Neuromuscular diseases (NMD) are a group of pathologies that are transmitted at the genetic level from parents to children. Muscle functions are impaired, motor activity decreases. Characteristic clinical symptoms appear.
Pathological processes develop against the background of dysfunctions of neuromuscular connections, with damage to muscles and spinal neurons, nerves. Correctly selected therapy will not help to completely cure a person, but will improve his quality of life.
Record content:
- 1 Etiology and neurology
- 2 Classification
- 3 Stages and degrees
- 4 Symptoms
- 5 Reasons for the appearance
- 6 Diagnostics
- 7 When to see a doctor
- 8 Prophylaxis
-
9 Treatment methods
- 9.1 Medications
- 9.2 Traditional methods
- 9.3 Other methods
- 10 Possible complications
- 11 Videos about neuromuscular diseases
Etiology and neurology
Neuromuscular diseases disrupt the normal synaptic transmission of impulses from nerve endings to muscle fibers. Autoimmune processes are the cornerstone of each type of pathological changes.
A large group of diseases is characterized not only by damage to muscle tissue, but also by peripheral nerves, anterior horns of the spinal cord. Among the often diagnosed pathologies, myopathy, myotonia, myasthenia gravis are distinguished.
Classification
Neuromuscular diseases are distinguished according to the following types:
| Name | Description |
| Myotonia | The disease is congenital or acquired, more common in women. The transmission of nerve impulses is impaired, which provokes weakness in the striated muscles. The functioning of the neuromuscular system deteriorates, as a result of which malfunctions of the internal organs occur. |
| Primary progressive muscular dystrophies (myopathy) | A group of diseases characterized by primary damage to muscle tissue. The provoking factors are not only heredity, but also viral infection of the body, metabolic disorders. Pathologies that affect the central core and the endocrine system are rare. |
| Progressive secondary muscular dystrophies | A condition characterized by malfunctioning of the peripheral nerves. The supply of organs and tissues with nerve cells is disrupted. Dystrophic processes develop. In medicine, congenital, early childhood and late secondary muscular dystrophy are distinguished. Patients with this diagnosis live from 9 to 30 years. |
| Congenital non-progressive myopathies | Congenital muscle disorders that are poorly developed or do not progress at all. The pathological condition is diagnosed in children who are in the womb or immediately after their birth (sluggish child syndrome). The disease is characterized by muscle hypotonia and severe weakness. The lower extremities are more often affected. Rarely, cranial muscle myopathy is diagnosed, in which facial expressions and eye movement are impaired. When a child begins to grow and develop, parents notice a lack of motor skills in the baby. Children constantly fall, sit up late and start walking. Neuromuscular abnormalities appear, the intellect is not affected by pathological processes. |
| Hereditary paroxysmal myoplegias | Genetic diseases characterized by paralysis of the limbs and muscle weakness. In medicine, there is hypokalemic, hyperkalemic and normakalemic myoplegia. Pathological processes occur against the background of improper redistribution of potassium. In the intercellular fluid and plasma, the amount of this element decreases, in cells it increases. The diseases are characterized by severe weakness in the limbs and trunk. Muscle damage can also occur in the pharynx, larynx, and respiratory system. With such dystrophic processes, there is a high probability of death. |
Neuromuscular diseases are inherited, more often appear in people whose family had relatives with such a diagnosis.
Acquired pathological processes develop as a result of hormonal or metabolic disorders in the human body. There is a failure in the functioning of the immune system. She produces cells that attack her body. Autoimmune diseases lead to muscle weakness.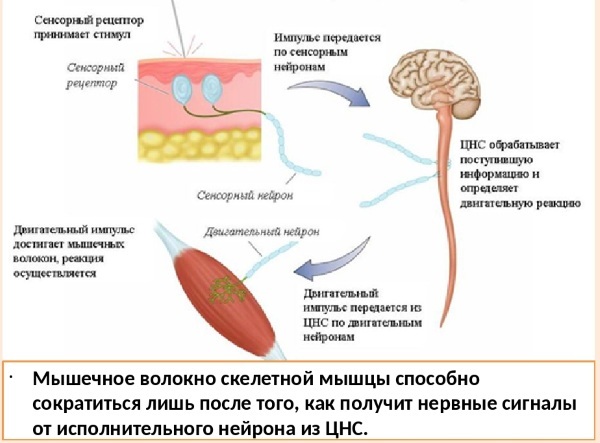
Neuromuscular pathologies accompanied by dystrophic processes affect the following areas of the human body:
- muscles;
- neuromuscular endings;
- motor neurons;
- peripheral nerves.
With myopathy, a person has a high chance of becoming disabled as a result of loss of mobility. All types of neuromuscular diseases have consequences without timely therapy. It can be not only disability, but also the death of a person.
Stages and degrees
Neuromuscular diseases proceed in stages. A neurologist will help to determine the stage of development of pathological processes with the help of medical diagnostics.
| Name | Description |
| Stage I | Movement disorders are mild. |
| Stage II | The patient has pronounced clinical signs and serious motor changes. |
| Stage III | The patient cannot move independently. |
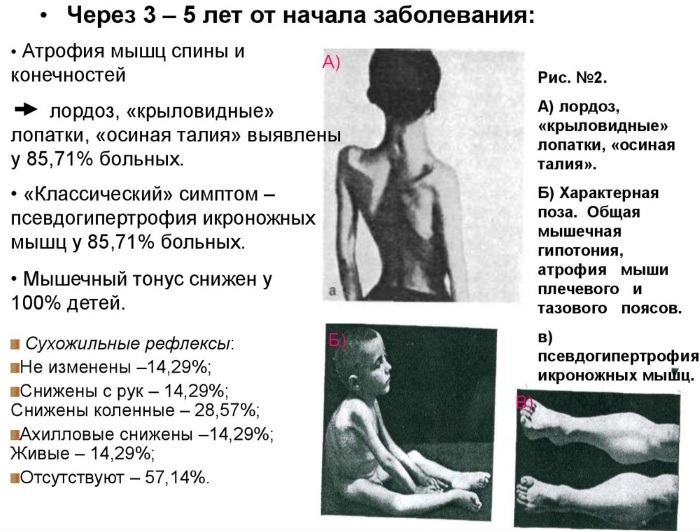
The clinical picture depends on the rate of development of pathological processes and the severity of the disease. A neurologist will help to establish an accurate diagnosis.
Symptoms
The main symptom of neuromuscular disease is muscle weakness. The clinical picture depends on the area of the lesion (shoulder girdle, hips, pelvis, lower limbs).
In most cases, patients are diagnosed with the following symptoms:
- muscle volume decreases;
- painful spasms are observed;
- muscles involuntarily contract;
- the affected tissues become numb;
- tendon reflexes are reduced;
- the patient feels a tingling sensation;
- double vision (diplopia);
- swallowing and respiratory reflexes are disturbed.
With neuromuscular diseases, the eyelids drop, muscle weakness manifests itself symmetrically and gradually progresses. In most cases, with developing muscular dystrophy, weakness occurs in the pelvic and shoulder girdle. The same goes for the proximal extremities.
Sometimes neural amyotrophy is accompanied by paresthesia, a violation of deep or superficial sensitivity. Clinical signs of neuromuscular disease appear gradually. As the pathological processes progress, a person loses the ability to independently serve himself. The same goes for movement.
Reasons for the appearance
Neuromuscular diseases in most cases occur due to autoimmune pathologies.
The following circumstances are also a provoking factor:
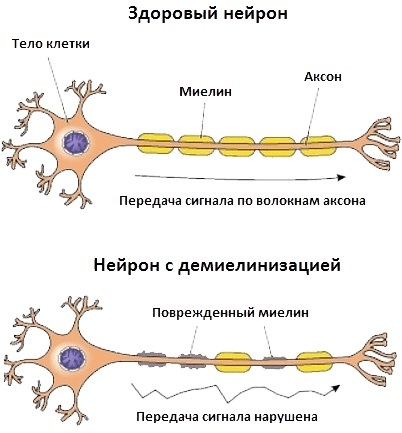
- hereditary factor;
- damage to the peripheral nerves and motor neurons of the spinal cord;
- malfunctions in the functioning of neuromuscular connections;
- poisoning of the body with various substances;
- congenital metabolic failure;
- pathological changes in the muscles.
Neuromuscular diseases also develop against the background of disturbances in the functioning of the motor neuron in the region of the brain stem.
A neurologist will help determine the cause and make an accurate diagnosis. Taking into account the patient's condition, the degree of development of pathological processes and the individual characteristics of the human body, the specialist will select an effective treatment.
Diagnostics
A medical examination will allow the doctor to establish an accurate diagnosis. The specialist prescribes testing for the patient, taking into account his complaints and symptoms.
For the diagnosis of neuromuscular diseases, the following examination methods are prescribed:
| Name | Description |
| Biochemical | Studies allow us to determine the level of muscle enzymes, which increases with LMD. The results will also show the amount of myoglobin and aldolase. |
| Electrophysiological | Electroneuromyography and electromyography are performed. Diagnostic methods help identify primary and secondary myopathy. Also assess the degree of damage to the spinal cord and peripheral nerves. |
| Pathomorphological | Patients are given a muscle biopsy. The resulting material is examined under a microscope. The diagnostic results help to establish an accurate diagnosis (Duchenne myopathy, Becker's muscular dystrophy), which is important for the selection of the correct therapy. |
| DNA diagnostics | The most informative diagnostic method, which is prescribed for neuromuscular diseases. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) helps in 70% of cases to identify genetic abnormalities and confirm their nature. |
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | A specialist evaluates the heart rate. |

A cardiologist is engaged in the study of the state of the heart muscle. The specialist prescribes not only a cardiogram, but also an ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the heart.
When to see a doctor
You should consult a doctor immediately when the first signs of muscle disturbances appear. But if the family has relatives with neuromuscular diseases, it is necessary to undergo a complete medical examination and understand how high the likelihood of the appearance of pathological processes by hereditary lines.
A neurologist is involved in diagnostics and treatment. The specialist will conduct an examination and select the most informative research methods.
Prophylaxis
In most cases, neuromuscular diseases develop due to a hereditary factor. It is impossible to prevent pathological changes. A woman is recommended to undergo medical examinations during pregnancy planning, especially if there are relatives in the family with such a diagnosis.
Diagnostic measures are also prescribed during the period of carrying a baby in the early stages. With a high likelihood of developing neuromuscular diseases, a special medical commission advises the expectant mother to terminate the pregnancy.
Treatment methods
Therapy of neuromuscular diseases is carried out using complex methods. Patients are prescribed medications, physiotherapy exercises. In the absence of serious contraindications, you can use the recipes of healers and healers. The main goal of therapy is to maintain muscle strength and slow down atrophic processes.
Medications
Medicines are selected by a neurologist, taking into account the results of medical diagnostics, the degree of development of pathological processes and the individual characteristics of the human body.
It is not recommended to take medications on your own, as many drugs cause side effects.
For neuromuscular diseases, the doctor prescribes the following medications: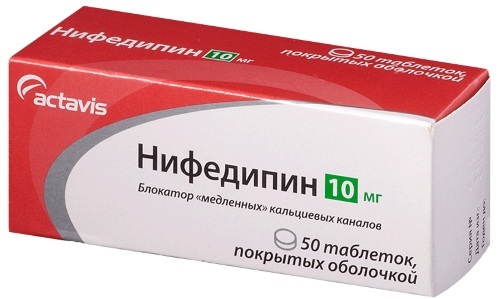
| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Antagonists | Nifedipine | The initial adult dosage is 10 mg 2 times a day. If necessary, the attending physician increases it to 20 mg 4 times a day. |
| Metabolic drugs | Phosphaden, Vitamin E | The medicine is taken orally or administered intravenously. The recommended dosage for adults is 0.025-0.05 g per day. The course of therapy lasts 2-4 weeks. |
| Corticosteroids | Methotrexate, Azathioprine | The adult dosage is 30 mg 2 times a week. The course of treatment lasts 14 days, between them you should take breaks for 2-3 weeks. |
Medicines allow you to eliminate the deficiency of energy and protein, have a positive effect on material metabolism in muscle tissues. Additionally, vitamin complexes are prescribed.
Traditional methods
Neuromuscular diseases can be treated with prescriptions from healers and healers, but as an adjunctive therapy. Folk remedies improve the patient's quality of life and his general condition. The means used should be discussed with the attending neurologist.
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Oats | Rinse the grains well and add water (500 ml). The resulting mass is put on fire, brought to a boil and heated for 30 minutes. Then leave for 2 hours, filter and take according to the scheme. | The finished product is recommended to be taken orally before meals 4 times a day. The course of therapy lasts 3 months. Then you need to take a break for 30 days and continue therapy. |
| Onion | Clean the product and mix 200 g with sugar (200 g), add water (0.5 l). Put the resulting mass on low heat and heat for 1.5 hours. Cool and add 2 tbsp. natural honey. | The finished product is recommended to take 2 tsp. 3 times a day. |
| Garlic | Peel and chop 3 heads of garlic. Add 4 pre-chopped lemons. Pour all components with honey (1 l) and linseed oil (200 g). | The resulting product should be taken 1 tsp. 3 times a day. |
For neuromuscular diseases, it is useful to conduct contrast baths for the lower extremities. After water procedures, it is recommended to wrap your feet in a warm blanket.
Other methods
Complex therapy of neuromuscular diseases slows down their development, prolongs the period of remission and improves the patient's quality of life.
Together with traditional and folk treatment, patients are prescribed the following methods of therapy:

| Name | Description |
| Physiotherapy procedures | The treatment improves the conduction of nerve impulses in the muscle tissues, promotes their nutrition. Blood circulation and material exchange are enhanced. |
| Massage | The targeted effect helps to increase muscle tone. To achieve a therapeutic effect, it is necessary to carry out several sessions throughout the year. |
| Physiotherapy | Gymnastics is carried out in a specialized complex under the supervision of a specialist. |
Special orthopedic devices allow the patient to maintain independent movement. Physiotherapy in the form of active and passive movements improves the patient's condition.
Exercise should be done regularly with moderate stress. Swimming is also recommended for neuromuscular diseases. It is easier to exercise in water without stress on the spine.
Possible complications
The negative consequences of pathological processes appear as a result defeat of various internal organs and systems of the human body:
| Name | Description |
| Respiratory system diseases | Against the background of muscle weakness, shallow breathing occurs, as a result of which it is difficult for the patient to fully clear his throat. The accumulation of phlegm in the lungs and bronchi leads to the development of serious diseases of the respiratory system. |
| Cardiomyopathy | As a result of the weakening of the heart muscle, the patient develops arrhythmia, heart failure. The pathological condition is accompanied by shortness of breath, edema of the lower extremities and general weakness in the body.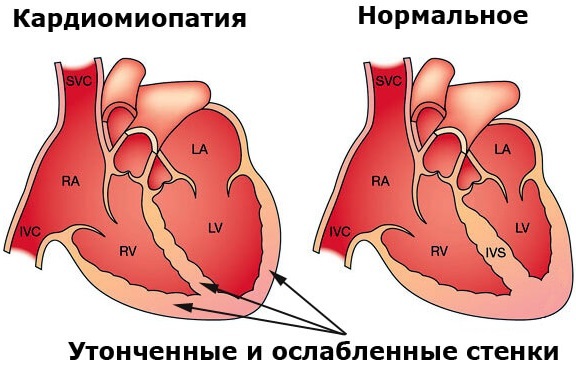
|
| Osteoporosis | Decreases in bone density. This happens against the background of taking certain medications and due to a sedentary lifestyle. |
| Stool disorder | Constipation occurs as a result of a sedentary lifestyle. In such a situation, it is necessary to adjust the diet so that the menu includes more fiber-rich foods. |
| Increase or decrease in body weight | The loss of kilograms occurs while taking medications or as a result of muscle atrophy. Proper nutrition will help restore body weight. |
Progressive pathological processes can also provoke curvature of the spine (kyphosis, scoliosis). Patients need to wear special corsets. In difficult situations or at advanced stages of the development of neuromuscular diseases, the patient is shown surgical intervention. The decision is made by a neurologist, taking into account the condition of the person and the individual characteristics of his body.
With neuromuscular diseases, motor function is impaired, muscles are weakened. Symptoms gradually intensify against the background of progressive degenerative processes.
The patient needs to undergo a complete examination for diagnosis and a specially selected treatment. Medicines, traditional medicine, physiotherapy procedures will only help to make life easier for the patient, but they will not be able to completely get rid of genetic pathology.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Videos about neuromuscular diseases
Teleseminar on neuromuscular diseases: