When the movement is beyond the will.
In neurological practice, under the notion of decreased motor activity( akinesia - hypokinesia - oligokinesia) means states in which for one reason or another comes the inability to perform active actions by limbs and body movements in full.
But these terms mean not only the levels of decline of this activity, but also the characteristics of the movements themselves.
So, bradykinesia refers to the slowed pace of movements, oligokinesia - their small expressiveness.
The concept of akinessia, literally translated as the complete absence of the possibility of arbitrary movements( inherent in terminal states and cases of severe akinetic crises), is not entirely correct for variants with incomplete loss of motor abilities. It is more appropriate to use the term "hypokinesia", which is accompanied by a partial decrease in motor activity.
Thus, brady- and oligokinesia are, as it were, "paints", expressive means for a canvas called hypokinesia-an insufficient degree of motor activity.
If the manifestation of bradykinesia is a low speed of movement, slowing of their rhythm, then oligokinesia is:
- difficulties with the initiation of movement;

- inability to develop adequate goals for the movement of the strength and rhythm of muscle tension, which necessitates the production of a series of short interim actions( fragmentation of movement);
- loss of both amplitude and speed of automatism when performing movements, especially requiring the involvement of several joints;
- inability to achieve the goal of producing one smooth action, or simultaneous execution of several movements not related to each other, or actions that require bimanual coordination;
- disorder of mechanisms of postural correction( with untimely movements, slow implementation, with insufficient amplitude and inadequate direction).
Causes of movement disorders
Movement disorders are caused by a disorder in the function of the brain structures responsible for the dynamics of movement.
Thus, the onset of akinesia may be due to damage to the base of the brain or its frontal lobes due to encephalopathies associated with:
- with severe renal( uremic catatonic syndrome) or liver failure( hepatic depressive akinesia);
- pathology of hematopoiesis( severe variations in the course of pernicious and hemolytic anemia);
- diseases of the respiratory system( encephalopathy due to hypoxic disorders).
Either it can be caused by severe intoxications and neuroinfections.
 The cause of hypokinesia may be the dysfunction of the structures that make up the extrapyramidal( construction-pallidar) system, which includes such formations of the subcortex as the pallidum and red nuclei, the beginning of the Monak's extrapyramidal tract realizing the realization of unconditioned reflexes, impulses from all parts of the large brain below the cortex to the anterior horns of the braindorsal.
The cause of hypokinesia may be the dysfunction of the structures that make up the extrapyramidal( construction-pallidar) system, which includes such formations of the subcortex as the pallidum and red nuclei, the beginning of the Monak's extrapyramidal tract realizing the realization of unconditioned reflexes, impulses from all parts of the large brain below the cortex to the anterior horns of the braindorsal.
In turn, pathological changes in the extrapyramidal system can be triggered by various mental and neurological conditions.
The first category includes:
- schizophrenia;
- post-traumatic and postpartum depression;
- disorders-affects the discharge of manias;
- hysteria;
- autism;
- mental retardation.
A group of neurological causes that trigger the development of hypokinesia include:
- temporal lobe epilepsy;
- Tourette syndrome;
- postencephalitic syndrome;
- disorders of the thalamus, pallid sphere, frontal and parietal lobe due to stroke, brain tumors or trauma.
Hypokinesia may also result from hypodynamia-lack of movement or a lack of muscular activity of a local nature with the production of monotonous movements that do not require high energy inputs. 
To the same results lead and chronic industrial and household intoxications and other factors.
This development extrapyramidal syndromes category:
- catatonic, depressive or apathetic stupor;
- Parkinsonism.
The most typical symptoms are hypokinesia in Parkinsonism.
Briefly on the neurochemistry of
The study of brain biochemistry has led to the conclusion that there is a special role in the development of kinetics of dopamine deficiency kinetics in the striatal system due to the inadequacy of production by its nigrostrirous cells of a black substance due to the onset of degeneration of its structures.
The disinhibition of striatal palliative cholinoactive neurons in the striatum body is accompanied by the super-blocking of pale ball structures that excite motor activity.
 The fact of damage of dopaminergic nigroreticular neurons of a black substance, whose axons directed to the mesh formation of the brain stem, are switched in it to neurons, the axons of which take part in the creation of the reticulospinal tract.
The fact of damage of dopaminergic nigroreticular neurons of a black substance, whose axons directed to the mesh formation of the brain stem, are switched in it to neurons, the axons of which take part in the creation of the reticulospinal tract.
The decrease in the multiplicity of impulses traversed by the reticulospinal tracts leads to a slowdown in the activity of motoneuron cells, which means an increase in the tone of the transversely muscled muscles and the onset of its rigidity.
We should not discount the suppression of the cerebral cortex due to the depressing influence of the activated reticular formation on it.
Hypokinesia as the main parkinsonism syndrome
Hypokinetic syndrome manifests itself in parkinsonism both in limbs and in the body.
These are all the aforementioned varieties of motor function disorders on the background of plastic hypertension of the muscles, including paradoxical movements, pallidar tremor, micrographic handwriting, "wax doll" and "cogwheel" pose phenomena, walking - body drifts to the side with falls, Parkinson's trampling on the spot, aheyrokinesis.
A typical posture with a slope of the head and body forward with a touch of the chest with the chin, with hands pressed to the body, bent in the wrist and elbow joints, with the bending of the fingers in the metacarpophalangeal and extension in the interphalangeal articulations, with the opposition of the first finger to the other fingers of the hand, withlegs slightly recessed and bent at the knees.
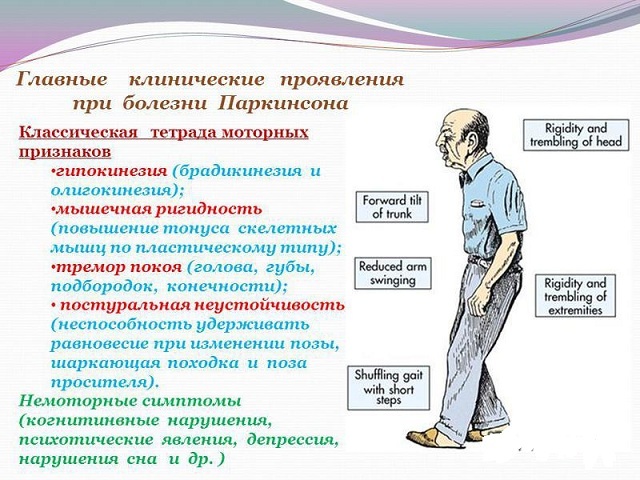
Hypertension of the neck causes the patient to turn around on the call with the entire body or to maximally rotate the eyes, while the head remains fixed.
The motor muscles of the muscles that provide the liveliness of facial expressions are also upset, hence the face masquerade( hypomia) with a virtually unblinking gaze, the monotony of a quiet voice due to difficulties with articulation of speech( hypophonia).
A feature of hypokinesia in parkinsonism( in addition to maintaining muscular strength) is its combination with a high degree of rigidity of muscles.
Unlike spasticity, rigidity manifests itself:
- is a positive symptom of the "lead tube"( uniformity of the muscular waxy resistance, as in the flexion of the lead tubule) - the spastic musculature responds with the phenomenon of recoil and a "folding knife";
- invariance of tendon reflexes - when spasticity they increase.
An illustration of rigidity is a symptom of a "cogwheel", not characteristic of spasticity.
The similarity of motor disorders makes patients with parkinsonism similar to each other, differing only in their expression.
Treatment and prevention of disorders
Depending on the cause of the disorder, the treatment will be fundamentally different according to the methods used.
In the presence of a brain tumor, its operative excision is performed, at the factor of intoxication( household, industrial) it is necessary to take measures to prevent the effect on the body of a toxic compound.
Neuroinfections are treated with the use of medications that are effective against the pathogen causing the pathogens, and the effects of their effects are eliminated using the entire arsenal of drugs that improve blood supply to the brain and detoxicant medicines. 
It is necessary to apply therapies that reduce muscle rigidity:
- rational psychotherapy;
- hypnosis;
- massage;
- methods of exercise therapy and physiotherapy, including relaxing baths.
Preventive measures include measures aimed at preventing the causative agents of neuroinfections, preventing head injuries and the risk of toxic effects of industrial and domestic poisons.
Increased motor activity by mental workers( prevention of hypodynamia) is also an essential measure to prevent movement dynamics disorders.