Content
- What is hormetonia, a description of the syndrome
- Mechanism of origin, pathogenesis
- Causes of hormetonia
- Vascular thrombosis
- Tumors
- Severe head injuries
- Brain stroke
- Provoking factors
- Clinical manifestations, symptoms of an attack
- Limb position, body muscle spasms
- Babinsky's symptom
- Rossolimo's "upper" symptom
- Klippel-Weil reflex
- Symptoms in the interictal period
- Giving help
- Forecast
- Video about hormone
Hormetonia is a consequence of an acute or chronic brain disease, which led to extensive destruction of its individual sections. This medical term was first proposed in 1919 by the scientist in the field of neurology S.N. Davidenkov.
What is hormetonia, a description of the syndrome
Hormetonic syndrome is a combination of seizures and disorders in the work of the nervous system, which are expressed in involuntary spasms of skeletal muscles. The muscle tissues of the patient's upper and lower extremities are in a state of paralysis, but at the same time they retain pronounced hypertonicity.
The main cause of dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system is damage to the central nervous system. There are many factors, short-term or long-term exposure to which can lead to the development of hormetonia. In 99% of cases, patients with this pathology are unconscious.
Hormetonia is not an independent disease of the central or peripheral nervous system. This is a complication of an already acquired brain pathology, or a consequence of a previously suffered skull injury.
Comprehensive diagnostics of the central nervous system using MRI and CT equipment makes it possible to identify areas of brain tissue with signs of total damage. Hormetonia is a symptom that is almost always present in patients who are in a coma. It is believed that due to dysfunctions of the central nervous system, certain areas of the brain activate protective reflexes, which lead to extensive spasm of the skeletal muscles.
Hormetonia is classified into early and late muscle tissue contracture. The table below provides a detailed description of this pathology, taking into account the stage of development of involuntary muscle spasm.
| Stage of pathological hypertonia | Description of the hormone syndrome |
| Early contracture | The development of hormetonia with early contracture is characterized by the paralysis of one or several limbs at once. In response to external stimuli in the form of tingling with a needle or pinching with fingers, the patient experiences a reflex contraction of muscle tissue. A similar reaction of the body is caused by the activation of defense mechanisms. The extent of muscle paralysis depends on the reasons that provoked it, as well as the extent of the brain damage. Paresis of certain muscle groups without signs of dysfunction of the lower or upper extremities is also referred to early contracture of the hormone syndrome. This stage of pathology is characteristic of the first signs of a cerebral stroke. |
| Late contracture | Hormetonia with late contracture of the musculoskeletal system is characterized by the presence of a flexion reaction in the upper limbs and an extension reflex in the legs. This condition is persistent and difficult to correct with medication. The patient has extensive tonic spasms of skeletal muscles. Involuntary flexion and extension of the limbs occurs. Hypertonicity of muscle tissue leads to periodic seizures. |
Muscle spasms that appear with a certain frequency in response to external stimuli, or they arise without obvious for that reason. The average duration of an attack is from 3-5 s to 1-2 minutes. depending on the general condition of the patient's central nervous system.
Mechanism of origin, pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of hormetonia is caused by disturbances in the work of several parts of the central nervous system at once.
This pathology has the following mechanism of occurrence:
- Within 1-2 seconds, there is a simultaneous shutdown of most of the centers of the brain responsible for the functions of skeletal muscles and other parts of the musculoskeletal system.
- The person becomes unconscious.
- The process of lightning-fast disinhibition of spinal cord areas that take part in the transmission of nerve impulses from the center to the periphery is started.
- The parts of the brain, which are also responsible for the work of the musculoskeletal system, but do not show signs of damage, go into a mode of increased irritation.
- The muscle tissues of the upper and lower extremities do not receive full innervation, which leads them to a state of hypertonicity, causes convulsions and prolonged paralysis of the skeletal muscles.
Hormetonia always has the same developmental mechanism in terms of dysfunction, as well as the interaction between the central and peripheral nervous system. Only the causal factors that caused the extensive brain damage are different.
Causes of hormetonia
The causes of hormetonia are determined by a neuropathologist using MRI or CT diagnostics. Elimination of pathological factors is a prerequisite for stabilizing the patient's condition and stopping attacks of muscle hypertonicity.
Vascular thrombosis
The occurrence of hormonemia may be associated with thrombosis of large vessels that feed the brain tissue. In this case, the deterioration of the patient's well-being occurs rapidly. A dense clot forms inside the main vessel, blocking further blood flow to most parts of the central nervous system.
As a result of this process, the cells of the brain experience oxygen starvation and do not receive the nutrients necessary for stable functioning. A person loses consciousness, and then the mechanism of irreversible damage to extensive parts of the central nervous system is triggered, with the further onset of coma, as well as the appearance of signs of hormonemia.
Patients with thrombosis of the vessels feeding the brain tissue need to restore stable blood circulation as soon as possible. Otherwise, the patient will die without coming out of a coma.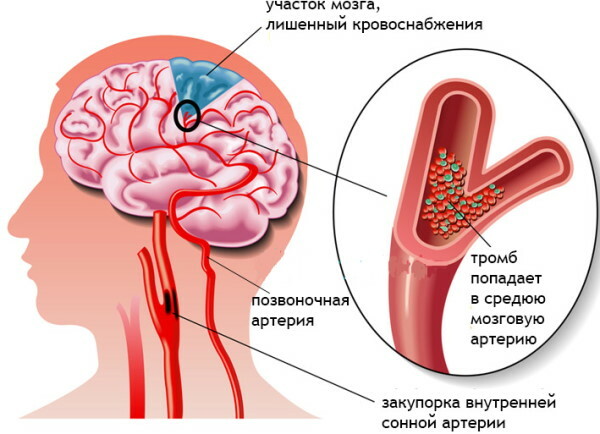
Thrombosis of the great vessels of the brain is caused by the following negative factors:
- a change in the cellular composition of the blood towards a sharp increase in the level of platelets;
- trauma to the walls of a blood vessel;
- slowing down the speed of blood flow due to chronic heart disease;
- morbid obesity;
- alcohol abuse and smoking;
- taking drugs;
- hereditary predisposition to blood vessel thrombosis;
- high cholesterol levels, particles of which lead to a narrowing of the internal lumen of the arteries;
- age-related changes in the body.
The main danger of hormetonia, which is caused by blood vessel thrombosis, lies in the severity of the clinical manifestations of the pathology. The patient's condition deteriorates so quickly that in most cases the onset of a coma occurs before the arrival of the ambulance team.
Tumors
Hormetonia occurs in people with oncological and benign brain tumors. In this case, hypertonicity of muscle tissues occurs due to the germination of an extraneous neoplasm into the structure of the central nervous system.
The damaged areas of the brain cease to perform the previous functions of controlling the motor activity of the upper and lower extremities. In a similar situation, the occurrence of hormetonia occurs at stages 3 and 4 of the tumor process.
The appearance of extraneous neoplasms in the brain is caused by the following factors:
- irradiation of the body with radioactive waves;
- prolonged contact with chemicals that have toxic properties (formaldehyde, acrylonitrile);
- complications of severe head injuries;
- hereditary predisposition to cancer;
- the consequences of a previously suffered inflammation of the cerebral cortex.
Hormetonia caused by a tumor process can be eliminated by surgical intervention with the removal of an extraneous neoplasm. In the case of the spread of cancer metastases to all parts of the central nervous system, the prognosis for the complete elimination of muscle hypertonicity is unfavorable.
Severe head injuries
Open traumatic brain injuries with damage to the meninges cause severe hormetonia, which is accompanied by a deep coma, periodic convulsions of the upper and lower limbs of the patient. Falls from great heights, blows to the head, car accidents are negative factors that lead to traumatic damage to the central nervous system.
Brain stroke
One of the most common causes of hormone production is a cerebral stroke.  A patient with this pathology has extensive hemorrhage with the breakthrough of a large amount of blood into the lateral ventricles. In this case, the patient's condition worsens gradually as the pathological process develops. There is a direct relationship between the extent of hemorrhage and the severity of clinical manifestations of the hormone syndrome.
A patient with this pathology has extensive hemorrhage with the breakthrough of a large amount of blood into the lateral ventricles. In this case, the patient's condition worsens gradually as the pathological process develops. There is a direct relationship between the extent of hemorrhage and the severity of clinical manifestations of the hormone syndrome.
Provoking factors
Another attack of hormetonia causes not only a deterioration in the functions of the central nervous system, but also the effect of the following provoking factors:
- squeezing the muscles of the chest;
- irritation of the plantar part of the leg or the surface of the palm with a slight tingling sensation from the needle;
- applying a few drops of ether to the skin of the foot;
- stretching of the spasmodic muscles of the forearm.
All of the above actions provoke protective reflexes in a sick person, which increase the functional activity of the centers of the brain. At the moment, both lower or upper limbs begin to automatically move in the rhythm of muscle spasm. Upon completion of the hormetonic convulsion, a short-term period of absence of signs of muscle hypertonicity occurs. At this time, the patient has muscular rigidity with varying degrees of manifestation.
Clinical manifestations, symptoms of an attack
Hormetonia has a standard list of signs that are determined visually at the time of the onset of the next attack of hypertension.
Limb position, body muscle spasms
Pathological changes in the position of the limbs are preceded by paralysis of muscle tissue.
The patient has the following symptoms:
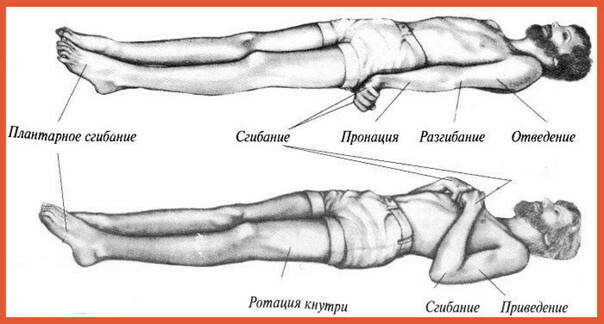
- the upper limbs are automatically bent at the elbow joints towards the lateral parts of the chest;
- the muscles of the legs remain paralyzed, maintaining hypertonicity (this muscle reaction leads to the fact that the patient's lower limbs are straightened all the time, and are also in strong tension);
- the function of the deltoid muscle, which is responsible for the rotation of the shoulder joint inward, is disrupted;
- the flexors of the forearm do not work correctly, and are also involved in a state of hypertonicity;
- the patient's legs acquire an equinovarus position;
- skeletal muscle cramps extend to all segments of the upper and lower extremities.
In especially severe cases, a clinical picture is observed when involuntary spasms of the muscle tissues of the arms and legs cause a pathological contraction of the muscles of the trunk and neck. The occurrence of such symptoms indicates total brain damage, as well as an unfavorable prognosis for the patient.
Babinsky's symptom
With the help of Babinsky's symptom, the possible presence of systemic damage to the motor neuron is checked. In people with preserved functions of the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system at the time of stroke irritation the plantar part of the foot, the toes of the lower extremity are reflexively brought together and then extended forward.
In patients with signs of hormetonia, the following reaction is observed when a neuropathologist conducts a diagnostic hammer along the lateral surface of the foot:
- the plantar part of the lower limb acquires an arched shape;
- toes are spread apart, and also cannot be brought together due to dysfunction of the motor neuron of the peripheral nervous system;
- the patient's big toe rises up, towering over the rest of the phalanges of the limb.

The presence of a pathological reaction in response to Babinsky's irritable reflex indicates the possible presence of tumor neoplasms in the structure of individual parts of the central nervous system, impaired blood supply to the brain tissues, a consequence of previously transferred stroke. Babinsky's symptom is found in all children of newborn age, since they still have a poorly developed cerebral cortex.
Rossolimo's "upper" symptom
The use of the upper Rossolimo symptom allows you to determine the presence or absence of signs of hormonal syndrome.
The practical application of this diagnostic method involves performing the following actions:
- With the help of a hammer, a neurologist applies light blows to the tips of 1-5 fingers of the patient's upper extremity.
- The reflex reaction of the patient in response to external irritation with diagnostic tools is recorded.
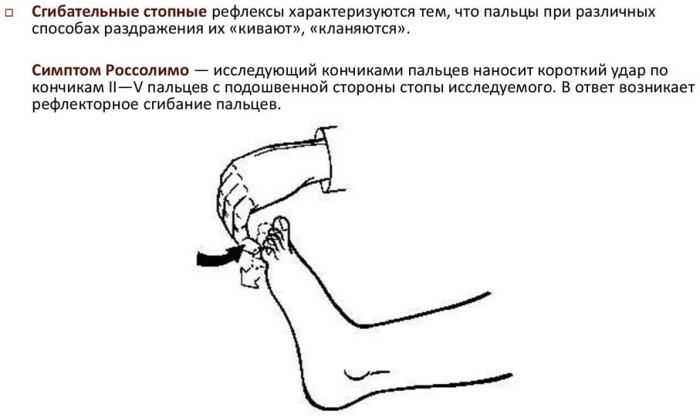
In a person with hormonal syndrome, the response is a reflex contraction of the muscles of the upper limb, aimed at flexing the index finger and adjacent distal phalanges. Definition of the upper Rossolimo symptom is possible only in the period between seizures and hypertension. The patient's hand under examination should be freely hanging.
Klippel-Weil reflex
The manifestation of this reflex symptom also reflects the presence of extensive lesions of the central nervous system with the development of progressive signs of hormone production.
The definition of this reaction of the body is as follows:
- A neurologist performs passive flexion of 2-5 fingers of the patient's upper extremity.
- Reflex activity of 1 phalanx of the hand is recorded.
In a patient with a pathological condition of the central nervous system, the 1st finger is automatically bent in response to the above actions. The appearance of this reflex reaction occurs in patients with hormone syndrome with damage to nerve fibers, which are responsible for conducting neural impulses from the centers of the brain to the skeletal muscles of the upper limbs.
The Klippel-Weil reflex allows the identification of muscle tissue monoparesis. For example, when the state of pathological muscle hypertonicity is observed immediately on the right and left hands.
Symptoms in the interictal period
Hormetonia is accompanied by periodic attacks of muscle spasms of the lower and upper extremities. The time interval between successive seizures depends on the general condition of the patient's central nervous system.
The following symptoms are distinguished, which are characteristic of the interictal period:
- increased excitement of the nervous system;
- anxiety or panic attacks;
- paresis of the facial muscles;
- rapid breathing;
- tachycardia, as well as other disturbances in the rhythmic activity of the heart;
- paralysis of certain muscle groups;
- involuntary circular movements of the eyes (this symptom intensifies in its manifestation at moments of exacerbation of the hormonal syndrome);
- the patient is unconscious.
The above symptoms occur spontaneously. At the moment of deterioration of the patient's general well-being, an exacerbation of the hormone syndrome occurs with the occurrence of another seizure and hypertonicity of the skeletal muscles.
Giving help
Treatment of patients with signs of hormone syndrome is carried out in the hospital of the neurological department. To relieve attacks of hypertonicity and muscle tissue cramps, antispasmodics are used in the form of injection solutions for intravenous administration. Measures are being taken to eliminate pathological factors that cause dysfunctions of the central nervous system.
For example, drug therapy is carried out to restore full blood supply to the brain tissues, or a tumor neoplasm is removed using a surgical method. Patients with a violation of the cellular composition of the blood towards an increase in the level of platelets receive treatment with antiplatelet drugs to prevent thrombosis.
Forecast
The presence of hormetonia indicates an unfavorable prognosis for the patient's recovery. At the same time, the causal factor is of great importance, which provoked the hypertonicity of the muscle tissues.
A cerebral stroke, accompanied by hormone, is fatal in 97% of cases.
Patients with skeletal muscle spasms, which are caused by severe traumatic brain injury, have a chance of recovery only if promptly performed surgical treatment. In this case, the patient is urgently removed intracranial hematomas formed due to severe brain injury.
After a successful surgical operation, the paralysis of the muscle tissues of the arms and legs completely recedes. The patient may retain signs of a pathological state of synkinesis, which are expressed in involuntary contraction of skeletal muscles when trying to make independent movements with the upper or lower limbs.
The patient loses the physiological ability to maintain balance, maintain body balance at moments of physical activity, the functions of the shoulder, elbow, knee and ankle joints are impaired. In the absence of total brain damage, the patient remains sane, but loses the ability to lead a full-fledged lifestyle. The prognosis of hormetonia is an imminent onset of death, or a lifelong disability.
Hormetonic syndrome is a painful condition of the central nervous system that disrupts most of the functions of the human musculoskeletal system. Pathology develops suddenly or gradually, depending on which causal factors provoked large-scale cerebral brain damage.
The etiology of hormetonia is associated with the consequences of stroke, severe craniocerebral trauma, thrombosis of the great vessels supplying the central nervous system. Skeletal muscle paralysis and involuntary muscle contractions occur in people with tumors in the brain. The development of hormetonia is characterized by a simultaneous dysfunction of all segments of the musculoskeletal system or only the upper and lower extremities.
Video about hormone
Diagnostics and algorithm of emergency care for coma: