In all walks of life, there are famous people who are suffering Tourette's syndrome. The name of this disease appeared in 1885. It was proposed by the psychiatrist Jean Martin Charcot in honor of his follower Georges Albert Edouard Brutto de la Tourette, who was engaged in the scientific study of patients with such a pathology.
Record content:
- 1 What is Tourette's Syndrome?
- 2 The prevalence of the disease
-
3 Symptoms
- 3.1 Simple physical tics
- 3.2 Simple sound tics
- 3.3 Difficult physical tics
- 3.4 Complex sound tics
- 3.5 Preliminary sensations
- 4 Tick triggers
- 5 Severity
- 6 When to seek medical attention?
- 7 Establishing a diagnosis
- 8 Confirmation of the diagnosis
-
9 Treatment for adults
- 9.1 Behavioral therapy
- 9.2 Muscle relaxants
- 9.3 Antipsychotics
- 9.4 Limbic leukotomy
- 9.5 Deep brain stimulation
- 10 Treatment of children. Recommendations for parents
-
11 Complications
- 11.1 Obsessive compulsive disorder
- 11.2 Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
- 11.3 Behavioral problems
- 11.4 Learning difficulties
- 12 Personal life with Tourette's syndrome
- 13 Is it possible to be completely cured?
- 14 Tourette Syndrome Videos
What is Tourette's Syndrome?
Tourette's disease refers to hereditary pathologies based on defects in the functioning of the central nervous system (CNS). Its distinctive characteristic is the presence of many motor tics and at least a single vocal tic.
Tics are involuntary short-term physical movements and vocal disorders that appear with repeated repetition throughout the day.
According to the US nomenclature of mental disorders, the disease is placed in a series of neurotic defects ontogenetic nature, characterized by motor and vocal disorders, which are manifested with childhood.
Until the end of the 19th century, Tourette's syndrome belonged to the list of rare and strange diseases that were associated with shouting obscene phrases, inappropriate statements, and insults. According to recent studies, this symptom refers to a smaller number of people suffering from pathology.
Patients have a normal level of intelligence and a normal life expectancy. The number of tic attacks decreases in most patients after adolescence. In adulthood, severe illness is considered rare.
The prevalence of the disease
Today, the syndrome does not belong to rare diseases, due to its course in most cases in a mild form, which cannot be correctly diagnosed.
However, there are different statistics as shown below:
- signs of the disorder are detected in 1-10 children out of 1000;
- more than 10 out of 1000 patients have typical disorders;
- other sources indicate the prevalence of the disease in 3-5 cases per 10,000 people;
- An indisputable fact is the prevalence of the disease in males compared with women (the ratio is 3-5: 1).
Symptoms
Tourette's syndrome is a complex of symptoms that consist of 2 types of disorders: movement and vocal. The violations are simple or complex. The person is unable to control the symptoms. They can appear a hundred times a day, have a different frequency, intensity, duration.
Over time, motor and vocal signs can change places. Often there is a change in the picture of the disease: the symptoms are more severe or easier.
The most severe stage of the disease occurs at the age of 10-12 years. During adolescence, the intensity and severity of the syndrome decreases and in about 70% of children, symptoms stop as they approach adulthood.
Simple physical tics
Simple motor tics are performed by one muscle group. They appear at the very beginning of the disease (at the age of 2-8 years). The first tics are considered simple movements of the head and neck.
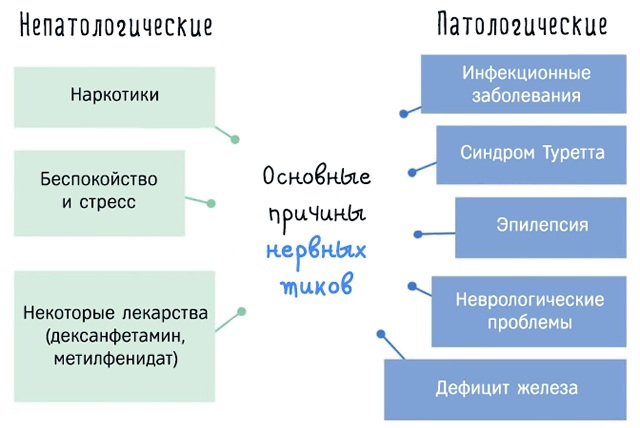
The following can be distinguished as signs:
- blinking and winking;
- lip movements;
- making grimaces;
- moving the nose;
- rolling eyes;
- opening the mouth;
- tongue clicking;
- spitting.
Simple sound tics
Simple vocal disturbances are created using sounds produced when air passes through the nose or mouth. Earlier sound disorders are considered, which appear from 2 years of age.
The most common symptoms of the disease are:
- coughing or coughing;
- imitation of sounds made by animals, birds;
- hiss;
- chest sounds.
Distinctive features of violations are the following pathologies:
- the presence of echolalia (uncontrolled automatic repetition of what was heard);
- the appearance of palilalia (constant repetition of sounds with increasing speed and decreasing volume).
Difficult physical tics
Complex motor disorders are manifested in a combination of simple movements or a series of movements in which more than one muscle group is involved.
The list of symptoms includes twitching of the facial muscles, to which may be added:
- limb movements;
- lifting the shoulders;
- patting;
- stomping;
- bouncing;
- flexion-extension of arms and legs;
- clenching fists;
- snapping fingers;
- a sharp lunge with the foot forward.
Complex physical tics are characterized by echopraxia - involuntary repetition of gestures, postures and movements by patients.
Complex sound tics
Complex vocal impairments involve speaking out by ear of individual words, phrases and sentences.
Disorders that manifest themselves when diagnosing pathologies can be of the following nature:
- spontaneous shouting of words or repetition of phrases;
- the presence of coprolalia (an irresistible impulsive attraction to obscene statements for no reason).
According to statistics, such signs appear in 10% of patients or in 30-50% of all cases.
Preliminary sensations
A distinctive feature of pathology is monotonous, non-periodic, non-rhythmic movements, which are previously accompanied by an inexorable desire to carry them out. Moreover, the desire is stronger than the very need to sneeze or scratch.
Patients often describe the preliminary sensations before the onset of the disorder: as a build-up of tension that they need to release in order to regain calmness. This description of the disease characterizes the syndrome as a semi-voluntary response of the body to insurmountable stimuli.
Tick triggers
Tourette's syndrome is a disease that can be triggered by the following aspects:
- psycho-emotional state of the patient (concerns people who spend a lot of time watching TV or playing computer games);
- negative emotions in the form of anger, resentment, embarrassment increase the frequency of occurrence of violations and make their nature heavier;
- the presence of physiological disorders of the central nervous system, since most often in the risk zone there are patients suffering from attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, with minimal cerebral dysfunctions;
- chronic stress increases the appearance of the disorder by 80%;
- the beginning of classes in an educational institution (inability to adapt to new conditions);
- conjunctivitis (when a person blinks to eliminate discomfort in the eyes, eventually turning into spontaneous processes)
Severity
Scientists divide classes of severity of the disease into 4 types:
- Easy a form that sometimes proceeds imperceptibly even for the next of kin. The patient can independently cope and manage his condition. The period is characterized by a long time without disorders.
- Moderate a stage that is more noticeable compared to a mild degree. The patient is unable to control himself and the disorder becomes visible.
- Expressed the form is characterized by a complete loss of control over the motor skills of his body and voice. It is difficult for him to get used to society, to work, to carry out household tasks.
- Heavy the degree where the behavior is absolutely beyond the control of the person. All types of tics are severe and incapacitated.
When to seek medical attention?
Medical attention is required by a small percentage of children who inherit the gene, reveal symptoms of severe and severe severity. However, there are a number of infectious and psychosocial aspects that can cause illness and affect its severity.
These factors include:
- autoimmune disorders;
- post-streptococcal disorders of autoimmune processes;
- magnesium deficiency in the body, which provokes metabolic disorders that cause the syndrome;
- the presence of other mental disorders.
In the presence of mild severity, medical attention is not required. At a moderate stage of the disease, experts recommend seeking psychological help from doctors. The last two degrees of pathology require complex drug therapy.
Establishing a diagnosis
Diagnosing Tourette's syndrome is a difficult procedure, as there are a large number of other diseases with similar symptoms. Diagnosis is made as other nervous disorders are ruled out.
Diagnostic measures may include research:
- electroencephalography - determination of the modes of operation of the brain;
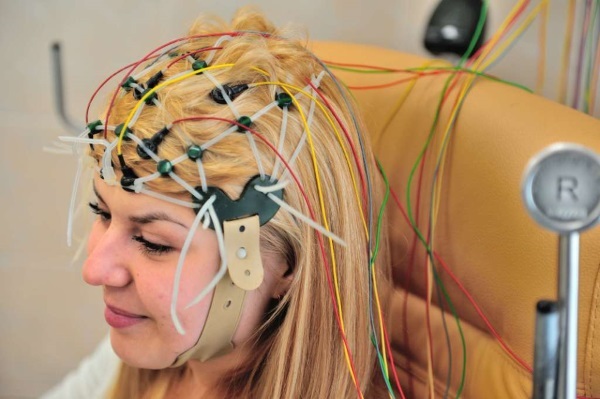
- computed tomography, which can detect lesions in the brain leading to seizures or other nervous disorders;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- results of biochemical blood tests.
After conducting a series of studies, the following pathologies must be excluded:
- conditions after the use of amphetamines;
- rare medical conditions;
- violation of copper metabolism.
Confirmation of the diagnosis
Tourette's syndrome is a pathology in which the diagnosis is made by excluding other neurological diseases.
Patient classification depends on the extent of the disorder:
- Short-term disturbances are characterized by the presence of motor and vocal tics lasting from 4 weeks to a year.
- Prolonged syndrome is characterized by the observation of tics for over a year.
The disease is confirmed if the patient has multiple motor symptoms and at least one vocal tic for more than a year.
In medical practice, the disease is diagnosed by the presence of the following criteria:
- Disorders should manifest themselves for at least a year in a protracted or short-term form.
- Violations should manifest themselves multiple times throughout the day, almost daily for 1 year and longer. The remission period can be less than 2 months.
- The onset of the onset of violations should be determined before the age of 18 years.
Treatment for adults
Treatment of adults depends on the severity of the syndrome, the individual characteristics of the organism. Medical treatment and expert advice will be required if the disease has a strong negative impact on a person's life. Most cases of manifestations of violations are mild, which does not require medical therapy.
Treatment of the syndrome aims to alleviate problematic symptoms in patients with comorbid conditions that are more severe than the disorder.
Behavioral therapy
The patient's understanding of his illness helps to significantly alleviate the condition. This leads to the ability to manage ticks. Relief of symptoms of any severity includes psychotherapy and behavior correction. These treatments help relieve depression and social isolation.
In mild cases of pathology, only explanatory work is needed in the patient's family, among the people around, in the place of study, work. Clinical therapy is carried out by medical psychologists and is used to model the behavior of patients. Treatment extends to adults and children and is aimed at changing established habits.
Habit elimination is based on the idea that people are unaware of the antagonist, and one must learn to control the uncomfortable feelings before they arise. When the patient begins to recognize the moment the tick appears, then he needs to turn on protection, the main one in a less noticeable way that relieves discomfort.
An example of behavior correction is that if a person feels the need to make a vocal sound or cough, they may instead take a series of deep breaths. Very often, behavioral treatment regimens include relaxation procedures.
Muscle relaxants
In severe and severe severity of the disease, neurologists treat tics with muscle relaxants. Scientists' studies have shown the temporary effectiveness of this group of drugs and its lower productivity compared to antipsychotics.
Relaxants help to exercise control over motor skills by eliminating the defect of spasticity (stiffness) of the muscles. A list of drugs with a description of the action, contraindications is summarized in the table.
GABA-B agonist
| Name | Action | Indications | Contraindications |
| Baclofen | Has a muscle relaxant, antispastic effect |
|
|
| Clonazepam | Has an anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant, sedative effect |
|
|
| Mydocalm | The drug belongs to centrally acting muscle relaxants |
|
|
Antipsychotics
Tourette's syndrome is a medical condition that is treated with antipsychotics. Drugs are used when symptoms interfere with a person's normal life.
The mechanism of action of drugs is aimed at blocking the effects of dopamine on the nervous system. A number of funds, summarized in the table, are prescribed by doctors if drug treatment is necessary.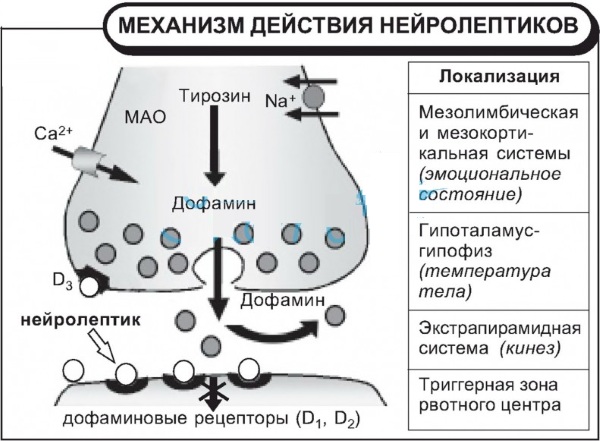
| Name | Properties | Indications | Contraindications |
| Risperidone | Has a depressing activity of the nervous system |
|
Hypersensitivity |
| Haloperidol | Has antipsychotic, neuroleptic, antiemetic, sedative effect |
|
|
| Pimozide | Has antipsychotic, sedative effect |
|
|
| Olanzapine | It is characterized by a depressing effect on the nervous system |
|
Allergy, lactation period |
| Fluphenazine | Has an action inhibiting the nervous system |
|
|
Limbic leukotomy
Limbic leukotomy is a neurosurgery performed under local anesthesia with intravenous sedation.
The essence of the intervention is that an electric current is sent to the brain with the purpose of destroying a small area of the limbic system responsible for certain emotions and behavioral functions.
The procedure is indicated in the presence of chronic depression, obsessive-compulsive disorders and anxious behavior.
Deep brain stimulation
In a large number of studies, deep brain stimulation has been shown to be effective in treating the syndrome. At the same time, there was a decrease in the frequency and intensity of tics in adults.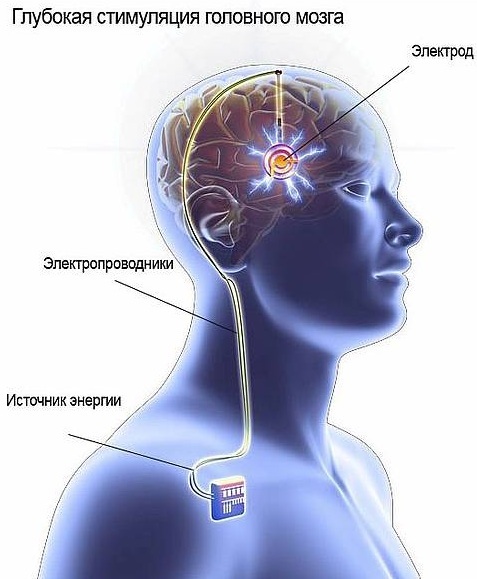
The essence of the therapy is to connect electrodes to specific parts of the brain.
At the other end, the electrodes are connected to an apparatus (generator) that is surgically placed in the chest.
The device generates signals to the brain that prevent tics from occurring.
At present, specialists are only studying the method of treatment together with the risks of side effects in the form of cerebral bleeding or other changes in motor functions.
Treatment of children. Recommendations for parents
Psychologists, neurologists and neuropathologists have a list of recommendations for parents whose children have encountered Tourette's syndrome:
- You should not focus on existing problems. At the same time, it is not recommended to often remind the child about the illness.
- You can not put pressure on the child. It is necessary to create a comfortable psychological environment in the house: not to discuss everyday problems aloud, to speak negatively about his friends, classmates, to sort things out.
- It is necessary to reduce psycho-emotional stress by reducing the time of watching TV, working on a computer. More time should be spent outdoors, walking.
- Children must adhere to a strict daily routine.
The main emphasis in treatment is carried out on the correction of the child's behavior and environment.
Complications
Tourette's syndrome has no effect on IQ. However, despite this, schoolchildren experience difficulties in the learning process. According to statistics, only 10-15% of patients have symptoms so severe that they require training in special conditions.
The list of complications includes:
- behavioral disorders;
- obsessive-compulsive disorder;
- attention deficit disorder.
Obsessive compulsive disorder
In a particularly severe form, obsessive-compulsive disorder turns into obsessive thoughts and monotonous repetitive actions, which become the main types of the patient's daily activity.
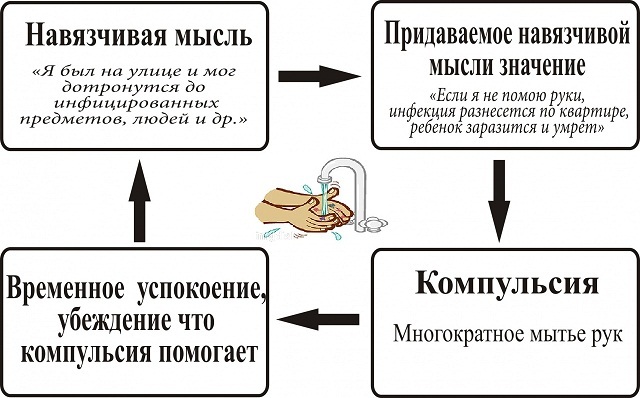
Violations can have a strong negative impact on all areas of life: family, work, educational, social adaptation, leisure, emotional and behavioral sphere. Obsessive states are triggered by triggers containing an involuntary unwanted thought perceived as a threat.
The mechanism, in turn, triggers anxiety in a person, which he can get rid of only when performing monotonous actions and rituals. People suffering from the disorder are more likely to live a life of loneliness, without a job and meaningful companionship.
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is the main cause of learning difficulties. Symptoms of the disease are characterized by the appearance of problems with a lack of attention (especially when performing monotonous types of work) and tremendous activity.
These cerebral dysfunctions negatively affect studies, social life, reduce academic performance, and interfere with adaptation in teams.
When planning a treatment regimen, doctors pay attention to the development of the patient's cognitive abilities, which more often suffers from lack of attention, lack of planning ability and visual-motor coordination.
Behavioral problems
The list of cognitive (behavioral) impairments manifested in Tourette's syndrome includes:
- neurodynamic and regulatory disorders;
- rapid depletion of cognitive processes;
- trouble concentrating and switching attention;
- a decrease in speech functions, namely a decrease in the number of verbal associations that are actualized within a minute;
- disorder of the ability to copy images;
- underdevelopment of the planning mechanism;
- manifestation of impulsivity in conversation and behavior;
- inhibition of switching between the cerebral hemispheres during the implementation of complex tasks divided into stages.
Behavioral problems can bring discomfort to life: misunderstanding of the people around, inability to adapt in society, difficulties in performing any type of work.
Learning difficulties
Violations in the learning process can manifest themselves in the form of pathologies:
- dyslexia - lack of development of reading and writing skills with existing learning abilities;

- dysgraphia - the presence of problems with writing, literacy;
- dyscalculia - lack of numeracy skills.
Psychological difficulties may also arise in the form of:
- emotional instability;
- mood swings;
- addiction to fantasies;
- difficulty concentrating on one activity;
- rapid loss of interest;
- direct behavior;
- uncertainty;
- absent-mindedness;
- fear of mistakes.
Personal life with Tourette's syndrome
In personal life, a misunderstanding on the part of a partner is possible. People suffering from the disease note that the main thing when starting a relationship is not to talk about the diagnosis immediately, as this can scare off another person. In such cases, they recommend telling them that tics are abnormalities from childhood. Usually, others are tolerant of their manifestations.
Is it possible to be completely cured?
Subject to the treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor, the patient, as a rule, manages to stop severe symptoms of the disease. At the same time, patients should observe the daily regimen, try to do without stress and monitor their health.
There are statistics according to which, after completing the full course of treatment, there is a decrease in symptoms with persistent remission in 20% of cases. However, Tourette's syndrome cannot be completely cured. This is stated by people suffering from pathology, they are forced to adjust to the symptoms all their lives and get along with them.
Tourette Syndrome Videos
What is Tourette's Syndrome: