Content
- What is hemoglobin responsible for in the body?
- Norms of hemoglobin in children by age from birth in the table
- Hemoglobin in premature babies
- How is the level of hemoglobin in the blood determined?
- Reasons for deviation of indicators, symptoms
- Enhancement
- Downgrade
- Why deviations are dangerous
- What to do with decreased hemoglobin?
- Drugs
- Food and diet
- How to lower the level when increasing?
- Video about hemoglobin is normal
Important laboratory diagnostic the indicator is the level of hemoglobin - a blood element that performs several basic physiological functions. The norm of iron-containing protein in a child differs significantly from the reference values for adults.
What is hemoglobin responsible for in the body?
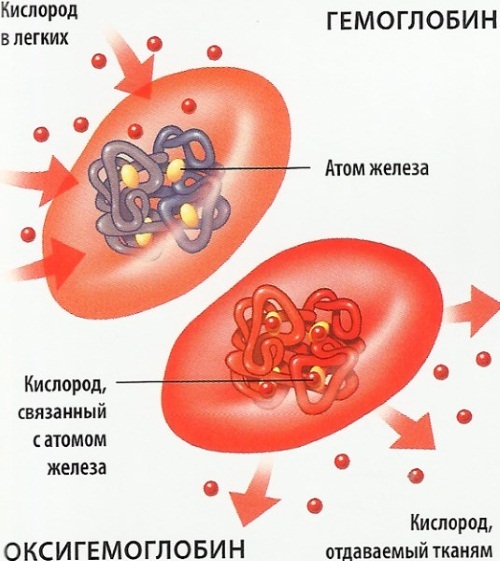
The substance has a complex molecular structure and a large mass in comparison with other biochemical elements of the blood. The key function of a protein compound is gas exchange. Hemoglobin transports oxygen atoms to the tissues of organs, removing from them by-products of respiratory activity.
The main evacuated substance is carbon dioxide. The oxygen delivered to the cells of the organs is necessary for the stable course of metabolic processes and recovery reactions. Deficiency of hemoglobin is one of the causes of hypoxic conditions.
The iron-containing protein in the blood is not found in free form. It is part of the red blood cells - erythrocytes. Hemoglobin consists of a specific protein substance called chromoprotein. The biochemical compound additionally performs a buffer function and regulates the blood viscosity index.
The norm of hemoglobin in a child is variable.
The content of gas exchange protein in plasma blood fraction depends on:
- age;
- diet;
- immune status;
- quantitative and functional characteristics of erythrocytes;
- genetic characteristics;
- the work of the red bone marrow.
Hemoglobin reduces the level of oncotic compression of plasma, which prevents disruption of fluid balance in tissues. Chromoprotein has a moderate ability to bind toxic elements and foreign particles.
It is involved in detoxifying the body. Saturation of cells with sufficient oxygen is especially important for children. The constant growth of cytological units and proliferative processes require more energy resources than an adult organism under similar biological conditions.
Norms of hemoglobin in children by age from birth in the table
Highest level of oxygen-carrying protein in newborns. In children, this laboratory value varies widely and is highly dependent on age.
In the first year of a child's life, there is a gradual decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood. The indicator is distinguished by a high dynamics of changes depending on age and numerous influencing factors.
Small deviations from the reference values established by the world health organization are allowed. The high concentration of hemoglobin in the blood of a newborn is due to the inoperability of the lungs during intrauterine development.
The embryo receives oxygen supply through the umbilical vein from the mother's body. For the full course of such a physiological process, an increased number of erythrocyte cells and the chromoprotein protein itself are required.
After birth and the beginning of spontaneous pulmonary respiration, a regular daily decrease in hemoglobin concentration is observed. The reference values of the chromoprotein protein content established by WHO in children under 5 years of age are presented in the table.
| Child's age | Hemoglobin level, g / l |
| The first day of life | 180-240 |
| 5th day | 170-200 |
| 1 month | 140-160 |
| 6 months | 110-160 |
| 1 year | 110-130 |
| 1-2 years | 110-130 |
| 2-5 years | 130-140 |
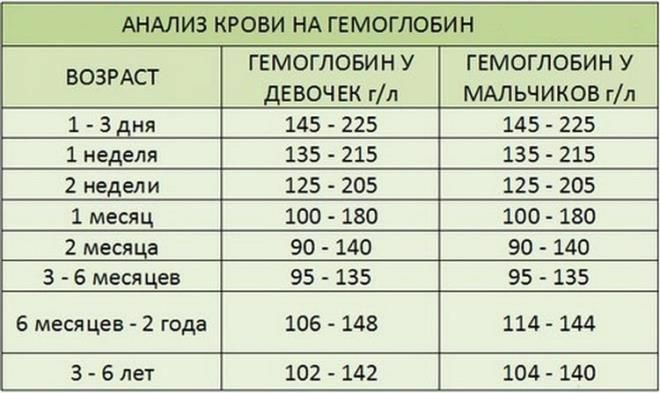
The given laboratory parameters are established for normally full-term, on-term and completely healthy children. The results of the analysis are influenced by the physiological state of the child at the time of taking a control blood sample.
Hemoglobin in premature babies
In such infants, the level of the oxygen-carrying protein element in the blood is lower for the first 30 days of life than in those born naturally at term. The lower limit of the plasma chromoprotein content for premature infants is 160 g / l.
After a month of spontaneous pulmonary respiration and the formation of its own gas exchange mechanism, the hemoglobin concentration decreases to 100-120 g / l. In children born prematurely, anemic conditions are more often observed, which is due to insufficient development of internal organs.
In premature infants, the plasma fraction of blood contains mainly fetal hemoglobin - a uniform component of the hematological fluid, which is formed in the embryonic period.
Such a protein runs in the blood for a limited time and is necessary for the full development of the fetus. In laboratory practice, fetal hemoglobin is abbreviated as hbf. It matures in the embryonic body at 9-13 weeks of gestation.
With premature birth, fetal hemoglobin does not have time to transform into a full-fledged functional blood unit. The chromoprotein substance remains in the infant's body in an embryonic state.
After the onset of spontaneous pulmonary respiration, gas exchange processes and intracellular redox reactions, such a protein is not able to perform its own biological destination.
Early or late anemia is recorded in premature infants. The first option is considered benign and has a favorable prognosis. Late anemia is malignant and is finally formed by the 3rd month of life.
Such a pathological disorder requires the intervention of a neonatologist and pediatrician. It is necessary to develop effective therapeutic tactics to eliminate hypoxia of internal organs and restore the normal level of complete gas exchange protein.
How is the level of hemoglobin in the blood determined?
Use standard laboratory diagnostic methods. To determine the concentration of chromoprotein protein in the plasma fraction of blood, a clinical analysis of the collected sample of biological material is prescribed.
The norm of hemoglobin in a child is subject to fluctuations under the influence of numerous influencing factors.
Simultaneously measure:
- the number of red blood cells;
- their relationship with the plasma component;
- color indicator;
- leukocyte formula;
- platelet count.
The analysis is taken on an empty stomach in the morning - usually 8.00-11.00. Before the procedure, you must not give the child medicine, feed him fried, sweet and flour foods. The stability of physiological parameters is important. To ensure it, the child must be in a calm state.
Reasons for deviation of indicators, symptoms
The concentration of chromoprotein protein in the blood of a newborn depends on the course of pregnancy, the presence or absence of intrauterine disorders. One month after the stabilization of physiological parameters, the hemoglobin level is brought to a conventional common denominator, adjusted for individual factors.
The reasons for the decreased and the overestimated relative to the established reference values of the oxygen-carrying protein compound differ. Such conditions have their own etiology, clinical symptoms and noticeable signs. Sharp fluctuations in the level of hemoglobin in the child's blood signal latent pathologies.
Enhancement
A common cause of excessive concentration of erythrocyte bodies carrying chromoprotein protein is dehydration (dehydration) of the body. The condition accompanies acute gastrointestinal infections, type 2 diabetes mellitus, ARVI.
Respiratory pathogens of a bacterial or viral nature that cause a decrease in the laboratory indicator provoke a febrile syndrome, which is noticeable without examining the child.
Common causes of low hemoglobin levels in children 2-5 years old:
- Thickening of the blood. Changes in the rheological properties of hematological fluid provoke extensive burn injuries, severe endocrine diseases, and digestive disorders.
- Chronic respiratory dysfunction. Such conditions are associated with respiratory failure, which the body tries to compensate for by increasing the number of red blood cells with hemoglobin contained in such cells.
- Congenital heart defects. In violation of cardiac activity, a similar effect is observed. The body tries to compensate for hemodynamic insufficiency by increasing erythrocyte synthesis.
- Polycythemia. Chronic hemoblastosis disorder is characterized by unlimited proliferation of cells involved in the process of myelopoiesis of the processes. Systemic disease is manifested by pronounced cerebral symptoms - a feeling of heaviness in the head, tinnitus, periodic pain syndromes. The pathogenesis of polycythemia is associated with the uncontrolled production of red blood cells in the bone marrow substance.
- Nephrological diseases. In renal failure, there is an increased secretion of erythropoietin, a hormone responsible for the control and regulation of the process of erythropoiesis. The disorder leads to excess production of red blood cells and an increase in hemoglobin in the blood.
From non-hazardous to health factors of increasing the level of iron-containing protein, intense physical activity and living in high mountains in conditions of rarefied atmospheric air are distinguished.
The hemoglobin norm temporarily deviates upward due to the child's stay in a warm room with low humidity. Excessive protein concentration, not associated with systemic disorders or severe pathological processes, usually does not have noticeable symptoms in children.
The condition is determined exclusively by laboratory methods. In some children, an increased concentration of hemoglobin in the blood plasma is expressed by lethargy, lethargy, and suppression of appetite.
With a strong increase in the protein compound, an increase in blood pressure, spontaneous and unreasonable occurrence of subcutaneous hematomas, and periodic dizziness are observed. Cephalgic paroxysms, malaise, sleep disorders are possible.
Downgrade
Deficiency of iron leads to a decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood plasma. This condition is typical for newborns. In infants, the deficiency of this trace element is due to the mother's iron deficiency anemia during the gestational period.
Children over 6 months. characterized by a low level of hemoglobin due to an unbalanced diet. Breastfeeding should be combined with the supply of special mixtures saturated with trace elements, minerals, vitamin complexes.
Among the common reasons for a decrease in the concentration of gas transport protein in the blood in children 2-5 years old are noted:
- massive blood loss after surgery or chronic nasal effusion of hematological fluid;
- iron deficiency anemia provoked by a lack of folic acid and cyanocobalamin;
- accelerated destruction of red blood cells with the release of excess volume of indirect bilirubin;
- chronic pathologies of hemostasis;
- digestive disorders;
- infectious and inflammatory processes;
- the consequences of drug therapy with taking medications that affect the biochemical composition of the blood;
- autoimmune diseases;
- oncological hyperplasia.
In newborns, a reduced level of chromoprotein protein is often associated with hemolytic anemia, which develops due to the Rh-conflict between the mother and the child during the gestational period.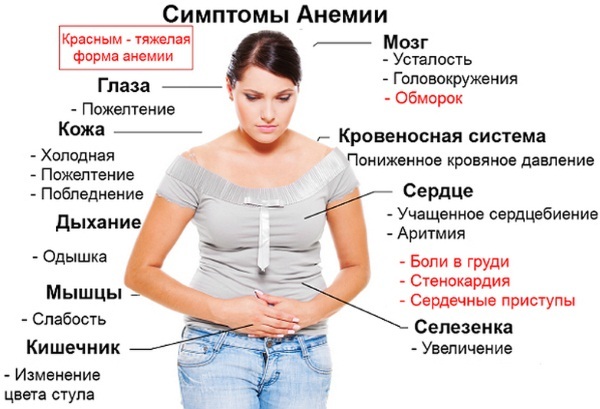
This condition is caused by parasitic invasions, prematurity due to incomplete development of internal organs and the mechanism of hematopoiesis.
Typical symptoms of decreased hemoglobin:
- pallor of the skin;
- weakness;
- vertigo syndrome;
- sleep function disorder.
The pathological condition is manifested by rapid fatigue, irritability and tearfulness of the child, tachycardic symptoms. Periodic increases in body temperature to subfebrile values are possible.
Why deviations are dangerous
The anemic state is fraught with oxygen starvation of vital organs, the development of hemolytic hypoxia, and suppression of the immune defense.
In children with a low hemoglobin content in blood plasma, the following are more common:
- colds;
- seasonal respiratory virus infections;
- chicken pox;
- cardiac dysfunction;
- underweight.
There is a risk of mental retardation in chronic iron deficiency anemia. Reduced resistance to pathogenic agents is dangerous by inflammatory processes with impaired tissue trophism and dysfunctions of the kidneys, liver, and lungs.
Oxygen starvation leads to a slowdown in physical development in childhood and adolescence. With an increased content of chromoprotein protein, the rheological properties of the blood are disturbed.
The norm of hemoglobin in a child is an important biochemical indicator that affects the development and functioning of a growing organism.
Thickening of hematological fluid due to increased concentration of iron-containing protein:
- hinders cardiac activity;
- worsens cerebral hemodynamics;
- provokes blood clots;
- increases the size of the spleen;
- affects the renal mechanism.
An excessive level of hemoglobin in the blood causes hemosiderosis, a pigmentary dystrophy associated with excessive accumulation of iron in tissue structures.
The trace element is deposited in:
- bone marrow;
- liver;
- renal tubules;
- pulmonary apparatus;
- spleen;
- salivary and sweaty glands.
Violation of the metabolism of the iron-containing pigment hemosiderin leads to inhibition of the functions of the above organs and the development of severe systemic pathological processes.
What to do with decreased hemoglobin?
The deviation of the physiological indicator is diagnosed by the pediatrician during the initial examination. To clarify the clinical picture, he directs the child for a biochemical blood test, apparatus examinations. For the selection of adequate and effective therapy, it is necessary to establish the cause of the deviation of hemoglobin from the norm. Comprehensive treatment includes taking iron-containing drugs, changing the diet.
Drugs
Children 2-5 years old are prescribed syrups saturated with trace elements, mineral and vitamin compounds, amino acids. In case of impaired iron absorption function, parenteral administration is recommended - bypassing the gastrointestinal tract.
Such methods of drug delivery include injection and inhalation. With iron deficiency anemia against the background of impaired absorption, intramuscular solutions are used.
Such therapy is considered intensive and is used when the hemoglobin level is critically reduced. After the end of the injection treatment, the patient is transferred to oral medications, provided that iron is normally absorbed.
The duration of corrective therapy is approximately 45-60 days.
Children 2-5 years old are prescribed the following medications:
- Maltofer. The liquid dosage form intended for drinking use contains iron in the form of polymaltose hydroxide.
- Ferronate. The syrup enhances the synthesis of iron and compensates for the deficiency of this trace element.
- Aktiferrin. Antianemic agent in the form of drops for oral administration. The medicine can be added to any drinking liquid - juice, compote, fruit water.
- Ferrum Lek. 5 ml of sweet syrup for children contains 50 mg of iron hydroxide.

The pediatrician calculates the duration of taking antianemic drugs individually, depending on the severity of the child's condition and the susceptibility of the drug.
With a laboratory value reduced in an infant to 85 g / l, a critical disorder is diagnosed, requiring immediate hemosorption using compatible donor blood.
Children over 12 months. transfusion is performed when the level of iron-containing protein drops to a critical level of 70 g / l. Hemolytic anemia, depending on the provoking factor, requires the use of glucocorticosteroid drugs, immunosuppressants.
Food and diet
The norm of hemoglobin in a child 2-5 years old with a small deviation not associated with systemic pathologies is easily restored by correcting the diet.
The diet includes:
- boiled low-fat meat;
- fish fillet;
- vegetable purees;
- legumes;
- red fruits;
- dried apricots;
- prunes;
- unsalted cottage cheese.
Rosehip decoction, dried fruit compotes improve the absorption of iron. Apples, plums, pears are saturated with a trace element.
With severe iron deficiency anemia, a special corrective diet is used, which contains the following foods:
- peanut;
- buckwheat porridge;
- green pea;
- corn grains;
- Pine nuts;
- oats;
- pork, beef or chicken liver;
- spinach.

Of the meat products, the most iron is found in beef liver and tongue. Such nutrients are more easily absorbed by the child's body than herbal counterparts. A portion of buckwheat porridge compensates for the daily requirement for a trace element.
Drinking a dish as part of a diet should be orange or apple juice. Dairy products slow down the absorption of iron due to their high calcium content in their chemical structure.
Pomegranate juice, which has a significant concentration of iron, is suitable. When choosing drinks for a child, an individual approach is practiced. Some fruit liquids can cause allergic reactions.
It is better to include freshly squeezed juices in the dietary food for the correction of hemoglobin in a child. In cooked more than 2-3 tsp. back or canned store drinks, iron oxidation is observed.
Such a transformation of a trace element sharply impairs its absorption from the structure of the gastrointestinal tract into the systemic circulation. Iron-infused rabbit meat. It is advisable to feed the child with a boiled product.
Fortified with iron fillets:
- hake;
- mackerel;
- carp;
- pike perch;
A lot of trace elements are found in seaweed. Foods fortified with iron are combined with foods rich in animal and plant proteins, ascorbic acid. Such substances improve the absorption of the trace element and promote the synthesis of hemoglobin.
How to lower the level when increasing?
This condition is sometimes a symptom of a systemic pathological process, endocrine disorder, or kidney disease. For successful treatment, it is important to find out the reason for the deviation of the laboratory value.
After the initial examination, the pediatrician directs the child to advanced hardware diagnostics and additional tests. If the increase in hemoglobin is not caused by pathological reasons, correction of the diet with restriction or complete rejection of the use of iron-fortified foods is sufficient.
As a therapeutic and prophylactic measure, air humidification in the children's room is used. With an increase in hemoglobin due to an infectious-inflammatory process, antibiotic therapy, fungicidal agents or antiviral drugs are prescribed.
Such medicines are combined with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines, antipyretic and pain relieving pills. Such methods allow you to quickly bring the level of hemoglobin back to normal. To correct the consequences of an increased concentration of iron-containing protein in a child, anticoagulants are used.
Video about hemoglobin is normal
Hemoglobin norm for women and men:



