In the body human lower limbs perform the function of support and movement. Knowledge of the topography of muscles, the course of nerves and blood vessels, the structure of the joints allows you to navigate the diagnoses and make the correct diagnosis. This makes it possible to treat promptly and adequately without leading to persistent loss of function.
Record content:
- 1 Features of the structure of the lower limbs
- 2 Lower limb functions
-
3 Human lower limb skeleton
- 3.1 Femur and patella
- 3.2 Pelvic girdle
- 3.3 Shin
- 3.4 Foot
-
4 Joints
- 4.1 Knee
- 4.2 Ankle
- 4.3 Foot joints
- 5 Muscles and tendons
- 6 Blood supply
- 7 Nerves
-
8 Common diseases of the lower limb
- 8.1 Bones and joints
- 8.2 Soft tissue
- 8.3 Nervous system
- 9 Treatment
- 10 Video about the structure of the lower limbs of a person
Features of the structure of the lower limbs
The legs can withstand high static loads. The ankle joint is responsible for this, which can withstand a heavy load of weight. In this case, the foot is located perpendicular to the axis of the limb. This allows for shock absorption while walking.
The vessels (veins) are equipped with a powerful muscle component to push blood in a retrograde direction.
Lower limb functions
The main support for a person falls on his feet. Many biologists and physicians argue that mankind paid for upright walking with its joint diseases.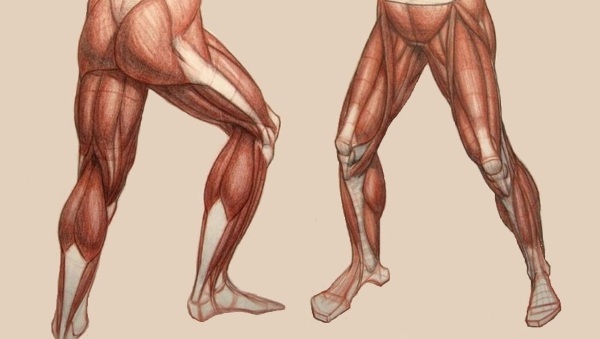
The lower limbs of a person (muscles, joints) also perform the function of locomotion. With diseases of the joints or blood vessels, this function can be severely affected, leading to disability, as it disrupts self-service.
Human lower limb skeleton
Paired and unpaired bones make up the bone base. Distinguish between the bones of the pelvic girdle and the free skeleton of the lower limb.
Femur and patella
It is the longest tubular bone in the entire body of the human body. Of the main landmarks, a head and a neck are distinguished. In these places, fractures are usually localized in the elderly and aseptic necrosis in people of the same age group.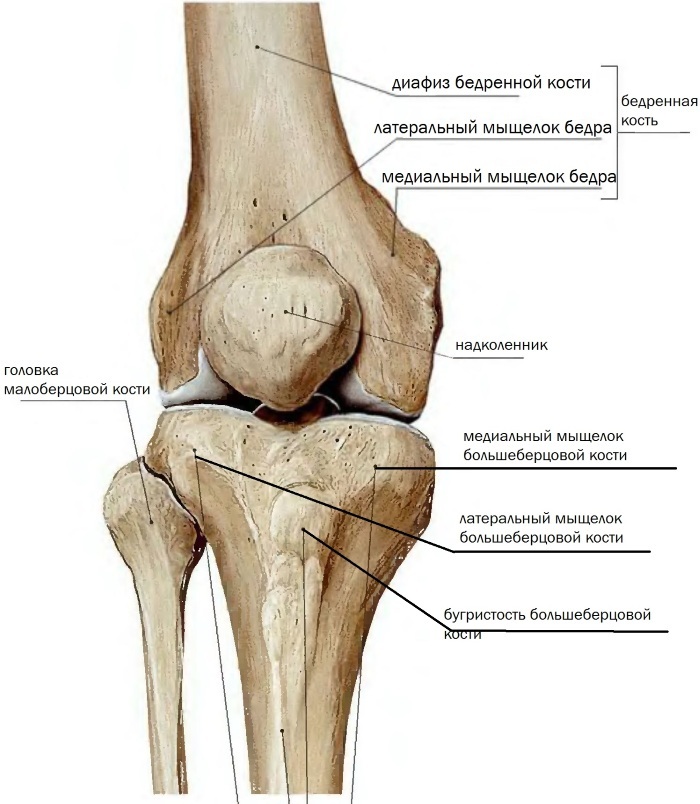
The femur body consists of a long shaft and two epiphyses. There are 2 ends - proximal and distal. The distal pineal gland is involved in the formation of the knee joint, while the proximal is part of the hip joint. The condyles are located on the sides. Between them is the surface necessary to form an articulation with the patella.
The patella or patella is the largest sesamoid bone. She is involved in the formation of the knee joint. This bone is framed within the tendon structure of the femoral quadriceps. Anatomically, the apex, which is facing downward, and the base, which is seen from above, are distinguished.
Pelvic girdle
The pelvis is an integral bone structure. It consists of paired and unpaired bones. The cavities of the large and small pelvis are conventionally distinguished. This unit is important for functional diagnostics doctors and gynecologists. The line dividing these 2 formations is called the border line.
It runs along the tops of the pubic bones, the arc lines of the ilium. In front, it goes along the pubic articulation, and in the back it touches the promontory of the spinal column. Among the paired bones of the pelvis, the iliac, pubic and sciatic. All of them are combined into a large pelvic bone. In post-puberty, after 16 years, it is a whole bone.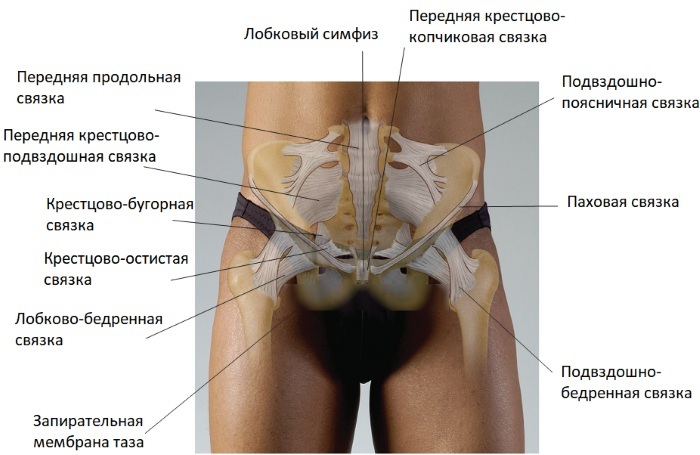
The largest of these is the ileum. Of the anatomical structures, the wing and the ridge deserve attention. The pubic bone is located in front. In her body, upper and lower branches are distinguished. The ischium is responsible for the formation of the lower pelvis. Its thickening - the ischial tubercles - form the lower protrusions of the pelvis.
Shin
This segment of the lower limb contains 2 bone structures. These are the tibia and fibula.
The tibia is a long, tubular bone. It consists of a body and proximal, distal ends. The body resembles a triangle in shape. The proximal part is more massive. After all, it is the condyles that are located on it that articulate with the condyles of the thigh.
From the lateral surface on the condyle there is an articular surface to form an articulation with the fibula. The ankle is visible at the lower end. At the same time, the bottom is the surface for the formation of the joint with the talus of the foot, as well as the articulation with the lower edge of the fibula.
It, in turn, is thinner and smaller than the tibial. The fibula also consists of a body, a head (top), and an ankle below.
Foot
The upright walking and vertical orientation of the human body dictate the structural features of the lower limb in general and the foot in particular. In humans, they consist in the presence of a spring vault, as well as the perpendicular position of the axis of the foot in relation to the length of the limb (lower leg, thigh).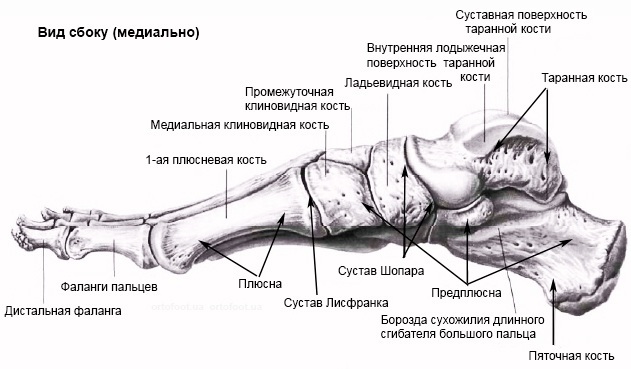
The bones of the tarsus and metatarsus are distinguished by analogy with the metacarpus and wrist of the hands. The tarsal group has 7 bones. The metatarsus has 5 of them. The toes are composed of 3 phalanges. The exception is thumbs: they include 2 phalanges.
Joints
The bony structures of the leg, together with the cartilaginous layers and ligaments, form the joints. Among them, the largest is the hip. But it is worth noting that a large load still falls on the ankle joint.
Hip
It is a ball-shaped joint between the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvis. The articulating surfaces are incongruent (they do not coincide in shape and area of contact), therefore there is an articular lip, consisting of cartilage. This increases the mobility and stability of the joint. The shape of the bowl or ball allows movement along three axes.
Among the many ligaments that strengthen the joint, there is the ligament of the femoral head. It is she who is responsible for the occurrence of aseptic necrosis of the femoral head.
Among the diseases that affect the hip joint, one should first of all remember about arthrosis. Coxarthrosis often reaches 4 degrees, leading to ankylosis (immobility) and the need for total arthroplasty.
Knee
Traumatologists, surgeons and orthopedists consider this joint to be one of the most complex and intricate. No wonder, because the femur, tibia, and patella are articulated in this joint. In addition, in the knee joint there is a phenomenal number of turns of the articular capsule - there are 9 of them.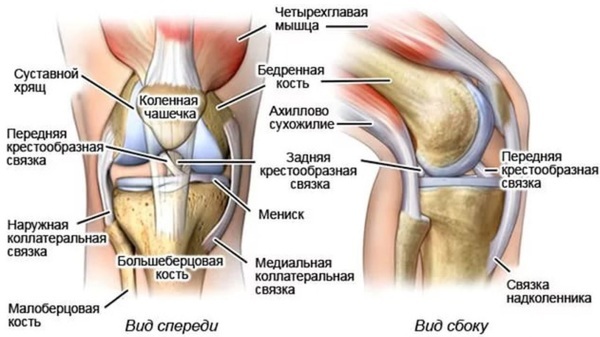
In shape, the joint is classified as block-shaped. The surfaces of the articulating bone structures also differ in shape and area. The menisci give the maximum congruence to the joint. There are 2 of them - lateral and medial.
They are composed of coarsely fibrous connective tissue. A relatively large load is very often placed on these structures, therefore, tears and damage to the menisci occur, requiring prompt treatment.
9 synovial bursae (curls) can accumulate fluid during inflammation and trauma. This is hydrarthrosis, hemarthrosis. Only an experienced surgeon or traumatologist will be able to “pump out” fluid from the damaged joint.
Among the ligaments that strengthen the joint, attention should be paid to the cruciate ligaments. In case of traumatic injuries, it is they that break, requiring surgical intervention.
Osteoarthritis (gonarthrosis) ranks first among chronic diseases of the knee joint. Rheumatoid arthritis occurs. Reactive arthritis may develop in young patients with a tendency to autoimmune aggression.
Ankle
The biaxial block joint withstands maximum loads when comparing all the joints of the lower limb. This is a kind of support for the whole body when walking, running and other types of movement.
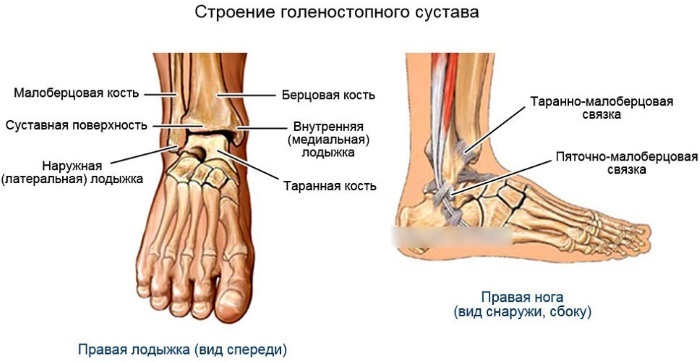
This joint is most often prone to traumatic injury. Therefore, post-traumatic crusarthrosis occurs more often than primary osteoarthritis. Among the inflammatory causes, rheumatoid arthritis is in the first place. This systemic disease often makes its debut precisely with pain and stiffness of movements in the ankle area.
Foot joints
In this group, the joints are heterogeneous.
They include:
- interphalangeal joints;
- tarsometatarsal joints;
- metatarsophalangeal joints;
- subtalar joint;
- calcaneal-ram-navicular joint.
The small joints of the foot are a target for rheumatoid arthritis. They are also affected within the framework of polyosteoarthritis with the progression of the disease.
Muscles and tendons
The lower limbs of a person (their muscles are numerous and they are very powerful) can withstand heavy loads. The muscle mass of the thigh is rather large. There are 3 groups: anterior, posterior, and also the medial thigh muscle group. The most powerful is the front. This is where the famous powerful quadriceps are located.
There are also 3 muscle groups on the lower leg. These are the anterior, posterior, and also lateral tibia massifs. The back group is more powerful. Therefore, in it, in turn, the surface and deep layers are distinguished. The medial surface of the lower leg is devoid of powerful muscles. The synovial bags are located here.
The calf muscles are numerous. They very much resemble the structure of the structure of the hands, only here it is less complex, since in the process of evolution the foot has lost its grasping function.
The muscles and tendons of the lower limb in humans are mainly prone to bruises, lacerations and other traumatic injuries. Inflammatory diseases are extremely rare.
Blood supply
The lower limb is supplied with arterial blood from the basin of the femoral artery. It originates as a branch of the external iliac artery. The described vessel is very large, therefore, if she is injured, bleeding can be fatal.
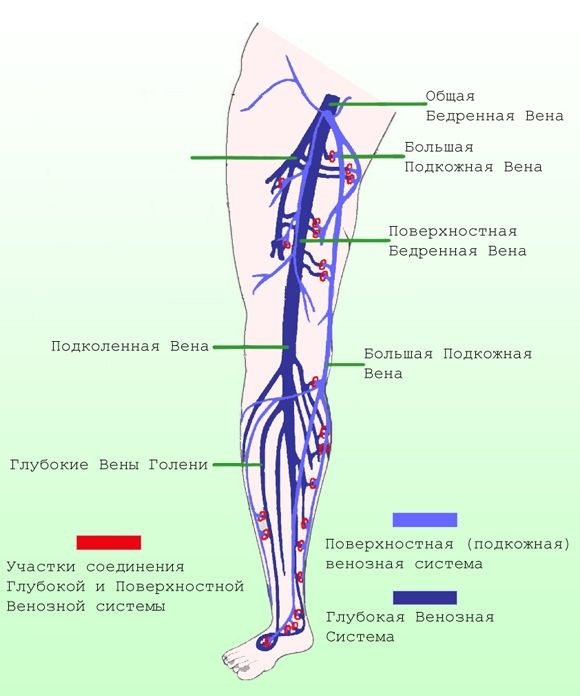
The femoral artery is projected onto the anterior surface of the thigh. Its largest branch is called the deep artery of the thigh. On the back of the thigh, immediately at the level of the popliteal fossa, the popliteal artery branches off from the femoral artery.
It nourishes the knee joint as well as the calf muscles. Its branches, in turn, become the anterior and posterior tibial arteries. On the foot, these arteries create vascular arches that anastomose with each other, which is a factor that protects against critical ischemia.
Blood flows through the arteries from the heart to the peripheral tissues (muscles, joints), and through the veins, on the contrary, from the tissues to the heart. There are only 2 superficial veins: small and large saphenous. Deep veins accompany the arteries of the same name. As a result, blood enters the heart through the inferior vena cava.
The lower limbs of a person (muscles are very well developed in this area) require a high metabolic rate. The peculiarities of the veins of the lower extremity are considered to be a very large load on the valve apparatus.
Indeed, in order to “pump” blood in a retrograde direction from bottom to top, overcoming gravitational forces, a pronounced muscle layer is needed. It is the veins of the lower extremities that are primarily susceptible to varicose veins.
Nerves
The lower limbs of a person (muscles, joints) are innervated by the lumbar plexus. From it, 2 large nerves are formed - the femoral and obturator.
The femoral nerve is responsible for the movement of all the pelvic muscles, as well as the femoral muscles. But it contains not only motor, but also sensory fibers. This is the so-called long saphenous nerve.
It is responsible for the sensation of pain, temperature and pressure throughout the antero-medial surface of the lower limb. The obturator nerve innervates only one muscle - the external obturator.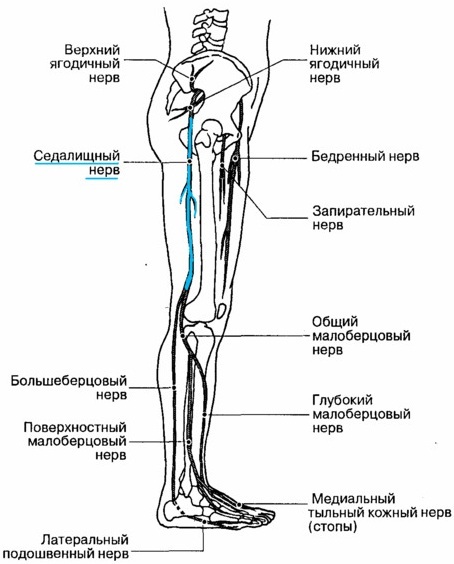
The sciatic and posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh is formed from the sacral plexus. The latter is responsible for extension in the hip joint. Sensitive fibers of the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh are responsible for the sensitivity of the posterior surface of the femoral region. The nerve also captures the upper half of the lower leg.
The sciatic nerve is the longest nerve in the lower limb. It innervates the knee joint as well as the inner thigh muscle group. It is divided into tibial and common peroneal nerve.
Common diseases of the lower limb
The contingent of sick patients is older people. In young people, pinching of the sciatic nerves is possible due to herniated intervertebral discs or severe hypothermia.
In old age, the limbs are most often affected by vascular diseases. Diseases of muscles, joints fade into the background. They are associated with both arterial and venous beds. Varicose veins appear earlier. These are vascular networks on the legs, which are replaced by coarse nodes with signs of inflammation. Disturbed by convulsions, trophic changes in the skin already in the later stages.
In chronic arterial insufficiency in the framework of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, pain in the legs is disturbed, forcing to stop and rest.
This is the so-called intermittent claudication syndrome. The skin on the limbs becomes atrophic, the condition of the nails is worn out. Often, cramps and loss of sensation are troubling. The disease is dangerous by the development of gangrene requiring amputation.
Bones and joints
The bone apparatus is damaged due to 2 main reasons: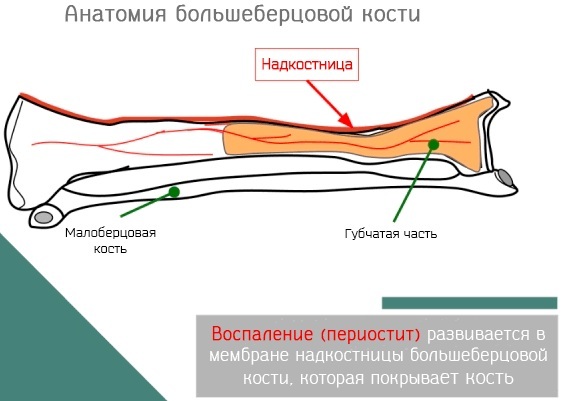
| Disease | Description of the clinical picture |
| Tuberculosis | Tuberculosis of the skeletal system is less common, but affects not only the adult contingent, but also children. It flows very torpidly (slowly), but without treatment leads to disability. The femur is affected in the projection of the neck. In this case, the tissues of the hip and, less often, the knee joint are involved. Signs of damage are nonspecific: pain syndrome, limitation of mobility against the background of low-grade fever. |
| Periostitis | Periostitis is an inflammatory disease of the periosteal layer of the bones. It manifests itself in sharp pains, sometimes throbbing. In this case, the skin of the affected area is hot, sometimes the general body temperature rises, reaching a febrile level. Severe edema is revealed. |
Both diseases have an infectious origin.
Articular lesions are reduced to the following diseases:
- osteoarthritis;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- psoriatic arthropathy;
- peripheral form of ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis);
- reactive arthritis.
In arthrosis, the first place is the limitation of joint mobility, while in arthritis, pain is more worried. The defeat of the joints during exacerbation is accompanied by inflammation of the articular bag with the development of synovitis. In this case, the joint swells. Inflammation can also cover the periarticular tissue.
Soft tissue
Not only joints, bone structures and blood vessels are affected. There are a number of formations called periarticular tissues. Another name is periarticular. This group includes tendons, ligaments, muscle masses, tendon sheaths of muscles, fascia, aponeuroses, and entheses. The latter include the protrusions on the bones to which the tendons are attached.
Therefore, among the diseases of the soft tissues of the lower limb, the following varieties are distinguished:
- bursitis with inflammation of the joint capsules;
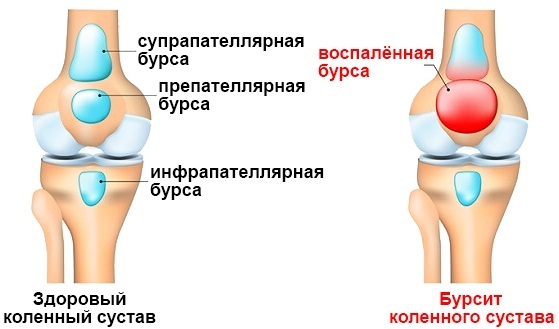
- enthesitis (inflammation of enthesis);
- ligamentitis with damage to the fibers of the ligaments;
- tendinitis with tendon involvement;
- myositis is an inflammation of muscle tissue.
The treatment is carried out by a traumatologist or rheumatologist, depending on the cause that was found during the examination.
Nervous system
Among the diseases of this group, lumboischialgia is in first place. This is a pain syndrome that is initially localized in the lumbar region, but radiates or “gives off” to one or both limbs. The causative factor is the degeneration of the intervertebral disc as a result of osteochondrosis, protrusion or hernia.
The pain is shooting in nature. The disease itself is chronic, therefore it proceeds with a change in the phases of remission and exacerbations. With exacerbation, shooting pains are so pronounced that they block the work of the muscles due to their spasm. As a result, it is extremely difficult for the patient to bend and straighten, as well as to make movements in the knee and hip joints.
The second important group of pathologies affect the peripheral nervous system of the lower extremities. These are polyneuropathies of various origins.
Treatment
Treatment approaches depend on the specific disease. In case of bruises and injuries, the treatment of a surgeon or traumatologist is required. The operation is required for severe wounds, open wounds.
Joint diseases require adequate anti-inflammatory therapy in the early stages. These are NSAIDs, or glucocorticoid hormones. In the phase of remission, chondroprotectors are prescribed to nourish the cartilage and prevent the progression of the disease. Physiotherapy methods also come to the rescue. With the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, they resort to endoprosthetics.
Diseases of veins in the early stages are treated by phlebologists. They bark recommendations for wearing elastic knitwear, taking phlebotonics. At later stages, with deformed veins, removal of the affected vessels is indicated.
The same treatment tactics for chronic arterial disease. Instead of phlebotonics, drugs are shown that dilate blood vessels and improve microcirculation of the tissues of the lower extremity.
For neuropathies, thioctic acid preparations are prescribed. Today it is the only pathogenetic agent for this pathology with a proven effect.
The lower limbs in humans are affected by diseases of the vessels, joints, and nerves. These can be injuries to bones, muscles, or tendons. Only knowledge of the topography of these formations will make it possible to correctly diagnose and begin adequate treatment.
Video about the structure of the lower limbs of a person
Lower limb anatomy:



