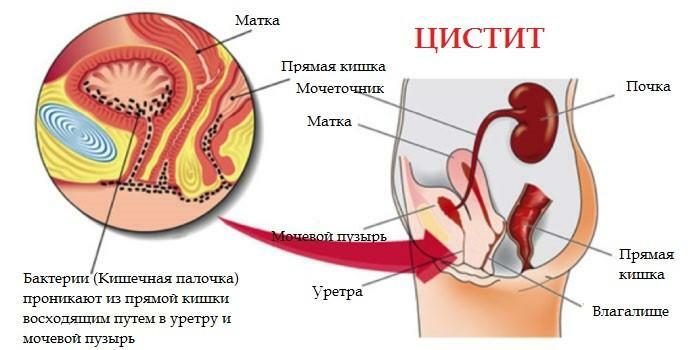
Analyzes for intestinal infection - a common type of laboratory study that allows you to identify the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the gastrointestinal tract.
The diagnostic method is used when the characteristic symptoms of an intestinal infection are manifested, as well as during periodic medical examinations. These analyzes allow not only to identify the morphological affiliation of the causative agents of the disease, but also to determine the sensitivity to various groups of antibiotics.
Record content:
- 1 Indications for research
- 2 How is it determined
-
3 Preparation and analysis
- 3.1 Analysis for intestinal infections
- 3.2 Analysis for staphylococcus
- 3.3 Analysis for typhoid fever
- 4 Decoding the results
- 5 When to see a doctor
- 6 Possible complications
- 7 Videos about Intestinal Infection
Indications for research
Tests for the presence of an intestinal infection are prescribed in cases of manifestation of symptoms that indicates the presence of a bacterial pathogen:
- colibacillus;
- staphylococcus;
- salmonella, which provokes the development of typhoid fever.
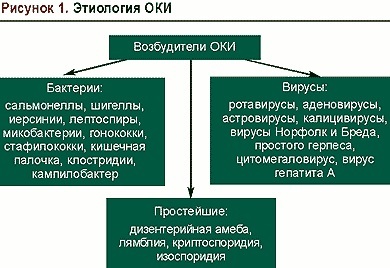
The following symptoms will indicate the presence of one or another pathogen in the gastrointestinal tract:
| Intestinal infection |
|
| Staphylococcal intoxication |
|
| Typhoid fever |
|
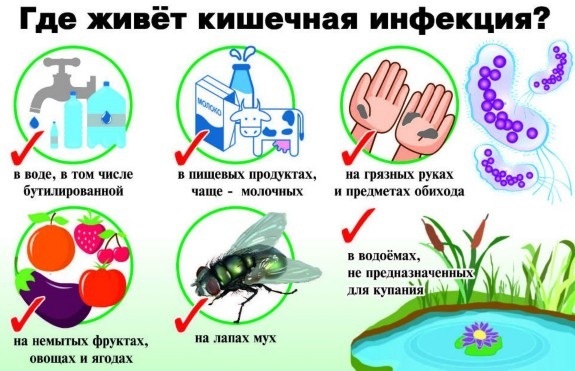
With the combination of the listed characteristic symptoms, an urgent consultation with an infectious disease doctor is necessary, who will prescribe the necessary laboratory tests.
How is it determined
Tests for intestinal infections, including staphylococcus aureus and typhoid fever - laboratory research methods in children and adults, which make it possible to identify a specific causative agent of the infection and determine the tactics of further treatment.
Fecal matter is used as a biomaterial for the study. However, in the case of diagnosing typhoid fever, blood serum is used, since the study of feces has low sensitivity and allows you to identify the pathogen in 30-40% of patients.
The presence of pathogenic flora in feces is determined using laboratory methods, consisting of 2 types of research:
- bacteriological;
- microscopic.
Bacteriological analysis of feces is considered the most accurate method for determining a specific infectious agent. For the study, part of the material taken is placed in special nutrient media, under which active bacteria multiply for 5 days.
After the end of the cultivation of colonies, the nature of their growth and belonging to certain types of infections are determined. The grown colonies are tested for sensitivity to antibiotics or bacteriophages. The cost of the analysis varies from 450 to 850 rubles.
Microscopic examinations are carried out using a microscope. For this, a stool sample is stirred with water, and then the resulting mixture is applied dropwise onto a glass slide, where pathological elements are determined using the native material.
When diagnosing an intestinal infection caused by staphylococci, microscopy of Gram-stained feces is used.
The essence of the analysis consists in staining biomaterial samples with a special set of dyes, with the help of which the bacteria are determined to be gram-positive or gram-negative. In the presence of staphylococcus in the smears, gram-positive cocci will be detected. Research cost - from 580 rubles.
In cases where an infection in the intestine is provoked by a virus or protozoa, the analysis for the intestinal group may not be sufficiently informative. Then they carry out a polymer chain reaction (PCR diagnosis) of feces - a diagnostic method that allows you to identify or refute the presence of a gastrointestinal infection within 1 day.
PCR is referred to as a molecular genetic study, in which the isolation of RNA / DNA of pathogens and an increase in their number with further recognition occurs. The cost of a comprehensive analysis to determine the main pathogens is 1200 rubles. and higher.
Additional methods for studying infection in children and adults include a culture tank and a serological blood test, which allows detecting antibodies to pathogens. Such analyzes only indirectly indicate the presence of an infectious process, therefore, they are not used as the main method of diagnosis.
Preparation and analysis
Tests for intestinal infection require careful preparation in order to avoid obtaining unreliable results. Before the study, patients refuse to take drugs, follow a special diet and the rules for collecting biological material.
The basic rules for collecting feces apply to all types of laboratory tests and are considered generally accepted:
- To collect biomaterial, only sterile dishes are used - a plastic container purchased at a pharmacy or a sterilized glass jar.
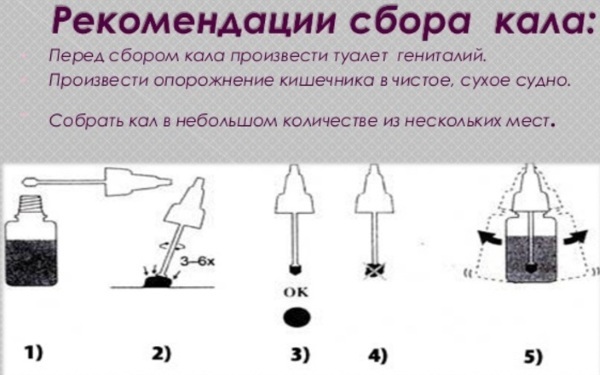
- Collecting feces for research is carried out in the morning after hygiene of the external genital organs. If the child needs an analysis, he is pre-washed and offered to urinate.
- After natural defecation, feces are collected from a clean surface to avoid colonization of the material by foreign microorganisms. It is forbidden to take feces from the toilet. The collection of material from infants is carried out from the surface of the diaper.
- The study requires about 20 g of feces taken from the middle part of the biomaterial.
- Purulent discharge and mucus present in the feces are also collected for research.
- For a more accurate result, the stool must be delivered within 2 hours after collection. If this is not possible, the collected material can be stored in the refrigerator for no more than 4 hours.
If a biomaterial is taken by a medical officer in a hospital setting, then the process is accompanied by the following manipulations:
- The patient is placed on a couch in the position of the legs bent to the stomach.
- To collect a biological sample, use a sterile tube with a loop placed in a special solution.
- With the help of a loop, they penetrate into the patient's rectum to a depth of 4-5 cm in adults, and 2-3 cm in children. Then the loop is removed and placed in a test tube with a solution.
The collected material is delivered to the laboratory immediately after all the manipulations. It is allowed to store the sample in a test tube for 24 hours at a temperature of 2-4 ° C.
Analysis for intestinal infections
The analysis for intestinal infections requires careful preparation from the patient in order to avoid obtaining unreliable results:
- 7 days before stool sampling, stop taking antibacterial drugs and laxatives;
- 3a 3 days before the study, make adjustments in the diet, giving up foods that provoke fermentation in the intestines. These products include: legumes, meat and fish, cabbage, flour and bakery products. It is also forbidden to drink alcohol.
- Do not use rectal suppositories for the last 3 days before donating feces.
- Do not use wash enemas on the day of stool collection.
The feces collected immediately after the act of defecation without urine impurities in a sterile container are sent to the laboratory. Feces are inoculated on solid colored media. If a stool sample was collected on a swab in a hospital setting, it is applied to a solid medium and then dispersed with a spatula. Then the crops are sent to a thermostat and kept at a temperature of 37 ° C for 24 hours.
A day later, the grown colonies are examined using a microscope, studying the cultural characteristics of bacteria. Then the identified bacteriological colonies are stained according to Gram in order to subculture them to other specific media for further cultivation of pure cultures of the pathogen.
On days 5-7 of the study, the isolated pure culture is identified with further study of the biochemical properties of bacteria. The final test results are received a week after the delivery of the material.
Analysis for staphylococcus
The development of an intestinal infection of a staphylococcal nature provokes Staphylococcus aureus. To detect its presence, bacteriological and bacterioscopic research methods are used. The material for the study is feces, the collection of which is carried out after all the conditions of preparation are fulfilled.
3 days before the study, patients must stop taking the following groups of drugs:
- iron-containing;
- enterosorbents;
- laxatives;
- broad spectrum antibiotics.
The biomaterial is collected in the morning after natural bowel movements and within 2-3 hours. delivered to the laboratory in a sterile container.
After stool specimens arrive at the laboratory, they are subjected to bacterioscopy using Gram staining. The presence of staphylococcal infection will be indicated by the identification of cocci, located in groups of 2-3 bacteria in the form of grape bunches.
Next, a bacteriological study is carried out. The collected biomaterial is inoculated on 2 nutrient media - yolk-salt and blood agar. Then the seeded media are incubated for a day at a temperature of 37 ° C.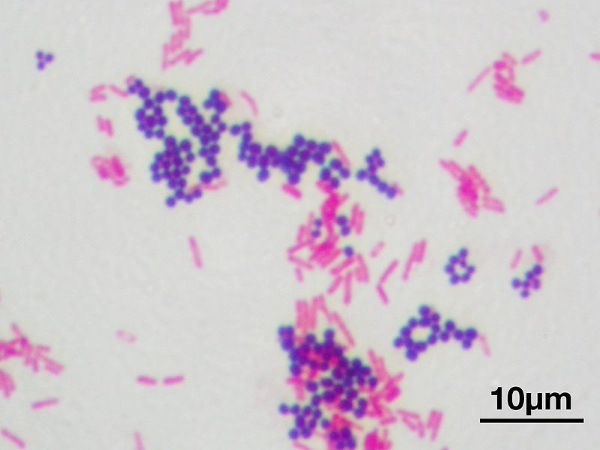
On the second day, the growth pattern of the colonies is assessed. On yolk-salt agar there are staphylococcal colonies of golden or white color, with a smooth surface and smooth edges. On blood agar, zones of destruction of erythrocytes are formed along the perimeter of the location of the colonies.
Seeded colonies on both media are Gram stained and examined by microscopy. On the 3rd day of the study, the type of staphylococcal infection and its sensitivity to antibiotics are determined.
Analysis for typhoid fever
Typhoid fever is caused by bacteria of the genus Salmonella.
To diagnose the presence of an infection in the body, a bacteriological study is chosen, the biomaterial for which is:
- blood serum;
- feces;
- urine;
- bile;
- Bone marrow.
The most informative in the first week of the disease is a bacteriological blood test, which is taken from a vein.
Before diagnosing, the patient needs to undergo training:
- 3 days before the test, stop taking all medications.
- Smoking and drinking alcohol is prohibited on the day of blood collection.
- 1 day before the study, stop taking spicy, fatty foods.
- The analysis is carried out on an empty stomach or not earlier than after 4 hours. after the last meal.
The research is carried out in stages:
- The taken venous blood in a volume of 15-20 ml is inoculated on a special Rapoport medium in a ratio of 1:10 (1 ml of blood per 10 ml of medium).

- The resulting crops are placed in a thermostat at 37 ° C for 18-24 hours.
- A day later, the bacteria are subcultured onto Levin's medium. Suspicious bacteria that are black or clear in color are re-plated on agar.
- On the formed environment, Salmonella is recognized by its characteristic features: the ability to break down glucose to form acid.
As an additional diagnostic method, a general blood test is performed. The presence of salmonella in the body, which provokes typhoid fever, will be indicated by leukopenia and high ESR detected in the collected biomaterial.
Bacteriological examination of feces is possible only from the 2nd week of the disease, since it is during this period that typhoid bacilli can be found in the crops of the material.
Decoding the results
Tests for intestinal infection allow you to get results 3-7 days after the study. They are presented in the form of special forms, on which information on the presence of beneficial, opportunistic and pathogenic bacteria is submitted in the form of a table. The quantitative content of microorganisms is indicated in degrees.
In order to decipher the result obtained, it is necessary to compare it with the indicators of generally accepted standards.
Normally, the intestines of a healthy person are inhabited by:
- bifidobacteria;
- bacteroids;
- lactobacilli;
- colibacillus;
- enterococci;
- bacilli;
- clostridia;
- peptococci;
- saprophytic and epidermal staphylococci.
In this case, the norms of indicators will differ depending on the age of the patient.
The presence of an infectious process will be evidenced by the completed column next to the section "pathogenic microflora".
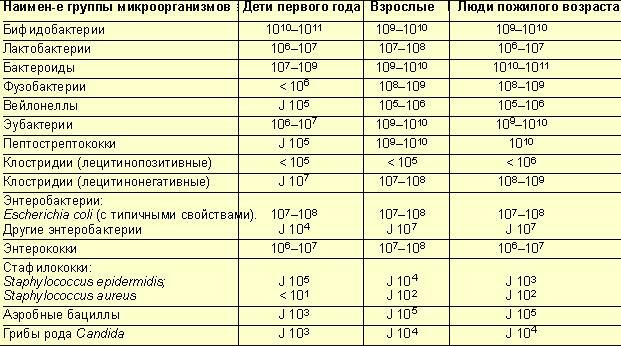
In this case, one of the types of pathogenic bacteria will be indicated:
- shigella;
- salmonella;
- cholera vibrio;
- Staphylococcus aureus.
When detecting Escherichia coli, it is worth paying attention to the specified strain. So, some Escherichia coli are pathogenic and provoke the development of infectious processes.
When to see a doctor
The need to see a doctor will become known after receiving the test results. If, during the study, pathogenic organisms were identified in the intestinal microflora, you need to contact your local therapist.
Tests for intestinal infection, containing positive results for the presence of salmonella, aureus staphylococcus, pathogenic Escherichia coli or Vibrio cholerae, require further decoding by a doctor infectious disease specialist.
If, in addition to the results of the analysis, the patient has signs of intoxication of the body, fever or increased diarrhea, urgent hospitalization in the infectious diseases department is necessary.
Possible complications
The main complications caused by the prolonged course of intestinal infection are associated with dehydration of the body against the background of rapid fluid loss due to increasing diarrhea and vomiting. This is especially true for pediatric patients, for whom severe dehydration in a short time leads to hypovolemic shock and renal failure.
Other consequences of intestinal infection include the generalization of the pathological process in other organs, which can provoke:
- sepsis;
- DIC syndrome;
- the development of acute heart failure;
- pulmonary edema.
A fairly common complication of an intestinal infection is an infectious-toxic shock that develops as a result of an increase in temperature.
Tests for intestinal infection are a diagnostic method consisting of bacteriological, microscopic and serological studies. The method is used to identify dangerous pathogens that provoke the development of acute intestinal infections of a bacterial nature. Based on the results of the collected analyzes, patients are prescribed treatment with antibiotic therapy.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Videos about Intestinal Infection
E. coli in analyzes: