Content
- Myocardial infarction symptoms
- What diseases and conditions can be confused with myocardial infarction
- Differential diagnosis of dangerous conditions with similar symptoms
- Differentiation and comparison of symptoms of heart attack with other pathologies
- Prolonged angina
- Intercostal neuralgia, plexitis, osteochondrosis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Dissecting aneurysm
- Acute pericarditis
- Pneumothorax
- Idiopathic myocarditis
- What are the most informative instrumental diagnostic methods
- Video about myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction is a condition, which threatens human life, which occurs due to partial or complete blockage of the blood supply to certain areas of the heart muscle. The development of this attack occurs gradually as the blockage of the arterial vessel that feeds the heart tissue.
In terms of the symptoms of its manifestation, myocardial infarction resembles a large number of other cardiological diseases characterized by the periodic occurrence of shortness of breath, pain in the retrosternal space, dizziness. Timely differential diagnosis allows you to determine the acute phase of ischemic disease with focal necrosis of the heart muscle.
Myocardial infarction symptoms
The development of myocardial infarction is manifested by the following symptoms of a painful condition of the heart and blood vessels:
- shortness of breath, which worsens during an attempt to move independently;
- burning and squeezing inside the chest;
- nausea and vomiting;
- pain in the abdomen;
- the spread of pain syndrome from the inside of the chest towards the spine, left arm or jaw (in medical practice, periodically there are cases when patients with a pre-infarction condition seek help from a dentist, since irrigation of pain in the jaw creates the illusion of a patient tooth);
- physical weakness;
- dizziness;
- heart palpitations;
- profuse sweating;
- unstable blood pressure;
- loss of consciousness.
Myocardial infarction is a pathological condition of the heart muscle, which always develops against the background of ischemic disease. Narrowing of the lumen of the main arteries leads to disruption of local blood flow, acute oxygen deficiency in the tissues of the heart.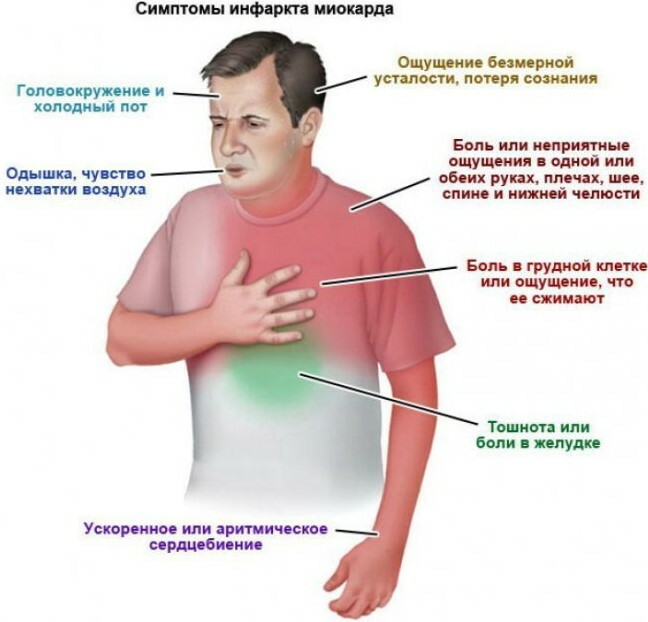
In the high-risk group are people with overweight, high blood cholesterol, metabolic disorders. Only a comprehensive differential diagnosis of cardiological diseases that has been carried out makes it possible to timely determine the presence of myocardial infarction, as well as prevent extensive necrosis of the muscle tissue of the heart.
What diseases and conditions can be confused with myocardial infarction
The classic manifestation of myocardial infarction, accompanied by attacks of pain in the sternum, can be confused with the following cardiac pathologies, which have similar symptoms:
- prolonged angina pectoris;
- pulmonary embolism;
- acute inflammation of the tissues of the heart muscle;
- dissection of the aortic aneurysm.
Painful sensations in the retrosternal space, stiffness of muscle tissues, shortness of breath can also cause diseases that are not associated with disturbances in the work of the heart. For example, intercostal neuralgia and exacerbation of chronic osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine show similar symptoms, but do not cause focal damage to the heart muscle.
Differential diagnosis of dangerous conditions with similar symptoms
Differential diagnosis of myocardial infarction is carried out by a qualified cardiologist who performs a comprehensive assessment of the patient's general condition based on the results of his hardware examination organism. This technique is detailed in the table below.
| Types of pathological conditions of the body | Lung function auscultation | ECG | Additional diagnostics |
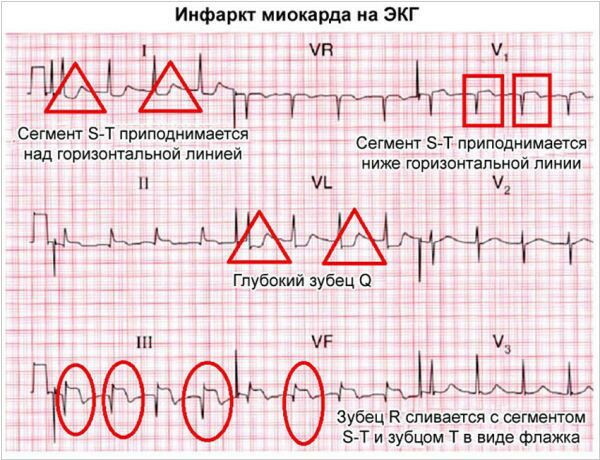
| Myocardial infarction | With the help of a phonendoscope, it is possible to fix distinct wheezing in the lower parts of the bronchopulmonary tissue. | On the ECG tape, the inversion of the T wave, as well as the rise of the ST segment, is recorded. | Carrying out scintigraphy of the heart myocardium, as well as the isolation of the MB fraction from the blood serum, determination of the AST and LDH indices. |
| Angina attack | There are no signs of impaired lung function. | The results of the cardiogram correspond to the indicators of the norm, or there is a slight depression of the ST complex. | Performing coronary angiography. Acquisition of ECG data with stress. |
| Consequences of pulmonary embolism | In rare cases, additional sounds are heard in the chest during deep breathing. | The patient's ECG has no pronounced changes. Overload of the right heart muscle is very rarely recorded. | Pulmonary angiography and scintigraphy of the lungs. |
| Aortic aneurysm dissection | There are no signs of pulmonary dysfunction. | Signs appear on the cardiogram that are similar to myocardial infarction. | Echocardiography, which is done through the wall of the patient's esophagus. Performing CT and MRI diagnostics to obtain the most objective information about the functional state of the aortic walls. |
| Pericarditis | The organs of the respiratory system work stably. | Most leads have ST segment elevation. | Perform echocardiography to exclude cardiac tamponade. |
| Pneumothorax | Attenuated breathing sounds are present. | ECG signs of a pathological condition of the heart are absent. | The use of additional survey methods is not required. |
Based on the results of differential diagnosis, the cardiologist confirms or refutes the fact of acute myocardial infarction. In case of detection of other cardiac diseases or disorders in the work of the lungs, an appropriate course of therapy with the use of drugs is prescribed.
Differentiation and comparison of symptoms of heart attack with other pathologies
Differential diagnosis of myocardial infarction requires a mandatory comparison of the signs of this pathology with the symptoms of other diseases that have similar clinical manifestations.
Prolonged angina
One of the signs of prolonged angina pectoris is prolonged pain inside the chest. The occurrence of this disease is associated with a narrowing of the lumen of the coronary arteries, which feed the tissues of the heart.
The following distinguishing features of the symptoms of protracted angina pectoris are distinguished, which can be used in the differential diagnosis of myocardial infarction:
- another attack of extensive pain inside the chest occurs at the time of an increase in the level of physical activity;
- while inhaling cold air or smoking another cigarette, the patient experiences a sharp spasm in the region of the heart, and then a feeling of acute pain joins;
- localization of pain syndrome systematically turns into a girdle form with an even distribution of discomfort in all parts of the chest;
- after taking a horizontal position and complete cessation of physical activity occurs slight relief of general well-being, and taking a nitro-containing drug restores stable heart rhythm.
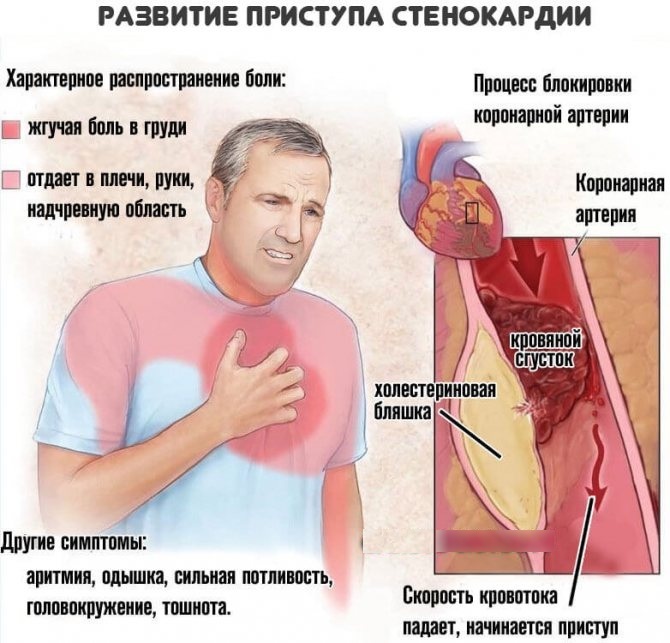 In patients with myocardial infarction, there are similar symptoms in the form of a feeling of compression of the heart muscle and the spread of extensive pain throughout the chest, but with angina pectoris, these signs are less pronounced, and also last 3-5 minutes The average duration of myocardial infarction is about 15-20 minutes.
In patients with myocardial infarction, there are similar symptoms in the form of a feeling of compression of the heart muscle and the spread of extensive pain throughout the chest, but with angina pectoris, these signs are less pronounced, and also last 3-5 minutes The average duration of myocardial infarction is about 15-20 minutes.
Intercostal neuralgia, plexitis, osteochondrosis
Intercostal neuralgia, chronic osteochondrosis and plexitis are diseases that arise from inflammatory lesions of the peripheral nerves of the back. These diseases are a complication of previous spinal injuries, scoliosis, infectious invasions, chronic alcoholism.
In the process of differential diagnosis, attention is paid to the presence of the following symptoms that distinguish intercostal neuralgia, plexitis and osteochondrosis from myocardial infarction:
- the patient complains of acute pain that penetrates the entire chest, and its main areas of localization are the intercostal space and the spine;
- pain syndrome is concentrated only in one part of the sternum, where the largest number of inflamed peripheral nerves is located;
- acute attacks of pain caused by intercostal neuralgia, plexitis or chronic osteochondrosis are worn shingles, extending from the thoracic spine along the ribs down to the hip joint;
- pain syndrome becomes more intense and pronounced during dry coughing, sneezing or laughing;
- there is a tingling sensation of the skin in the area of the inflamed peripheral nerves;
- at the time of an acute attack of intercostal neuralgia, plexitis and chronic osteochondrosis, blanching of epithelial tissues in the region of the ribs and thoracic spine occurs.
In the process of palpation of the patient's chest, individual parts of the body are found that react with an increase in pain. Pathological symptoms are manifested during touching the patient's epithelial tissues.
Such a reaction indicates the close location of the damaged peripheral nerves to the surface of the skin. With myocardial infarction, this symptomatology is completely absent, and the pain syndrome is localized inside the chest without encircling signs from the ribs and spine.
Pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of only one or several arterial vessels that provide blood supply to the lungs. The onset of this pathology is caused by blood clots that migrate in the general blood flow system. The severity of signs of pulmonary thrombosis depends on how many vessels are involved in the blockade process.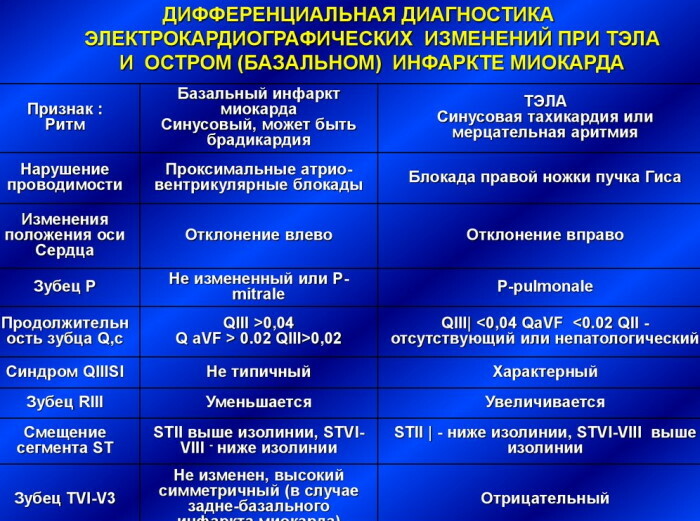
There are symptoms of pulmonary embolism that are important in the differential diagnosis of myocardial infarction:
- shortness of breath and a feeling of shortness of breath occurs suddenly without the influence of an additional factor in the form of physical activity;
- painful sensations inside the chest resemble a heart attack, but their occurrence is accompanied by the urge to dry cough;
- the feeling of discomfort in the chest increases at the time of eating, tilting the body to the sides;
- during an attack of dry cough, mucous contents are separated from the patient's respiratory system, which contains a large amount of blood;
- immediately after the onset of the first attacks of pain inside the chest, swelling of the right or left leg begins, depending on which side the arterial vessel is blocked;
- strong wheezing is heard in the lungs, which increase in proportion to the increase in pain;
- the pulsation of the radial artery is weak;
- there are progressive signs of cyanosis of the skin;
- palpitations are unstable and rapid.
Thromboembolism of the pulmonary arteries, which is manifested by the above differential symptoms, almost always ends in severe dizziness or loss of consciousness. Unlike myocardial infarction, an acute shortage of blood supply is experienced not by individual parts of the heart, but by lung tissue.
Dissecting aneurysm
Dif-diagnosis of myocardial infarction is carried out immediately after the patient is admitted to the emergency department. A dissecting aortic aneurysm is characterized by the sudden appearance of a defect on the inside of the aortic wall. An excess amount of blood enters the damaged tissues of the middle layer of the blood vessel, which leads to the formation of an intramural hematoma with further stratification of longitudinal fibers aorta.
The signs of this pathology depend on the extent of degenerative changes inside the blood vessel. In terms of clinical manifestations, the dissecting aorta resembles most severe cardiac diseases.
During the examination of patients with signs of myocardial infarction, attention is paid to the possible presence of the following differential symptoms of a dissecting aneurysm:
- swelling of the right or left lower limb;
- cyanosis of the skin of the anterior chest wall;
- localization of pain not only in the chest area, but also its active irradiation to the lower back, abdomen and legs;
- maintaining a stable bradycardia at the initial stage of the pathological process;
- the development of progressive tachycardia after damage to the 3rd layer of the aorta with the opening of internal bleeding;
- sharp pain in the center of the chest;
- deep fainting due to a violation of the blood supply to the brain tissues.
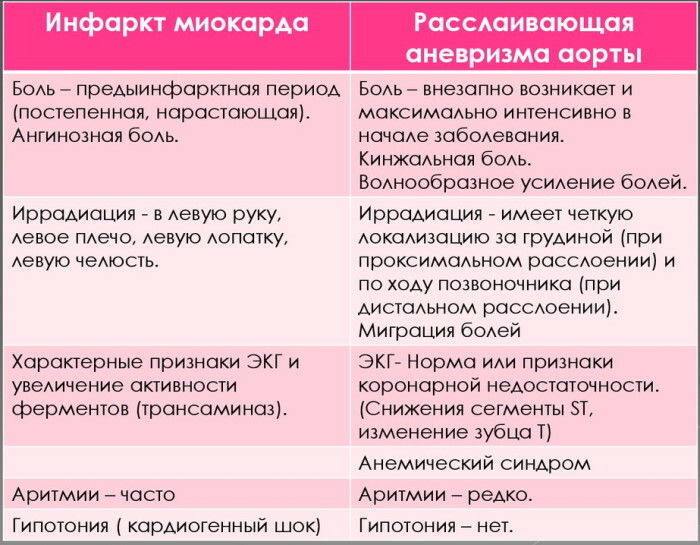
Differential diagnosis of myocardial infarction and dissection of the aortic aneurysm requires immediate cardiac ECG and MRI, chest CT. If the arterial vessel is damaged, the results of the electrocardiogram do not show radical changes in the work of the heart muscle. In rare cases, minor symptoms of coronary insufficiency are found.
Acute pericarditis
The acute form of pericarditis is an inflammation of the serous membrane of the heart muscle, the visceral leaf, which occurs as a complication of a previously transferred infectious or autoimmune diseases. The presence of this pathology provokes the onset of symptoms that resemble an attack of myocardial infarction.
To carry out a qualitative differential diagnosis of these two pathological conditions of the heart, it is necessary to pay attention to the following distinguishing features that are characteristic of acute pericarditis:
- an increase in the volume of fluid inside the pericardium;
- the formation of local fibrous strictures in the tissues of the heart muscle;
- the appearance of symptoms of lupus erythematosus;
- dry cough that ends in coughing up blood clots;
- heart palpitations;
- long-term preservation of a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium, which is completely absent in patients with myocardial infarction;
- an increase in the volume of the abdomen, which is caused by the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- rapid weight loss;
- physical weakness, which is present even during those periods when a person is at rest;
- shortness of breath and feeling short of breath;
- compressive pain in the region of the heart without spreading it to the abdominal cavity, left arm, jaw, thoracic or lumbar spine.
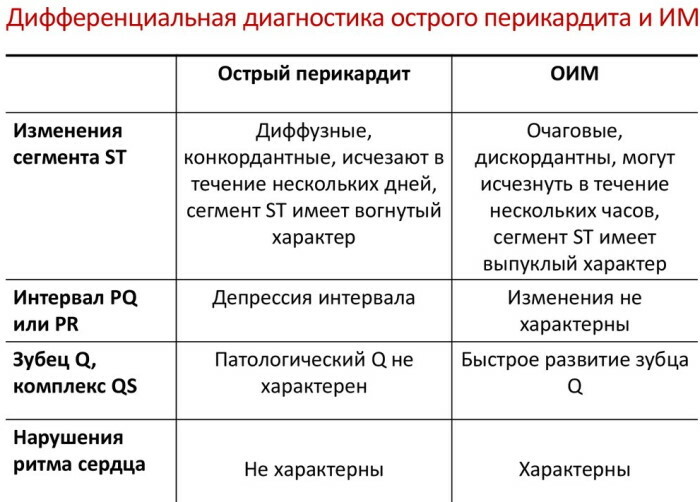 The acute phase of this disease is manifested by a dry or effusion type of pericarditis. Any form of this pathology is dangerous to the human body no less than myocardial infarction. Inflammation of the serous membrane of the heart can damage the deeper tissues of the heart muscle. A more detailed examination of patients with signs of acute pericarditis shows that there is an elevation of the ST segment on the ECG results.
The acute phase of this disease is manifested by a dry or effusion type of pericarditis. Any form of this pathology is dangerous to the human body no less than myocardial infarction. Inflammation of the serous membrane of the heart can damage the deeper tissues of the heart muscle. A more detailed examination of patients with signs of acute pericarditis shows that there is an elevation of the ST segment on the ECG results.
Pneumothorax
Dif-diagnosis of myocardial infarction is performed by a cardiologist at the stage of preliminary examination of the patient. Pneumothorax is a dangerous condition of the human respiratory system, which is caused by compression of the lungs.
The development of this pathology is associated with the ingress of air into the pleural cavity. The presence of atmospheric gases in this part of the body disrupts the work of the bronchopulmonary tissue, complicates breathing. The occurrence of pneumothorax is caused by traumatic injury to the chest, puncture of the pleura as a result of diagnostic or surgical procedures.
To perform differential diagnosis of myocardial infarction in patients who have signs of pneumothorax, pay attention to the presence of the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath, which persists even during the period when a person is in a state of physical rest;
- dry cough;
- a feeling of strong squeezing of the right or left side of the sternum, depending on which side the pleural membrane was injured;
- lowering blood pressure;
- blue discoloration of the skin of the upper and lower extremities, lips, nasolabial zone;
- increased heart rate, regardless of the level of physical activity.
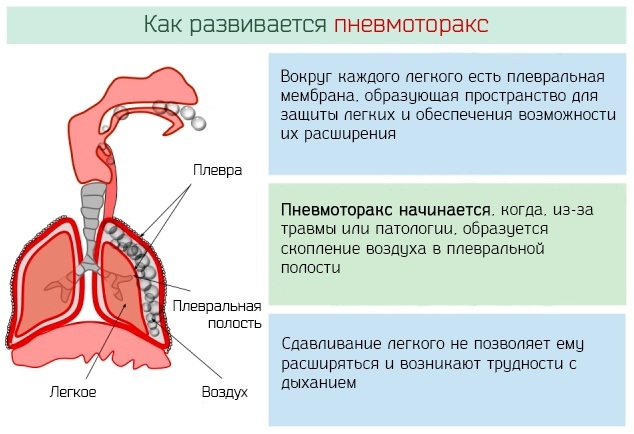
Conducting an ECG of the heart shows that the functions of the heart muscle are preserved, and there are no signs of cardiac pathologies at all. With pneumothorax, tachycardia and a decrease in blood pressure are caused by a violation of gas exchange, air compression of the lungs.
Idiopathic myocarditis
The development of myocarditis occurs due to extensive inflammation of the tissues of the heart muscle. At the same time, the patient has no signs of impaired systemic circulation, pathological narrowing of the lumen of the coronary vessels. The disease leads to the destruction of the middle layer of the heart. The emergence of idiopathic myocardium is expressed by the sudden development of acute inflammation of the muscle tissue of the heart for no apparent reason.
The results of laboratory studies of the diseased organ show the complete absence of infectious microorganisms in its structure. Scientists and cardiologists cannot give a reasoned answer to the question of which factors provoke this type of disease. In 95% of cases, idiopathic myocarditis is fatal.
In the process of differential diagnosis of myocardial infarction, attention is paid to the following symptoms of idiopathic myocarditis:
- burning pain in the left side of the chest, which radiates to the upper limb;
- attacks of night fever and profuse sweating;
- lethargy;
- drowsiness;
- loss of physical strength;
- violation of the motor function of the respiratory system;
- dyspnea;
- the formation of bruises and puffiness under the eyes;
- blue skin of certain parts of the body.
Idiopathic myocarditis is characterized by damage to the muscle layer of the myocardium. In this regard, most of the symptoms of this disease are similar to the clinical manifestations of coronary heart disease. Differential diagnosis of cardiac disorders based on external signs of pathology is extremely problematic. The ECG method is used to confirm the final diagnosis.
What are the most informative instrumental diagnostic methods
The table below lists the most informative and effective methods for instrumental diagnosis of myocardial infarction.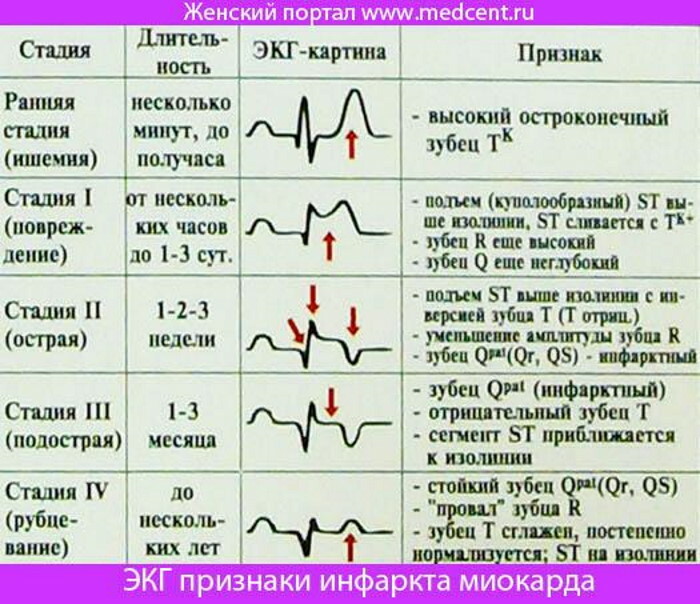
| Instrumental examination techniques | average cost |
| Echocardiography | RUB 3800 |
| Installation of a device for daily monitoring of blood pressure level | RUB 500 |
| Holter monitoring of ECG-ST parameters for 24 hours | RUB 3050 |
| Decryption of data from the daily blood pressure monitor | 4000 RUB |
| Electrocardiography with exercise tests and additional leads | 2250 RUB |
The above instrumental research methods are performed in specialized diagnostic centers, state polyclinics and in the hospital of cardiology departments.
Myocardial infarction is a life-threatening pathological condition of the human heart muscle, which is caused by a complication of coronary artery disease. This disease is characterized by impaired blood flow in the coronary vessels with the development of hypoxia in certain areas of the heart.
Myocardial infarction is manifested by burning pain in the retrosternal space, which spreads to the left arm, gives to the shoulder and jaw. At the time of the acute phase of the attack, the sick person experiences shortness of breath, dizziness, heart palpitations, and is in a light-headed state. Patients with primary signs of myocardial infarction are shown to carry out differential diagnostics to exclude other cardiac diseases with similar symptoms.
Video about myocardial infarction
Differential diagnosis of myocardial infarction: