Eyesight tested always by examination by an ophthalmologist, after which the doctor may prescribe an additional examination. One of the methods for examining the eye is the study of the fundus or ophthalmoscopy. The fundus is the inner surface of the eyeball, which is visible when a directed beam of light is passed through the pupil.
They check it in order to examine the condition of the optic nerve head (optic nerve disc), the retina with veins, arteries and small vessels, the condition of which can be qualified according to special criteria. As part of the study, the general condition of the body is assessed, as well as the presence of concomitant changes in addition to diseases associated with vision.
Record content:
- 1 Indications for research
-
2 How is it determined
- 2.1 Direct ophthalmoscopy
- 2.2 Reverse ophthalmoscopy
- 2.3 Biomicroscopy
- 2.4 Through the Goldman lens
- 2.5 Ophthalmochromoscopy
- 2.6 Laser ophthalmoscopy
- 3 Preparation and analysis
- 4 Decoding the results
- 5 When to see a doctor
- 6 Possible complications
- 7 Video about fundus check
Indications for research
The fundus of the eye is not checked in every patient, since the procedure is complex and unpleasant. An ophthalmologist prescribes an analysis during examination and identification of patient complaints.
Such a study can be prescribed without the presence of complaints when one or more indications for the study are identified, which include:
- formations of various sizes in the retina of the eye;
- a sharp decrease in the level of visual acuity;
- in order to inspect the condition of the optic nerve;
- retinal detachment or suspicion of retinal degeneration;
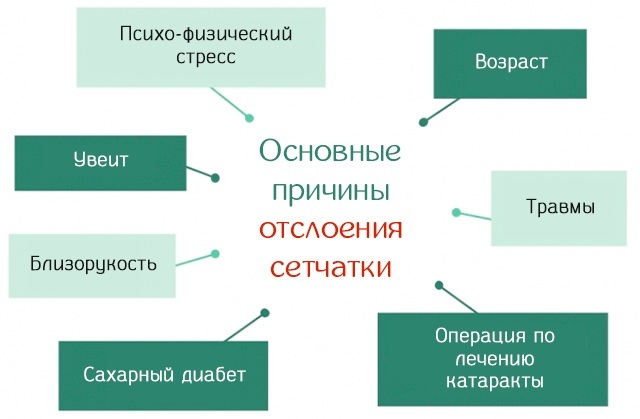
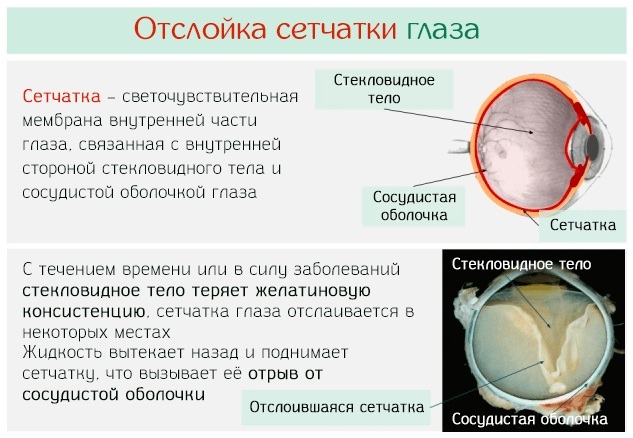
- retinopathy in newborns born prematurely;
- hemorrhages that appear on the retina of the eye;
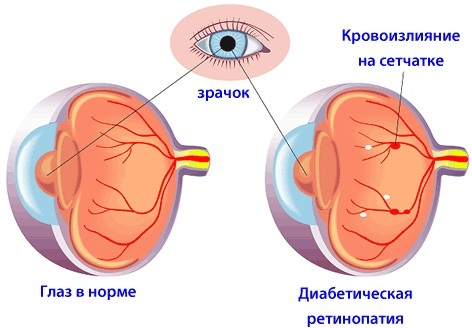
- retinopathy of a diabetic nature;
- non-standard changes in the retina of the eye;
- changes in the macular area;
- genetic diseases of vision (night blindness, lack of hyperopia);
- suspicion of cataract.
In rare cases, for additional examination of the patient and to eliminate doubts about his state of health, an examination of the fundus may be assigned to others. a specialist with a narrow focus:
- neuropathologist;
- endocrinologist;
- gynecologist;
- cardiologist.
A similar appointment is necessarily indicated if the patient has:
- diabetes mellitus;
- various blood diseases (anemia);
- increased intracranial pressure or neoplasms in the skull;
- suffered a stroke;
- hypertension;
- neuralgia of various etymologies;
- atherosclerosis;
- complications during pregnancy;
- autoimmune diseases (multiple sclerosis).
Mandatory examination of the fundus is prescribed by a surgeon, therapist or ophthalmologist in the following cases:
- frequent loss of balance or consciousness;
- severe headaches that are systematic;
- head injuries;
- loss of the ability to distinguish between different colors;
- taking special medications.
After the procedure for examining the fundus, the patient can be assigned a repeated or systematic prophylactic analysis. The state of the eyeball changes slowly, therefore, in these cases, the procedure is carried out for adults no more often Once a year, and for children once every 3-4 years (at 3 months, at 3.5-4 years old and at 7 years old when passing the commission before school).
| Age, years | Frequency of repeat ophthalmoscopy |
| 10-18 | Once every 3 years |
| 18-55 | Once a year |
| Over 55 | 1 time in 1-2 years, depending on the state of health |
How is it determined
The fundus of the eye is checked in a regular polyclinic in a specially equipped ophthalmologist's office or in a clinic that has an appropriate department.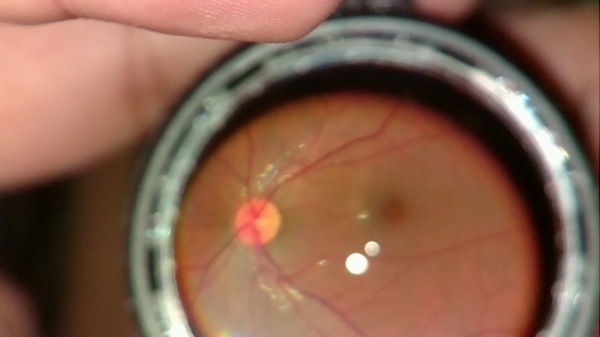
For the study, a medical device is used - an ophthalmoscope, based on a small concave mirror with a pinhole in the center. A directed beam of light is passed through a hole in the device, which allows you to inspect the fundus.
The eye-pleasing treatment is performed in a darkened room. For additional stimulation, special drops are instilled into the patient's eye prior to examination, which dilate the pupil and reduce the number of blinks by 10-15 minutes.
The wider the patient's pupil, the more information will be provided by the ongoing study about the state of the tissues of the eyeball, including the periphery.
The fundus examination allows you to obtain information about the patient's state of health on the date of the procedure, therefore, a research error of 5-10% is considered normal for this procedure.
Even with this level of accuracy of the procedure (90-95%), when checking the fundus, it is possible to easily recognize some types of diseases at an early stage of development. For example, cataracts. With timely treatment, the likelihood of complete recovery increases significantly.
The study of the fundus is carried out according to different methods, which can be carried out both separately and complement each other in difficult cases.
Types of fundus studies:
- slit lamp ophthalmoscopy;
- reverse ophthalmoscopy;
- laser ophthalmoscopy;
- ophthalmoscopy through the Goldman lens;
- ophthalmochromoscopy;
- direct ophthalmoscopy.
Direct ophthalmoscopy
With direct ophthalmoscopy, the fundus is examined under conditions of magnification up to 15 times.
An ophthalmoscope with a highly magnifying attachment is used for the analysis. During the procedure, the patient's eyes should be located at a distance of 3-4 cm from the device, otherwise the effectiveness of the procedure will sharply decrease. With direct ophthalmoscopy, the macula and the vascular bundle of the eye, which are located in the center, are clearly visible.
At the end of the procedure, attention is paid to the non-central areas of the fundus. This type of procedure allows a detailed examination of the fundus over the entire surface. However, due to the lack of the ability to study individual areas of the retina, direct ophthalmoscopy is rarely reveals retinal detachment and detachment height, so a different type is used in these cases research.
Reverse ophthalmoscopy
Reverse ophthalmoscopy is considered a more modern research method.
 A feature of reverse ophthalmoscopy is that the specialist receives the fundus visibility with a magnification of up to 5 times in a completely inverted form. In this type, mono or binocular ophthalmoscopes are used, which often have a built-in video camera that transmits the entire image to the computer screen.
A feature of reverse ophthalmoscopy is that the specialist receives the fundus visibility with a magnification of up to 5 times in a completely inverted form. In this type, mono or binocular ophthalmoscopes are used, which often have a built-in video camera that transmits the entire image to the computer screen.
Thanks to the use of a new type of lens, the patient's eyes do not need to be brought close to the instrument for examination.
When it is carried out, the peripheral parts of the retina of the eye are perfectly visible, even in cases of severe opacity in the eyeball. The width of the view during the procedure reaches 360 ° and allows you to get a high-quality volumetric image that can be transferred to the attending physician.
Biomicroscopy
In biomicroscopy, a 70-80 diopter lens is placed in front of the patient's eye, through which a beam of light is passed from a slit lamp built into the ophthalmoscope.
The fundus is checked in small and well-lit areas. The resulting image allows you to easily view the fundus in an inverted form at the desired angle, carefully examining individual parts of the eye. This type of procedure gives a 10 times larger image, which allows you to fully assess the condition of the fundus.
Through the Goldman lens
When viewing the fundus through a Goldmann lens, due to the large number of additional mirrors, the light beam is scattered.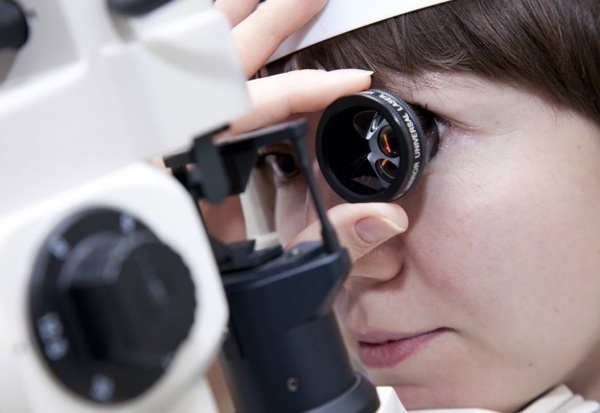
As a result, the eyeball is fully illuminated. This gives a clear picture from the central fundus to the periphery. The procedure is gentle and does not cause complications. The Goldman lens is best suited for examinations for pregnant women and those with myopia.
Ophthalmochromoscopy
Ophthalmochromoscopy is based on the use of lenses of various shades in an electric ophthalmoscope. The study of the fundus in the color range (yellow, red, green) helps to notice microscopic changes, to establish a deviation from the norm in the shade of the eyeball and retina. Most often, this type of ophthalmoscopy is used for retinal inflammation and neuralgia.
Laser ophthalmoscopy
When conducting a laser ophthalmoscopy study, a special laser beam is directed into the fundus of the eye, which is reflected from the tissues of the eyeball.
The inner parts of the eye are clearly visible even in the presence of neoplasms or opacities. Laser ophthalmoscopy is considered the newest method of performing the procedure, which simultaneously allows you to view the fundus and the retina of the eye. The resulting picture is displayed in the form of a video recording on a computer and can be used for additional research and diagnosis.
All types of ophthalmoscopy have their own advantages and disadvantages. The type of procedure in each individual case is chosen by the attending ophthalmologist or a specialist directly conducting the study, depending on its purpose and characteristics.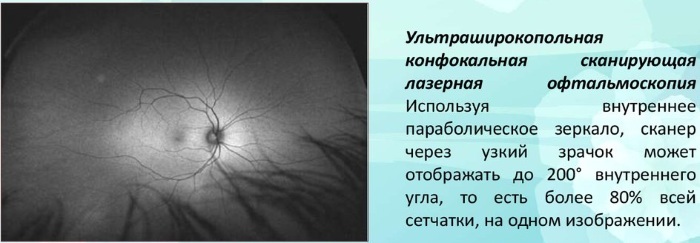
Each of the methods of ophthalmoscopy provides a different amount of information about the patient's fundus, so the ophthalmologist has the opportunity to choose the type of examination that will give the most effective results. In some cases, if several different diseases are suspected or for the purposes of a comprehensive study, ophthalmoscopy can be prescribed in 2 different ways.
Preparation and analysis
The fundus check procedure, like any procedure that examines the state of systems and organs through examination, provides information about the state of health only at the time of the study. There are no special preparatory measures before the procedure.
To obtain objective information about the state of the optic nerve and fundus vessels 2 days before the procedure, it is recommended:
- exclude heavy physical activity;
- remove stressful situations and anxieties;
- exclude the use of alcohol and drugs, the use of which is not associated with a vital necessity.
- on the eve and before the study, it is not recommended to smoke, as well as to read a lot, watch TV and a computer.
Immediately before the procedure, the patient must remove glasses and lenses, which may interfere with the examination of the fundus.
At the stage of preparation, the doctor instills drops (Cyclomed, Tropicamide or Irifrin) into the patient's eyes to obtain the desired effect and dilate the pupils. The study itself is carried out in a dark room, where the patient's pupils are naturally enlarged even more and the analysis efficiency is increased.
The fundus of the eye is checked as follows:
- The patient is instilled with drops in both eyes, then it is left for 2-3 minutes. at rest in order for the medicine to take effect.
- The patient is then seated on a special chair in a dark room and placed on a support that regulates the position of the head and ensures immobility during the procedure.
- Beams of light are periodically directed into the patient's eye through an ophthalmoscope. In this case, the doctor asks the person to look in different directions in order to examine more of the fundus area.
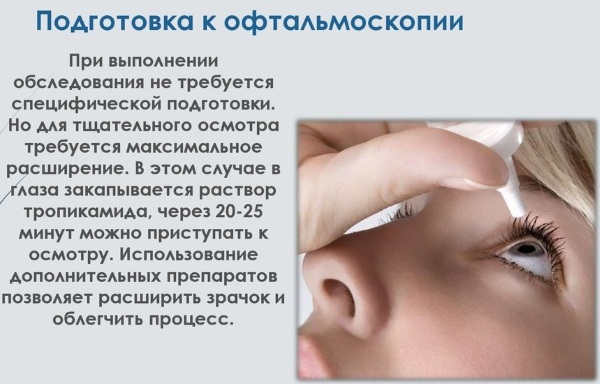
Before checking the fundus, drops are instilled to expand the pupil
The procedure lasts no more than 15 minutes. and allows you to clearly see all the features of the vessels, the optic nerve and veins inside the eye.
More modern ophthalmoscopes work with a halogen source. They can not only enlarge and illuminate the research site, but also take pictures, which are automatically transferred to the computer screen for a more detailed examination. All this allows not only to increase the clarity of the picture, objectivity and the amount of data received, but also to reduce the procedure time to 7 minutes.
Due to the strong glow in the eyes during the procedure, the patient may experience discomfort. However, these sensations are easy enough to endure. After the procedure, the eyes quickly return to normal and recover. Vision becomes clear.
After examination, the patient may feel dizzy or feel nausea, which disappear after 10-30 minutes. after the end of the procedure. To alleviate such symptoms, it is better to sit in the fresh air for 20 minutes after the examination. and drink cool water.
Decoding the results
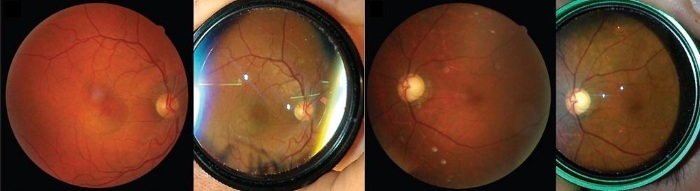
The fundus of the patient is checked by a specialist ophthalmologist. During the procedure, the patient does not see anything and must sit still to ensure the clarity of the picture. The condition of the fundus is visible to the doctor, and also, if possible, the images are recorded by the device and displayed on the monitor screen for additional viewing.
After the procedure, the patient is provided with an extract from the study of the fundus with the results, which are quite simply deciphered.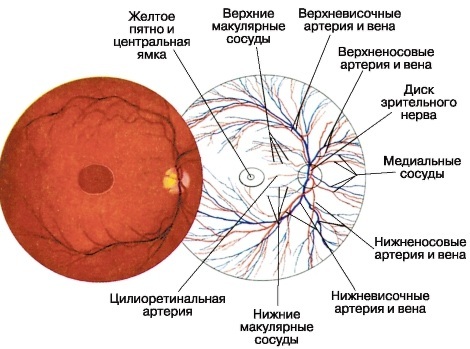
The document indicates, in addition to the patient's data and the method of conducting the study:
- the patient has deviations in visual acuity, the degree of farsightedness or myopia;
- the presence of astigmatism, indicating its degree. In this case, the readings are less than 0.7 units. is considered the norm and refers to physiological astigmatism. Readings are higher than 0.75-1.0 units. considered elevated and capable of affecting vision;
- condition of the optic nerve head (optic nerve disc). Its color, contours and state are indicated. It should be pink in color. In the case of his pallor, there are signs of atrophy. An increase or decrease also indicates a violation;
- condition of arteries and veins. In healthy people, the arteries should be narrower than veins in a 2: 3 ratio. The arteries should be red and the veins should be dark. There should be no nodes or growths on the arteries and veins. If there are deviations from the norm, they are described in detail. For example, the number and size of areas with sharply narrowed vessels;
- the central part of the retina and the region of the periphery are described. In the presence of retinal detachment, the size of the area, location, ply is indicated;
- additional features of the fundus and pathology are indicated.
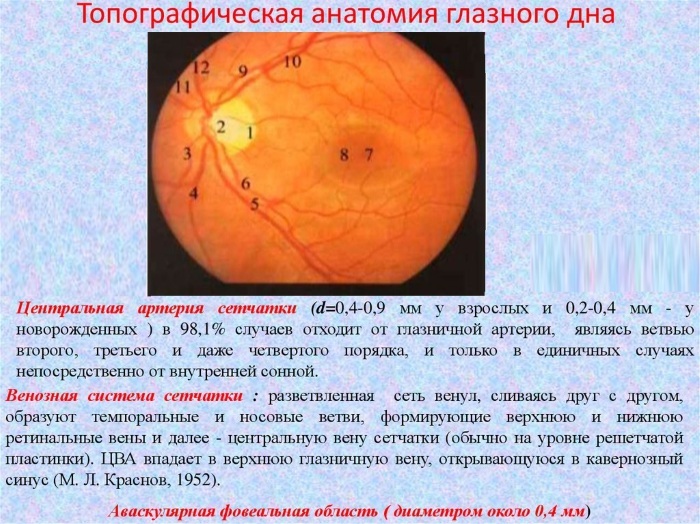
In the conclusion, the ophthalmologist is obliged to indicate the predisposition or suspicion of the diagnosis, which will then be confirmed by the attending physician after a second examination. Depending on the result of the conclusion of ophthalmoscopy, the patient is assigned the main course of treatment.
When to see a doctor
In any case, after passing the fundus examination, the results of the study must be presented to the attending physician for their assessment. If ophthalmoscopy does not reveal any abnormalities in the eyeball, the patient is considered healthy. In some cases, the doctor may prescribe a repeated prophylactic procedure after 1 year.
If any deviations from the norm are detected, the doctor assesses the condition and harm to health. In case of non-dangerous changes, the patient can be shown a course of vitamins with re-taking the analysis after the specified period.
However, there are cases when urgent treatment is needed.
Such cases include detection after ophthalmoscopy:
- retinopathy, in which the vessels of the eyeball significantly increase and suffer. Often a similar disease develops against the background of hypertension or difficult pregnancy;
- megalopapilla of the optic nerve, which is expressed in the increase and paleness of the optic nerve;
- hypoplasia, where there is a decrease in the size of the optic nerve disc in comparison with the vessels of the fundus;
- stagnant nipple or its edema, when the papilla of the optic nerve turns pale and increases, gradually atrophying;
- optic neuritis, in which the optic nerve becomes inflamed and gradually atrophied;
- retinal inflammation caused by infection or allergy of varying degrees;
- retinal detachment of varying degrees;
- neoplasms;
- suspicion of cataract.
All these cases require a qualified approach to diagnosis and treatment, which is better to be entrusted to a specialist - an ophthalmologist. In the case of a neoplasm, the patient is treated by an ophthalmologist in conjunction with an oncologist.
If any disease is detected at an early stage as a result of timely ophthalmoscopy, the probability of complete the patient's recovery after 1-2 courses of treatment is considered the maximum, which is confirmed by the results of repeated research.
Possible complications
An ophthalmologist in the case of examination and diagnosis after ophthalmoscopy of a deviation from the norm, which does not affect visual acuity and does not lead to accompanying complications, can recommend general strengthening exercises for the eyes and drugs, as well as preventive systematic monitoring of the condition fundus.
In case of detection after the examination of the fundus of any of the severe diseases, the ophthalmologist must necessarily carry out a course of treatment in the following cases:
- when the disease affects visual acuity;
- causes constant discomfort and pain;
- can lead to various complications for the patient's health.
In these cases, the patient is prescribed treatment, which must be started immediately. If the symptoms of the disease are ignored or the prescribed medication course of treatment, the symptoms of the disease will gradually progress.
In the future, this can lead to:
- severe decrease in visual acuity;
- loss of vision;
- the development of malignant tumors;
- mycosis of tissues;
- removal of 1 or 2 eyeballs;
- infectious infection of adjacent tissues or blood.
In parallel with the increase in the main symptoms, pain in the eyes, constant discharge from the lacrimal duct and burning sensation in the eyes, as a reaction to light and wind, may appear. The visibility of the surrounding world deteriorates, the picture in front of the patient's eyes gradually becomes cloudy, which can be avoided if you consult a doctor in time.
Highly qualified specialists check the eyes during ophthalmoscopy, using modern equipment, painlessly. The fundus of any person is a source of information about the state of vision, cardiovascular and nervous systems.
Examination of the fundus will help identify many congenital and serious diseases that can be treated with modern drugs for several weeks. As a result, not only discomfort goes away, but vision improves for many years.
Video about fundus check
How is the fundus examination carried out:



