OCD, or obsessive-compulsive disorder, is a mental illness. Against the background of developing pathology, a person loses the ability to suppress stress and anxiety.
He has negative thoughts that the patient cannot get rid of on his own. To alleviate the general condition of a person, sessions with a psychotherapist and long-term treatment with antidepressants are required.
Record content:
- 1 What is OCD (Obsessive Compulsive Syndrome)?
-
2 OCD causes
- 2.1 Inheritance
- 2.2 Biological causes
- 2.3 Due to personality disorder
- 2.4 Because of study
- 2.5 Social reasons
- 3 Classification
-
4 How to recognize obsessive-compulsive disorder?
- 4.1 Fear of germs or dirt
- 4.2 Unhealthy cleaning passion
- 4.3 The need to keep things in order (literally)
- 4.4 Excessive self-doubt
- 4.5 The need to constantly double-check everything
- 4.6 Obsessive counting
- 4.7 Building life according to clear rituals
- 4.8 Hoarding things
- 4.9 Obsession with relationships
- 5 Normal and pathological thoughts (OCD)
- 6 Diagnostics
-
7 Treating OCD. Types and methods
- 7.1 Psychological treatment
- 7.2 Drug treatment
-
8 Diet for obsessive-compulsive disorder
- 8.1 Diet for the nervous system
- 8.2 Diet for depression
- 9 Consequences of obsessive-compulsive disorder, prognosis
- 10 OCD video
What is OCD (Obsessive Compulsive Syndrome)?
Obsessive-compulsive mental disorder is characterized by the formation of obsessions in a person, which are called obsessions. They appear uncontrollably, often repeated. These thoughts in most cases are unpleasant for the patient, because they are directed towards himself, and not those around him.
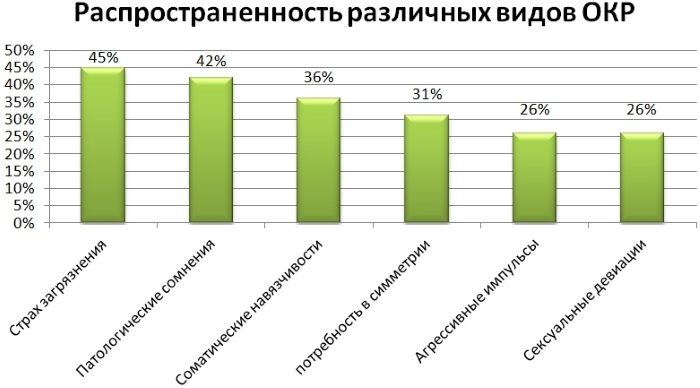
Examples of obsessions include:
- infection with any disease, injury;
- considering the possibility of the development of an accident;
- thoughts of aggressive actions;
- ideas of a religious nature;
- obsessive collecting;
- achieving perfect symmetry or accuracy of their actions;
- thoughts of sexual attraction.
Compulsions - tedious cyclical actions - are often present in the behavior of the patient with OCD. They cannot be stopped on their own, they are often performed unconsciously.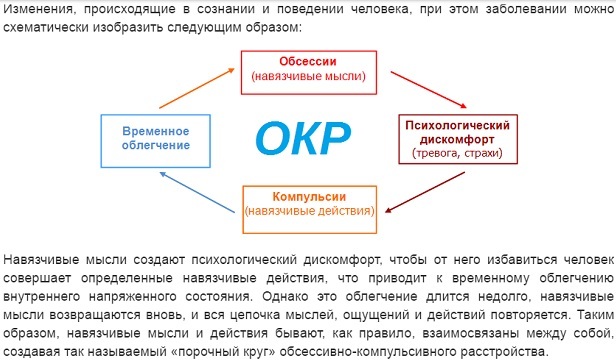
Compulsions form daily rituals, manifested in the form of:
- constant cleaning;
- washing;
- calculations of surrounding things;
- slow, measured actions;
- checks: whether the electrical appliances are turned off, whether the shelves are dust-free;
- creating a symmetrical arrangement of things.
Thanks to these cyclical actions, a person reduces anxiety and the degree of manifestation of obsessions. As a result, he partially copes with the expression of feelings, removes unjustified fear.
The patient with OCD does not have the ability to influence in any way his own feeling and the forming worldview. Constant annoying thoughts make a person feel fear, oppression, anxiety, because his the brain may decide that at the moment an insignificant thing is a vital need. For example, a person coughing nearby can infect a fatal disease.
As a result of the appearance of an obsessive thought, a compulsion is formed. Therefore, after each forced touch of other people, the patient with OCD will use an alcohol antiseptic. This ritual will help a person feel safe for a short time.
OCD causes
OCD is a mental illness that can be triggered by stressful situations or prolonged depression.
The main risk factors for this syndrome are:
- hereditary predisposition;
- congenital anomalies such as developmental disorders of the nervous system;
- getting a birth injury;
- setting high demands on yourself and others, manic perfectionism;

- strict upbringing in a family that requires adherence to certain standards of behavior.
Inheritance
People who have close relatives with manifestations of obsessive-compulsive syndrome are most vulnerable to developing a mental disorder. Only the nature of the disease is transmitted genetically, but not the specific signs of pathology.
If the grandmother had an obsession with perfecting everything, then her grandson may have a fear of injury. Compulsions in both people can also be different.
Biological causes
In laboratory tests, you can see that there is a reduced level of the neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine in the blood of an OCD patient. The latter are responsible for the emotional background of a person. With their lack, the development of depression, apathy is observed, and stress resistance decreases.
People who have a birth injury or have congenital neuroanatomical features may be prone to OCD. These pathologies also inhibit the production of necessary neurotransmitters.
Due to personality disorder
A mentally and emotionally unstable person is more easily exposed to stress and difficult experiences. Against this background, not only complexes can form, but also obsessive-compulsive syndrome.
Your risk of developing OCD is increased when you have the following signs of a personality disorder:
- tendency to obey;
- increased morality;
- anxiety due to children's fears, loneliness;
- perfectionism;

- rejection of change;
- nervous exhaustion against the background of workaholism;
- fear of risk;
- ambivalence towards something, or ambivalence;
- increased emotional sensitivity.
Because of study
During childhood and adolescence, a child can be exposed to a lot of stress during lessons or exams. High psychological stress can trigger the development of obsessive-compulsive disorder as a result actions of the following factors:
- there is a strict religious upbringing, in which it is necessary to monitor your actions, because they may be considered vicious or bad;
- a limited learning format contributes to the formation of perfectionism, often suppresses the child with increased responsibility;
- the teacher or respected person in the educational institution had pronounced signs of obsessive-compulsive disorder;
- children were taught a strict moral education.
As a result, the child tries to completely control his thoughts and actions. Children overestimate their responsibilities and the severity of the consequences. When they make mistakes, they are exposed to severe stress, guilt and anxiety. In the future, the child may become more demanding of himself and those around him, because he does not want to experience negative emotions again.
Social reasons
In particular cases, the formation of OCD occurs in people who find it difficult to adapt to life in society. An example is the oppression of one person in a group for lack of skills, physical features, or personality traits.
The stress experienced has a negative impact on the personality and behavior of the individual. In an attempt to adapt to life in a group, he sets himself high demands, he develops perfectionism, compulsions are formed, which are necessary to relieve overstrain.
Classification
OCD is a mental illness that is classified according to the duration and characteristics of the pathological process.
| Classification | Disease types |
| According to the peculiarities of the flow (according to Shmaonova, Snezhnevsky) |
|
| According to ICD-10 |
|
| The nature |
|
How to recognize obsessive-compulsive disorder?
Despite the different manifestations of obsessions and compulsions, OCD follows the same type of scenarios. Thanks to the symptoms that appear, specialists can diagnose a mental disorder, determine its severity and prescribe the correct treatment regimen.
Fear of germs or dirt
The uncontrolled pursuit of perfect cleanliness is most common among people with OCD. Constant cleaning and the use of antiseptics suggests that a person is afraid of infection with pathogenic microorganisms. Living areas are illuminated by an ultraviolet lamp and can rival operating theaters in terms of sterility.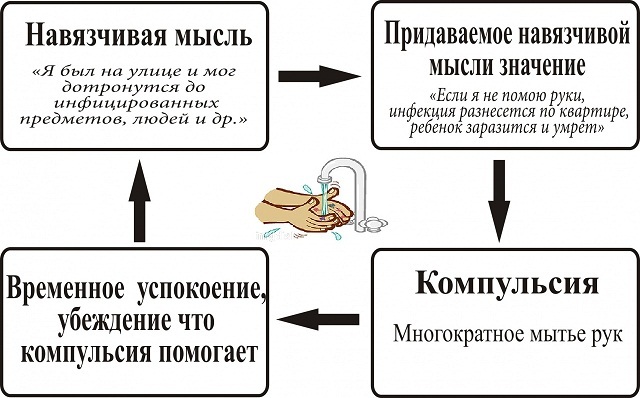
A person with this type of OCD washes their hands every time they touch the phone or doorknob. People with a fear of germs are uncomfortable with touching others, and they try to avoid contact with objects in public places.
Unhealthy cleaning passion
In addition to people with OCD who fear infection with disease-causing bacteria, there is a mental disorder with a manic desire for cleanliness.
In this case, a person is not afraid to get his hands dirty in the dirt, he cleans at home and at the workplace 2-3 times a day, which makes the room look like a museum. But, despite the achieved result, he will be eaten up by the thought that somewhere there is pollution. A person is forced to fight the urge to start spring cleaning every day.
The need to keep things in order (literally)
Lack of perfectionism in particular causes hysteria, anxiety, or severe aggression in people with OCD. They are convinced that an imperfect result has no right to exist.
A person experiences stress and begins to get nervous if the item is not placed as expected, for example:
- hung the shirt on a chair, not on a hanger in the closet;
- did not put your shoes in the hallway;
- placed a vase of flowers on the edge of the table.
Excessive self-doubt
Complexity with OCD takes the form of constant worries about how you look or what others will think.
Usually, a person with a mental disorder begins to engage in self-criticism:
- wonders if his clothes make him look fat;
- worries about smeared mascara;
- whether the work was done correctly;
- he is consumed by guilt and shame, the constant feeling that he has made a mistake.
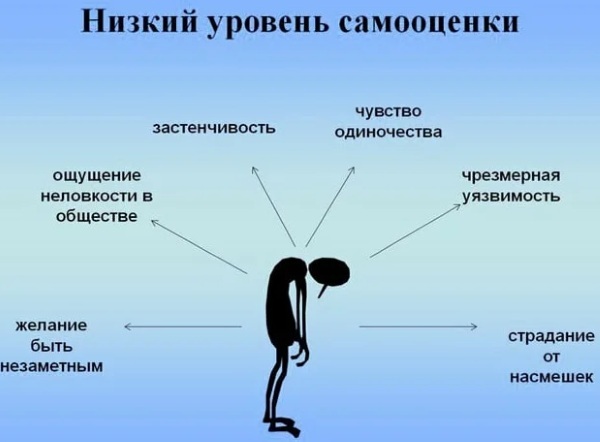
Constant reflections and negative thoughts cause nervous exhaustion. A person with OCD needs continuous reward for their own actions and good appreciation from others.
The need to constantly double-check everything
A person with OCD has the following obsessions:
- electrical appliances are not turned off at home;
- the candle is not extinguished;
- whether the work was done in the correct order;
- the front door is not locked;
- is everything written in the essay;
- whether the lights are off in all rooms.
As a result, people with mental disorders are forced to return home 2-3 times after going outside, re-read documents and count money.
Obsessive counting
To relieve stress or relieve tension, some people with OCD have an unusual compulsion to count things. They note the number of red cars passing by, the total amount of peas in the brought soup, or the black tiles on the sidewalk in front of the cafe.
Depending on the severity of the mental disorder, the patient may depend on the counting results. For example, 13 trees in the garden portend trouble.
In special cases, a person begins to perform any actions. If his favorite number is 9, then he can release 1 in 10 birds in a cage or throw "extra" pieces of carrots out of the salad.
Building life according to clear rituals
Man depends on stability. With OCD, some people develop a clear algorithm for themselves that they consider vital.
They can eat food in a dish strictly in alphabetical order, cook the same meal for lunch, commute only one route to work, despite traffic jams or late arrivals. Any changes in the usual rhythm of life cause panic and confidence that the day will be terrible.
Hoarding things
Normally, a person gets rid of old and unsuitable things for further exploitation, be it clothes, appliances or a piece of furniture. People with OCD mistakenly assume that such objects can still be useful in everyday life and leave them at home.
Over time, debris builds up, turning the apartment into a dusty, filled warehouse. Despite the physical discomfort, the person with the mental disorder feels calm and safe. Familiar things surround him.
Obsession with relationships
If a person is strongly attached to the people around him, any conflict becomes a disaster for him. Problems with coworkers, bosses, a fight with a friend, or a breakup in a love relationship can lead to anxiety, intense guilt, and depression that last for weeks or years. Stress contributes to the formation of obsessions - obsessive thoughts that by their actions a person can offend loved ones.
Normal and pathological thoughts (OCD)
Obsessions occur in 9 out of 10 people, so some people mistakenly assume they have a mental disorder. The main difference between normal and pathological ideas is the importance a person places on them.
Against the backdrop of OCD, an obsessive thought can arise that repeats cyclically. A person is not able to independently suppress the desire arising from this idea or throw it out of his head. Obsession is perceived by the brain as a threat that causes stress and anxiety.
To relieve stress, the person takes action that is soothing and safer. They are compulsions.
If the fear imposed by negative thoughts does not come true, then people with OCD associate this fact not with their innocence or coincidence, but with the action of the rituals performed. While compulsions can help relieve stress, they are a key factor in the development of a mental disorder.
Diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis, the therapist should observe signs of obsessive-compulsive disorder for about 2 weeks.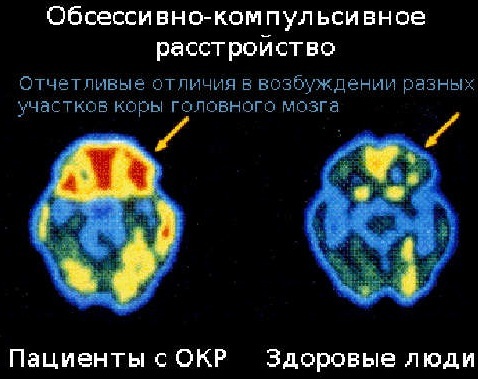
The specialist in his work is guided by the following criteria indicating the presence of pathology:
- a person perceives unpleasant ideas and actions as his own, and not imposed by other people;
- obsessions and compulsions limit social life, reduce performance and dull the patient's overall productivity;
- thoughts are realistic, are unpleasant to a person;
- performing the ritual helps to reduce stress, reduce tension and anxiety;
- a person is not able to suppress unpleasant thoughts on his own. attempts to be distracted by another activity will be unsuccessful.
When confirming the diagnosis of OCD, the therapist excludes the possibility of a person developing schizophrenia, depression, the presence of phobias, or a state of passion. This is necessary because these diseases have similar symptoms.
Treating OCD. Types and methods
OCD is a mental illness that requires medication and psychotherapy. Additionally, social rehabilitation is carried out. Treatment with drugs is focused on suppressing the symptoms of anxiety, relieving stress and normalizing the psychoemotional state.
Medications help the patient to form a new model of behavior, suppress obsessive thoughts and manifestations of compulsions.
Social rehabilitation allows a person to restore their ability to work, develop professional skills and establish communication with people around them. Treatment for OCD is done on an outpatient basis. With a severe degree of the disease, therapy in stationary conditions is possible.
Psychological treatment
The main method of psychological treatment is EPR - exposure and prevention of reactions. A person with obsessive-compulsive disorder is placed in a state of anxiety, artificially increasing the likelihood of intrusive thoughts.
During the session, the patient with OCD is convinced that his negative judgments are wrong. When conducting psychotherapy, it is important that the person does not use compulsions to normalize the emotional state. This is necessary to relieve him of discomfort and anxiety.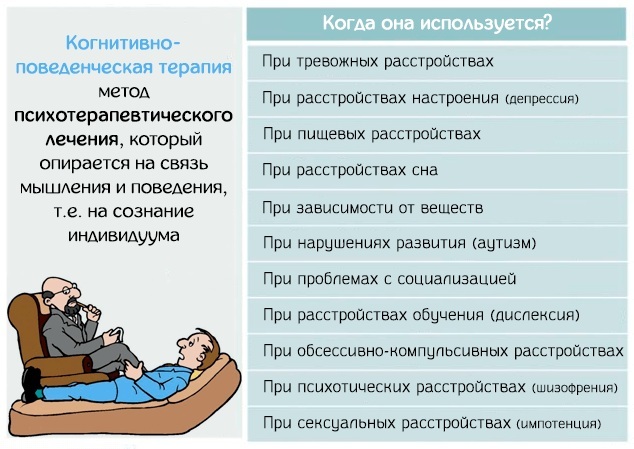
Psychotherapists often combine EPR with cognitive behavioral therapy. In this case, the patient is convinced that the importance of obsessions, the responsibility assigned to him, and perfectionism are exaggerated by him. 2 principles of treatment are used.
| Cognitive | Behavioral |
The specialist encourages the patient to acquire the following types of skills:
|
This technique allows the patient to more easily adapt to stressful situations and discomfort. The training is planned, the acquired skills are consolidated. For example, after shaking hands and hugging, it is not necessary to immediately wash your hands or wipe your palms with an antiseptic. A psychotherapeutic session can be either individual or group. In the first case, the specialist conducts classes at home so that the patient is comfortable and calm. |
Drug treatment
Drug therapy can improve the condition of the patient with OCD by 20-40%, depending on the severity of symptoms and psychological trauma.
In most cases, the therapist prescribes the following types of drugs:
- Tricyclic antidepressants: Mirtazapine, Clomipramine, Duloxetine, Amitriptyline.
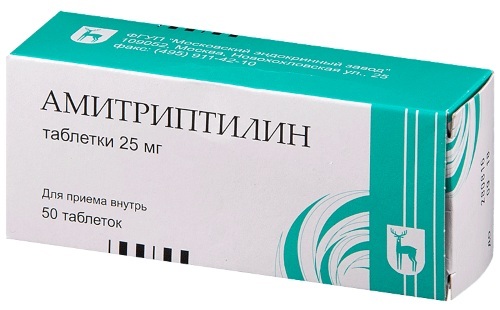
- Antipsychotics: Chlorprothixene, Sulpiride, Thiodazine.
- Tranquilizers: Clonazepam, Diazepam, Alprazolam, Tofisopam.
- Excipients: carbamazepine, lamotrigine, lithium carbonate, topiramate, valproic acid.
Diet for obsessive-compulsive disorder
To improve the effectiveness of medical and psychological therapies, dietary supplementation is used to treat OCD. A balanced diet provides the human body with the necessary vitamins, amino acids and mineral components, from which a number of neurotransmitters are formed. The latter have a positive effect on the psychoemotional state of the patient and increase his stress resistance.
OCD can be accompanied by neuroses. In this case, the treatment of mental illness is supplemented by a diet to restore the nervous system. When the disorder is complicated by prolonged depression, a special diet is prescribed, focused on stabilizing the emotional background.
Diet for the nervous system
To restore the normal functioning of the central and peripheral nervous system, it is necessary to reduce the consumption of carbohydrates, fats and table salt.
If you follow a diet, it is forbidden to include in the diet foods that cause neuronal excitation:
- caffeine;
- alcohol;
- fried food;
- hot spices.
To improve the psycho-emotional state, it is recommended to take foods saturated with phosphorus salts, such as milk, beans, animal liver. The total calorie content of the diet should be about 2200-2400 kcal.
An example diet menu for restoring the nervous system:
- Breakfast. Porridge with milk, herbal decoction, 2 soft-boiled eggs.
- Lunch. Uncooked biscuits, rosehip broth.
- Dinner. Potato soup with pieces of boiled meat, berry compote.
- Afternoon snack. Rosehip broth or cherry juice.
- Dinner. Pudding, fish cooked in sour cream sauce with baked potatoes. It is recommended that you drink a glass of warm milk before going to bed.
Up to 6 g of salt, 70 g of fat, 80 g of protein and 350 g of carbohydrates are allowed per day.
Diet for depression
If you suspect a depressive state, it is recommended to adhere to the following menu:
- Breakfast. You can make a vegetable or fruit salad with nuts. After 15 minutes, it is recommended to drink green tea with 50 g of dark chocolate.
- Lunch break. A stew garnished with red vegetables such as tomatoes, bell peppers, radishes.
- Afternoon snack. A small banana with assorted fruits.
- Dinner. 2-3 hours before going to bed, you need to drink tea based on chamomile, mint or lemon balm infusion, which has a calming effect.
During the period of depression in the body, there is a lack of neurotransmitters responsible for normalizing mood and vigor: serotonin, acetylcholinic acid, dopamine.

Therefore, it is necessary to supplement the diet with foods that stimulate the production of these active substances:
- fruits and vegetables: citrus fruits, tomatoes, plums, salads and various types of cabbage, bananas, avocados;
- nuts and seeds: sesame seeds, cocoa beans, macadamia, almonds;
- animal products: low-fat fish, any poultry meat, ricotta cheese, cottage cheese, beef liver.
It is recommended to adhere to fractional meals, eating food 4-5 times a day in small portions. The daily calorie content of the diet should not be lower than 1600 kcal.
Consequences of obsessive-compulsive disorder, prognosis
OCD is a mental illness with the following negative consequences:
- reduces performance;
- limits social life;
- causes isolation, social maladjustment;
- communication difficulties;
- limits the ability to acquire professional skills;
- stimulates the formation of complexes, feelings of guilt, shame and oppression, insecurity;
- causes apathy, depression.
Full recovery from OCD is not possible. The success of medication and psychotherapy depends on the timing of the visit to the doctor: the sooner the patient receives help, the faster he will be able to suppress obsessive thoughts and actions.
With the correct diagnosis at an early stage of disease progression, improvement occurs within 6-12 months. In severe mental disorders, it takes an average of 2 to 5 years to show positive results of therapy.
OCD is a mental illness that affects a person's social life and ability to work. The frustration can manifest itself as manic perfectionism, a fear of germs, or an uncontrollable urge to start cleaning.
As a result of obsessive thoughts about purity, ideal or pathogenic bacteria, a person loses the ability to withstand stress, easily succumbs to anxiety. To relieve his condition, he is forced to use daily rituals such as counting things, washing or washing his hands after each touch of others.
OCD video
What is obsessive-compulsive disorder:



