Meningococcal infection is a dangerous disease. The first symptoms in adults appear 1-10 days after infection of the body. The causative agents of infectious pathology meningococci live on the surface of the mucous membrane of the nose and mouth.
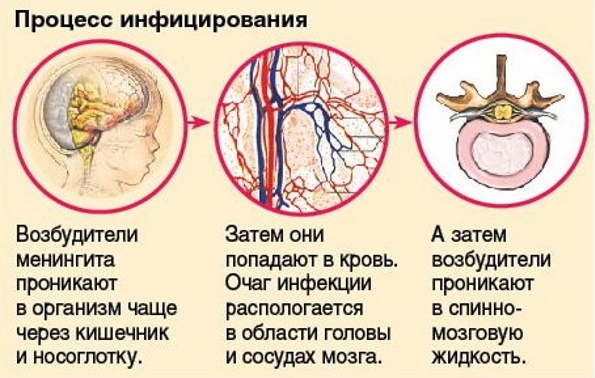
They enter the environment during coughing, sneezing. Infection of a healthy person occurs after close contact with a sick patient, mainly by airborne droplets.
Record content:
- 1 Disease types
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Traditional methods
- 8.3 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Video about meningococcal infection
Disease types
Given the area of the lesion and the spread of the infection, the following types of meningococcal infection in adults are distinguished in medicine:
| Name | Description |
| Carrier | The causative agents of the disease live on the mucous membrane for 6 weeks. They multiply and are released into the external environment. All this time, there are no clinical signs, the person is a carrier. |
| Nasopharyngitis | The inflammatory process affects the nose and throat. Symptoms of a common cold appear (cough, runny nose, fever, red throat). Given the provoking factors, the disease can result in a person's recovery or make him a carrier. The risk of developing serious complications remains. |
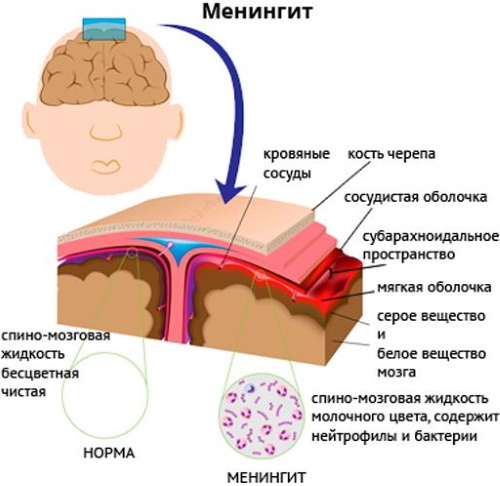
According to medical statistics, there are also generalized forms of meningococcal infection in adults:
| Name | Description |
| Meningitis | The disease begins abruptly, the person's body temperature rises. Back, neck, head ache, intolerance of sharp sounds, light appears. The patient is disturbed by severe vomiting, after which there is no relief. Consciousness is impaired. A person lies in a certain position: he draws his legs under him, being on his side. In some situations, characteristic symptoms appear as early as 2-3 days, which indicate damage to the cerebral membrane by an infectious and inflammatory process. |
| Meningococcemia | A form of the disease that develops sharply and rapidly. In some situations, it occurs against the background of nasopharyngitis. A sharp rise in temperature is accompanied by muscle aches, severe headache and clouding of consciousness. Over the next 1-2 days, a characteristic rash appears on the body. These can be small stars or large hemorrhages. In difficult situations, they provoke necrotic processes and tissue death. The early appearance of a rash on the face is an unfavorable symptom. |
| Meningoencephalitis | The inflammatory process spreads to the brain, sometimes even the spinal cord, affecting their membrane. The patient's body is covered with hemorrhagic exanthema (a rash of a different nature and size that occurs during an infection or an allergic reaction). The diameter of the papules ranges from 1 to 10 mm. |
Treatment of pathology is successful, but most of the patients die from severe consequences. There are rare forms of the disease (pneumonia, polyarthritis, iridocyclitis).
The severe course of meningococcal infection occurs rapidly. Not only the temperature rises, the rashes on the body merge and large spots are formed. There is a high likelihood of bleeding, blood pressure drops, heart rate increases, there is no urination. With such serious symptoms, the patient in most cases dies within 24 hours.
Stages and degrees
The doctor will help to determine the stage and degree of development of pathological processes by prescribing a complete diagnosis for the patient. The results obtained will allow you to choose the most effective treatment.
According to the degree of the inflammatory process, the following forms of meningococcal infection are distinguished:
| Name | Description |
| Light form | The disease proceeds like a common cold. A person is worried about a runny nose and general malaise. |
| Severe form | More often occurs in children, characterized by a sudden rise in temperature. The whole body and head hurt, hemorrhagic skin rashes appear. The patient needs urgent hospitalization. In most cases, the patient dies. |
Meningococcal disease (symptoms in adults at an early stage of the disease are similar to those of the common cold) requires careful diagnosis. In the absence of timely assistance, the likelihood of serious complications, including death, is high.
Symptoms
The incubation period of meningococcal infection in adults ranges from 1 day to 10 days.
In most cases, the disease develops quickly and acutely, sometimes a prodromal period is observed, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Strong headache;
- general weakness in the body;
- excessive sweating;
- slight rise in temperature.
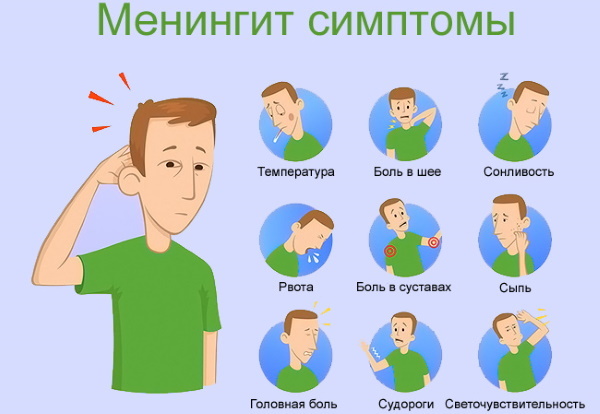
With an acute course, meningococcal infection is characterized by the following symptoms:
- high temperature (up to 40 ° C);
- sore throat;
- poor appetite;
- headache;
- nasal congestion;
- a sore throat;
- lethargy, severe malaise;
- recurrent vomiting.
On the second day after infection of the body, rashes appear on the patient's body. As the pathological processes progress, the pink rash turns into hemorrhagic papules. They have jagged edges, are dark red in color, and rise slightly above the skin.
Meningococcal infection (symptoms in adults will help the infectious disease doctor determine the extent and stage development of pathological processes) is often accompanied by rashes in the buttocks, legs and on the lower part torso. The size and shape of the papules is different; in a difficult situation, the death of the affected tissues is observed (necrotic process).
Reasons for the appearance
At risk are people of different age categories, but in 70% of cases, these are children. The body is more weakened in spring or autumn, it is during this period that it is easy to get infected with meningococcal infection. The immune system lacks vitamins, which leads to frequent hypothermia.

The causative agents of the disease are transmitted by airborne droplets, after close contact with a sick person.
Meningococcal disease is dangerous for the following people:
- medical workers;
- children under 5 years of age (at this age, immunity is just being formed, the probability of infection is the highest);
- adolescents 13-17 years old (at this age, carriers of pathogens are more common);
- conscripts for military service;
- personnel and inmates of stationary social organizations, where round-the-clock stay is provided;
- persons who plan to visit areas with an increased likelihood of infection (pilgrims, tourists, biologists, geologists, military personnel);
- adolescents and adults who live in a hostel;
- persons who take part in major sporting or cultural events of an international scale.
Elderly people over 60 are also at risk. In most cases, 80% of those infected are carriers of pathogenic microorganisms. They are not worried about the symptoms of the disease.
In 15% of patients, the pathology is mild. According to medical statistics, 1% of patients have an extremely serious condition. The central nervous system is affected, resulting in disability or death.
Diagnostics
First of all, when a person turns to a doctor, a specialist examines his body and conducts a survey.
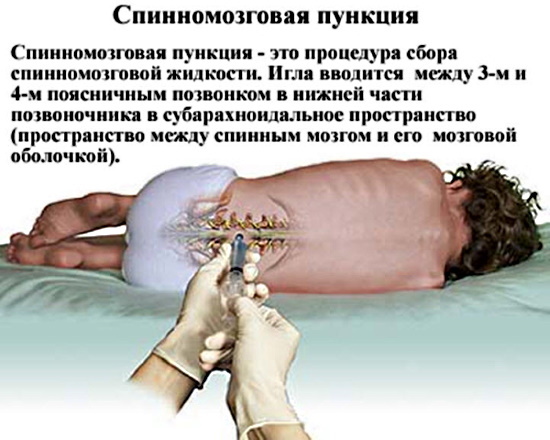
If necessary, additional tests are prescribed:
| Name | Description |
| Blood analysis | Allows you to set the level of leukocytes in the blood, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). A sick person has an increased level of neutrophils. Indicators of anemia are also present. |
| Analysis of urine | The results will help determine kidney function. An acute inflammatory process provokes an increase in protein levels. Shock is characterized by a decrease in the quantity and quality of urine. |
| Bacterioscopy | For research, blood and cerebrospinal fluid are taken to detect the presence of pathogens of meningococcal infection. |
| Spinal puncture | The examination helps to determine the development of purulent inflammation. |
| Nasal swab | The results make it possible to identify the causative agents of meningococcal infection, especially in the absence of a clinical picture. |
| Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of blood and cerebrospinal fluid | The test allows you to determine the DNA of pathogens of pathological processes in the test material. |
| Biochemical blood test (coagulogram, hepatic and renal complex) | Diagnostics allows you to determine the general condition of the patient and the degree of development of pathological processes. |
In addition, to diagnose the disease, you may need the help of a neurologist, ophthalmologist, ENT doctor. Studies of the sensitivity of pathogens to antibacterial drugs are also being conducted.
To diagnose complications of meningococcal infection, the doctor directs the patient for echoencephalography and computed tomography (CT). The methods allow to determine the state of the brain.
When to see a doctor
Meningococcal infection (symptoms in adults appear at least 12 hours later. after infection of the body) is dangerous to human life. It is recommended to go to the hospital as soon as the first clinical signs appear.
An infectious disease specialist is involved in the treatment of meningococcal infection.
A doctor should be consulted if the following symptoms appear:
- heat;
- vomit;
- hypersensitivity;
- convulsions;
- headache.
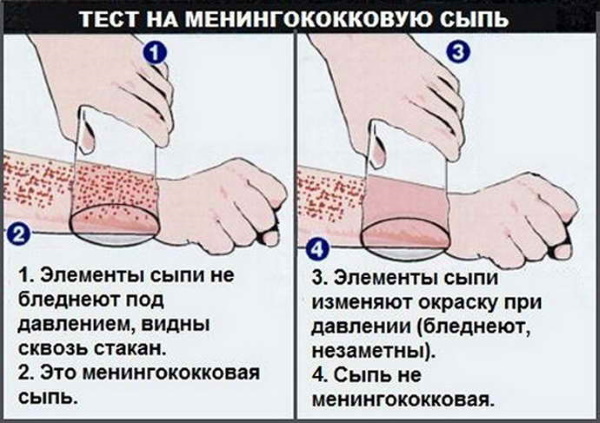
Pathological processes are accompanied by various clinical signs, depending on the form of the disease. It is important to make a timely diagnosis and start treatment in order to prevent serious complications.
Prophylaxis
You can prevent a terrible disease if you remember the simple recommendations of an infectious disease doctor:
- Conduct planned or emergency vaccination (the injection is done after direct contact with the patient).
- Use chemoprophylaxis. A patient who has been in contact with an infected person is prescribed a specific antibiotic.
There is also non-specific prevention, when people are advised to follow these rules:
- do not smoke one cigarette for two;
- wash your hands thoroughly;
- do not use other people's personal hygiene products;
- refuse to eat foods together (ice cream, drinks, chewing gums);
- you can not gnaw a pen or pencil;
- protect the body from hypothermia, dress for the weather in cold weather;
- in living quarters to carry out wet cleaning and more often to ventilate the room.

It is strictly forbidden to lick the baby's nipple before giving it to the baby. It is important to maintain the immune system and exercise moderately. It is also correct to eat, walk more in the fresh air. During epidemics, viral and bacterial diseases are less in places where a large number of people gather.
The body's resistance is also helped to increase water procedures and the correct daily routine. If a child or an adult is sick in the family, it is better to wear gauze bandages. They will reduce the chances of infection for other members.
Treatment methods
Meningococcal disease (symptoms in adults appear after 24 hours. after infection of the body) is a potentially fatal disease, therefore, the patient needs hospitalization. The doctor selects the treatment after a complete diagnosis based on the results obtained.
Medications
More often, the patient is hospitalized and isolated until complete recovery. It is important to start therapy quickly in order to prevent irreversible consequences. The drugs are prescribed by the doctor, taking into account the patient's condition and the results of the medical examination. Medicines help not only eliminate the main source of the pathological process, but also prevent possible complications.

| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Antibacterial agents | Ceftriaxone, Tetracycline | The medicine is administered intramuscularly or intravenously. The adult dosage is 1–2 g every 24 hours. In case of serious damage to the body, the dose is increased to 4 g. |
| Corticosteroid drugs | Dexamethasone, Hydrocortisone | The preparation for injections, taking into account the severity of the disease, is administered at 5-50 mg. The therapeutic effect occurs in 6-24 hours. and lasts up to 3 weeks. |
| Anticonvulsants | Relanium, Sibazon | The medicine helps to stop psychomotor agitation, which is accompanied by high anxiety. The adult dosage is 10-20 mg every 3-4 hours. The medicine is administered intravenously or intramuscularly. |
| Cardiac medications | "Cordiamin", "Korglikon" | The course of treatment and dosage depends on the severity of the patient's condition. In most cases, the drug is administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly. The adult dosage is 1-2 ml 1-3 r. per day. |
| Antipyretic drugs | Ibuprofen, Paracetamol | Medicines are needed to lower body temperature and eliminate pain. The adult dosage is 200-400 mg (1-2 tablets) once. The time between doses should not be less than 4 hours. The maximum daily dosage is 6 tab. |
| Nootropic drugs | "Glycine" | The active substances that make up the preparations protect neurons from death. They also help to preserve the mental activity of the patient. The recommended dosage is 1 tab. 2-3 p. per day for 10-14 days. |
| Medicines to restore water-salt balance | "Trisol", "Sodium chloride" | Solutions are prescribed to remove toxins from the patient's body. They restore water-salt balance and maintain blood pressure. Glucose and electrolyte solutions are given intravenously. |
In some situations, patients are prescribed diuretics (Lasix, Mannitol), which help prevent cerebral edema. They also reduce urine output in order to restore renal filtration.
Antiseptics wash the nasopharynx ("Furacilin", soda solution 3%).
Additionally, funds are used to strengthen the body, vitamin complexes (C, B) are prescribed. They protect the nervous system and support the functioning of the immune system. Rashes on the body are treated with special antiseptic agents (Fukortsin, Brilliant Green, potassium permanganate solution).
In a difficult situation, you will need anti-shock, dehydration and anticonvulsant therapy. In case of disruption of the respiratory system, the patient is connected to artificial ventilation.
Traditional methods
Treatment of meningococcal infection in adults is carried out strictly under the supervision of a physician. You can use folk remedies, but only to eliminate clinical symptoms. The prescriptions of healers and healers will not help cure the main disease.

| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Dog-rose fruit | Pour the fruits of the plant (2 tablespoons) with hot water (2 tablespoons), put on fire and heat for 10 minutes. Then leave for a day in a closed container. Strain the finished mixture and take it according to the scheme. | A vitamin remedy that will help strengthen the functioning of the immune system. Also eliminate headaches and increase the body's resistance to disease. The resulting product is recommended to take ½-1/4 tbsp. 2-3 p. per day. |
| Herbal collection | Mix in equal proportions primrose and valerian root, lavender flowers and peppermint leaves with rosemary. Pour the resulting mass (20 g) with hot water (200 ml). Insist 1-2 hours, strain well and take every day. | The medicine helps to relieve severe headaches and irritability. The resulting product is recommended to drink 2 tbsp. daily. |
| Lime tea | Brew ¼ tbsp. linden flowers with hot water (1 l). The remedy should be infused for 10-15 minutes, strain and drink the medicine according to the scheme. | Linden tea as an adjunct to drug therapy helps to reduce pain and inflammation. It is recommended to drink the product in 0.5 tbsp. 3 p. per day. Linden tea also supports the immune system of the human body. |
Mint infusion has a sedative, anticonvulsant, diuretic and anti-inflammatory effect. Chamomile baths help relieve pain, relieve anxiety and relieve cramps.
The use of folk remedies should be discussed with a therapist or infectious disease specialist, since many components can aggravate a health condition or provoke an allergic reaction.
Other methods
The tactics of treating meningococcal infection in adults depends on numerous factors, including:
- the age of the patient;
- the severity of the disease;
- the presence and nature of complications.
During therapy, it is important not only to take medications strictly according to the scheme, but also to adhere to the daily regimen and eat right. Foods are added to the diet, which include easily digestible protein.
After recovery and discharge, the patient needs to be registered with a local therapist for a year. A person during this period must be examined in order to timely detect repeated relapses of the disease. In case of negative results, he returns to a fulfilling life.
Possible complications
In the absence of timely medical care, the risk of developing serious complications increases:
- hormonal disorders;
- partial or complete paralysis;
- epileptic seizures;
- toxic and infectious shock;
- swelling of the brain;
- cerebral hypotension;
- pulmonary edema;
- acute renal failure;
- gastrointestinal bleeding.
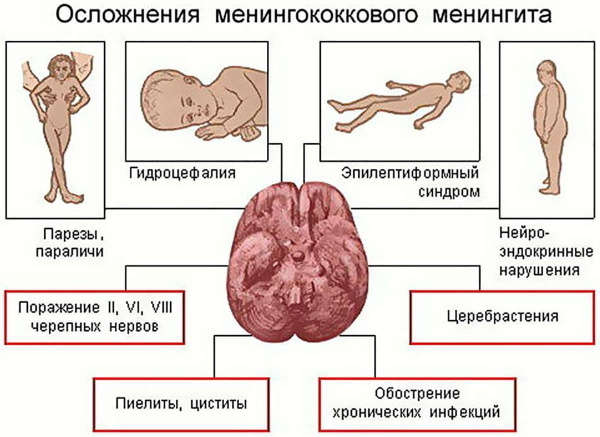
Rarely, when a meningococcal infection in an adult proceeds without consequences.
Sometimes the development of asthenic syndrome is observed. The patient recovers completely, but he is worried about weakness, lethargy and headaches. In some situations, a complication after pathology is increased intracranial pressure (hypertensive syndrome). Decreased hearing or decreased muscle strength on one side of the body.
Meningococcal disease is a serious illness, the complications of which occur not only during treatment, but also after recovery. A timely ambulance will help save the patient's life, for which it is recommended to go to the hospital when the first symptoms appear in adults.
Video about meningococcal infection
Doctor of the children's medical center about meningitis: