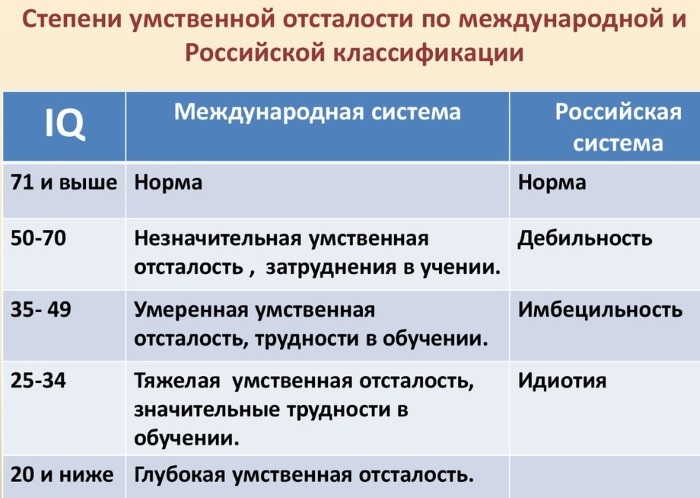
PTSD - this is a state of mindcharacterized by negative reactions and symptoms that occur in a person after a traumatic event. Symptoms of psychological trauma were described in different historical periods and, most often, were associated with the consequences of hostilities.
For example, in the United States, research on PTSD began after the Civil War; the phenomenon acquired special significance after the Russo-Japanese War, when military psychiatry was created, dealing with the nervous disorders of participants in hostilities.
The First World War showed a huge number of cases of PTSD, which later led to the recognition of PTSD as a disease and active research of the phenomenon.
World War II, the Vietnam War and other events, not even directly related to hostilities, showed the strong effect of PTSD on human mental health, which prompted doctors to explore possible treatments disorders.
Record content:
- 1 Definition
- 2 Views
- 3 Stages and degrees
- 4 Symptoms
- 5 Reasons for the appearance
- 6 Diagnostics
-
7 Treatment methods
- 7.1 Medications
- 7.2 Traditional methods
- 7.3 Other methods
- 8 Possible complications
- 9 Video about PTSD
Definition
PTSD is, in psychology, a difficult mental state of a person who has experienced a traumatic event. Researchers note the description of the symptoms of the disorder as far back as antiquity, but the first systematic definition of the phenomenon was cited only in the 19th century by the English surgeon D.E. Erickson in the work "Railway injury and other injuries of the nervous systems ".
In this study, he studied patients who survived a train crash, describing their symptoms associated with disturbed sleep patterns, concentration and memory problems. The surgeon tried to define the disorder as "molecular damage to the spinal cord," with which many researchers disagreed.
At the end of the 19th century, one of the first theories of traumatic neurosis was proposed by the German physician Hermann Oppenheim. The scientist studied women and men with negative mental symptoms and came to the conclusion that it manifests itself after traumatic stressful situations, accidents. He saw the causes of violations in damage to the nervous system and brain.
The end of the 19th century is characterized by the formation of 2 models of the idea of the impact of trauma on the human psyche. The first model was called dissociative, the second - the response model.
French psychologist Pierre Janet, a representative of the first model, focused on the psychological unpreparedness and inferiority of a person who is further exposed to strong emotional experiences after injury.
He defined a phenomenon as a state that arises due to "shock emotions", the inability to find new adaptive behavior, refusal of self-reflection. The impossibility of mental completion of the lived situation forms obsessive thoughts in a person, repeating the traumatic event over and over again.
The second model belongs to Z. Freud, who saw the causes of painful reactions to trauma in the sexual sphere. He also believed that PTSD is caused by a short-lived event that causes severe irritation, which is then difficult to get rid of on your own.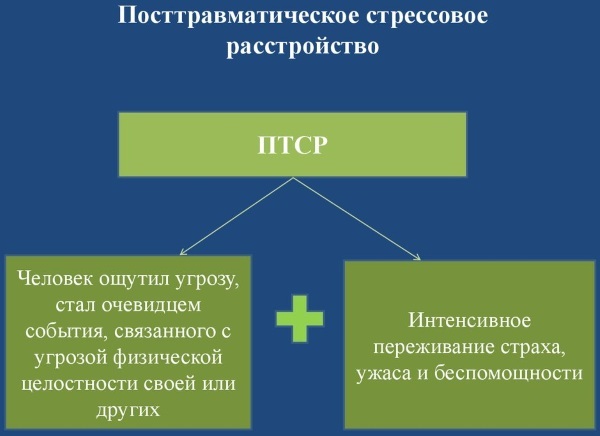
To treat the disorder, it is necessary to turn the unconscious into a conscious one in order to eliminate amnesia by remembering your experience and keeping it as part of the past.
After the American Civil War, the phenomenon was termed "soldier's heart", due to heart problems arising as a symptom of traumatic events. During the First World War, several thousand cases of military neurosis were recorded.
It was determined for the following types:
- exhaustion;
- hysteria;
- nervous breakdown;
- contusion.
The Second World War drew special attention of psychiatry to the problem of military mental trauma. The disorder "combat exhaustion", which means "mentally traumatized in the course of hostilities", was introduced into the US disease classification scheme.
Massive depressive or aggressive state of veterans was noticed in America after the Vietnam War, then the disorder began to be called "Vietnamese". Many war veterans committed suicide, some began to lead a secluded life and stopped communicating with anyone. Also in this period, a surge in violence was identified due to the dysfunctional state of families.
Trauma symptoms have also been reported in people not participating in hostilities, but surviving an accident or a situation of severe emotional distress. Revealed data by the end of the 70s led to the conclusion that the definition of PTSD includes a wide range of events that cause mental trauma.
Views
PTSD is a disorder psychologically classified into the following types:
- Anxious type. The disorder is manifested by attacks of severe anxiety, which causes severe nervous and physical stress. The patient becomes very irritable and suffers from sleep problems. Others may notice his frequent mood swings and quick temper. The patient can either withdraw into himself or actively communicate in order to distract himself from disturbing thoughts.
-
Asthenic type. The disorder is manifested by problems with sleep, eating, communicating with other people. The patient becomes very vulnerable and sensitive to criticism, often looks for a reason for accusations and is suspicious. At the same time, a person can be aware of his difficult condition and strive to receive appropriate help.

- Dysphoric type. The disease is characterized by a special degree of anger and irritability. A person is constantly gloomy and dissatisfied in appearance, suffers from feelings of envy and hatred for healthy people, including relatives and friends. The patient either does not consider himself in need of treatment, or requires special attention to himself and is very suspicious of procedures and therapy.
- Somatophoric type. The somatophoric group of diseases includes deviations of a psychogenic nature, in which the mental problems of patients are hidden behind somatic symptoms. In PTSD, these symptoms can include headache, heart problems, and dyspeptic disorders. Patients can also suffer from hypochondria, constantly look for symptoms of the most dangerous diseases and worry about the attacks of fear that arise.
- Hysterical type of PTSD manifests itself in the form of demonstrative behavior, the desire to attract attention to oneself, increased suggestibility and self-hypnosis.
- For the depressive type low mood and pessimism are characteristic.
Stages and degrees
PTSD is characterized by 3 stages of the course of the disorder: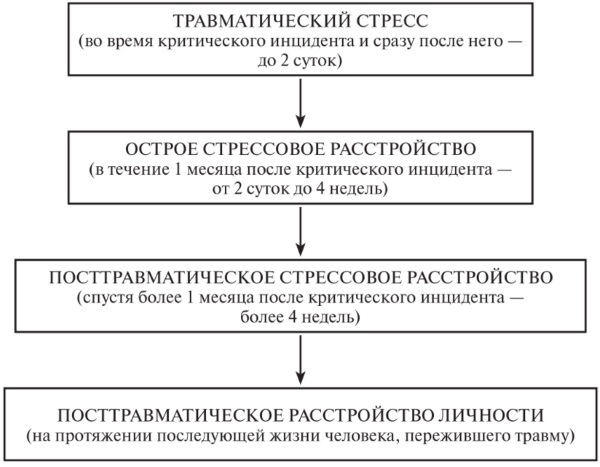
| Stage name | Description |
| Sharp | This phase occurs immediately after the traumatic event and is characterized by a state of shock. The phase lasts several days and is characterized by the following symptoms:
|
| Chronic | At this stage, the patient has a chronic overexcitation of the autonomic nervous system, because of which he begins to have problems with sleep, outbursts of anger, constant expectation of a threat from the outside. The person begins to react sharply to sudden movements and sounds. A distinctive symptom at this stage is the flashback effect - an involuntary and unpredictable revival of a traumatic experience through unusually vivid memories in the form of images, sounds, tastes or tactile sensations, lasting from a few seconds to several hours, during which it seems to a person that a terrible reality from the past invades the present a life. |
| Recovery stage | At this stage, the symptoms become less pronounced. If untreated, negative symptoms may develop:
|
Symptoms
PTSD is a serious condition in psychology that occurs as a result of a traumatic event.
PTSD symptoms:
- paranoia (unhealthy suspicion, a tendency to see the intrigues of enemies and complex conspiracy theories against oneself in random events);
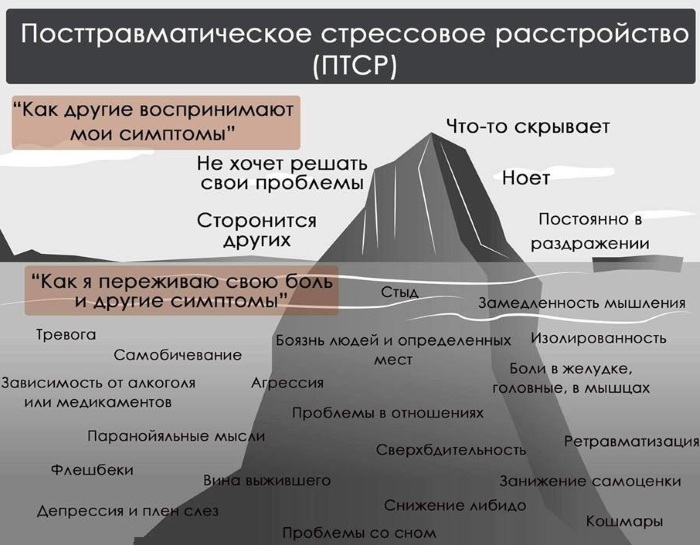
- high sensitivity to external influences (these can be sounds, touches, from which the patient involuntarily shudders and jumps up);
- psychopathological re-experiencing (a person has sudden, usually strong, repeated experiences of past experience or its elements);
- sleep problems (most often, after a negative experience, patients have nightmares that prevent them from recovering from sleep. Due to the seeming reality of what is happening, a person can, upon awakening, scream, jump up, attack a partner);
- dissociation (displacement of negative experiences can occur to varying degrees. The first degree is distinguished by the forgotten separate fragments of the event. In the second degree, the patient begins to perceive his life from the side of the observer, which allows him to distance himself from fear. In the third degree, subpersonalities may arise that are responsible for living experience and emotions. A person can behave in different ways, depending on which subpersonality dominates in him. The extreme degree of dissociation is dissociative identity disorder);
- amnesia (the patient loses memory for events of a mainly personal nature, which is a consequence of stress);
- derealization (problems with perception, when the patient perceives the world as unreal or distant);
- depersonalization (loss of one's own "I", loss of feeling of oneself as a person with mental properties);
- dissociative fugue (moving the patient to an unfamiliar place, where he completely forgets all information about himself, right down to the name);
- avoiding situations that can cause negative emotions;
- increased irritability, fits of anger;
- shame (the feeling of shame makes the victim think that she herself is to blame for the situation he has lived through, which only exacerbates her suffering. Shame often arises from negative situations in childhood, after general condemnation and as a result of the lack of any support after the incident);
- inability to experience positive emotions (such people seem "cold" and insensitive);
- perfectionism (the need to meet the standards and expectations of other people, as well as the desire to control the situation).
Reasons for the appearance
PTSD occurs after experiencing severe stress, an event that has had a profound effect on the human psyche. Such situations can be both objectively traumatic and subjectively negative, depending on the individual experience of the person.
The causes of PTSD can be:
- combat mental trauma;

Almost all combatants suffer from PTSD - sexual abuse;
- Act of terrorism;
- natural and man-made disasters;
- serious illness;
- accidents;
- poisoning;
- operations, surgery;
- the consequences of taking psychedelic substances;
- parting with loved ones;
- death of a loved one;
- any manifestations of violence;
- participation in torture and murder.
Diagnostics
PTSD is in psychology a severe mental condition of a person, which is diagnosed by a psychotherapist or psychiatrist. The diagnosis is made on the basis of the patient's complaints, the presence of severe psychological trauma in the recent past, and the results of special questionnaires.
Possible diagnostic tests for PTSD:
- Minnesota Multidimensional Personality Questionnaire or MMPI. This questionnaire studies personality traits, identifies the main pronounced character traits, human behavior. In its full version, the test consists of 566 questions and calculates clinical scales for various disorders.
- Scale for assessing the impact of a traumatic event - a clinical test technique aimed at identifying the symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder and assessing the degree of their severity. The scale consists of 22 items, which are distributed in three scales: "intrusion", "avoidance" and "excitability".
- Questionnaire for the severity of psychopathological symptoms. The survey is used in the clinic to identify dissociative symptoms and consists of 28 questions to assess dissociative experiences.
-
Beck Depression Scale. The technique was developed on the basis of clinical observations, which made it possible to identify a limited set of the most relevant and significant symptoms of depression and the most frequently presented complaints by patients.
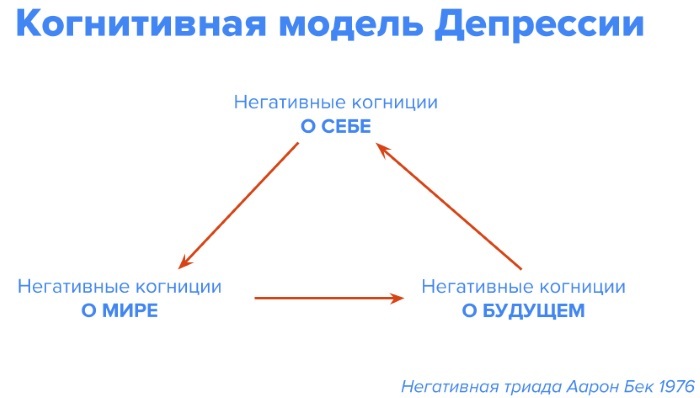
- GTR - traumatic stress questionnaire (I. Kotenev). The questionnaire is designed to study a person's condition after exposure to extreme factors, namely, being in extreme conditions and identifying the symptoms of PTSD in a patient.
- Spielberger-Hanin questionnaire for assessing the level of anxiety. This test examines the psychological phenomenon of anxiety and consists of 20 statements with which you can agree or disagree.
Correct diagnosis is a very important element, therefore, to accurately determine the diagnosis, you need to consult a specialist. It is important to correctly compose the techniques, choose one or several. Additional methods may be needed to determine PTSD, such as self-diagnosis tests.
Treatment methods
The main and most effective method for treating PTSD is psychotherapy. Her course may be accompanied by taking medications that are prescribed only by a specialist. Traditional methods are used only to relieve symptoms and are not a treatment to completely get rid of PTSD.
Medications
Taking medications is influenced by the individual characteristics of the patient and the severity of PTSD, so medications are prescribed exclusively by the attending physician.
The most commonly prescribed drugs during PTSD treatment are:
- Lithium preparations. The action of a psychotropic drug is aimed at reducing impulsivity and aggression, but the action begins manifest itself only on the 5th day of admission, therefore it is used as an additional tool in the course with others medicines.
-
Lamotrigine it is used as monotherapy or in combination with other drugs in the treatment of epileptic seizures. The drug is also used as maintenance therapy in patients with bipolar affective disorder to prevent episodes of mood disorders such as depression, mania, or hypomania. Since these symptoms are also manifested in patients with PTSD, the drug is often prescribed by the patient in the course of therapy.

- Normotimics (valproic acid, lithium carbonate, lithium oxybate). The drugs can prevent the development of depressive and manic symptoms, severe mood swings.
- Hypnotics (trypsidan, donormil, andante). The drugs are used for sleep disorders.
- Topamax (topiramate) is an anticonvulsant used to treat epilepsy and migraine. It is sometimes used to treat bipolar disorder and substance abuse that can develop in people with PTSD.
- Mirtazapine Is a drug against depression that has a combined effect on the central nervous system.
- Trazodone - the most common drug in combination with antidepressants, it not only treats insomnia, but also enhances the antidepressant effect.
- Risperidone - a highly effective atypical antipsychotic used in psychiatry and narcology. The drug helps to cope with the manic episodes that occur with PTSD.
Traditional methods
Recipes for folk remedies are aimed at calming, preventing nervousness and improving sleep:
- Collection for sedation. For cooking, you need 1 tsp. valerian, 1 tsp. St. John's wort, 1 tsp. chamomile, which must be mixed and brewed with a glass of boiling water. The resulting mixture should be left for 20 minutes, strain and drink 1 tablespoon each. each hour. A collection of about 2 weeks is accepted.
- A decoction of mint and lemon balm. Mint and lemon balm relieve stress and promote good sleep. 1 tbsp. l. a mixture of these two herbs must be poured with 200 ml of boiling water, allowed to cool and drink throughout the day in equal portions. The broth helps to calm down and normalize sleep.
-
Blooming Sally. Tincture of the herb relieves the patient from insomnia. To prepare the solution, it is necessary to brew 15 g of willow tea and leave it for at least 10 hours. The resulting drink must be filtered and taken before bedtime.

- Mint tea. For a soothing tea, brew 2 tbsp. l. mint and let it brew for about 2 tsp. Strain the tincture and take it one glass at a time.
Other methods
Psychotherapy is the most effective treatment for PTSD.
The main goals of therapy with the patient:
- the return of healthy self-esteem;
- building self-confidence;
- building relationships with other people;
- development of empathy;
- exit from the depressed state;
- getting rid of bad habits and addictions.
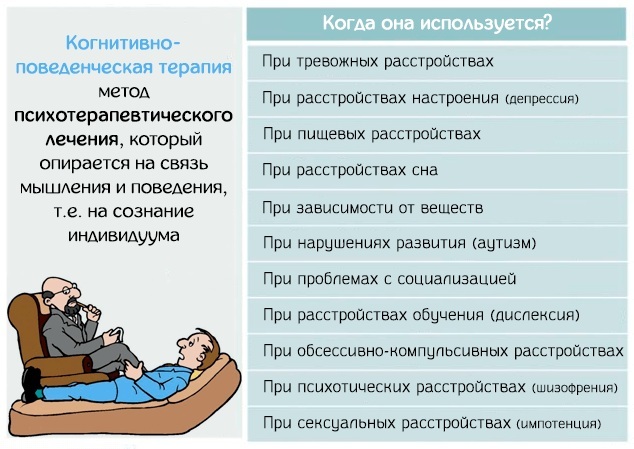
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is considered the most effective treatment for a wide range of disorders, including PTSD.
CBT is effective on its own or in combination with other therapies to relieve anxiety, depressive symptoms in patients with insomnia, and get rid of bad habits. The mechanism of work of therapy is to seek out and become aware of automatic thoughts that lead to negative reactions.
The therapy can consist of four stages:
- Identification stage. Here the patient learns to correctly find and analyze obsessive thoughts, learns techniques for filtering and ignoring them. For example, the doctor may suggest that the patient learn the “thought stopping” technique, which consists in stopping the memory of the trauma itself.
- Distance stage. At this stage, the patient learns to separate automatic thoughts from his personality.
- The stage of checking negative thoughts for validity. In the course of logical analysis, the truth of obsessions is tested.
-
The stage of replacing negative beliefs with adaptive ones. Here the patient's deep convictions are replaced by more adaptive ones. With the help of this technique, the patient tries to act in accordance with his new belief, without feeling doubts about its truth. Working with mental attitudes and actions leads to the fact that the PTSD sufferer develops self-confidence, stops feeling anxiety and begins to feel freer.
The following strategies can also be used in therapy:
- support for adaptive skills "I" (creating a positive attitude towards therapy);
- the formation of the perception of their symptoms as normal for living the consequences of trauma (the strategy allows you to prevent further traumatization of the patient by the fact of the existence of disorders);
- reduced avoidance (because the client's tendency to avoid everything related to mental trauma prevents him from reworking her experience);
- changing the attribution of meaning (the goal of this strategy is to change the meaning that the client attaches to the trauma suffered, and thus create a sense of “trauma control” in the client).
Possible complications
PTSD is a serious disorder in psychology that interferes with the normal functioning of a person in society. Left untreated, PTSD can lead to chronic illness and incurable disabilities.
In PTSD, the body is in a state of chronically increased stress load, which corresponds to a constantly increased concentration of stress hormones (adrenaline and cortisol) and often leads to high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol and blood glucose levels, and can cause problems with sleep.
Also, the disorder can be one of the risk factors for the occurrence of cardiac diseases, diabetes.
Negative consequences also apply to social life: a person with post-traumatic syndrome moves away from society, falls out of reality. He believes that no one can understand him. The patient perceives the world around him as a threat. This can lead to comorbid disorders, dissociative disorders and other mental illnesses.
PTSD is a condition that results from traumatic situations. If symptoms of the disease occur, it is necessary to contact an experienced psychologist as soon as possible, who will help to rethink the events and survive the trauma. The future life of a person who has experienced the negative consequences of PTSD depends on the timeliness of treatment.
Video about PTSD
About PTSD: