Content
- Characteristic
- Functions and properties
- Anatomy and structure
- Possible diseases and pathologies
- Adductor tendinopathy of the thigh
- Classification
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Femoral nerve neuropathy
- Classification
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Tailor muscle rupture
- Classification
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Tailor muscle video
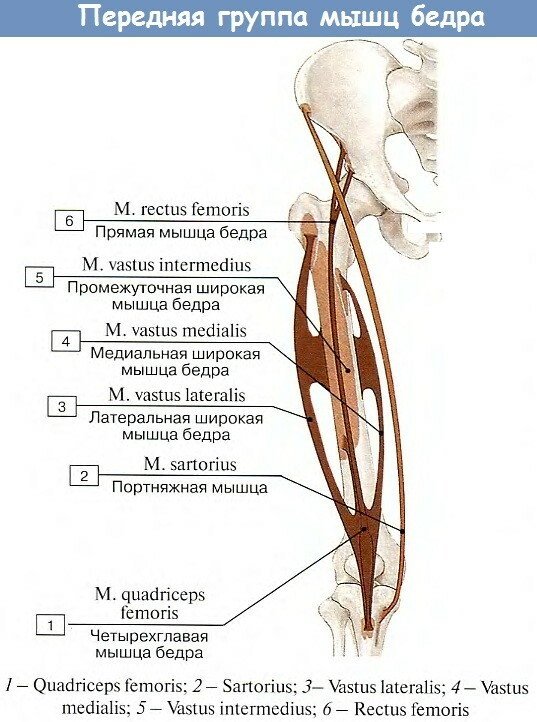
Tailor muscle - it is the longest muscle in the human body. The average fiber length is over 47 cm. It is located in the front of the thigh and is involved in the activity of both the pelvic joint and the thighs and lower legs.
Characteristic
Musculus sartorius belongs to the functional muscular system of the lower extremities. It is involved in the mechanisms of flexion, supination (rotation and positioning of the limb towards the outside) and pronation (rotation of the limb around the long axis).
The sartorius muscle is located in the fascia lata of the thigh. Muscle fibers are capable of significantly changing their length during contraction. A distinctive feature of the muscle is the absence of clear muscle bundles. The close location of large nerve channels provides innervation and correction of the movement of the muscular apparatus. Such a neighborhood creates a number of difficulties due to the possible pinching and trauma of the nerves.
The muscle is easily felt in the upper thigh. When the hip is flexed and abducted, or when the lower leg is extended, the entire length of the muscle fibers is clearly traced.
Basic Sartorius Facts:
| Source (from where it comes out) | Anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS). |
| Insert (which includes) | The proximal end of the tibia is below the medial condyle (through the pes anserinus). |
| Innervation | Femoral nerve (L2-L3). |
| Blood supply | Proximal third (closer to the center of the body): branches of the femoral artery, deep femoral artery, lateral circumflex femoral artery. Middle third: branches of the femoral artery. Distal third (further from the median plane of the body): branches of the femoral and descending geniculate arteries. |
| Function | Knee joint: leg flexion, internal leg rotation. Hip joint: flexion, abduction, external rotation of the hip. |
 The length of the muscle fiber and the constant involvement in movement increases the likelihood of injury. In addition, close proximity to the nerve pathways, large blood vessels leads to their pinching.
The length of the muscle fiber and the constant involvement in movement increases the likelihood of injury. In addition, close proximity to the nerve pathways, large blood vessels leads to their pinching.
Functions and properties
The sartorius muscle is superficial in the thigh and is involved in the flexion mechanism of the hip joint.
Due to its length, the muscle performs a function in both the hip and knee joints. At the same time, the force applied by the muscle in the hip joint is 2 times higher than in the knee joint. The sartorius muscle causes flexion and external rotation in the hip joint, and in the knee, contraction of the muscle causes flexion and internal rotation. In the knee joint, it works together with the quadriceps muscle.
The sartorius muscle is not primarily responsible for any movement, but rather forms functional units with several muscles.
Violation of the functionality of the tailor muscle is accompanied by the development of pain syndrome and a reduction in the motor activity of the lower extremities.
Anatomy and structure
The starting point of attachment of the sartorius muscle is at the anterior part of the superior iliac spine of the ilium. The projection of the attachment point falls on the upper part of the pubic area.
The direction of the muscle goes down the oblique line. It spirally stretches along the front surface of the thigh, passes to the inner surface and is attached by a tendon to the tibial tuberosity.
Having reached the medial condyle, a paired fragment of the femur that forms the knee joint, it passes into the anteromedial surface of the lower leg.
Further, the muscle is articulated with a flat tendon attached to the tibial tuberosity. In this case, a number of muscle fibers are intertwined with the fascia - the connective membrane of the muscles - the upper part of the lower leg.
At the site of attachment, 2-3 dry bursae are formed, which carry out the separation of muscle tissues. A distinctive feature of the location of the muscle is that it forms the hunter's canal (femoral-popliteal). This is a kind of vault over the femoral artery, vein and saphenous nerve.
The sartorius muscle is innervated by the femoral nerve. It extends from the lumbar plexus (L segments 2-4) and supplies the other muscles in the front of the thigh in addition to the sartorius muscle. Prolonged motionless state of the muscles leads to the development of atrophic processes and the appearance of contractures. Limitations of the range of motion are accompanied by a change in the normal location of the muscle and its displacement relative to healthy muscles.
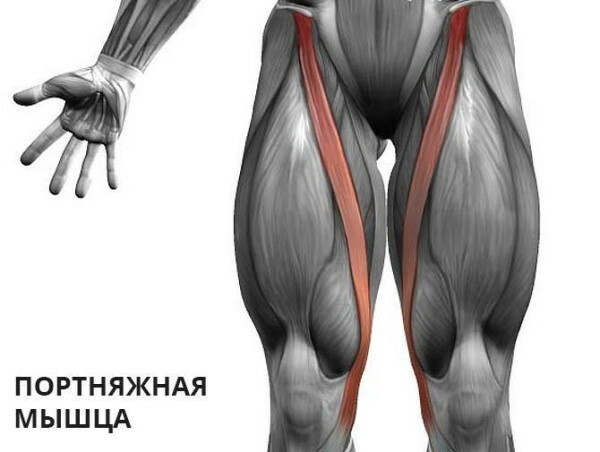
To find the tailor muscle, sit on a chair and feel the protrusion of the bone on the front surface of the pelvis, located above the junction of the thigh and trunk. Then, moving your hand down to the groin, turn the knee out. In this position, the tension of the tailor muscle is clearly felt.
Possible diseases and pathologies
The sartorius muscle is in close proximity to the psoas muscle and the ilium. They all work together, and injury to one structure can affect others and cause pain in the front of the thigh. Too tight tailor muscle can cause severe discomfort in the front of the pelvis.
Like the iliopsoas muscle, the sartorius muscle can also become overextended, leading to chronic breakdown. The dysfunction has serious consequences for the whole body. For example, given the downward tension of the sartorius muscle, chronic overstrain in it can cause tension and impact in the lumbar spine.
As the sartorial tissue crosses the knee, it can cause medial knee pain. The inflammation manifests itself as pain or hypersensitivity to the inside of the knee.
The sartorius muscle is known for 2 types of pain: burning or tingling sensation and sharp stabbing pain. Since the muscle is located just under the skin, the pain and burning sensation is as if it were coming from the skin itself.
Pain syndromes are associated with trigger points in the muscles. They can originate anywhere along the length of the fiber, but most often occur towards the inner side of the knee.
Sudden sharp pain is an indicator of muscle strain. If the tension is light, the pain is more like a spasm. Moderate to severe sprains cause stabbing pain that can be debilitating.
Trigger point pain and muscle strain pain have some common symptoms but require different treatments.
Sports games with sharp turns around the lowered foot, such as basketball and soccer, or falling while skiing with one foot remaining sandwiched in deep snow can subject the sartorius muscle to unexpected and sudden twisting forces, resulting in fiber stretching and damage fabrics.
Improper posture and poor posture can also contribute to muscle-related pain. Identifying the problem at an early stage and promptly treating it will quickly restore muscle functionality.
Adductor tendinopathy of the thigh
Tendinitis is inflammation of any tendon that is part of the hip flexor. The most common symptom is pain that develops over time. It often diminishes after activity because the tendons have more blood and they can stretch, thereby preventing over-stretching. Despite this, pain tends to come back later.
Classification
The disease develops gradually:
-
Stage I. Pain appears only after participating in vigorous activity or after playing sports.
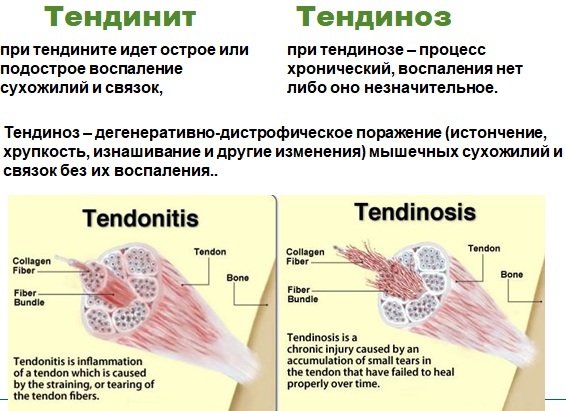
Tendinosis and tendon tendonitis - Stage II. The pain appears at the beginning and after the activity. As soon as the tendon heats up and stretches, the pain goes away, but after the end of sports or physical work, it returns.
- Stage III. The pain occurs at the beginning, during and after physical or sports exertion, but does not greatly affect the activity.
- Stage IV. The most painful stage with constant pain that develops before, during and after activity. At this stage, complete rest is needed.
Symptoms and Signs
In most cases, tendonitis begins with a microscopic rupture of the tendon, which gradually increases in size with repeated flexion of the hip. Hip flexor pain can be acute, resulting from injury, or chronic pain that gets worse over time.
Common symptoms include:
- Pain in the front of the thigh or groin.
- Soreness when walking or climbing stairs.
- Pain when lifting the knees to the chest.
- Altered gait or lameness.
- Muscle cramps in the thigh and groin area.
Causes
Tendonitis is common in sports such as cycling, running, swimming, baseball, golf, and due to repetitive overuse of the hip flexors.
Treatment methods
Traditional treatments include rest, ice, and pain relief, sometimes with NSAIDs and corticosteroids.
Other treatment approaches:
- ESWT (extracorporeal shock wave therapy) to stimulate cell regeneration and accelerate healing.
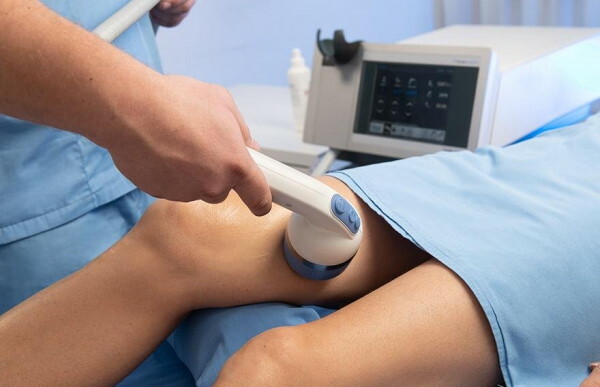
- EMTT (extracorporeal magnetotherapy).
- Injection therapy including PRP (Platelet Rich Plasma) to stimulate and accelerate tendon healing.
- Exercises to strengthen eccentric muscles.
- Range of motion exercises.
- Motor control training to improve hip flexor function and eliminate movement errors.
Femoral nerve neuropathy
The sartorius muscle is innervated by the femoral nerve. It is the main nerve located at the lumbar plexus and serves the tissues of the thigh and leg, including muscles and skin. Nerve signals transmitted by the femoral nerve are critical to the functioning of the legs, including standing, walking, and running. In the course of movement, one of its branches innervates the sartorius muscle.
Neuropathy is expressed in a pathological shortening of the sartorius muscle in the region of the inguinal ligament and a violation of its contractility. Reducing its length leads to disturbances in innervation and has a complex negative impact on the quality of life and health.
Classification
Distinguish between acute and chronic stages of the disease. In the first case, the pain syndrome is pronounced. The chronic stage is accompanied by an irregular onset of pain, relieved by the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Symptoms and Signs
Signs of the disease include impaired flexion of the limb. As development progresses, there is an increase in lumbar lordosis (curvature of the lumbar spine).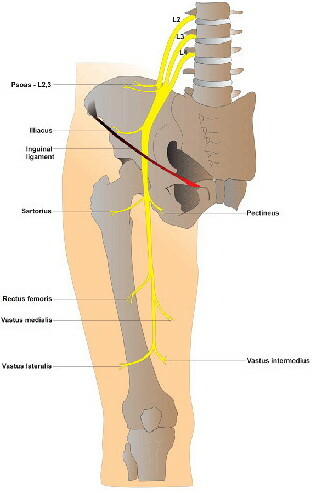 In the final stage, there is a shortening of the limb and a decrease in the muscle tone of the quadriceps muscle of the thigh.
In the final stage, there is a shortening of the limb and a decrease in the muscle tone of the quadriceps muscle of the thigh.
Causes
The basis for the development of neuropathy can be an injury in the groin area. Most often, the violation develops after surgical intervention in the hip or pelvic organs, as well as against the background of the development of diabetes mellitus.
Treatment methods
The tailor muscle is in a vulnerable spot, and therapy begins with a neurological examination and electrodiagnostics of the conduction and functioning of the neuromuscular apparatus. If necessary, CT and MRI of the retroperitoneal space are prescribed.
Drug therapy is effective. In the acute stage, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed for intravenous or intramuscular administration. A femoral nerve block is performed.
Physiotherapeutic measures are used in the form of:
- diadynamic currents;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetotherapy.
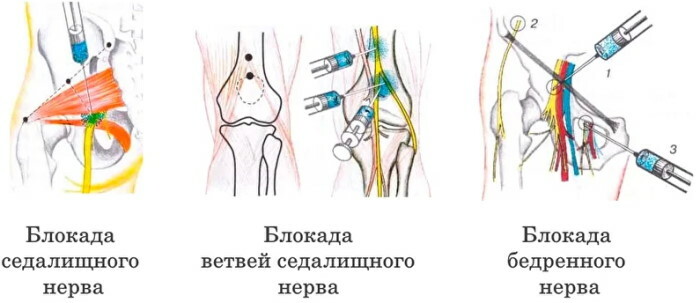
In the absence of positive dynamics, conservative surgical treatment is carried out.
Tailor muscle rupture
A muscle tear or strain means damage to the muscle and the tendons attached to it, caused by excessive or accidental pressure. This can happen at any time during daily activities, during a game, or at any other time.
The extent of muscle tear damage depends on the pressure exerted on the muscle by an external source or by some activity. In some cases, part or whole muscle fibers are affected, and in severe cases, the tendons attached to the muscle are also damaged. In many cases, the damage can be serious, such as bleeding, bruising, and irritation from damaged nerves.
Classification
According to the severity, the muscle rupture is divided into 3 stages:
- 1st degree: at this stage, microcracks appear due to external trauma, and the person does not face functional problems.
- 2nd degree: A partial muscle tear is classified as a tear or sprain. In this condition, the functionality of the muscle is greatly impaired. Muscle pains become worse than usual.
-
Grade 3: the muscle is completely severed, causing severe pain and bleeding. The condition requires medical attention.

In the first place, it is difficult to diagnose the severity of a muscle tear or strain. Functional tests can assess the possibility of muscle activation, which really helps determine the extent of damage; however, doctors recommend different diagnostic procedures depending on the situation.
Symptoms and Signs
The tailor muscle is located in a place where, when it is damaged, external signs are immediately visible. They include swelling at the site of injury, flushing of the skin due to internal hemorrhage.
Depending on the severity of the disease, pain occurs, either insignificant or strong. In the event of a complete rupture, a decrease in the range of motion occurs or the natural function of the muscle is lost.
Causes
Some Causes of Acute Muscle Tear:
- Poor muscle flexibility.
- Excessive physical activity or hard work.
- Fatigue.
- Poor posture.
Sometimes athletes do not warm up enough before a game in which the muscles are intensively used, as in football or tennis, which leads to pathology.
Treatment methods
A person with a torn muscle should see a doctor if home remedies are not working after 24 hours.
Experts believe that if the affected muscles receive first aid within 15 minutes. after any accident or injury, many tearing problems resolve within a few days.
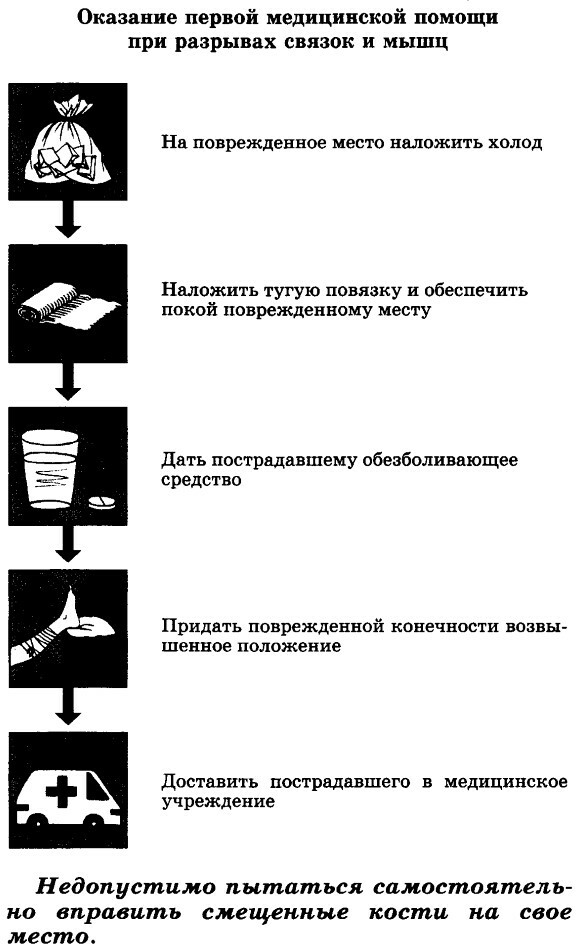 Primary first aid methods or home remedies:
Primary first aid methods or home remedies:
- Applying ice immediately after injury minimizes swelling and greatly reduces pain.
- The affected muscle should be given adequate rest. This will help the muscle tissue to heal damaged cells by its own autoimmune system. However, prolonged rest can weaken muscles. Physical movements should be started as soon as possible, without creating much tension in the muscles.
- Treatment of a muscle tear associated with compression may be required if the swelling is too noticeable. Compression with an elastic bandage is the best way to reduce swelling.
- If possible, the affected muscle should be elevated at heart level for a few minutes. This will strengthen the muscles and facilitate circulation.
Aside from first aid, there are other home remedies available for fixing minor tears.
- Medications such as Ibuprofen and Naproxen are helpful in relieving primary pain and inflammation, so they can be used along with first aid initially.
- Treatment with hot compresses at least 5 times a day helps to facilitate blood circulation and muscle movement.
- Adequate rest and care during movement or work is necessary, but at the same time, the muscles should be used normally 3 days after injury in the event of a minor muscle rupture. It is very helpful to stretch the muscles as much as possible, but this should only be done during the recovery phase.
If home remedies are ineffective or the pain is unbearable, it is advisable to see a specialist. Doctors follow specific procedures when examining the extent of muscle damage. Imaging tests, such as X-rays and MRIs, are done after certain medical procedures, including physical therapy, medication, and rest.
Complete rupture is treated with surgery. The torn muscle fiber is connected by stitching, after which a fixation splint is applied to the limb.
The sartorius muscle, which is part of the muscles in the front of the thigh, is one of the longest. Its functionality is to ensure the correct movement of the joints of the lower extremities. However, due to the long length, trauma in this area, in addition to pain, is accompanied by a violation of gait. In case of failure to provide medical care, a pathological state of a decrease in the tone of other muscle fibers and the development of paralysis develops.
Tailor muscle video
Tailoring muscle. Anatomy and Biomechanics:



