There are a number of pathological conditions preceding the formation of a cancerous tumor. These include dysplasia, adenomatosis, leukoplakia, erythroplakia. A distinctive feature for them is atypia (changes in the structure of cells) of the mucous membrane of the cervix. All these processes can be attributed to a precancerous condition, but we note that this is not yet oncology.
However, all the changes that occur require immediate treatment and control, since there is a high risk of converting a pathological condition into cancer. In many patients, precancerous conditions have an erased picture, in rare cases, watery leucorrhoea, bleeding during the intermenstrual period and during sexual intercourse may disturb.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prevention
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Drug treatment
- 8.2 Surgery
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Video about cervical dysplasia
Views
The oncological process in the cervix develops against the background of predisposing factors and structural changes. A precancerous condition is not yet cancer, but the danger lies in the fact that, due to the worn out clinical manifestations, women seek medical help late.
Pathological processes in the cervix occupy one of the first places among the development of diseases associated with reproductive function. In patients of reproductive age, the incidence is 15-20%, in patients during menopause - 5-9%.
Precancerous conditions are classified depending on the degree of damage to the internal epithelium, they appear due to background and precancerous diseases. In the first case, there are minor mechanical changes in the mucous membrane of the internal epithelium, while the cells do not change their structure and properties.
But in cases of precancerous diseases, cell transformation is diagnosed, the prerequisites may be aggressive infections that can penetrate cell tissue and change the genetic material of a healthy cell layer.
Background diseases that can trigger the development of cancer: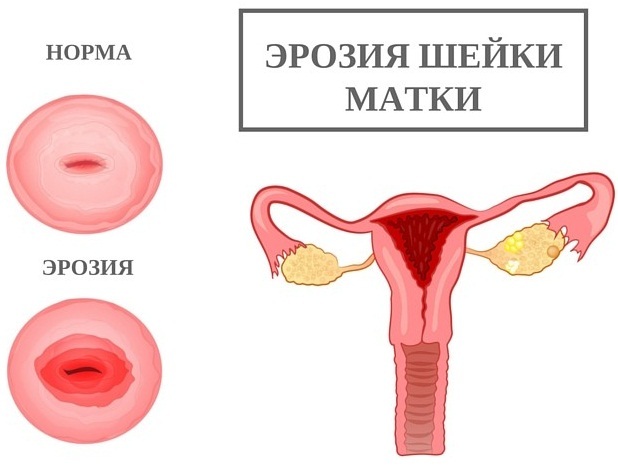
| Disease | Description | Manifestations |
| Ectopia | The easiest and least dangerous disease in which the columnar epithelium lining the cervical canal moves to the vaginal region of the cervix. Ectopia can be congenital or acquired. | At the initial stage, the problem is not clinically manifested in uncomplicated forms. |
| Ectropion | In medical practice, this problem is considered as a consequence of ectopia, when deep tissues are involved in the pathological process. The provoking factors are sclerotic and inflammatory processes. Also, the reason may be childbirth, which takes place with a tear of the cervix, and numerous abortions with mechanical trauma to the tissues. | Clinically, the problem manifests itself during intercourse, bloody discharge and recurrent pain in the lower abdomen appear. |
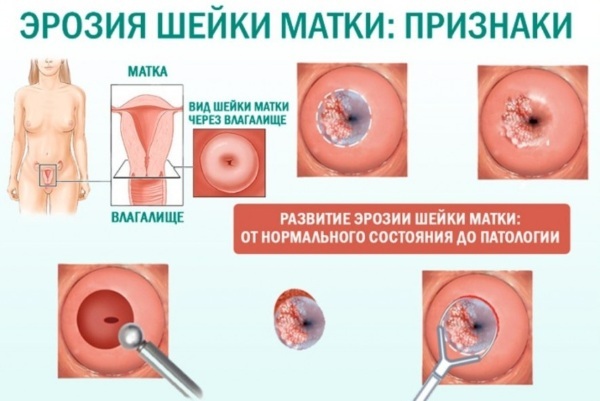
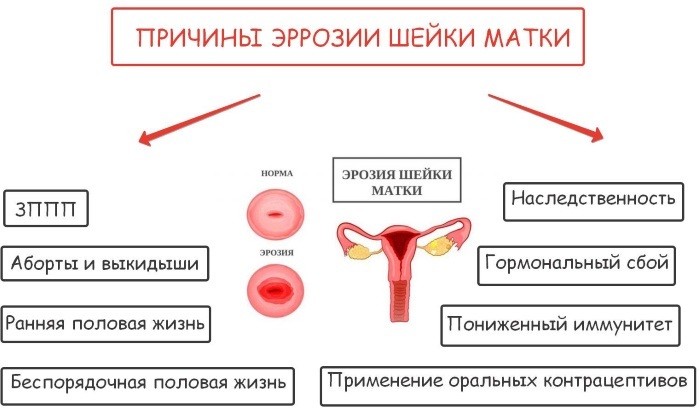
| Erosion | A disease characterized by damage to the cell layer lining the cervix and tissue exposure. Without proper treatment, the process moves deeper into the tissue. The disease can be provoked by inflammation, which further leads to desquamation of the epithelium. | During intercourse, bloody discharge appears, often accompanied by periodic pain. |
| Leukoplakia (dyskeratosis) | Keratinization of the internal epithelium occurs, the mucous membrane of the uterus becomes dry, its compaction is noted. During a gynecological examination, whitish stripes are observed on the surface of the epithelium. There are several reasons for the development of the pathological process, among them hormonal imbalance, immune diseases, infections (in particular PVI), mechanical damage and ionizing radiation. | Clinical manifestations are blurred and mild. |
| Erythroplakia (erythroplasia) | This disease is quite rare, characterized by a serious thinning of the squamous epithelium, through which the blood vessels are visible. The lesion looks like a red spot with uneven contours. | The clinical picture is blurred or absent altogether. When the process is neglected, atrophy of the underlying cellular tissue appears. |
| Endometriosis | The problem is characterized by the proliferation of the internal endometrium outside the uterus. It covers adjacent organs, can be localized in the peritoneum or grow into the muscle tissue of the uterus. The etiology of the disease has not been fully investigated, but traumatization of the mucous membrane during surgical treatment, ruptures and examinations can act as provoking factors. Also, gene mutations can be prerequisites for endometriosis. | Pathology is accompanied by pain in the pelvis, as a rule, they are cyclical, but can also be permanent. Menstruation becomes profuse and longer. The appearance of periodic pain during intercourse. The complex course is characterized by pain during miction or emptying of the intestine, the syndrome of "bloody tear" is rarely noted. |
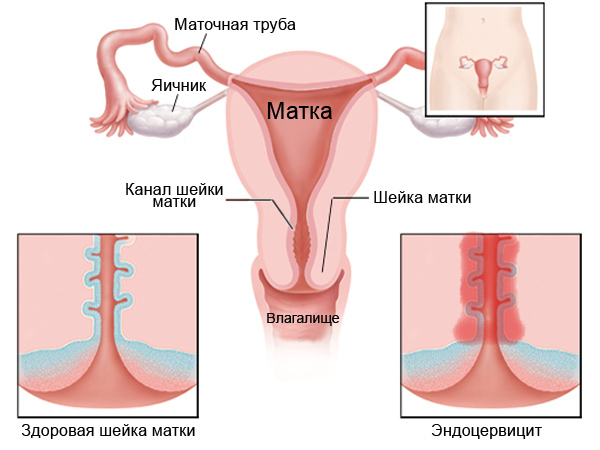
| Cervicitis (inflammation of the vagina) | The inflammatory process affects the vaginal part of the uterus. The cause is infection (chlamydia), fungi, E. coli, amoeba, staphylococcus, treponema. Also, the prerequisites for development include incorrectly performed operations of the reproductive organs. | Symptoms of cervicitis are as follows:
|
A precancerous condition of the cervix cannot be triggered only by the presence of one of these background diseases, since by themselves they cannot be transformed into oncology. But this is still a cause for concern, because under certain conditions and provoking factors, a precancerous process can develop.
Stages and degrees
A precancerous condition of the cervix is dysplasia, the scientific term cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). It summarizes all types of precancer. They say about dysplasia when intracellular changes are determined in the epithelium of the cervix, their size, shape, number of nuclei are disturbed, additional vacuoles appear.
Pathologically altered cells are prone to rapid division, but do not spread beyond the mucous epithelium. Dysplasia develops from the deep layers, moving to the superficial. The uppermost layer is not damaged during the pathological process, all changes develop hidden in the middle layers of the cellular tissue of the uterus.
Stages of dysplasia depending on the severity of the pathology: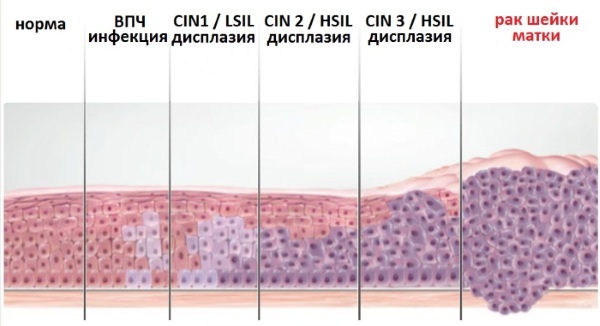
| Degree | Determination of severity |
| CIN-1 - mild degree | A third or less of the thickness of the epithelium is damaged, the process begins from the basal layer. |
| CIN-2 - moderate | A change in the structure of cell tissue is noted, an atypical process develops. Half of the thickness of the mucous epithelium is involved in the damaging process. |
| CIN-3 - severe severity | The affected area is 2/3 of the cell tissue. Serious cell abnormalities occur, and their rapid multiplication is noted. |
Dysplasia does not have a fourth stage, the further development of the pathological process degenerates into oncology.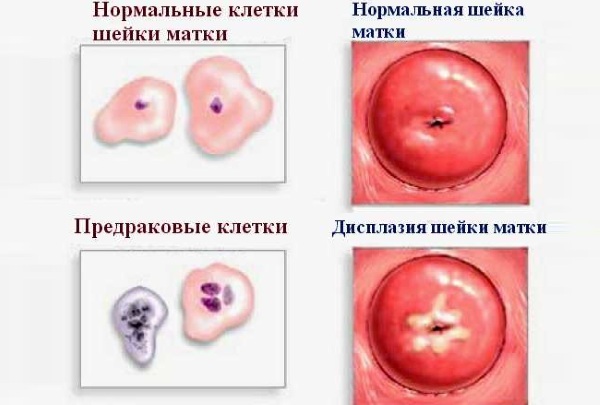
Mild and moderate severity with adequate and timely treatment have a reversible process. Abnormal cells are pushed out and rejected by the body through the proliferation of healthy cells. The third degree of severity is characterized by serious changes in the structure of cell tissue. The pathological process requires surgical therapy, it is impossible to get rid of the problem in other ways, further development will certainly lead to cancer.
Symptoms
There are practically no signs of any underlying disease, which is the danger of the problem under consideration. Pathology develops asymptomatically or has a blurred clinical picture. A woman is able to determine the presence of a problem only at an advanced stage.
Common signs of precancerous diseases of the cervix are as follows:
- periodic pain in the lower abdomen;

- profuse whitish discharge;
- contact spotting spotting;
- increased profusion and duration of menstruation.
The clinical picture depending on the underlying disease:
| Disease | Symptoms |
| Erosion and dysplasia | They have no independent signs. Erosion is detected when a secondary infection is attached, as a result of which cervicitis and vaginitis begin to form. With a hormonal disorder, the patient has an absence of menstruation or their excessive abundance. There is no pain at all. |
| Leukoplakia | Abundant discharge of leucorrhoea is rarely observed; during sexual intercourse, bleeding may be present. When diagnosing, the doctor determines the presence of a whitish-nacreous spot on the cervix. |
| Erythroplakia | There is a sticky yellowish discharge. The diagnostic results show the presence of dark red spots with indistinct edges and pronounced inflammation of the tissues, their swelling. |
Pain is one of the main signs of dysplasia.
It can have a different character, intensity and cause:
- pulling;
- paroxysmal;
- sharp, sharp.
Some patients experience discomfort during intimacy, some during menstruation. All this is an alarming signal and a reason to consult a gynecologist. Each case is studied individually. Various diagnostic techniques are used to diagnose the problem and identify the cause.
A precancerous condition of the cervix is not yet oncology, but without medical care, in 100% of cases it threatens the development of cancer.
In order to timely identify the pathological process, it is required to perform the following measures every six months:
- examination by a gynecologist;
- instrumental research;
- laboratory tests;
- clinical examination.
Reasons for the appearance
A precancerous condition of the cervix is a change in the structure, size, color, and number of cell nuclei. The main provocateur of their rebirth are aggressive infections. They invade the cell itself and penetrate the nucleus with their DNA.
According to medical observations, the main infectious provocateurs of precancer are:
- HPV (human papillomavirus) - the majority of cases (95%) of the development of precancer;
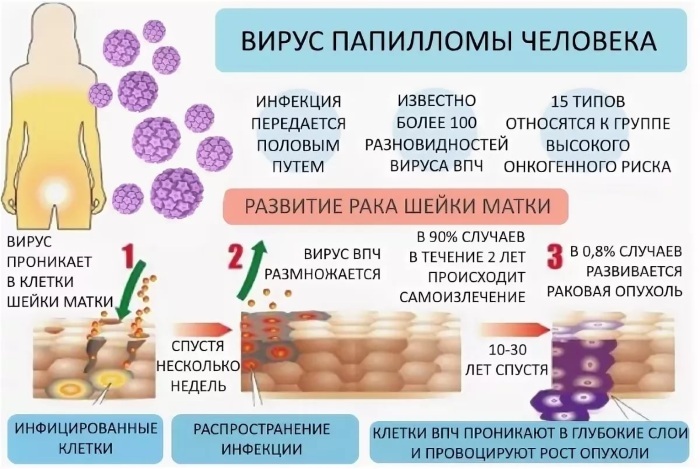
- Herpes virus type 2 and 1;
- bacteria that penetrate into cells (chlamydia trachomatis).
There are also predisposing factors for the development of a precancerous process in cells, they create a favorable environment for the reproduction of pathologically altered cells.
This is:
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol, drugs);
- weakened immune defenses;
- early sexual activity;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- uncontrolled intake of hormonal drugs against conception;
- mechanical damage to the cervix against the background of difficult childbirth, frequent abortions, the use of intrauterine contraceptives;
- improper nutrition;
- avitaminosis;
- aging of the reproductive organs;
- heredity;
- endocrine diseases.
The influence of several detrimental factors at once increases the risk of the formation of abnormal cells, complicates the treatment process and worsens the prognosis of recovery. To achieve a high result of therapy, it is necessary (if possible) to exclude all factors that have a detrimental effect.
Diagnostics
The precancerous condition of the cervix is asymptomatic, therefore, women are advised every six months undergo a medical examination in order to control and identify possible background pathologies.
Diagnostic measures:
- Gynecological examination. The need for further examination is determined.
- Colposcopy. Allows you to identify visible changes in the tissues of the cervix. Colposcopy is performed with contrast enhancement, which makes it possible to identify pathological areas. The procedure has high efficiency, it is comparable to a histological examination, but it does not violate the integrity of the cellular tissue.
-
Cytological examination of smears from various parts of the genital organ. The accuracy of the research results is equal to 50%, therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, the patient is referred for histology.
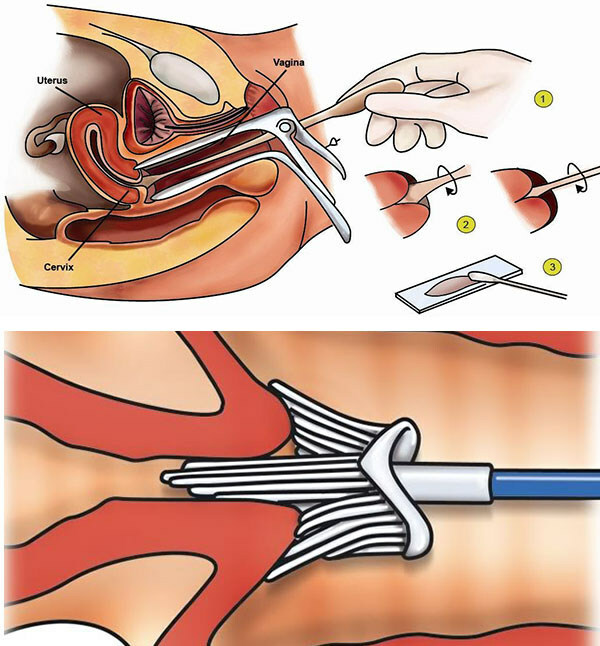
- Schiller's test. Areas for biopsy are determined. Staining with Lugol (a substance based on iodine) makes it possible to identify unstained areas, which are taken for further diagnosis.
- Blood test to detect HPV, chlamydia, Herpes virus and other infectious agents.
When unstained areas are detected (aceto-white epithelium), in addition to determining malignant cells, the study allows you to diagnose other changes in cells:
- mosaic (delicate and rough);
- puncture;
- vascular network.
If one or more of these parameters are present, an additional examination is required.
When to see a doctor
The danger of a precancerous condition of the cervix is an erased or absent clinical picture. Many patients turn to a gynecologist already at the last stages of the background disease or with an active proliferation of cancer cells. In view of this situation, all women are recommended to undergo a gynecological examination every six months.
The goal is to identify at the early stages of pathological processes of the reproductive organs. If there is a suspicion of a problem, the doctor directs for further diagnostics, according to the results of which appropriate drug therapy is prescribed. In more serious cases, the need for surgery and removal of abnormal cells is determined.
Prevention
Preventive measures allow blocking the development of precancerous conditions and background diseases.
Prevention includes:
- vaccination against various infections;
- refusal of casual sexual intercourse (and if the situation still exists - the mandatory use of local contraception);

- compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene;
- regular examination by a gynecologist;
- examination and control when planning pregnancy;
- timely treatment of underlying diseases and dysplasia.
Vaccination against HPV infection is a highly effective method of prevention.
Treatment methods
There are two approaches to treating precancerous conditions:
- medicinal;
- non-drug.
Drug therapy includes taking pharmaceuticals depending on the root cause of the pathology.
The drug-free approach is based on:
- laser action on the affected area;
- cryodestruction;
- surgical intervention.
Drug treatment
Conservative treatment tactics involves the use of certain pharmacological agents:
- for viral or bacterial infections, antiviral and antibacterial agents are prescribed (Isoprinosin, Panavir, Cycloferon);
- with fibroids, endometriosis, pseudo-erosion that appear against the background of hormonal disruption, hormonal drugs are prescribed (for women in of reproductive age, gynecologists recommend taking estrogens and gestagens, for women after menopause, estriol is prescribed hormone);
- to maintain, restore and stimulate the immune defense, immunomodulators and immunostimulants (Likopid, Immunomax, Isoprinosine) will be relevant in treatment;
- in addition to the main treatment, the intake of B vitamins and antioxidant complexes (Lycopene, Dibikor, Glutargin) is prescribed;
- taking local dosage forms to restore the vaginal microflora (Fluconazole, Pimafucin, Nystatin).
Conservative tactics are effective only if the patient is diagnosed with a mild background disease. In the presence of even the first stage of dysplasia, such treatment can only block the further development of pathology and prepare the female body for surgical treatment.
In addition, the operation can be prescribed if drug treatment is ineffective. The surgical approach can vary in volume, sometimes a local effect is sufficient while maintaining the integrity of the genital organ. But in more severe situations, complete or partial resection of the uterus is performed.
Surgery
Background pathologies, as a rule, are effectively eliminated using a conservative technique, but in some situations this approach cannot be applied as an independent one. For example, in the presence of polyps (especially adenomatous ones), surgical intervention is required.
The decision on radical methods of therapy is made by the doctor, having studied the research results, analyzing the clinical picture and the degree of threat to the woman's life. Surgical treatment is based on various techniques and approaches.
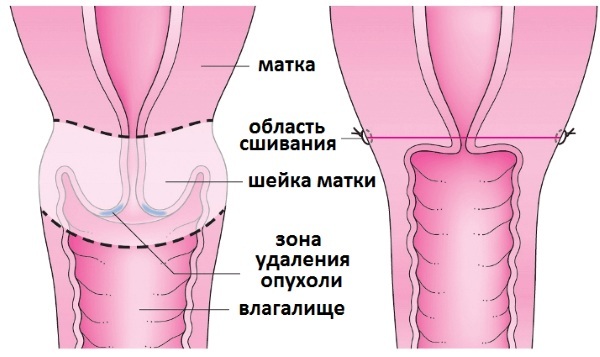
To eliminate the focus of damage, the following methods can be used:
- local destruction (radio waves, cryodestruction, laser, diathermy surgery);
- radical surgery (hysterectomy, excision, reconstructive plastic surgery, removal).
After the operation, the patient is prescribed a therapeutic course of treatment, including the use of drugs to normalize and stimulate the impaired functions of the reproductive organ.
This is:
- treatment of the postoperative area with topical antibacterial and antiseptic solutions;
- taking immunomodulators, vitamin complexes and hormones;
- the use of traditional medicine to restore the lost functions of the organs of the genitourinary system.
After the operation, all patients are under dispensary observation in gynecology for 2 years. This is associated with a high risk of relapse. In addition, doctors strongly recommend paying special attention to prevention.
A healthy lifestyle, prevention of infection and sexually transmitted diseases, changing the method of contraception and other contributes to the early restoration of the functions of the organs of the genitourinary system and the prevention of the development of pathology again.
Possible complications
Complications of a precancerous condition of the cervix are primarily the development of malignant oncology.
Also, a condition without adequate and timely treatment can lead to the following processes:
- severe intoxication, which occurs against the background of regular poisoning of the body with decay products and vital activity of cancer cells;
- oxygen deficiency and exhaustion of healthy cells resulting from metabolic disorders processes produced by beneficial nutrients are absorbed by malignant and atypical cells;
- involvement in the pathological process of a large volume of healthy cellular structures.
After the therapeutic treatment, as a rule, there are no complications, the lesions heal without scarring the tissue.
But after surgery, patients can expect the following consequences:
- failure of the menstrual cycle;
- the development of drug menopause;
- scarring of the cervical tissue;
- exacerbation of chronic inflammatory processes (if preventive measures are not taken);
- infertility.
Cancer is an insidious disease that can appear unexpectedly. That is why women need to undergo gynecological examinations every six months in order to prevent and timely detect background diseases and precancerous conditions of the cervix.
This is the most effective method to determine the development of pathology at its first stages, because almost all background diseases are asymptomatic.
Video about cervical dysplasia
Causes, symptoms and what is the danger of cervical dysplasia:



