Content
- What is heatstroke
- Determination of sunstroke
- Similarities and differences between states
- Symptoms
- Causes
- Severity of conditions
- Duration
- Consequences
- What to do with sunstroke
- PMP with heatstroke
- Heat and sunstroke video
Sunstroke at home often confused with heat. Both conditions occur when the body is overheated, which often happens due to being outside in hot weather. In fact, heatstroke is a broader concept: it can also occur in a stuffy room, where the air temperature is not so high. The difference between the two heat diseases is determined by some differences in their development and course.
What is heatstroke
Heatstroke occurs as a result of a violation of thermoregulation, when the production of heat in the body exceeds its dissipation. That is, internal heat from the surface of the body is not completely removed to the external environment. Hyperthermia develops - general overheating of the body with a sharp increase in body temperature, accompanied by appropriate symptoms.
The factors that hinder heat transfer are high ambient temperatures, high humidity and air immobility.
The condition occurs in the following situations:
- Increased physical activity in difficult conditions for heat transfer. In medicine, this type of heatstroke is called stress. At risk are people playing sports or muscle work in hot conditions or stuffy, poorly ventilated rooms.
- Long-term stay in conditions of high air temperature (27-32 ° C) of people with impaired sweating function. People with poor health, the elderly and young children overheat easily. Heatstroke can develop even without special physical exertion, which is explained by a defect in the thermoregulation system in adults and the immaturity of the heat transfer mechanism in children. In this case, one speaks of non-load thermal shock.
The resulting disturbances in well-being can be both minor and lead to serious consequences.
The mechanism of the development of the process is as follows: an increase in temperature causes an acceleration of biochemical processes in the body. The speed of the enzymes responsible for the course of various reactions gradually increases, and the body temperature rises more and more.
When it rises above 40 ° C, denaturation (folding) of the protein begins. Since enzymes are protein molecules, the reaction rate suddenly drops sharply. The functions of the cardiovascular system, internal organs and the central nervous system (CNS) are impaired.
The extreme degree of heatstroke is expressed in stupor or coma, which, with a delay in the provision of medical care, are fatal in 5% of cases.
Its mild form, proceeding without loss of consciousness, is called heat exhaustion.
Determination of sunstroke
Heliosis, or sunstroke, is a type of heatstroke. Its development is possible when direct sunlight hits directly on the head of a person. Usually occurs with prolonged exposure to the sun with a bare head.
Heat and sunstroke are characterized by an increase in body temperature from 37.5 ° C to dangerous values above 40 ° C, and, as a result, dysfunctions of various organs. But, unlike heatstroke, the state of heliosis is caused by overheating of the head, and not the whole body. With excessive exposure to the head area, the vessels dilate mainly in this area, increasing the blood flow to it.
It is a life-threatening condition in which the nervous system is mainly affected.
Similarities and differences between states
The conditions are so close in clinical presentation that it is often considered inappropriate to separate them in medical research and descriptions. Indeed, sunstroke is a special case of heat, and therefore has a number of features in common with it. However, in practice, understanding the differences between them is important, since it allows you to better predict the course of the process.
For example, heatstroke is characterized by an abrupt onset. It usually occurs in the overheating zone, and symptoms develop much less often after the heat is removed. Painful manifestations of sunstroke can develop both immediately and 6-8 hours after exposure to the sun.

On the other hand, a victim of general heatstroke cannot always associate the deterioration of his well-being with overheating, while in the case of exposure to sunlight, mainly on the head, more or less obviously. As a rule, in addition to the general disturbance of the condition, exposure to the sun also affects the skin. Her integument will be red, swollen and painful.
To distinguish between conditions, it is important to correctly see the picture of the totality of their clinical manifestations and features of the course.
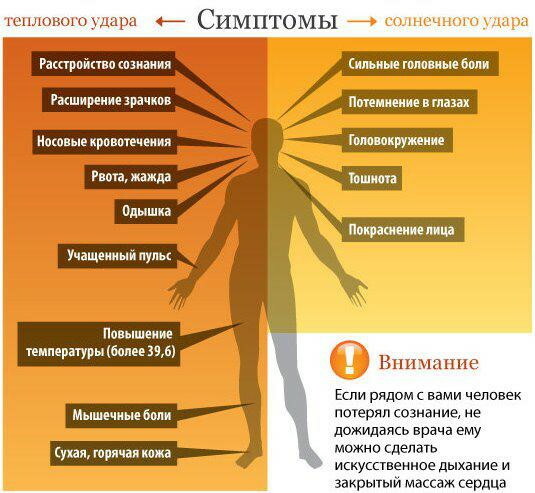
Symptoms
Heat and sunstroke are accompanied by a gradual increase in the "preliminary" symptoms common to both conditions:
- malaise, lethargy, weakness;
- increased body temperature;
- redness of the face;
- heaviness and pain in the head;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness.
Further events develop slightly differently.
With heatstroke, significant hyperthermia causes rapid breathing and intense sweating. Pulse increases: high temperature makes the heart work harder in order to use all available oxygen stores and protect myocardial muscles from heart attack.
Increased sweating is accompanied by the loss of fluid and electrolytes from the body. As the process develops, the blood thickens, its viscosity increases, which leads to disturbances in the circulatory system and oxygen starvation.
Excess potassium released from red blood cells has a toxic effect on the heart muscle. In addition to dystrophic lesions of the myocardium, there are punctate hemorrhages in the connective tissues of organs and mucous membranes. The brain suffers: hyperemia causes edema of its membranes and tissues.
Blood pressure first rises, then sharply decreases. With a severe development of the process, a state of stunnedness occurs, psychomotor agitation, and unsteadiness of gait are observed. With the development of vascular insufficiency, a person can lose consciousness.
For stress heatstroke, cramps and pains occurring in certain muscle groups, most often in the legs, are characteristic.
Sunstroke on the general mechanism of development and initial signs is similar to heatstroke. However, in this case, at the first stages, symptoms of CNS damage predominate. The hyperemic vessels of the brain dilate.
The liquid part of the blood leaves the vascular bed and enters the brain tissue. Edema occurs, which presses on the surrounding nerve cells. Following blood pressure, intracranial pressure also rises. In an unfavorable scenario, the walls of the vessels rupture, which causes cerebral hemorrhage.
In the future, the picture becomes similar to heatstroke, since all other organs begin to suffer from overheating and the toxic effects of protein breakdown products.
Causes
The main factor in the development of both states is a prolonged stay in conditions of elevated air temperature and hindered heat transfer. In this case, a direct hit of the sun's rays on the occipital-parietal region of the head leads to sunstroke.
The risk is increased by:
- Air humidity approaching 100% combined with heat. High humidity makes it difficult to dissipate heat by evaporation.
- Wrong clothes: too tight, vapor tight. When in the sun, there is no headgear to protect the head.
- Lack of wind and places to take a break from the heat.
There are a number of internal factors that can aggravate the condition:
- Insufficient fluid intake in the heat. Sweating is an effective physiological way to lower body temperature. When the lost fluid is not replenished, the body is unable to bring the temperature back to normal values.
- Drinking alcoholic beverages. Alcohol increases dehydration, which leads to blood clots and blood clots.
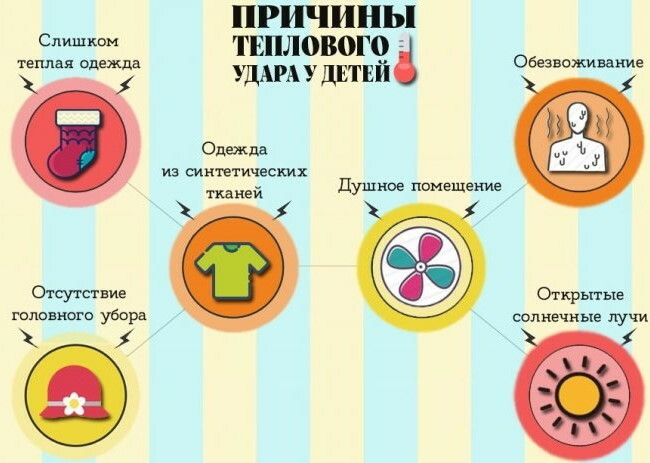
- Physical activity in which muscles generate heat.
- Concomitant cardiovascular diseases, thyrotoxicosis and diabetes mellitus.
- Overweight. The presence of a large amount of subcutaneous fat slows down the transfer of heat from the internal organs to the skin surface.
- Taking certain medications (diuretics, antihypertensives) and CNS stimulants.
- Childhood. Until the age of 3 years, the center of thermoregulation has not yet been formed, so children easily overheat.
Severity of conditions
There are 3 degrees of severity of heatstroke:
- Lightweight. The body temperature is subfebrile, the skin is moist. The victim feels nausea and headache. Breathing and pulse are slightly quickened. In general, the state of health is satisfactory.
- Average. Symptoms are more intense: the temperature rises to 40 ° C; severe headache, with nausea and vomiting. Intense sweating is accompanied by an even greater increase in heart rate and respiration. The face is red. Neurological symptoms join: impaired coordination, stunning, short-term fainting.
- Heavy. This form is characterized by a sudden onset and rapid flow. The body temperature rises to 42 ° C, the skin becomes dry and hot. The face turns pale. Breathing is shallow, frequent. The pulse is threadlike, reaching 140 beats in 1 min. The neurological symptoms are aggravated: the consciousness is confused, it is possible to fall into a coma. In this condition, the heart muscle is affected, the content of nitrogen and urea in the blood increases.
The same forms of damage characterize the development of sunstroke. In a severe degree, the moment of lowering blood pressure is especially dangerous. Tachycardia is replaced by a decrease in pulse rate, which is a signal of the rapid spread of cerebral edema. In this case, the centers of heartbeat and respiration, located in the brain stem, can suffer from compression.
The easiest way to cope with a disease that is mild is to take the patient out of the overheating zone. With an average degree of elimination of heat exposure is not enough, therapeutic measures will be needed. Life-threatening 3rd degree: death occurs as a result of cardiac arrest.

The degree of damage depends on the duration of exposure to adverse factors. Children are more susceptible to overheating, and the younger the child, the less resistant he is to high temperatures. For the development of sunstroke in young children who are without a headdress in hot weather outside, 15 minutes is enough.
Duration
Mild heat and sunstroke develops gradually and stops when the source of the problem - exposure to heat - is eliminated. The duration of a moderate state is determined by the success of symptomatic therapy. The rapid and catastrophic development of the pathological process is characteristic of severe forms of thermal disorders.
Consequences
Heat and sunstroke can lead to significant health problems and even death if assistance is not provided in a timely manner. The initial symptoms of these conditions should not be neglected.
At a body temperature of about 42 ° C, necrotic organ damage begins. Localization can be different: muscles, liver, cerebellum. The myocardium undergoes dystrophic changes. The heart and blood vessels are under great stress, so there is a risk of cessation of cardiac activity. It is especially great in people suffering from cardiovascular diseases.
With long-term hyperthermia accompanying heatstroke, thrombosis develops. The condition is often complicated by acute renal failure. Among the main long-term consequences of severe sunstroke: epileptic seizures, hydrocephalus, paresis of the upper and lower extremities.
The main differences between the two states are presented in the table:
| Pathology | Heatstroke | Sunstroke |
| Cause | Overheating of the whole body | Overheating of the head |
| Time of occurrence | Usually in the heat affected area | Outdoors in the sun or after a few hours |
| Predominant lesions | Violation of cardiovascular activity and the work of internal organs | Brain damage |
| Complications | Damage to the kidneys, heart, circulatory system | Neurological disorders |
What to do with sunstroke
Measures must be taken at the first sign of sunstroke: deterioration of health, combined with the fact of prolonged exposure to the sun.
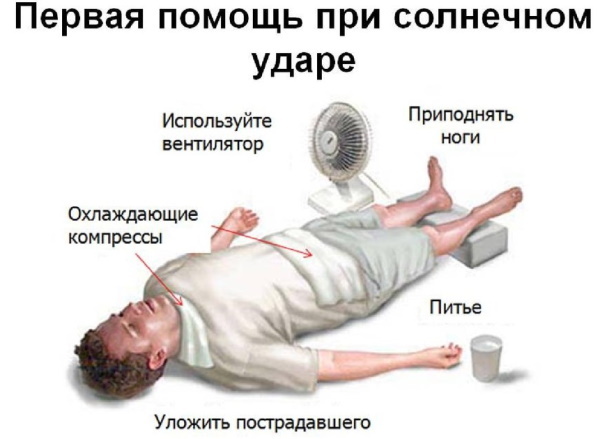
Algorithm of actions:
- Place the victim in a place protected from the sun. It is desirable to provide coolness and air flow (fan). Lay in such a way that the legs are slightly raised in relation to the head.
- Reduce body temperature. To do this, you can wipe the patient with cool water. If there is vodka, dilute it in a 1: 1 ratio, wipe your face and neck. Alcohol evaporates and carries away the heat.
- Put a cold compress or ice in a bag on your head. Also apply something cold to the vessels of the neck and armpits: you can use bottles of water.
- Give a cool drink to prevent dehydration. Coffee and alcohol are excluded.
- To lower the temperature, antipyretic drugs (aspirin, paracetamol) are used. In this case, you should be sure that there are no contraindications to these funds.
If the condition does not improve, a doctor should be called.
PMP with heatstroke
As in the case of sunstroke, the first step is to relieve the victim of damaging factors.



To do this, you should take the following steps:
- Move the patient to a cool place. Provide fresh air.
- Take off outerwear, undress to the waist.
- Cool his body with cold compresses, wet wraps. If possible, and the patient is conscious, place in a bath of water no colder than 37 °. Make sure that the victim does not freeze. Stop cooling when body temperature reaches normal values.
- Coldness on the head - only if there are general clonic convulsions.
- Drink plenty of fluids. To restore the water-salt balance, use the Rehydron solution.
- If necessary, give funds to support cardiac activity. In case of respiratory failure, oxygen is used.
The position of the victim, as in the case of sunstroke: lying down, with raised legs. In case of loss of consciousness, the patient is placed on his side. Moderate to severe heatstroke requires medical attention. Since it is not always possible to determine with certainty the degree of damage, it is better to call a doctor in any case.
Help with heatstroke must be provided quickly: only in this case it will be effective. The same is true for the condition caused by exposure to sunlight. To avoid complications, you should not immediately return to your usual way of life. It will take some time to regain health.
Heat and sunstroke video
Komarovsky about heat and sunstroke:



