Content
- The concept of an acute abdomen in surgery
- Causes of the condition
- Factors and risk groups
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- First aid
- Treatment based on the cause
- Injuries to the abdominal and retroperitoneal organs
- Acute inflammatory diseases of the abdominal organs
- Hollow organ perforation
- Intra-abdominal bleeding
- Acute intestinal obstruction
- Acute violation of mesenteric circulation
- Prognosis and clinical guidelines for patients
- Acute stomach video
Sharp belly indicates to the critical state of the body, which requires immediate hospitalization of the patient with further surgical treatment. This pathology is characterized by severe dysfunctional disorders in the work of vital internal organs, bouts of unbearable pain, and stiffness of movements.
The concept of an acute abdomen in surgery
A sharp abdomen in practical surgery is a collective medical term that includes a complex of painful symptoms arising from one or several diseases of internal organs, or life support systems organism.
A painful condition of the abdominal cavity can develop in children and adults of all age groups. A sharp abdomen is always accompanied by shooting attacks of severe pain, which manifests itself in the focus of the inflammatory process, and then spreads throughout the abdomen.
Patients with this symptomatology receive complex treatment in the hospital of the surgical department. Delay in the provision of medical care causes an increase in the inflammatory process, the opening of internal bleeding with the further development of sepsis and the onset of death. The table below describes the classification types of acute abdomen, depending on the nature of the pain syndrome.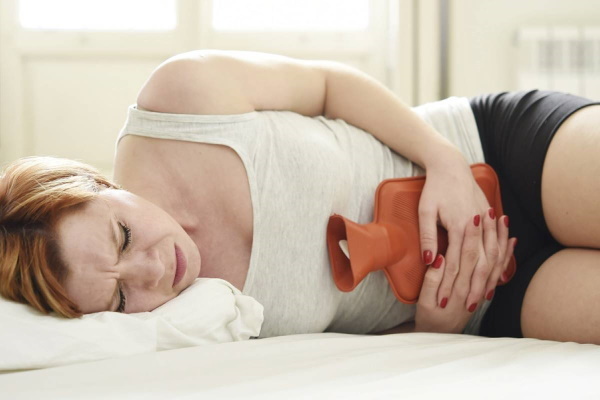
| Kind of pain | Characteristics of an acute abdomen depending on the clinical manifestations of pathology |
| Visceral | An acute abdomen with signs of visceral abdominal lesions is characterized by bouts of localized pain in the same place of the abdomen. The occurrence of pain syndrome is associated with the presence of a pathological process exclusively in the tissues of the diseased organ without spreading to the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space. |
| Somatic | An acute abdomen of a somatic type occurs due to irritation of all or some areas of the parietal peritoneum. In this case, the pathology also has a localized character, but the organs of the respiratory system are involved in the painful process. Attacks of acute abdominal pain are accompanied by a dry barking cough without sputum separation. |
| Reflected | An acute abdomen with signs of reflected pain is considered the most severe pathology of its kind. Pain syndrome simultaneously covers all tissues of the affected organ, spreads to the peripheral receptors of the nervous system, radiates to the stomach, liver, intestines, heart and kidneys. |
A sharp abdomen in surgery is characterized by a critical condition of the patient who cannot independently to move, forced to be in a horizontal position all the time, tucked in to the chest knees. Taking analgesics does not bring a positive result, or it slightly alleviates the patient's suffering only for a short period of time. The etiology of the acute abdomen is established in the process of differential diagnosis.
Causes of the condition
There are a large number of factors that contribute to the development of this pathology.
The following causes of acute abdomen in adults and pediatric patients are distinguished:
- acute form of appendicitis;
- hepatic colic;
- rupture of the walls of an aneurysm located in the structure of the abdominal aorta;
- perforated ulcer or damage to the duodenum;
- cholecystitis in the acute stage;
- inflammation of the tissues of the pancreas, which has passed from chronic to acute;
- an attack of hepatic colic;
- perforation of any internal organ that has a hollow structure;
- myocardial infarction (the occurrence of a heart attack is accompanied by acute and burning pain, which is not localized only in the chest, but also extends to the abdominal cavity, gives to the left arm, shoulder girdle and lower jaw);
- exacerbation of chronic diseases of the female reproductive system;
- complications of diabetes mellitus (a separate type of pathological condition of the body, which is called the term "diabetic belly");
- inflammation of the pleura;
- right-sided pneumonia of viral or bacterial etiology;
- renal colic;
- traumatic injury to internal organs, accompanied by profuse bleeding;
- exudative form of pericarditis;
- hydronephrosis of the kidneys;
- intestinal obstruction.

Sharp abdomen in surgery
A sharp abdomen in surgery is considered a life-threatening emergency. The cause of the pathology is established immediately. Measures are being taken to stabilize the patient's vital signs. Immediately after the diagnosis is made, complex treatment of internal organs is carried out, aimed at restoring their working capacity, as well as removing damaged tissues.
Factors and risk groups
The main causes of an acute abdomen are chronic diseases of the body, which have abruptly passed into the stage of exacerbation. At risk are men and women with pathologies of internal organs.
There are the following factors contributing to the development of an acute abdomen:
- frequent alcohol abuse;
- addiction;
- diabetes;
- cholecystitis;
- regular consumption of too fatty foods in the presence of chronic diseases of the liver, gallbladder and its channels;
- history of abdominal aortic aneurysm;
- chronic appendicitis;
- a tumor process in the intestine (in this case, an acute abdomen can occur in the presence of a benign or oncological neoplasm);
- stomach ulcer, the development of which is accompanied by frequent exacerbations, internal bleeding and degenerative processes in the walls of the digestive organ;
- coronary heart disease;
- weakened immunity, when initially a person often suffers from infectious diseases, suffers from chronic inflammatory processes in the organs of the respiratory system;
- cirrhosis of the liver of viral or intoxication etiology;
- Crohn's disease;
- ulcerative colitis;

- unbalanced and irrational nutrition, when semi-finished products, products predominate in the daily diet of a person industrial processing, containing chemical additives, preservatives that irritate the mucous membrane of the digestive organs;
- hereditary tendency to severe diseases of internal organs (for example, ulcerative lesions of the stomach and duodenal walls, cancer of the liver, intestines, gall bladder);
- the use of an insufficient amount of fluid, which gradually led to a pathological condition of the kidneys.
At risk are men aged 20 to 40 years, as well as women from 25 to 45 years. People in the age group from 60 to 70 years old are most often admitted to the hospital of the surgical department with signs of an acute abdomen, which has arisen due to intestinal obstruction or wall stratification aorta. Both pathological conditions are critical, as they can cause death.
Symptoms
A sharp abdomen is accompanied not only by bouts of piercing pain, which extends to the entire abdominal cavity, but is also characterized by the presence of additional symptoms:
- nausea;
- discharge of vomit;
- constipation or loose stools;
- internal bleeding;
- heaviness in the right, left hypochondrium or in the center of the abdomen;
- increased gas formation;
- the presence of blood in the feces;
- progressive decrease in blood pressure;
- bloating of the intestines;
- dry, paroxysmal cough without mucus separation;
- dizziness;
- an increase in body temperature to a level of 38-39 degrees Celsius, as well as to higher rates;
- loss of appetite;

- the release of blood along with vomit;
- yellowness of the skin (for example, if cholecystitis, hepatitis or cirrhosis of the liver became the cause of the acute abdomen);
- loss of consciousness;
- bacterial infection of the blood (the occurrence of this symptom is characteristic of advanced stages of internal bleeding or acute inflammation of organs);
- rapid shallow breathing with frequent lifting of the chest and absorption of small amounts of air;
- violation of the heart rhythm (for example, if an acute abdomen has arisen due to myocardial infarction, or a pathological condition of the aorta);
- uterine bleeding in women with chronic diseases of the reproductive system;
- urinary retention in patients with kidney disease.
The main danger of an acute abdomen is that its symptoms simultaneously indicate a large number of diseases of internal organs and body systems. To make an accurate diagnosis, a complex of hardware and laboratory examination methods is used.
Diagnostics
A sharp abdomen in surgery is a consequence of a critical state of internal organs. The examination of the patient begins immediately after his admission to the hospital of the medical institution. The table below lists the main diagnostic measures that are carried out to determine the underlying disease, causing unbearable pain inside the abdominal cavity, indigestion and other disturbances in the functioning of life support systems organism.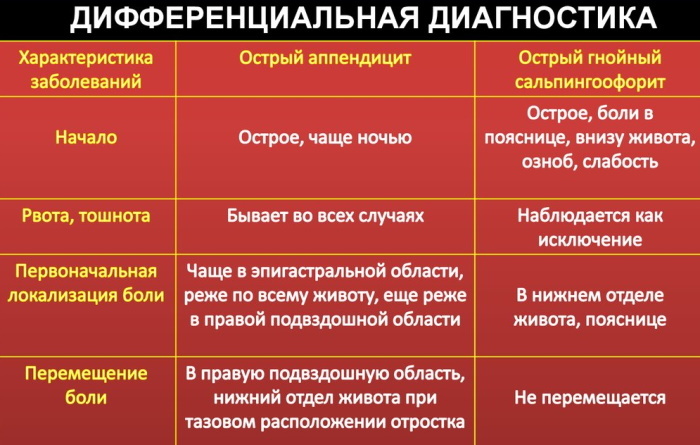
| Diagnostic method | The purpose of the survey |
| X-ray | An X-ray is indicated for patients who have signs of intestinal obstruction, as well as tumor neoplasms in the digestive tract. X-rays can also be given to patients with symptoms of pneumonia or pleurisy. The purpose of this diagnosis is to detect foci of the pathological process, as well as to determine their extent. |
| Ultrasound | The use of ultrasound is advisable in cases where acute pain attacks are localized in the area of the internal organ. An ultrasound scan of the kidneys, organs of the female reproductive system, bladder, liver and gallbladder is performed. |
| MRI | MRI diagnostics is considered one of the most informative, since within a short period of time allows you to scan all parts of the body, to detect the focus of the pathological process in any part of the abdominal cavity. This examination method displays areas of tissue with signs of inflammation and tumor neoplasms. |
| Colonoscopy | Colonoscopy is indicated for patients with signs of colon disease. The principle of this examination is that a special probe is inserted into the patient's anus, which in real time transmits the video image to the computer monitor. Colonoscopy is contraindicated in patients with Crohn's disease and symptoms of ulcerative colitis. In the presence of these pathologies, colon perforation is possible. |
| Gastroscopy | Gastroscopy is necessary for patients with peptic ulcer and other severe stomach diseases. An endoscopic probe with a digital video camera is inserted into the patient's digestive system through the mouth and esophagus. |
Patients with signs of acute abdomen donate urine, capillary and venous blood for clinical and biochemical studies. Based on the results of a comprehensive examination of the body, the final diagnosis is made and the methods of therapy are selected. In medical practice, there are cases when doctors urgently perform a surgical intervention with an opening of the abdominal cavity. In this case, the pathological state of the internal organ is determined directly on the operating table.
First aid
Providing first aid to a person with symptoms of an acute abdomen requires adherence to the rules:
- lay the patient in a horizontal position so that he is on his side (in case of vomiting, the contents of the stomach will flow out of the oral cavity and will not enter the trachea);
- immediately call an ambulance, or independently deliver the patient to the nearest surgical department of the hospital;

- a person with this pathology should not be given food and drink;
- an ice pack or cloth soaked in cold water should be placed on the surface of the patient's abdomen (these actions will allow reduce the severity of pain syndrome, inflammation, and also slow down blood loss in the case of internal bleeding);
- even in conditions of severe pain, a person should not be given antibiotics, laxatives and pain relievers, as this will complicate the examination and may lead to an incorrect diagnosis.
After the arrival of an ambulance, doctors also perform actions aimed at stabilizing the patient's condition before he is delivered to the hospital of the surgical department. In the case of internal bleeding, a critical decrease in blood pressure, the patient is injected intravenously with medicinal solutions with blood-substituting properties. Most often, 2 ml of the drug Cordiamine is used in combination with Sulfocamphocaine at a concentration of 10%.
Treatment based on the cause
An acute abdomen in surgery is treated using the method of surgical intervention.
Most operations are carried out on an emergency basis simultaneously with the resuscitation of the patient.
Injuries to the abdominal and retroperitoneal organs
In case of severe traumatic injuries of internal organs, an opening of the abdominal cavity is performed with further suturing of tissues that have signs of rupture. If necessary, complete or partial removal of the organ is performed.
For example, resection of the spleen, excision of the kidney. Most injuries to the abdominal and retroperitoneal organs are accompanied by internal bleeding, which complicates the treatment process. After performing surgical manipulations, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit, where he receives antibacterial, anti-shock, blood-substituting and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Acute inflammatory diseases of the abdominal organs
Inflammatory diseases of internal organs, which have an acute form of the course, are dangerous with a serious complication in the form of bacterial blood poisoning with a further onset of septic shock. Treatment tactics depend on the stage of the pathological process. In the presence of direct indications for surgery, an urgent operation is performed.
The surgeon opens the patient's abdominal cavity, opening access to the diseased organ. Removal of tissues is carried out, which, under the influence of acute inflammation, have acquired signs of a necrotic process. After suturing the wound, the patient receives long-term antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy. The selection of drugs is carried out individually, depending on the strain of microflora, which is found in the focus of the inflammatory process.
Hollow organ perforation
Traumatic perforation of hollow organs or a violation of the integrity of their walls due to a concomitant disease is treated only with the use of surgical intervention. The surgeon performs a strip operation, opening the patient's abdominal cavity.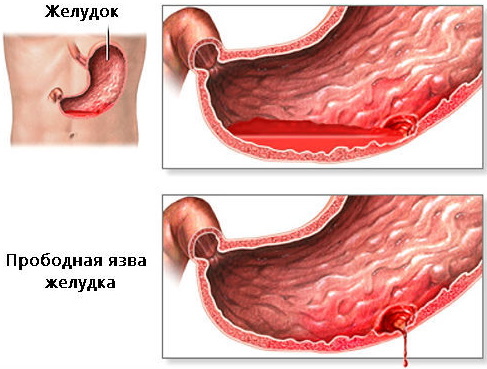
With the help of suture material, the integrity of the perforated organ is restored, sutured blood vessels, measures are being taken to fully restore physiological functions injured tissue. Upon completion of surgical procedures, sutures are applied to the patient's body. The patient spends the next 4-7 days in the intensive care unit in case of severe complications.
Intra-abdominal bleeding
Stopping intra-abdominal bleeding should be performed immediately. Otherwise, the patient will die from acute blood loss, inflammation and bacterial infection. Surgical treatment of this pathology is carried out in the sterile conditions of the operating room. The doctor cuts the patient's abdominal cavity and then identifies the source of acute blood loss.
After that, the doctor sews up the damaged vessel, restores the integrity of the internal organs. After stopping the bleeding, suture material is applied to the operated area of the abdomen. At the stage of rehabilitation, the patient receives hemostatic drugs, medicines with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Acute intestinal obstruction
Treatment of intestinal obstruction also involves opening the abdominal cavity. The surgeon opens access to the part of the intestine that no longer has a digestive function. The doctor assesses the general condition of the tissues of the diseased organ.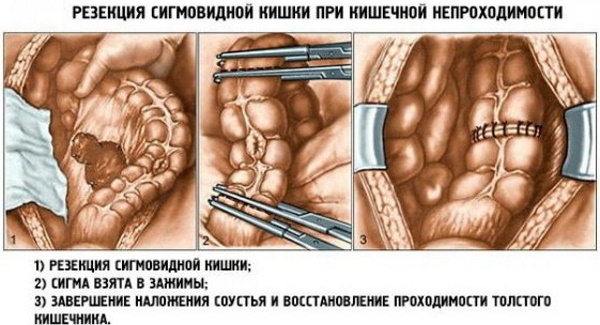
If there are signs of a necrotic process, a part of the intestine is cut out with further stitching of its segments. Simultaneously with the use of the surgical method, the causes that caused intestinal obstruction are eliminated. For example, a tumor that disrupts the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is removed.
Acute violation of mesenteric circulation
Violation of the mesenteric circulation causes ischemia of the intestinal tissues with the further development of the necrotic process. The mortality rate of this pathology is 55-80%. To save the patient's life, an emergency operation is performed to restore the disturbed blood supply to the intestines. If there are signs of thrombosis, the doctor restores the patency of the blood vessels.
Areas of the bowel showing signs of necrosis are excised. In most cases, the result of this operation is death or loss of a significant part of the intestine. After a successful surgical intervention, the patient will have a long rehabilitation. The absence of intestines causes a violation of the digestive function of the body, a deficiency of vitamins, minerals and other nutrients that cannot be fully assimilated.
Prognosis and clinical guidelines for patients
Patients with signs of an acute abdomen should not self-medicate. In such situations, it is necessary to immediately seek medical help at the hospital of the surgical department. Only under this condition can one expect a favorable outcome with further recovery.
Self-therapy at home with the use of pain relievers, antibacterial and laxative drugs will lead to the development of severe complications in the form of peritonitis, bacterial blood poisoning, septic shock, irreversible damage to internal organs with the onset of fatal outcome.
An acute abdomen is a combination of dangerous symptoms that indicate a painful condition of the internal organs, blood vessels of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space. The emergence of this pathology is facilitated by chronic diseases of the body, abdominal trauma, tumor neoplasms.
Patients with signs of an acute abdomen are immediately admitted to the hospital of the surgical department. Timely operation with the restoration of the functions of internal organs gives a chance for a favorable outcome of treatment. And for patients who ignored the visit to a medical institution, were engaged in self-therapy, the prognosis for recovery is unfavorable.
Acute stomach video
Symptoms of an acute abdomen:



