistatus that occurs in children is a sign of the onset of epilepsy, but it happens that convulsive attacks appear already in the late stages of the course of the disease.
In newborns, the seizure occurs with a partial loss of consciousness, while the reaction to external stimuli persists.
Generalized ES can be manifested by tonic-clonic, clonic, myoclonic cramps.
With an electrocardiogram with electroencephalography, there is a pyclonic stupor and slow waves that reflect the state of epileptic obscuration of consciousness. Partial ES can be simple, somatotrophic, dysphasic.
With a complex partial epistatus, a stable preservation of epileptic twilight of consciousness is observed.
The number of seizures can reach several tens or even hundreds a day. At the same time, there is a breakdown in the respiratory function, hemodynamics, metabolic processes in the brain are disrupted, the state of the coma can be deepened until the onset of death.
Danger of state
Mortality in case of epileptic status with previously diagnosed epilepsy is 5%, in case of symptomatic status - 30-50%.If the EC lasts more than an hour, such severe consequences can arise: 
- cerebral edema;
- oxygen starvation of the brain;
- excessive decrease in blood pressure;
- lactatacidosis - excessive accumulation of lactic acid in the body;
- electrolyte balance violation;
- delayed mental development and mental retardation - in children.
Anxistent ES is less dangerous than generalized, but in this case, violations of the cognitive sphere may develop.
For the prevention of
Epistaxis in persons suffering from epilepsy can be prevented by the selection and implementation of anticonvulsant therapy.
To prevent symptomatic epileptic status, it is necessary:
- to conduct timely treatment of head injuries;
- does not run the treatment of infectious diseases;
- to avoid intoxication;
- to refrain from excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- do not take narcotic substances.