Symptoms such as partial seizures are among the main typical symptoms of the next epileptic seizure in a sick person. This symptom can have different severity and will depend on the degree of damage to specific parts of the brain.
Record content:
- 1 What it is?
- 2 What seizures look like and first aid rules
- 3 Causal factors
- 4 Classification and symptomatology
- 5 Partial seizures with secondary generalization
-
6 Diagnostics
- 6.1 Taking anamnesis
- 6.2 Magnetic resonance imaging
- 6.3 Electroencephalography
- 7 Disease therapy
- 8 Epileptic seizure videos
What it is?
Partial seizures are symptoms that can be both generalized and unnoticeable for others by blackouts, short-term and quickly disappearing.
A pathology called epilepsy, formerly epilepsy, is characteristic not only of humans, but of animals, including cats, dogs and mice. A characteristic feature is a tendency to sudden onset of convulsive syndrome - an epileptic seizure.
The mechanism of development of the underlying pathology is associated with the formation of many foci of uncontrolled excitation in certain parts of the brain.
In this case, the following types of violations are manifested from the following sides:
- autonomic nervous system;
- physical activity;
- skin sensitivity;
- thinking;
- consciousness.
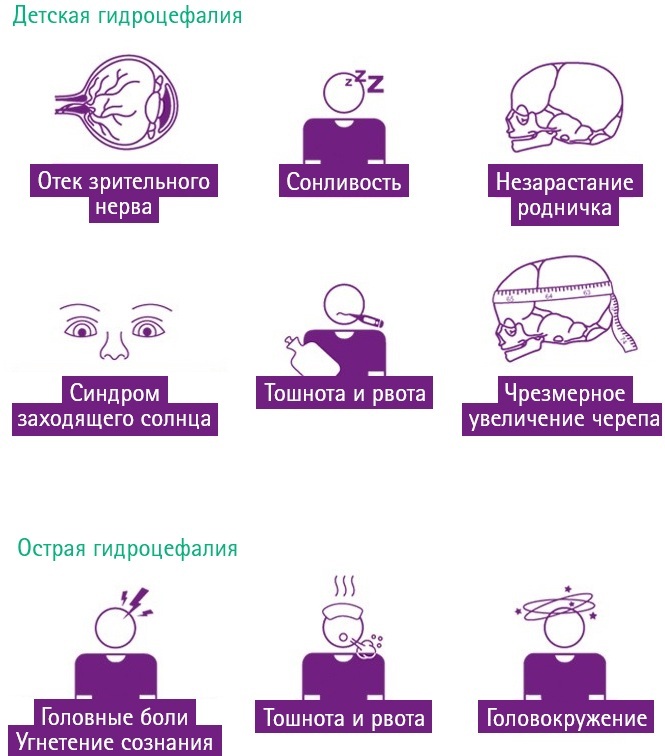
Most often, the first signs are found in children, since at a young age the body is biologically characterized by high convulsive activity. The brain at this time is extremely easily excited and reacts in a generalized manner to irritating factors.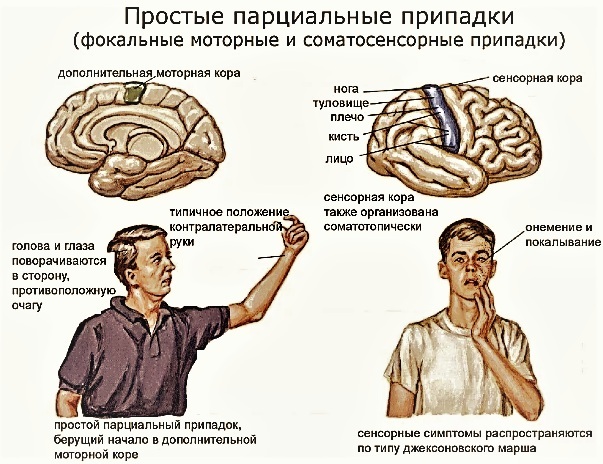
The incidence, prevalence of epilepsy among the population is about 1%. Partial seizures are very complex pathologies. The main factor due to which the signs of another attack suddenly appear is convulsive readiness. In this state, the body, under the influence of any provoking factor, will immediately respond with the occurrence of seizures.
The duration of an epileptic seizure can vary widely and on average ranges from 5 seconds to 10 minutes. Despite the relative rarity, the main danger in the active phase of the disease is associated with the risk of sudden death syndrome in epilepsy - SPSE. The prevalence of the disease among people reaches 10 cases per 1000 people.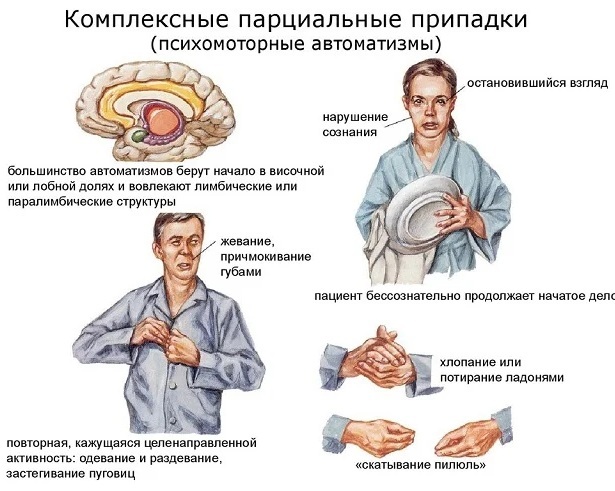
According to statistics, with this result, the victims had the following features:
| Connection | Factor |
| With the patient |
|
| With seizures |
|
| With treatment |
|
Taking into account these factors, the approach to treatment should be comprehensive and carefully thought out with prescribing clear, correctly calculated doses of traditional drugs for antiepileptic therapy.
What seizures look like and first aid rules
From the outside, others see that a person suddenly loses consciousness and falls. Sometimes a faint cry is added to the signs. Throughout the tonic phase, the muscles of the whole body are in a tense state, the respiratory function of the lungs is significantly hampered, the lips lose their natural color and begin to turn blue.
The most important thing that should be known not only to the close environment, but also to all other people in the general mass is the right actions that the victim needs before the arrival of the ambulance team:
- seizures almost always occur without any precursors;
- it is important to drop panic and be around during an attack;
- in this case, dangerous objects should be removed from the person;
- the time of the onset of the seizure should be roughly noted;
- it is forbidden to restrain the patient physically.
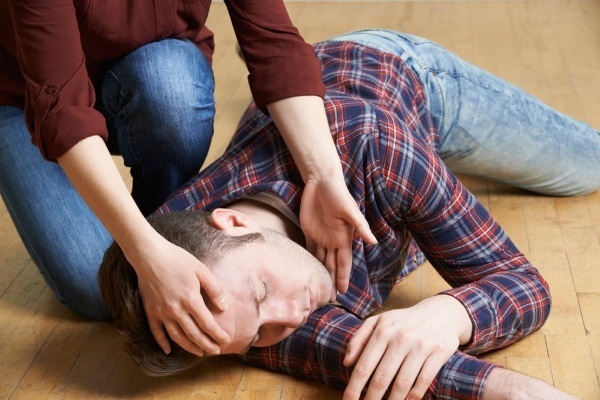

Partial seizures, as previously thought, can lead to suffocation due to the sinking of the tongue. Therefore, there have been advice to put something solid in your mouth. You don't need to do this.
During an attack, almost all muscles are tense, including the jaw and tongue. If you try to put an object in the mouth, it can injure your fingers or break the teeth of the sick person.
Causal factors
In the majority of sick people, the development of pathology was noted due to heredity.
The total number of reasons also includes the following factors:
- hidden defects in the electrical activity of the brain;
- addiction to alcohol and drugs;
- leakage or urinary incontinence;
- identical twins.
In the presence of blood relatives with epilepsy, it is recommended to undergo an EEG - electroencephalography. The technique allows you to register and evaluate fluctuations in the electrical potentials of the brain. Especially effective is noted in the case of prolonged recording in people with already developed epilepsy.
Other factors may include the following reasons:
- infectious diseases of the meninges;
- head injuries during birth;
- disturbances in the supply of blood to brain tissue;
- prolonged intake of toxins;
- pathology of metabolic processes;
- suffered a stroke;
- neoplasms.
In some cases, their result is damage of varying severity with different localization. After that, they can start the process of the onset of increased seizure activity.
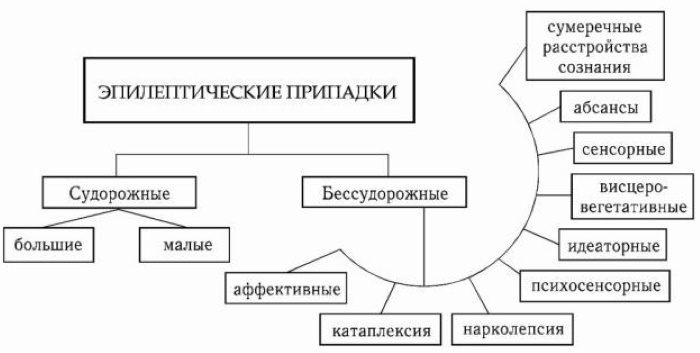
Classification and symptomatology
Partial seizures are only a symptom.
The group of diseases itself with the general name epilepsy includes the following main types:
- intermittent form - characteristic of the neonatal period, while symptoms are observed in the form of a convulsive syndrome of one of the limbs or halves of the body;
- childhood epilepsy - with its development, convulsions, interruptions in the respiratory rhythm, urinary or fecal incontinence, fainting, tension or trembling of the arms and legs appear;
-
absence type - it is characterized by a short-term fading and loss of spatial orientation, reactions disappear along with a directed gaze and attention;
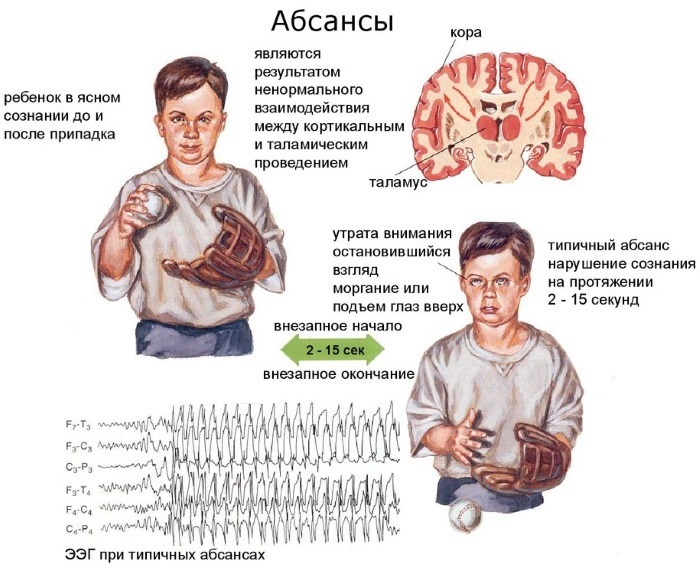
- rolandic form - the most common in children 3-14 years old, after which epilepsy disappears or passes into another type, symptoms include speech disorders, clonic and tonic seizures;
- myoclonic epilepsy - the debut is noted at the age of 10-20 years, the features include involuntary muscle tension in combination with mental disorders;
- post-traumatic type - occurs as a result of damage to brain tissue due to trauma, on average, epilepsy symptoms are observed in 1 in 10 people who have received serious bruises;
- alcoholic form - develops as a result of chronic use of large doses of alcoholic beverages, this type most often manifests itself a few days after an attempt to give up alcohol;
- non-convulsive epilepsy - refers to frequent cases, symptoms include a narrowing of consciousness and the patient's perception of only significant facts and phenomena, while hallucinations and mental abnormalities occur.
The classic development of epilepsy is a large seizure.
It is he who is characterized by some harbingers:
- in 2-3 days, the patient begins to experience severe anxiety for no apparent reason;
- behavior can change significantly compared to normal human actions;
- then a specific phase occurs, called the aura, accompanied by flashes of light, sounds, smells and other hallucinations;
- during the period of the aura, an epileptic focus is formed in the brain, which will become the source of the next seizure.
After the onset of convulsive excitement, the whole complex of standard symptoms arises - the tonic phase. It includes tension in the muscles of the body, cyanosis, irregularities in the respiratory rhythm, while the back bends in the form of an arc with the stomach up.
Then comes the clonic phase - rhythmic muscle contraction for 2-5 minutes, the appearance of foam from the mouth, biting the tongue. Then the condition gradually normalizes, breathing is restored, and the skin acquires a normal color.
At the next stage, the patient's body completely relaxes until the involuntary discharge of urine, feces or accumulated gases. At the same time, a person falls into stupor - a special condition, which in other cases leads to a subsequent coma. This happens due to excessive fatigue of the brain, which is in dire need of rest and begins to greatly inhibit.
The final stage is the exit from the stupor, in which even the simplest reflexes are absent, into a normal sleep. After waking up, the patient feels overwhelmed, weak, facial asymmetry and other unpleasant symptoms are observed. They can last for 2-3 days. After a seizure, bruises and abrasions remain on the body due to convulsions. Slurred speech may also be present.
Partial seizures with secondary generalization
Secondary generalized seizures begin with an increase in muscle tone and then develop into symmetrical contractions on both sides of the body. The tonic phase is replaced by a clonic period. At the same time, at first, the electrical activity in a limited area of the brain tissue increases, then the phase of muscle twitching begins.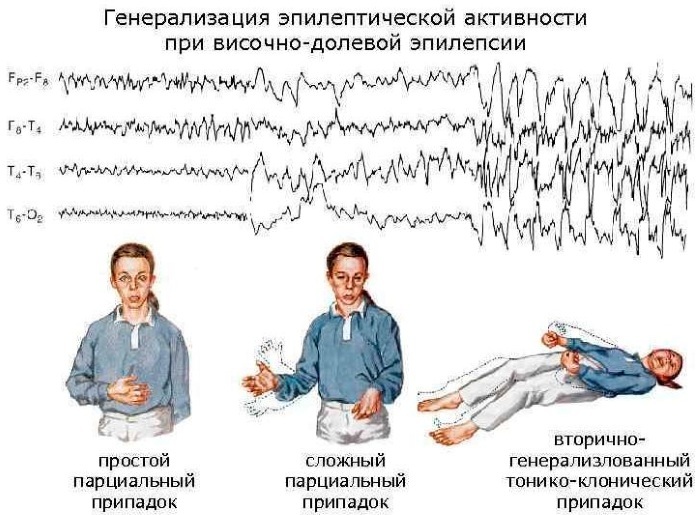
Vegetative symptoms and manifestations of a partial seizure:
- increased blood pressure;
- increased sphincter tone;
- profuse saliva;
- secretion of mucus in the bronchi;
- rush of blood to the skin;
- biting the tongue;
- increased heart rate;
- tachycardia.
Another characteristic symptom is apnea, a blockage of breathing that begins with a strong breath and continues during both phases. In this case, forced movements of the lung tissues can be observed, which in a seizure state occur due to convulsions of the muscles responsible for breathing.
The third stage is the period immediately after the epileptic seizure. Muscles do not relax immediately and not completely. After about 5 seconds, a repetition of the same symptoms and phases begins to develop. It lasts up to 5 minutes. During this period, the muscles of the head and neck are significantly strained. The body and limbs harden less and remain unbent.
At the end of the cycle described, the rest phase begins. At the same time, the respiratory rhythm is normalized, yawning appears and abundant saliva continues to be secreted. The heartbeat rhythm slows down dramatically. Cyanosis of the skin gives way to paleness. A person is in an unconscious state, reflexes can completely disappear. Duration - from 2 to 10 minutes.
After the expiration of this time, the time comes for the onset of the late post-attack period. In this case, the muscles are additionally relaxed. The pulse returns to normal rhythm. Reflexes continue to be depressed. The patient experiences a series of falling into a coma and impaired consciousness. Sometimes a person does not notice these sensations, but immediately plunges into a state of sleep.
Diagnostics
Partial seizures are an unpleasant and dangerous symptom for a sick person. When the first signs appear, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination to identify the causes of development disease, the degree of brain damage and the appointment of an effective complex of drugs for further treatment.
Taking anamnesis
The specialist will definitely study the patient's medical history, collect all the necessary information about heredity, the first manifestations and the timing of their limitation. You will also need to provide the doctor with all the information about the person's condition to the smallest detail.
Taking anamnesis becomes especially important with an already developed disease. The data obtained will allow the doctor to navigate the available diagnostic methods and prescribe the most appropriate option for each specific case.
Magnetic resonance imaging
The technique detects epileptic abnormalities with high accuracy and efficiency. The main advantage of this method is the absolute absence of any danger to the patient. For the diagnosis of epilepsy, the method of MR diffusion is mainly used - an assessment of the movement of fluids.
The procedure itself requires a small amount of time, during which the patient must lie motionless inside a special apparatus with headphones on. They are necessary to protect the auditory organs from loud rolls of sound during the examination.
The main and important condition is to completely stop any movements, remaining in this position throughout the entire procedure. Breathing does not affect the test results.
After processing the obtained images, the specialist will assess the bioelectrical activity of all parts of the brain and write out a conclusion that will need to be provided to a neurologist or psychiatrist. The doctor will be able to determine the stage of the disease and prescribe the appropriate complex of drugs.
Electroencephalography
The technique involves putting on a special mesh of electrodes to register electrical impulses in one or another part of the head. On the finished result of the study, the doctor will receive visual data about the place of occurrence, the nature of movement and the strength of electrical impulses in response to various stimuli.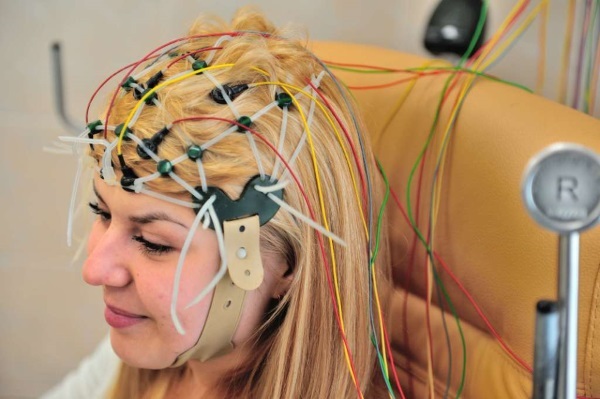
An important condition for obtaining correct data is the procedure directly during the attack. At other times, the sensors, most likely, will not be able to register significant violations. Therefore, in some cases, video-EEG monitoring is recommended in a hospital setting.
Disease therapy
Partial seizures are a complex of symptoms that can be dealt with by neurologists or psychiatrists. If possible, it is advisable to undergo examinations and discuss the possibility of certain methods of treatment with a narrower specialist - an epileptologist.
In addition to the basic set of medical knowledge in the specializations of neurology and psychiatry, such a doctor gains additional knowledge in several areas:
- pharmacological properties and features of drugs for epilepsy;
- mastering techniques for assessing the structure, biochemistry and functions of the brain;
- electrical physiology of all formations in the head;
- genetic characteristics of individuals;
- deviations of the paroxysmal spectrum;
- methods of patient rehabilitation.
This level of training allows epileptologists to comprehensively and multilaterally approach the study of each individual case in identifying the described disease. In addition to general specialists, in cases with children, you can go directly to a doctor who specializes in their treatment.
Such a doctor is additionally studying techniques that can be used at a young age to completely get rid of the recurrence of unwanted symptoms. With persistent treatment with all prescribed drugs, the chance of absolute recovery increases.
Partial convulsions that are dangerous to humans are only symptoms. This means that together with the complete relief of seizures, it is necessary to directly eliminate the cause of their occurrence. The modern level of medicine in the overwhelming majority of cases allows a person to return to a full life without the risk of recurrence of seizures.
Epileptic seizure videos
Types of epilepsy seizures: